EKG rhythms
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
60 Terms
Normal Sinus Rhythm
60-100 bpm
all complexes normal and evenly spaced (P, QRS, T)
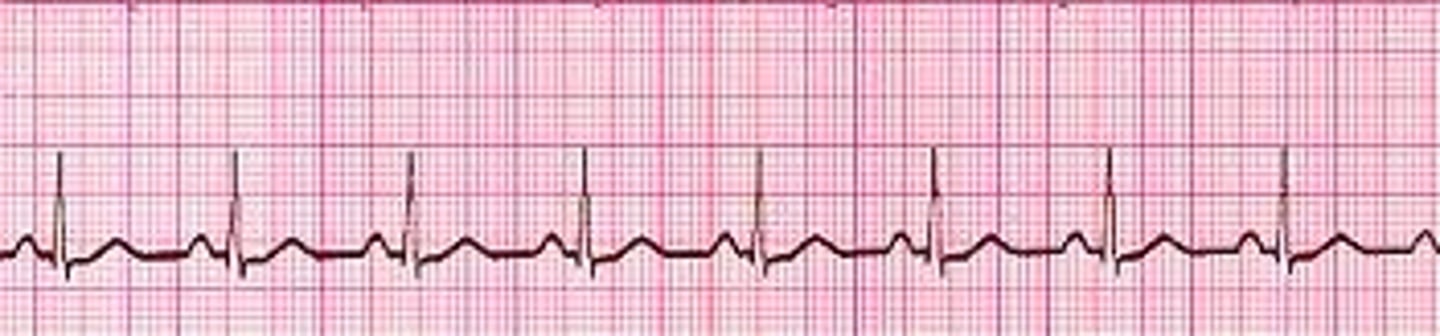
Sinus Arrest
- SA node doesn't fire
- notice absence of P-wave for a complete cycle (a missed cycle)
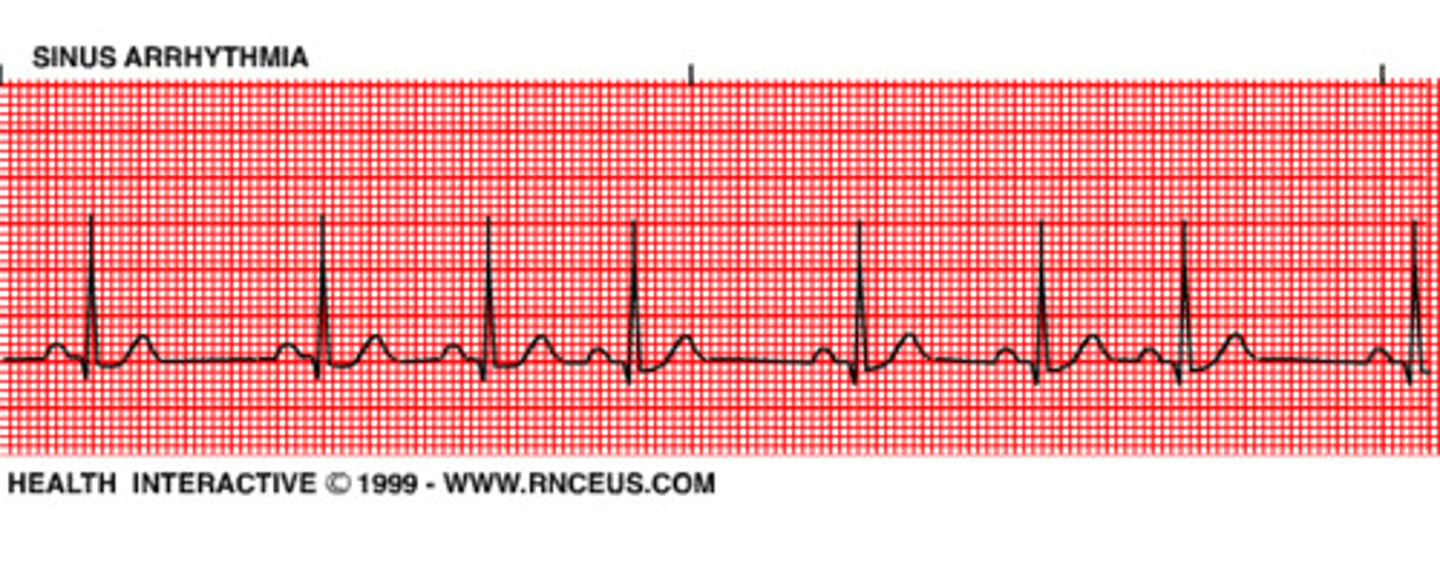
Sinus arrhythmia
all complexes normal but rhythmically irreg
- normal finding (esp in young pts) that has to do with breathing (rate: inhale-increase, exhale-decrease)
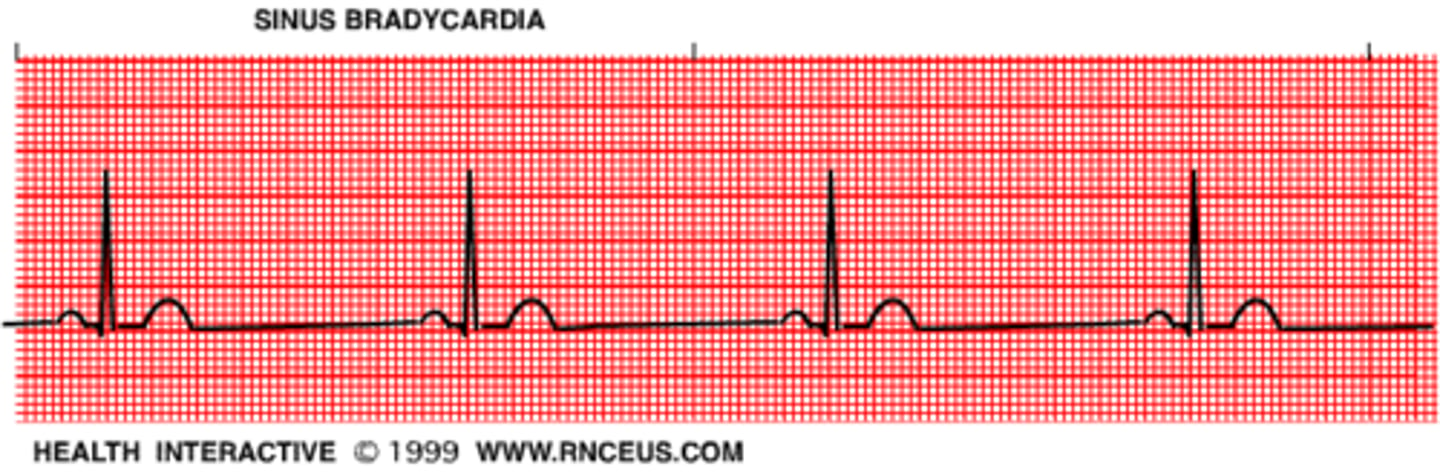
Sinus Bradycardia
<60
normal sinus rhythm
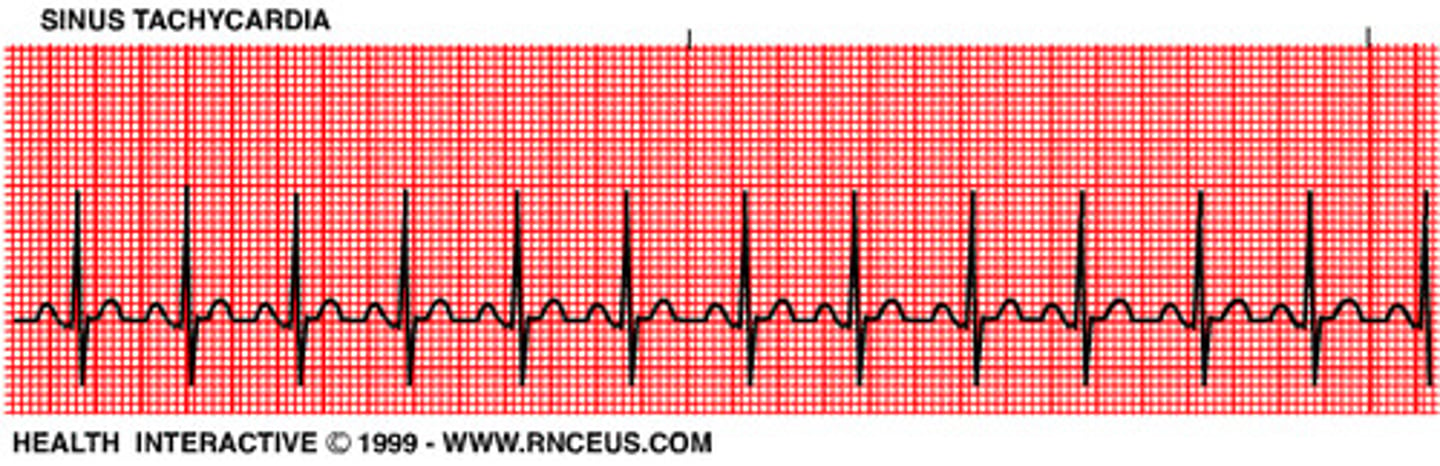
Sinus Tachycardia
>100 (100-150)
normal sinus rhythm
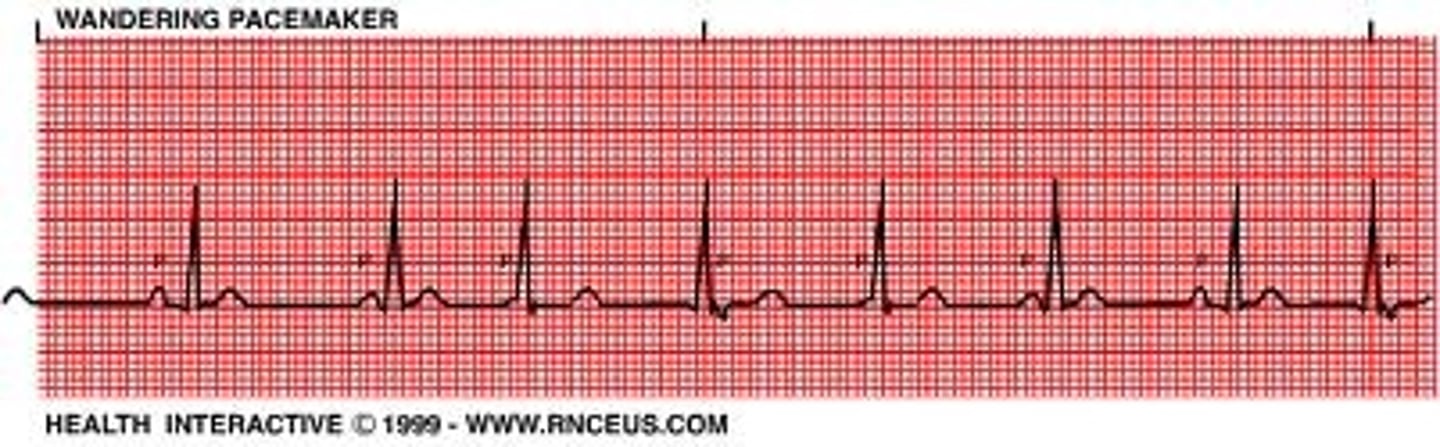
Wandering atrial pacemaker
Hint: try never to pick this
- impulse originate from varying points in atria
- variation in P wave contour, PR-I, PP-I and thus RR-I
P wave vs T wave
P generally smaller than T
