Exercise Metabolism and Energy Expenditure Overview
1/187
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
188 Terms
Exercise Physiology
Study of physiological responses to exercise.
Laboratory Testing
Evaluates athletic potential and conditioning effectiveness.
Skeletal Muscle Fiber Type
Indicates potential athletic success via biopsy.
Anaerobic Power
Power produced without oxygen during high-intensity efforts.
ATP-PC System
Energy system for short, explosive activities.
Glycolysis
Breakdown of glucose for energy production.
Aerobic Metabolism
Energy production using oxygen for prolonged activities.
Energy Pathways
Systems providing energy during physical activities.
Maximal Effort
Highest intensity exertion over a brief duration.
Specificity in Testing
Tests should match muscle groups used in sport.
Ultra Short-Term Tests
Assess ATP-PC system capacity under 10 seconds.
Short-Term Tests
Evaluate overall anaerobic capacity for 30-60 seconds.
Explosive Anaerobic Power Tests
Standing broad jump and vertical jump assessments.
Percent Contribution of Energy Systems
Shows energy source usage over time during exercise.
Transition Periods
Time when energy systems shift during activity.
Maximal Anaerobic Power
Peak energy output from anaerobic pathways.
Duration and Intensity
Key factors influencing energy system contributions.
Feedback for Athletes
Information on strengths and weaknesses in sports.
Physiological Factors
Biological elements influencing athletic performance.
Psychological Factors
Mental aspects affecting athletic success.
Barker et al. (2011)
Reference for testing elite young athletes.
Energy System Interaction
All systems work together for exercise performance.
Direct Calorimetry
Measures heat production to assess energy expenditure.
Substrate Metabolism Efficiency
40% energy converted to ATP, 60% to heat.
Calorimeter
Device measuring heat from metabolic processes.
Indirect Calorimetry
Estimates energy expenditure via O2 and CO2 measurements.
VO2
Volume of O2 consumed per minute.
VCO2
Volume of CO2 produced per minute.
Haldane Transformation
Calculates inspired air volume from expired air volume.
Respiratory Exchange Ratio (RER)
Ratio of CO2 production to O2 consumption.
RER for Fat
R = 0.70 for palmitic acid oxidation.
RER for Carbohydrate
R = 1.00 for glucose oxidation.
Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR)
Energy expenditure at rest in supine position.
Resting Metabolic Rate (RMR)
Similar to BMR; easier to measure.
Metabolic Rate
Rate of energy use by the body.
Energy Expenditure at Rest
RER ~0.80, VO2 ~0.25 L•min-1.
Total Daily Metabolic Activity
Includes all daily activities; 1,800 to 3,000 kcal.
Competitive Athlete Energy Needs
Can reach up to 10,000 kcal/day.
VO2 Drift
Upward VO2 increase at constant power outputs.
Type II Fibers
Less efficient muscle fibers recruited at high intensity.
Heat Production
Increases with energy production during metabolism.
Caloric Equivalent
Caloric value derived from O2 consumption.
Exercise Equipment Heat
Adds extra heat, affecting calorimetry accuracy.
Sweat Measurement Error
Sweat can skew calorimetry results.
VO2max
Maximum oxygen uptake during intense exercise.
Aerobic fitness
Best measured by VO2max performance.
Endurance performance
Not solely predicted by VO2max.
Training plateau
VO2max plateaus after 8-12 weeks.
Higher competition percentage
More training allows higher VO2max usage.
VO2max units
Expressed in liters per minute (L·min-1).
Normalized VO2max
Measured in ml O2·kg-1·min-1.
Body size comparison
Normalized VO2max allows fairer comparisons.
Untrained young men
Typical VO2max: 44 to 50 ml O2·kg-1·min-1.
Untrained young women
Typical VO2max: 38 to 42 ml O2·kg-1·min-1.
Sex difference
Due to lower fat-free mass and hemoglobin.
Anaerobic effort
Involves excess post-exercise O2 consumption (EPOC).