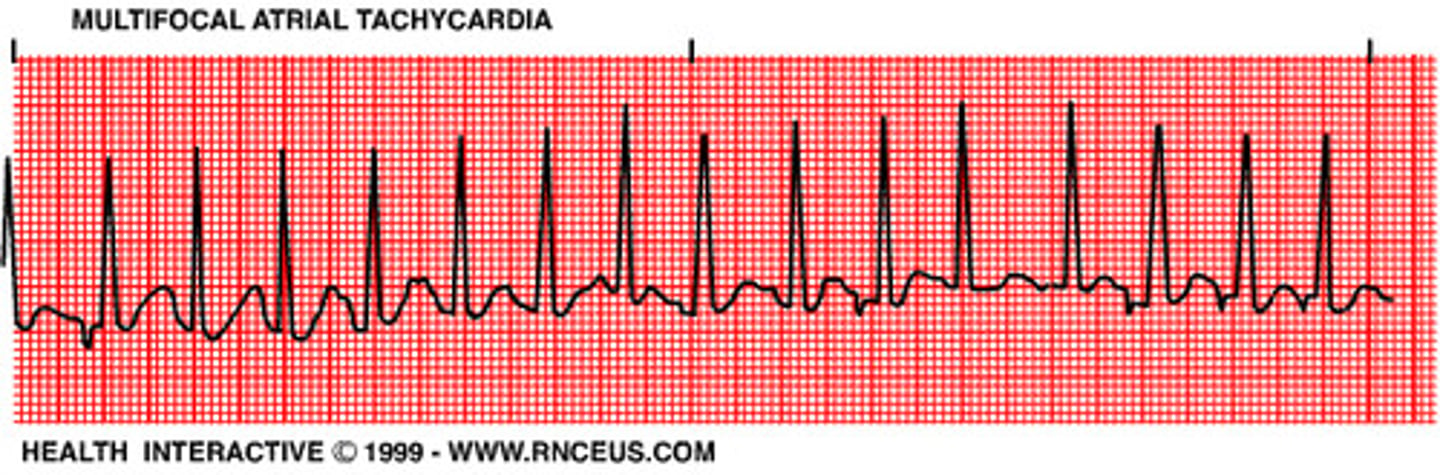
MAT (multifocal atrial tachy)
- impulse originates at diff places in atria so P waves diff and intervals might not be consistent
- assoc w/ severe pulm dz
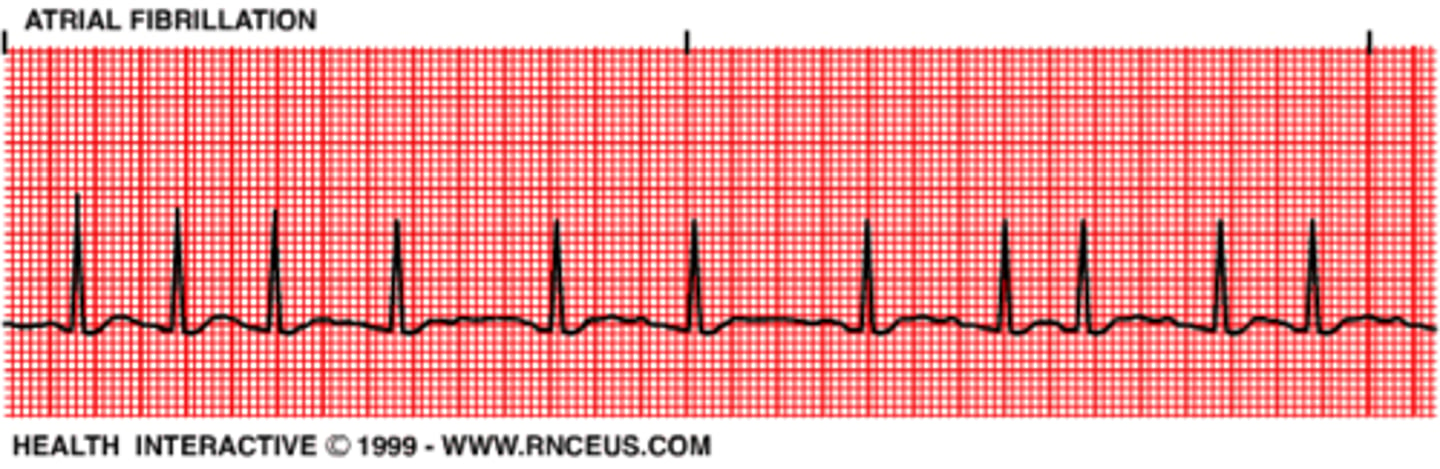
Atrial Fibrillation
A: 350-450 (atria quivering)
- irreg-irreg rhythm (R-RI=irreg)
*unsure/no P-wave (non-distinguishable)*
- irreg rhythm BUT reg QRS!
Danger: increase the risk of thromboemoblic events don't convert unless occurring less than 48 hrs, if don't know pt need to be put on thrombolytics)
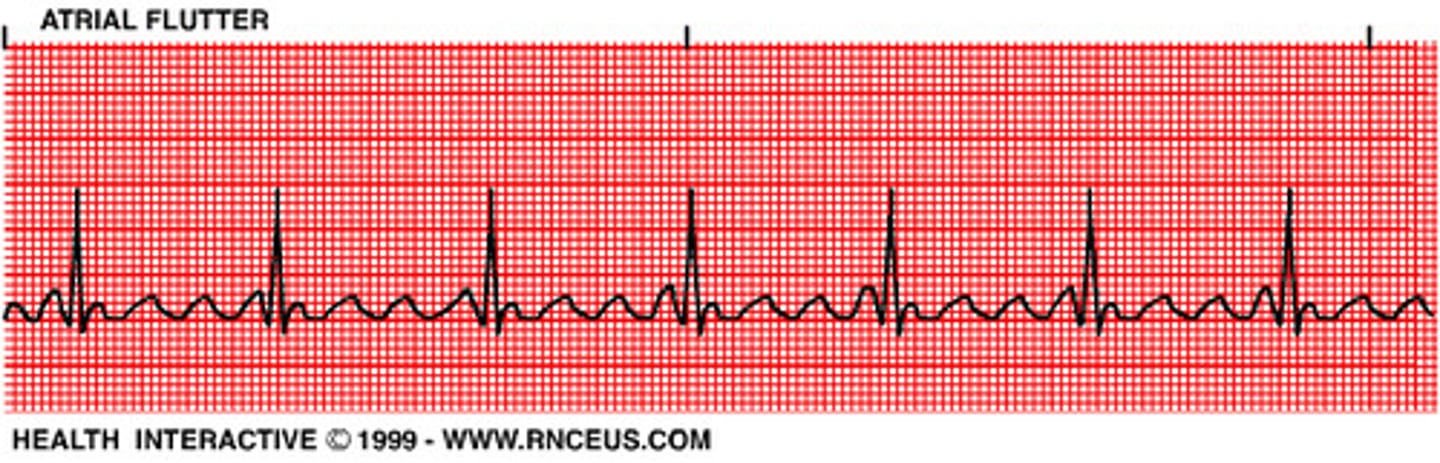
Atrial Flutter
A: 250-350
- "saw tooth" p-waves
- a continuous rapid sequence of atrial complexes from a single rapid-firing atrial focus
(hint: if see 2 P waves and QRS think A Flutter)
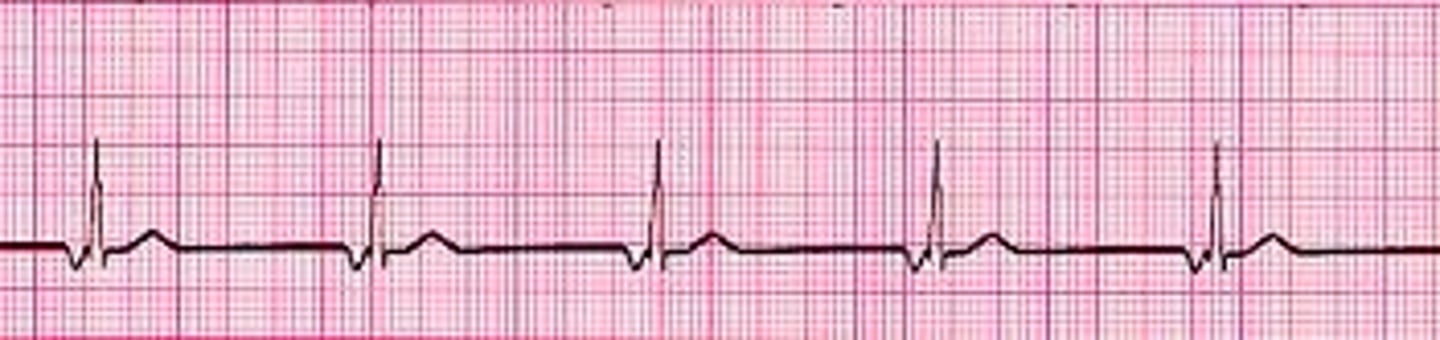
Junctional Escape beats
retrograde atrial depolarization
P' is inverted
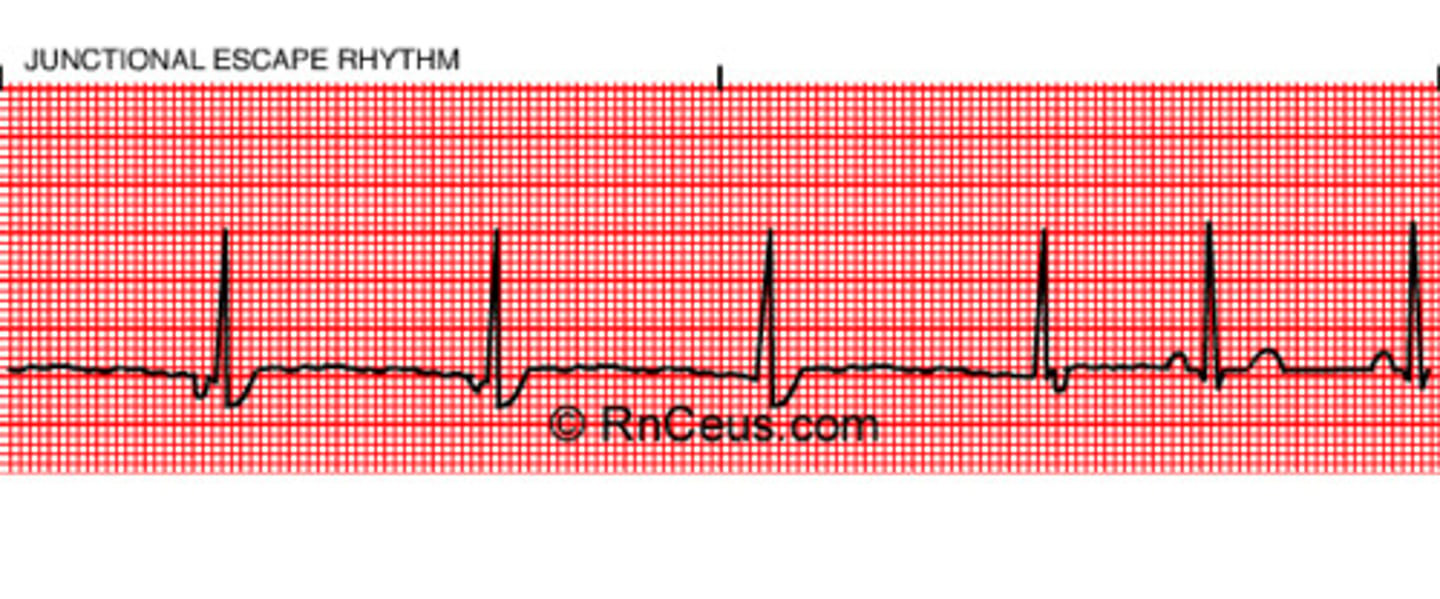
Junctional rhythm
40-60 Regular!
-impulse from AV node w/ retro/antegrade transmission
- P wave often inverted/buried/follow QRS
- slow rate
- narrow QRS (not wide like ventricular)
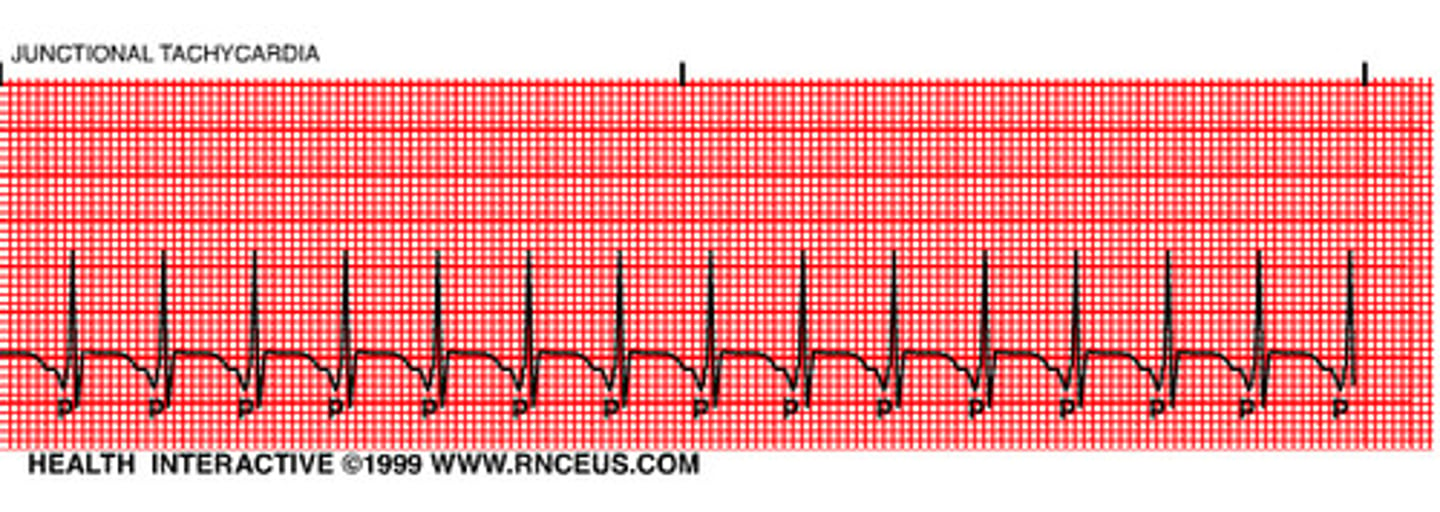
Junctional Tachycardia
>60 bpm (ms. K; 150-250)
- KEY: will be regular (consistent)
- AV junction produces a rapid sequence of QRS-T cycles
- p-wave often inverted/buried/follow QRS
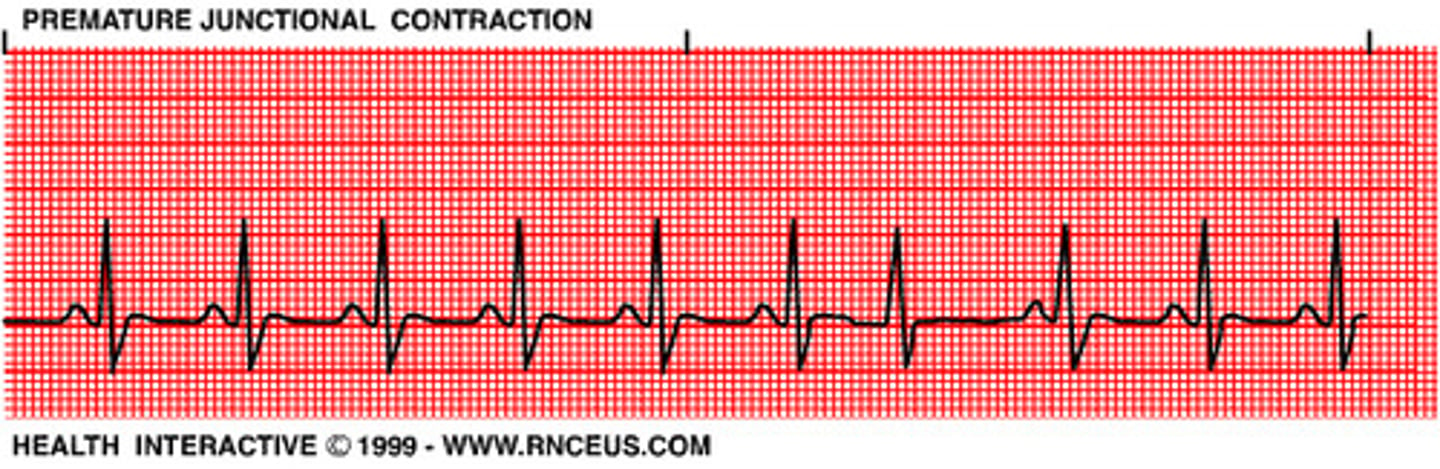
Premature junctional contractions (PJC)
- premature slightly widened QRS
- +/- inverted P', before or after QRS, sometimes disappears w/in QRS
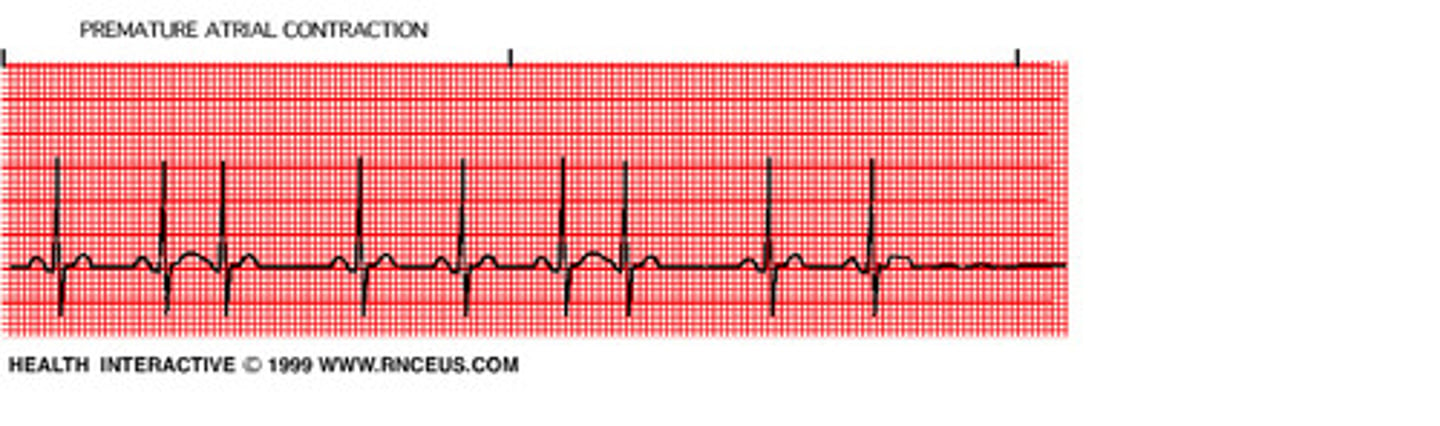
Premature atrial contractions (PAC's)
- originates suddenly in irritable atrial foci
- P' is earlier than expected and diff shape than P (often have a pause following PAC)
- can occur in Bigeminy, Trigeminy, Quadgeminy pattern
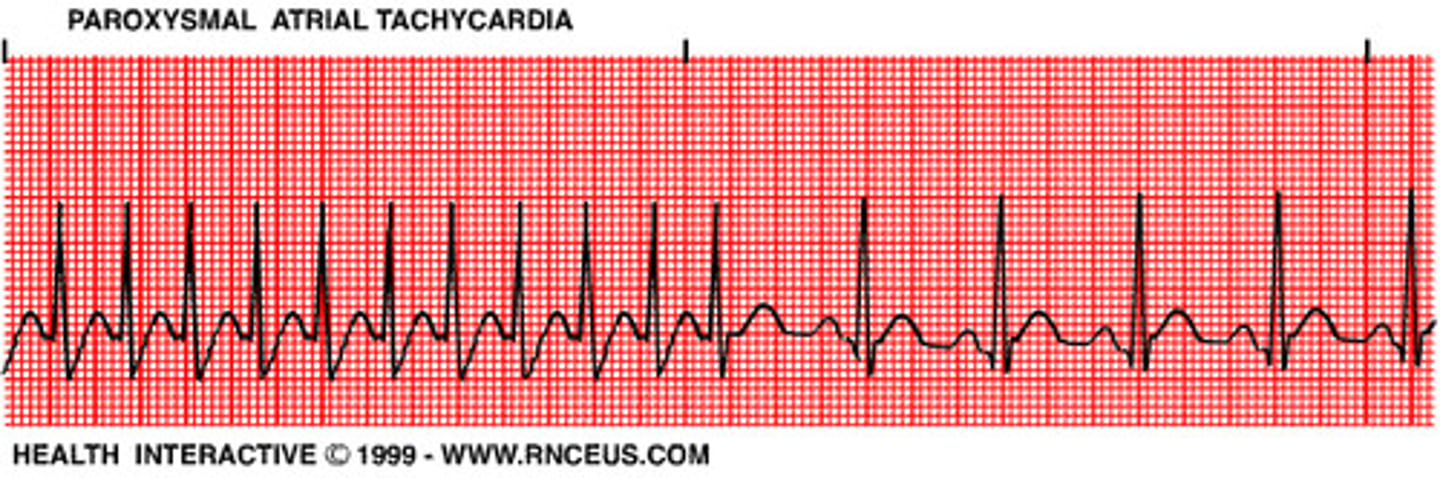
Supraventricular Tachycardia (SVT)
aka
Paroxysmal atrial tachycardia (PAT)
150-250 "sudden rapid heart rate"
- an irritable atrial focus discharging
- very fast and EVEN!