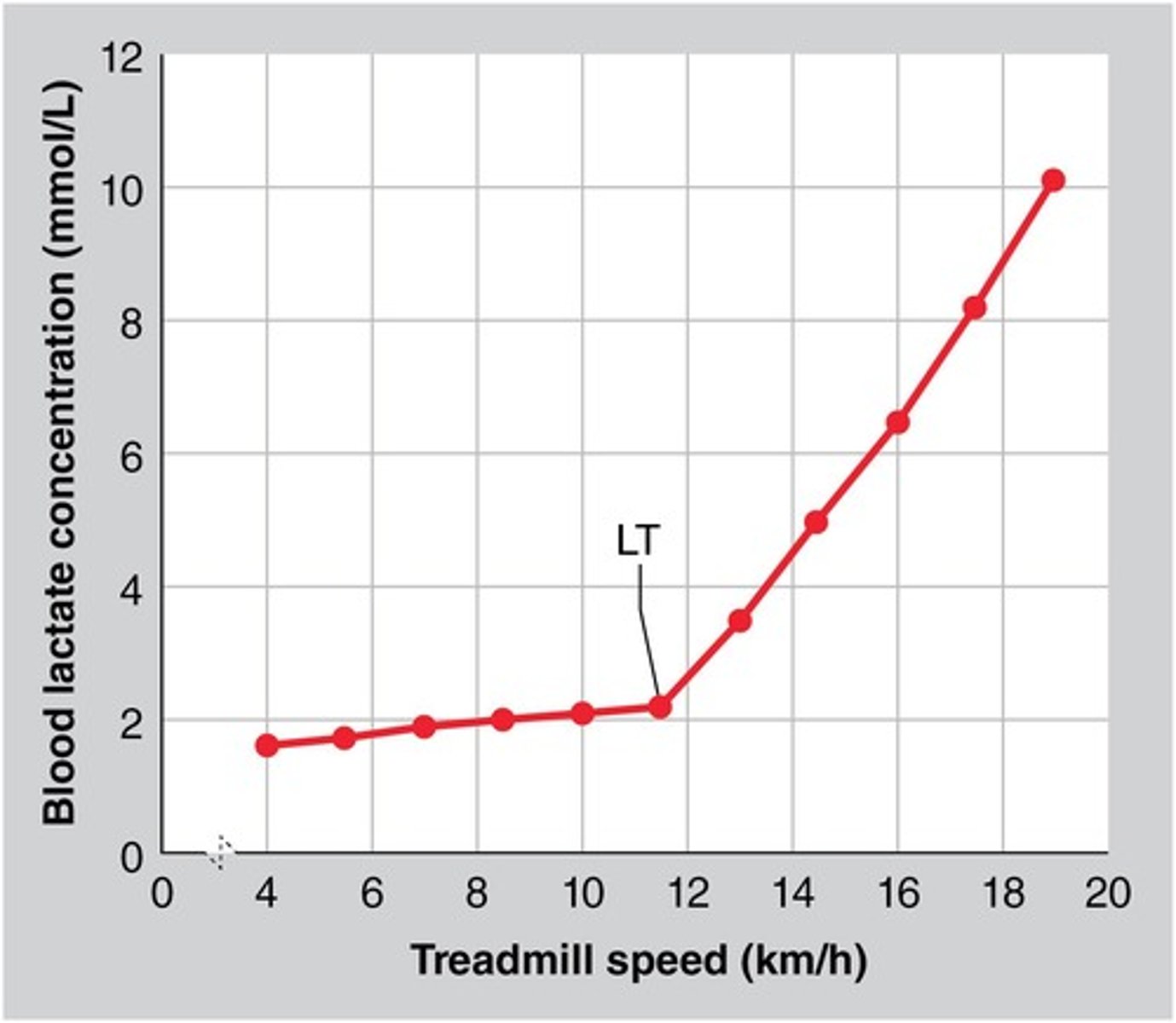
Lactate threshold
Point where lactate accumulates in the blood.
ATP at rest
Almost 100% produced by aerobic metabolism.
Resting blood lactate
Levels are low, typically <1.0 mmol·L-1.
Resting O2 consumption
0.25 L·min-1 or 3.5 ml·kg-1·min-1.
Energy expenditure increase
May rise 15-25 times during heavy exercise.
ATP production during exercise
Can increase 200 times over resting levels.
Homeostasis
Steady internal environment during rest.
Oxygen uptake lag
Delay in oxygen consumption at exercise onset.
Steady state VO2
Achieved within 1-4 minutes of exercise.
ATP supply-demand balance
ATP production meets ATP requirements during exercise.
Initial ATP production
Primarily through anaerobic pathways.
ATP-PC system
Immediate energy source for short bursts of activity.
Glycolysis
Anaerobic pathway for ATP production.
Bioenergetic pathways
Metabolic routes providing energy during exercise.
ATP production
Rate of ATP synthesis increases with exercise intensity.
Rest-to-exercise transition
Shift from low to high energy demand activities.
O2 consumption
Measurement indicating aerobic metabolism efficiency.
Skeletal muscle changes
Adaptations in muscle metabolism at exercise onset.
7 mph running
Speed requiring increased ATP for muscle contraction.
Instantaneous ATP increase
Rapid rise in ATP to prevent exercise interruption.
Treadmill exercise
Controlled environment for studying exercise metabolism.
Aerobic metabolism
Energy production using oxygen during prolonged activity.
Oxygen Deficit
Lag in oxygen uptake at exercise onset.
Anaerobic Energy Expenditure
O2 demand exceeds O2 consumed early in exercise.
Oxygen Debt
Repayment for O2 deficit post-exercise.
Excess Post-exercise O2 Consumption (EPOC)
O2 consumed exceeds O2 demand during recovery.
ATP-PC System
Energy system for immediate ATP production.
Glycolysis
Anaerobic pathway producing ATP from glucose.
Steady-state VO2
Constant oxygen uptake during submaximal exercise.
Upward Drift in VO2
Gradual increase in oxygen uptake over time.
Rapid Component of EPOC
Quick replenishment of ATP and oxygen stores.
Slow Component of EPOC
Prolonged recovery involving elevated metabolic rate.
Gluconeogenesis
Conversion of lactate to glucose post-exercise.
Factors Contributing to EPOC
Includes heart rate, temperature, and hormones.
Metabolic Responses to Exercise
Changes in energy systems based on intensity.
High-energy Phosphates
Stored energy sources in muscles for quick ATP.
O2 Required
Amount of oxygen needed for exercise intensity.
O2 Consumed
Actual oxygen uptake during physical activity.
Anaerobic Pathways
Energy production without oxygen, primarily during intense exercise.
Prolonged Exercise
Exercise lasting longer than 10 minutes.
Moderate Exercise
Sustained activity at a manageable intensity.
Heavy Exercise
Intense activity requiring significant energy expenditure.
EPOC Terminology
Reflects only ~20% O2 consumption for repayment.
Exercise Recovery
Period following exercise where physiological processes stabilize.