- +/- inverted P waves
- P often overlaps prior T wave
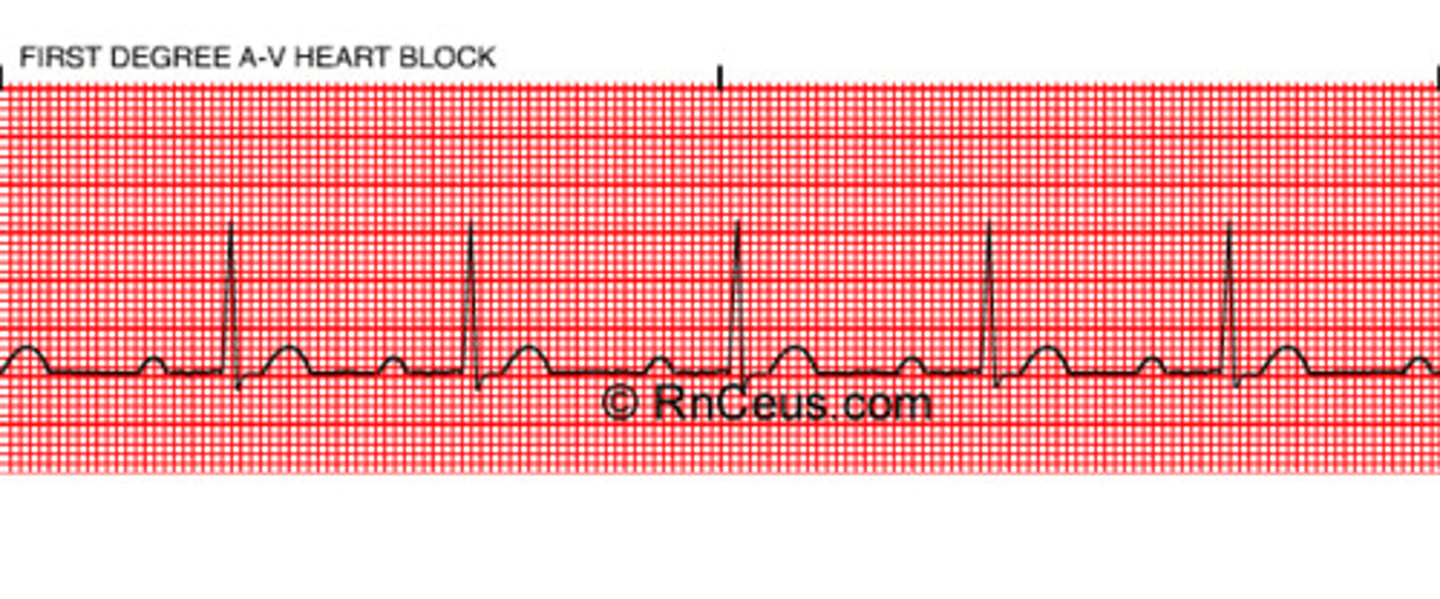
First-degree AV block
- PRI >5 boxes/.20 sec
- Fixed but prolonged PRI
(consistent but long)
- normally get bradycardia here
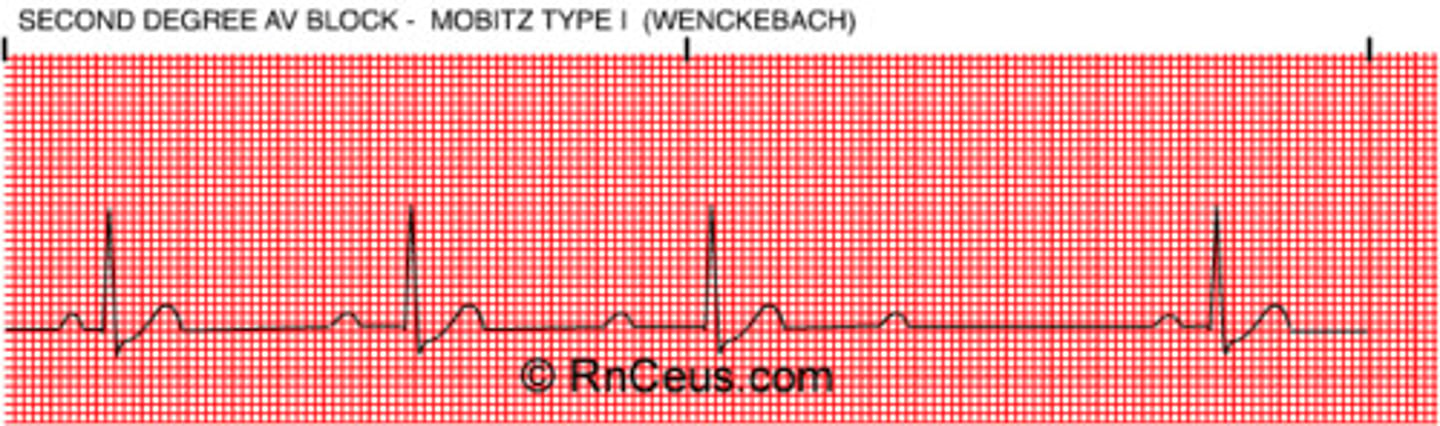
Second-degree block: Mobitz Type I Wenckebach)
"walk it back"
- PRI gradually lengthens then drops QRS "grouping and then a miss"
- typically pattern exists
(constant P-P interval, QRS is what is moving back)
- not really serious or dangerous
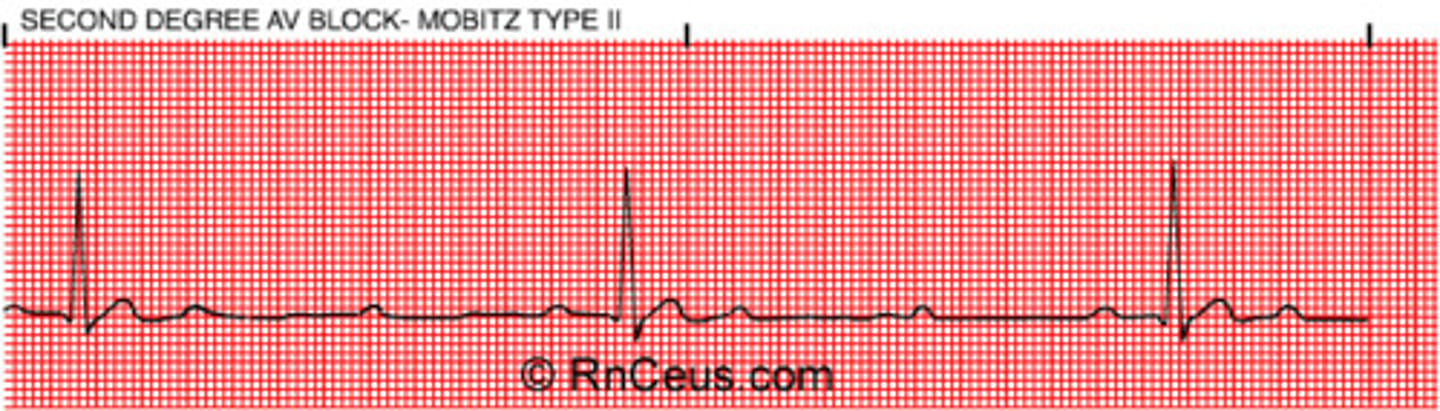
Second-degree AV block: Mobitz Type II
- normal PRI then sudden drop of QRS
- P wave doesn't always produce QRS
- P-R interval is constant (diff from 3rd degree)
- no hint just drops out -> is serious and dangerous pt needs tx!
- tend to be every other, so drops HR by 1/2) --> def bradycardia (rate=40bpm)
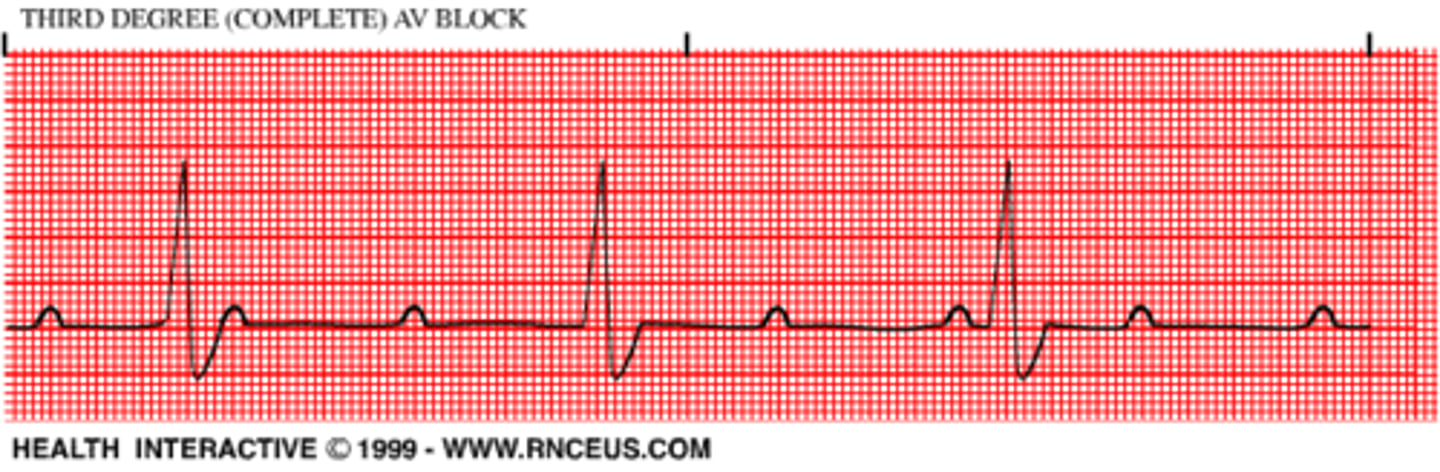
Third-degree AV block (complete block)
rate around 40's
- no relationship b/t P waves and QRS complexes (QRS slower than P rate)
- P-P reg (atrial reg) & R-R reg (vent reg)
but NOT connected (i.e P-R inconsistent)
- WIDE QRS
always serious and dangerous
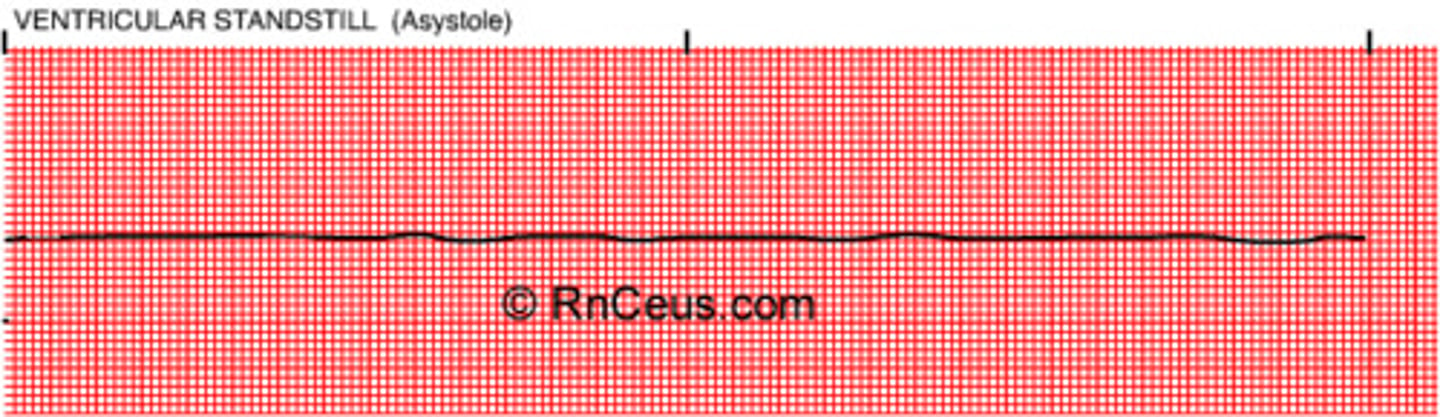
Asystole
- dead
- no electrical activity, only straight line (no rate/pulse)
A dire form of cardiac arrest in which the heart stops beating -- there is no systole -- and there is no electrical activity in the heart. The heart is at a total standstill.
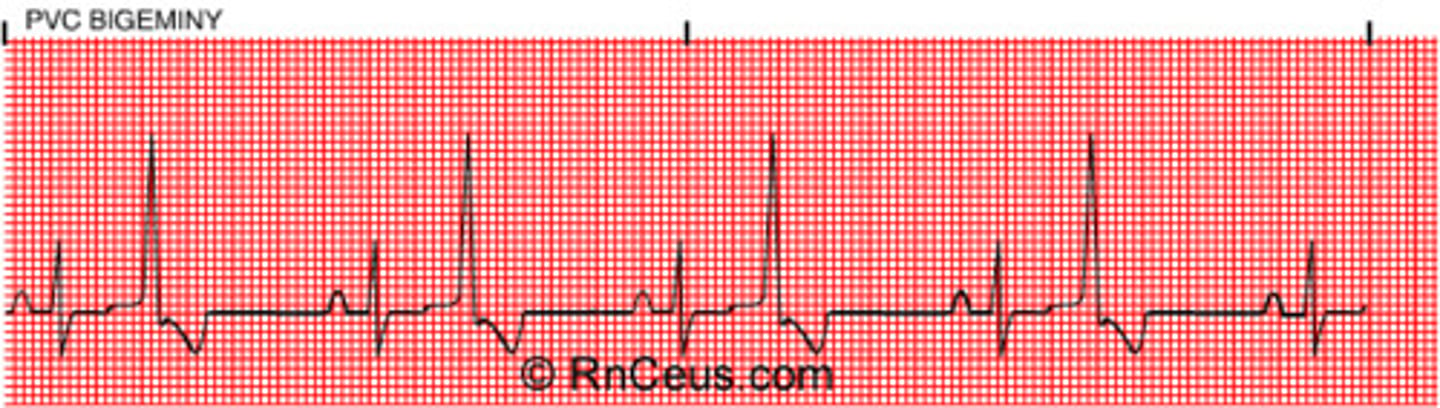
Premature ventricular contractions (PVC's)
Wide QRS
- may be unifocal or multifocal
- will have compensatory pause
- irreg rythm PVCs may be bigeminy, trigeminy, or quadrigeminy
- "run of" PVCS
- 3+ PVCs = Vtach!
Idioventricular rhythm
<40
looks like vtach but slow
- no P waves (from vent foci)
- Wide QRS
(serious, death like rhythm)
- called "dying heart" rhythm...occasional ventric beat b4 death (asystole)
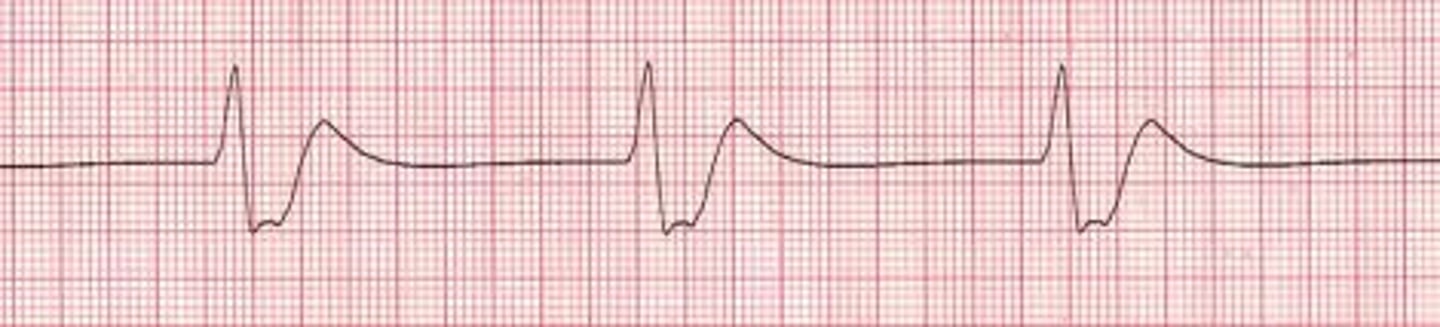
Accelerated idioventricular rhythm (AIVR)
40-120
- occur in short burst, usually following MI
- mostly asx with no progression to vtach / vfib
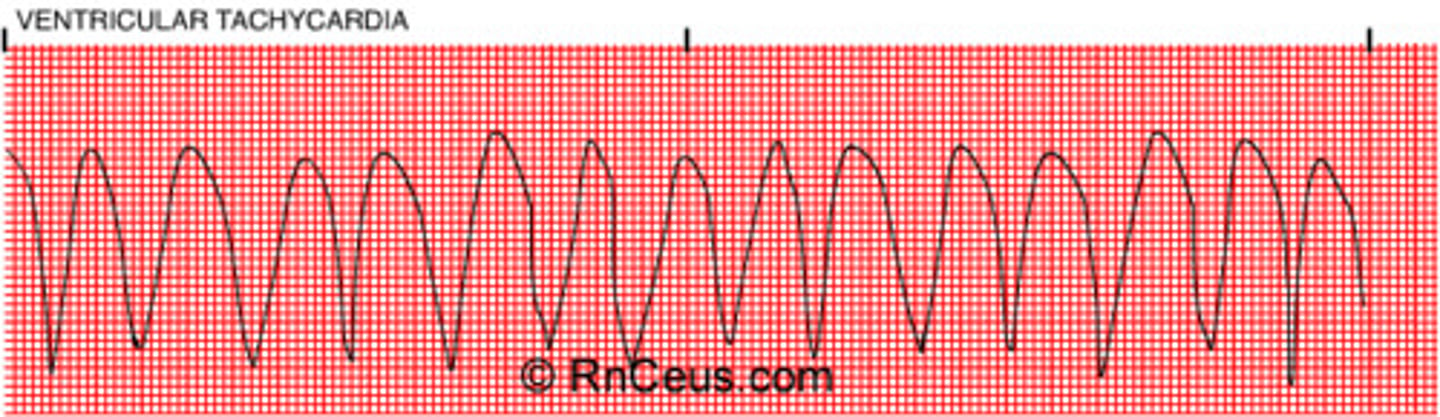
Ventricular tachycardia
150-250 (>120 from onysko)
- ventricle irritated and moving fast
- rapid, bizarre, wide QRS complexes
- 1 large QRS after another!
(in vtach pt may not have pulse)
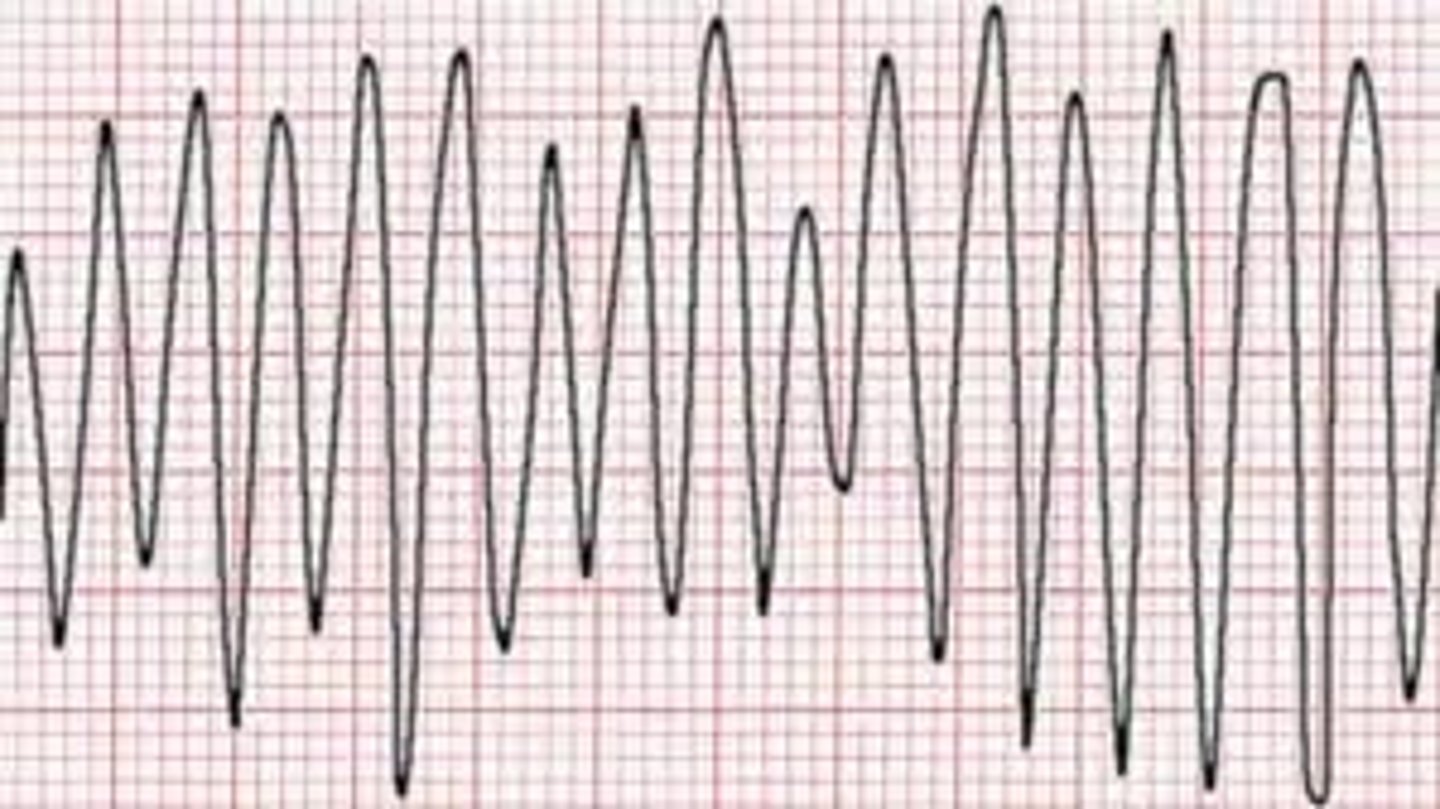
Ventricular Flutter
250-350
- smooth sine-waves w/ similar amp
- can lead to deadly arryth
goes right into vfib
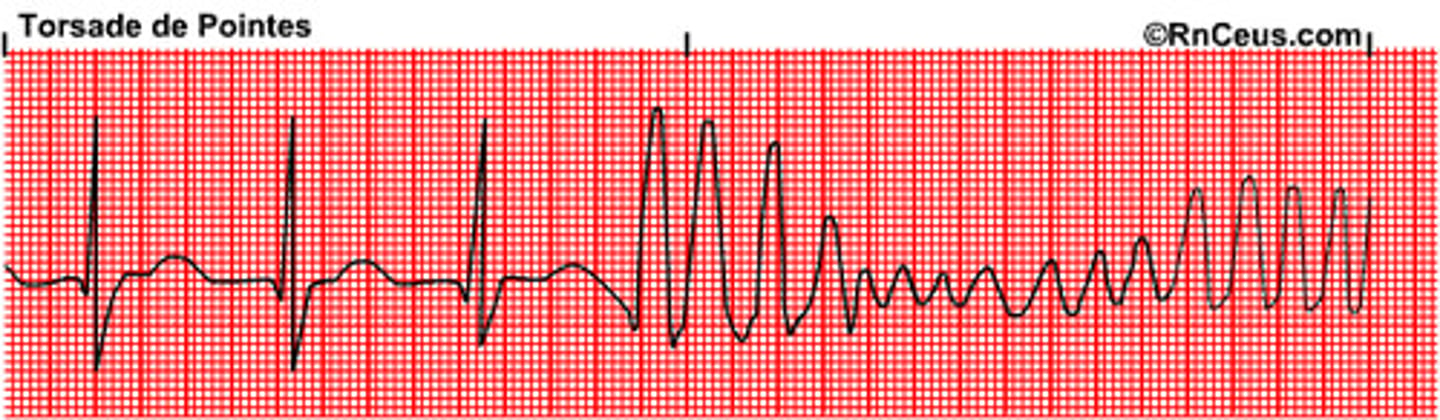
Tosades de Pointes
Flutter 250-350
- type of vtach, can lead to vfib
- ribbon like fashion (hallmark: up and downward deflection of QRS)
- d.t hypomagnesium
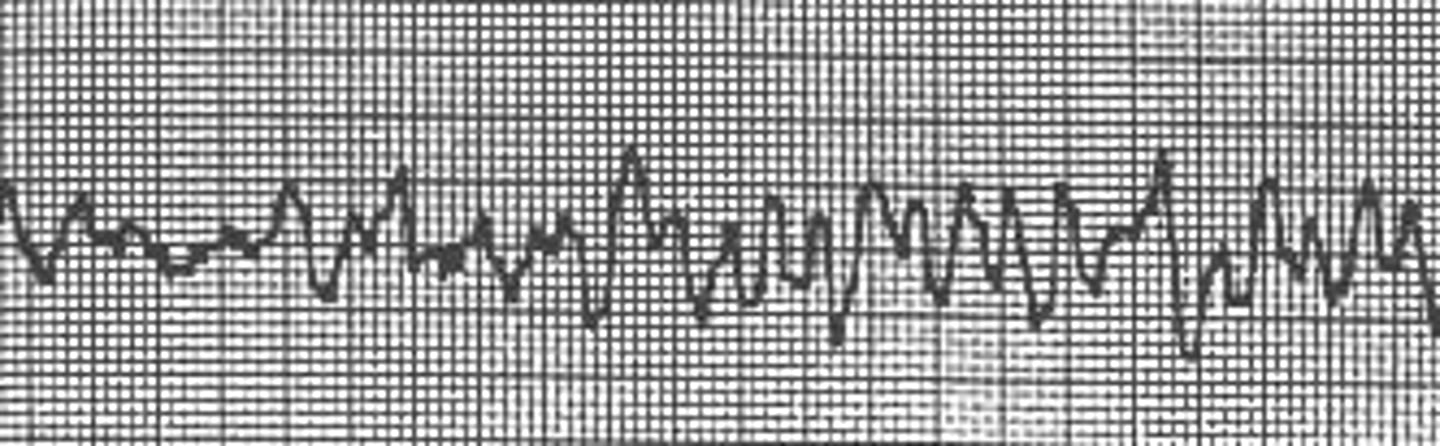
Ventricular Fibrillation
350-450
- "chaotic"
- mult vent foci rapidly discharging -> erratic vent rhythm
- no identifiable waves
- RESPOND IMMEDIATELY!
- no pulse or perfusion, pt=dead
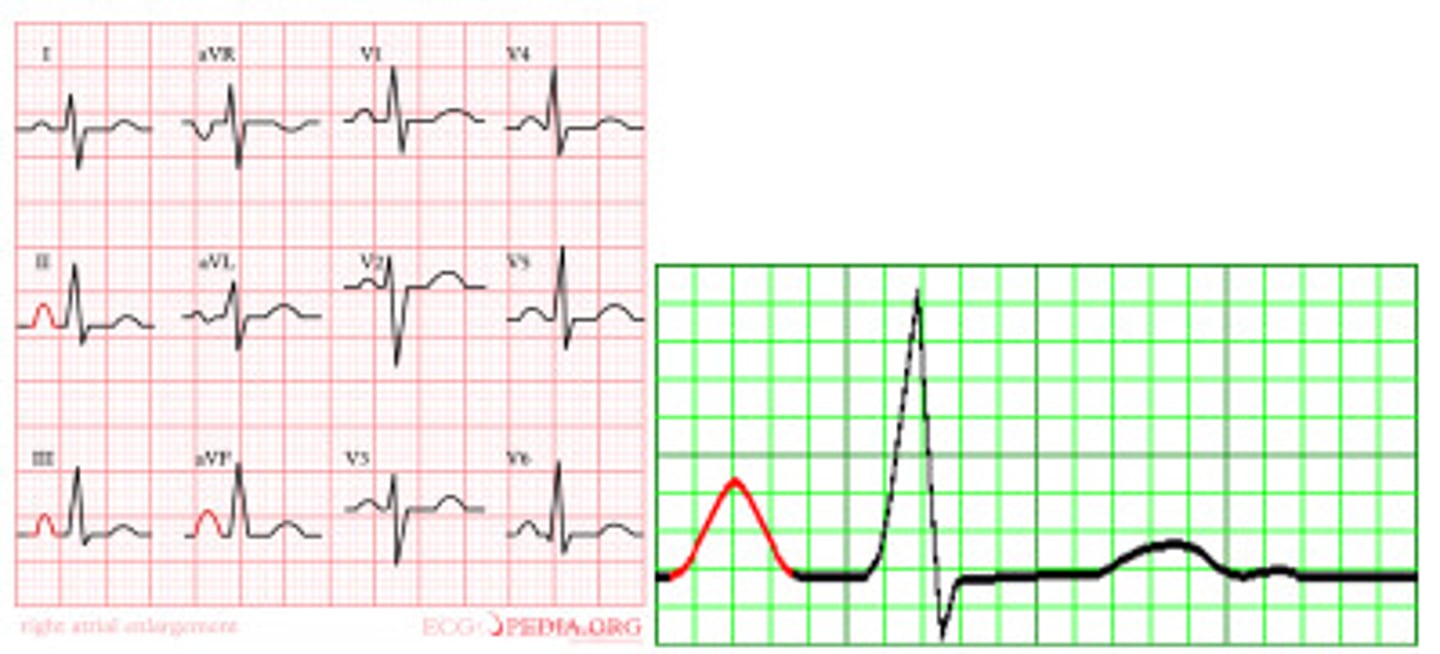
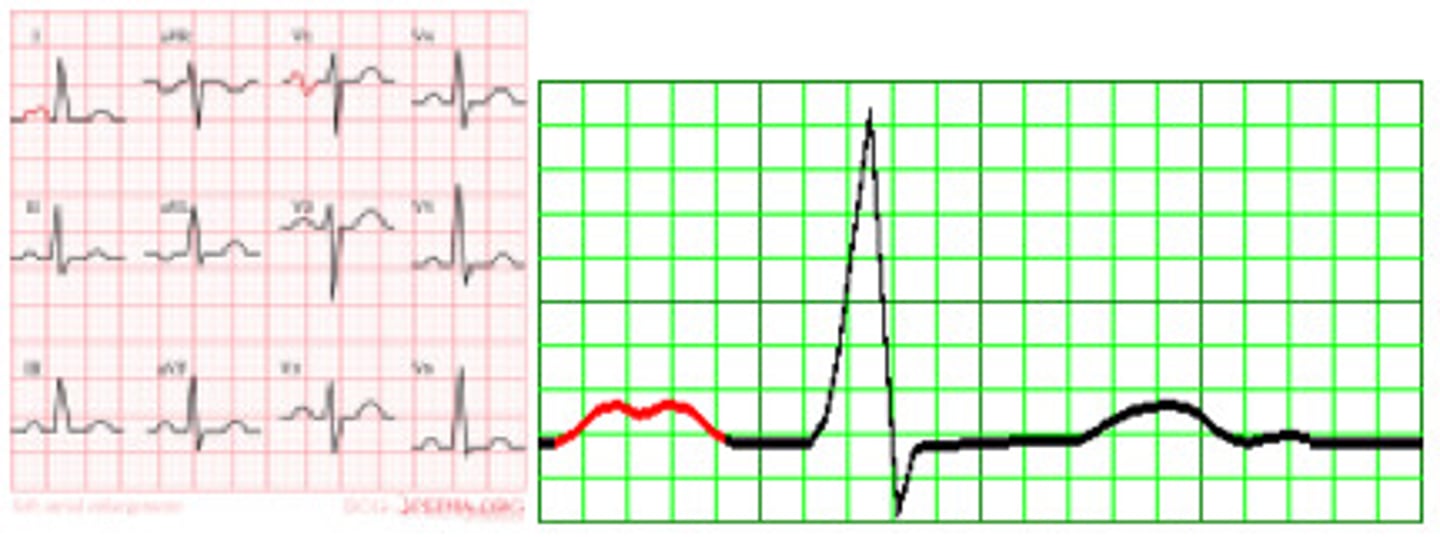
R atrial hypertrophy
tall P waves! (in lead II, III, and aVF)
- > 2.5 boxes
cause: pulm HTN, COPD, Pulm emboli
L atrial hypertrophy
I --> wide P wave (biphasic)
V1 --> P wave up & down like an S (terminal negativity)
R ventricular hypertrophy (RVH)
- tall R wave in V1 (inverted T here too)
- R gets progressively smaller as we go from V1-V4
- normally V1 has long S wave so looks like big V, when that is not the case think RVH
causes: Pulm HTN
(not too common)
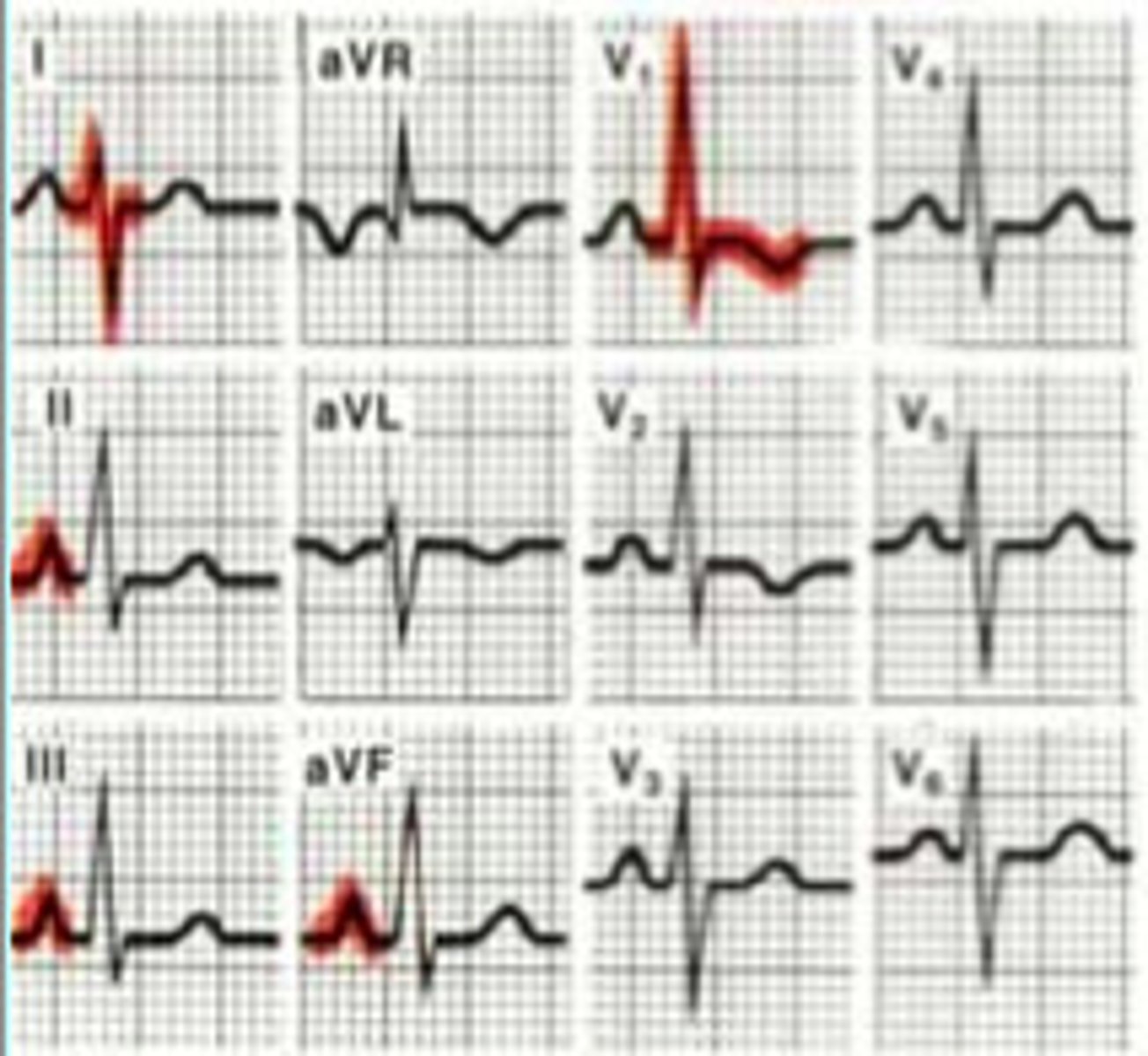
L ventricular hypertophy (LVH)
V1 --> deep/long S wave
V5/6 -> tall/high R wave
count boxes together if >35 LVH
causes: systemic HTN, aortic stenosis, mitral insuffic
(very common)
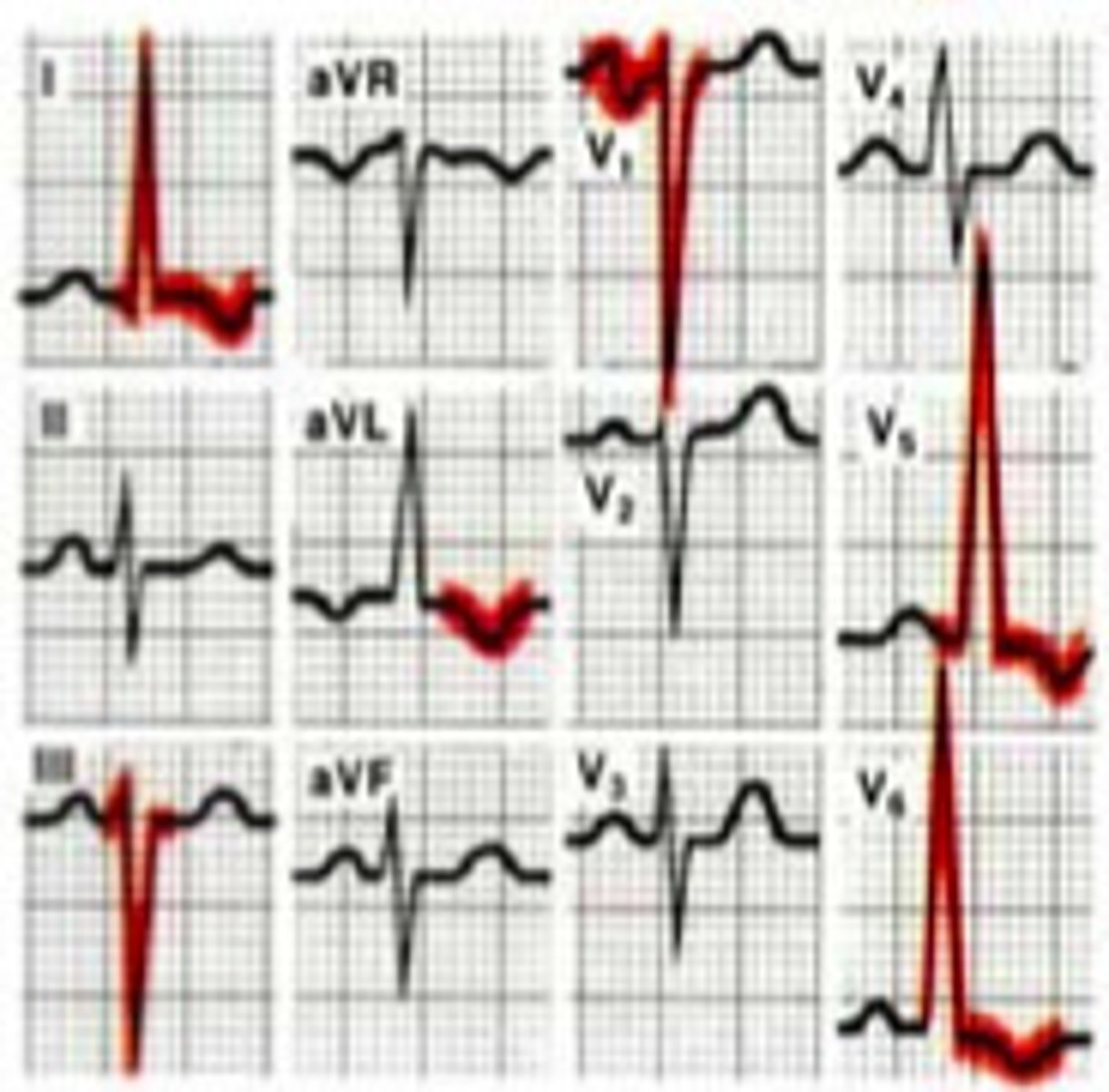
BBB
- Wide QRS >3 box
- 2-R waves "bunny ears"
A block in the Bundle Branch produces a delay in depol of the ventricle that it supplies
(note: can't read ischemia b/c BBB distort this)
if have L & R BBB = complete block
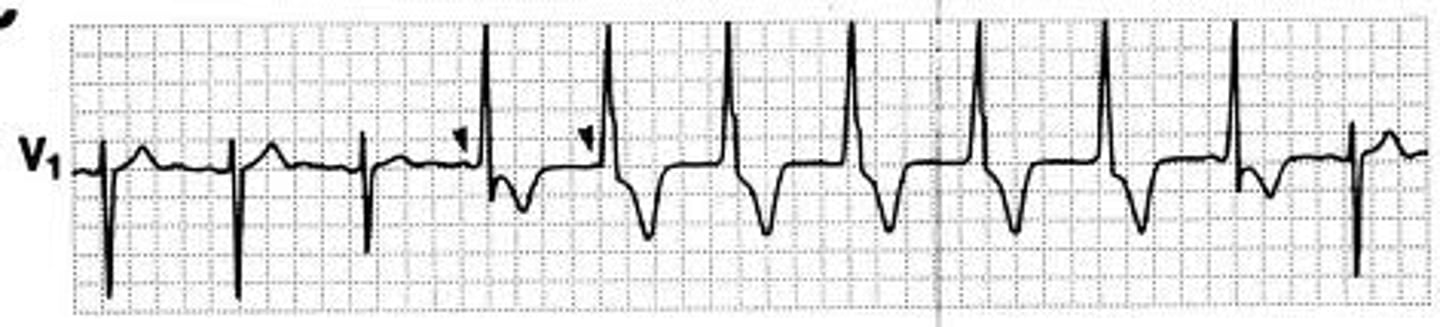
R Bundle Branch Block
- wide QRS >3 boxes (0.12)
- V1/V2 "bunny ears" (2-R waves)
(V1/2/3 all up)
- common, doesn't have much path assoc
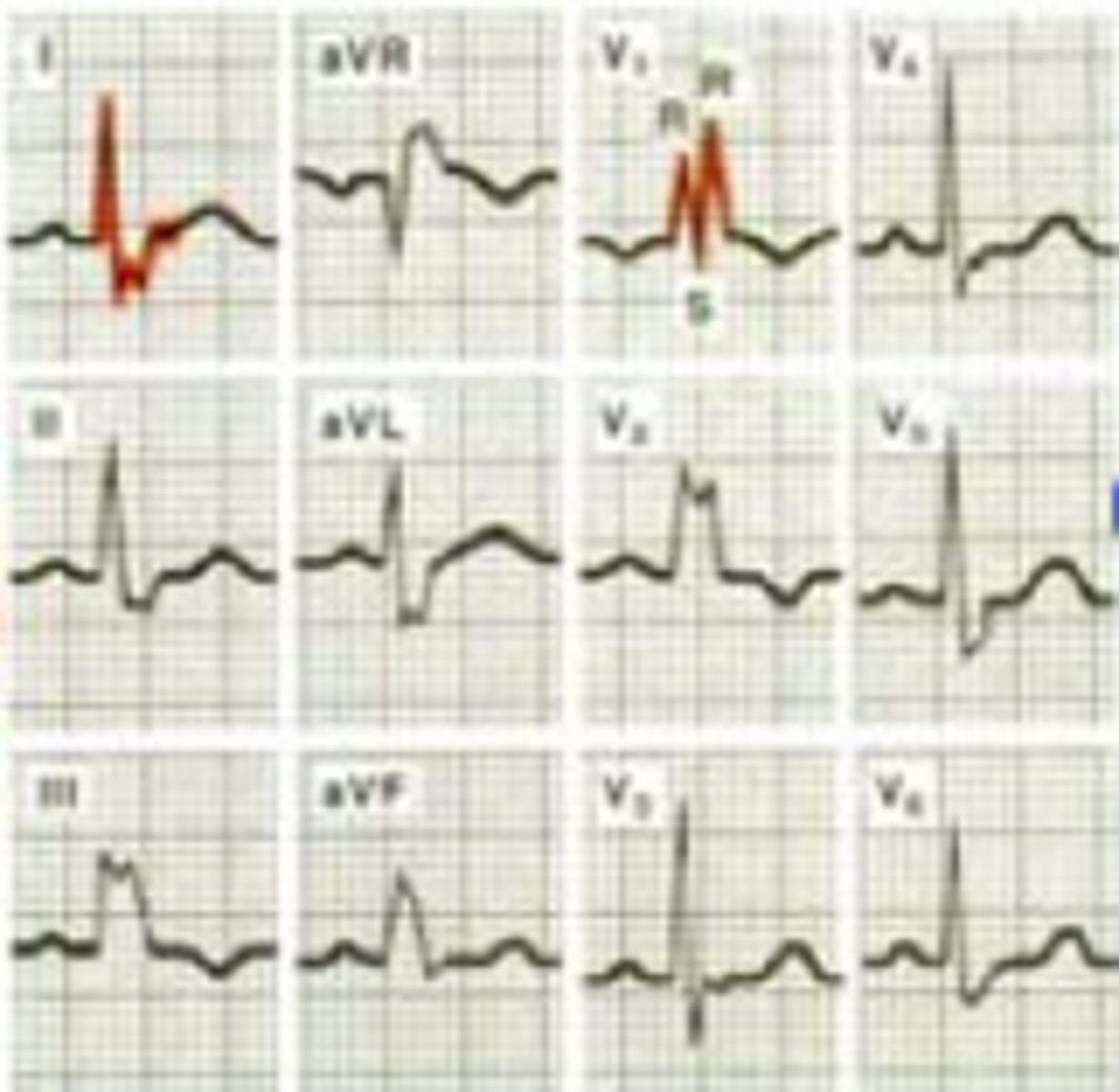
L Bundle Branch Block
- wide QRS >3 boxes (0.12)
- V5/V6 "bunny ears" (2-R waves)
(V1/2/3 all down)
- not as common, more patho
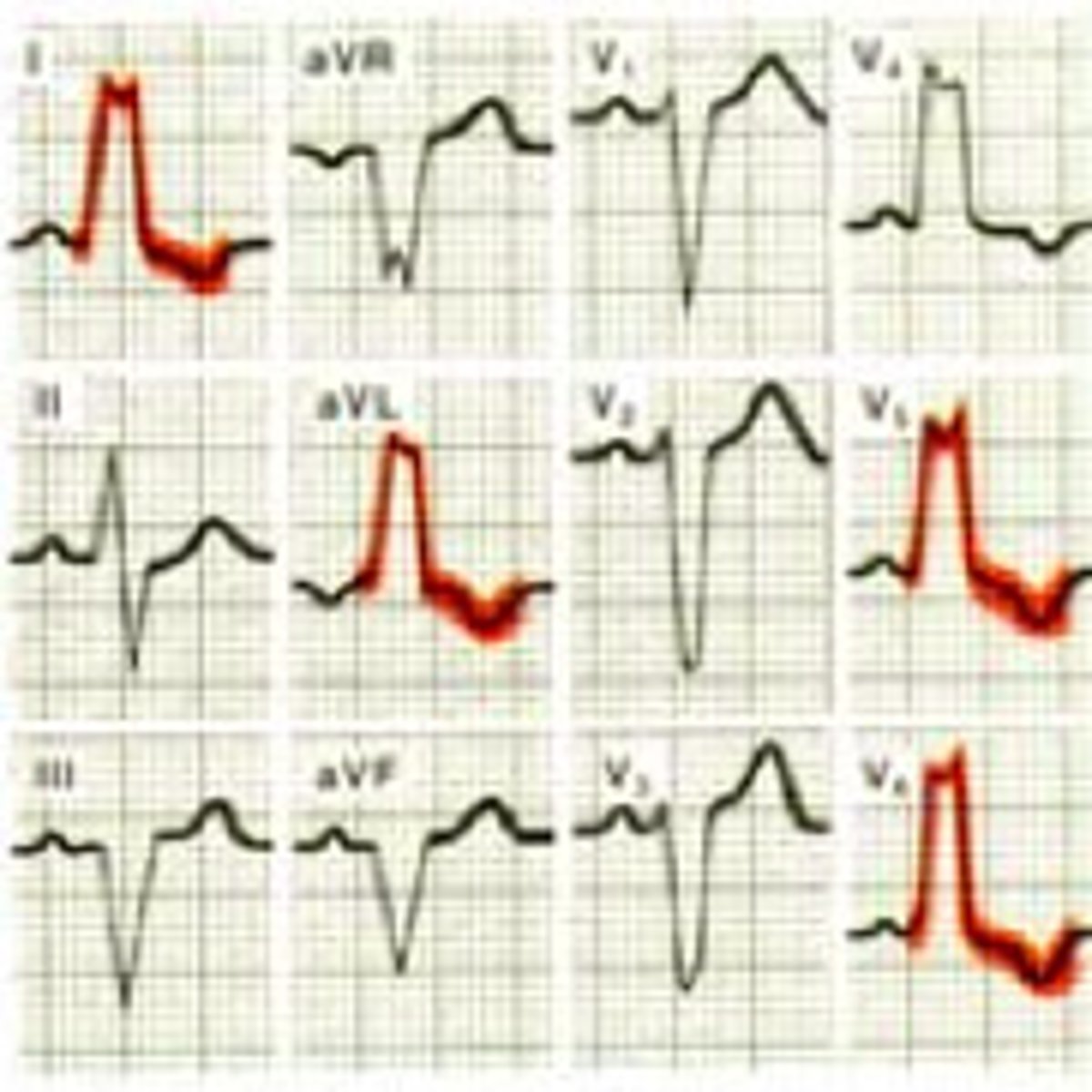
Myocardial Infarction (MI)
Ischemia: inverted Twave
Injury: ST seg elevation
Necrosis: Q wave present
- area of infarct doesn't conduct electrical activity
- infarction=cell death
(A MI (heart attack is) when blood vessels that supply blood to the heart are blocked, preventing enough oxygen from getting to the heart. The heart muscle dies or becomes permanently damaged)
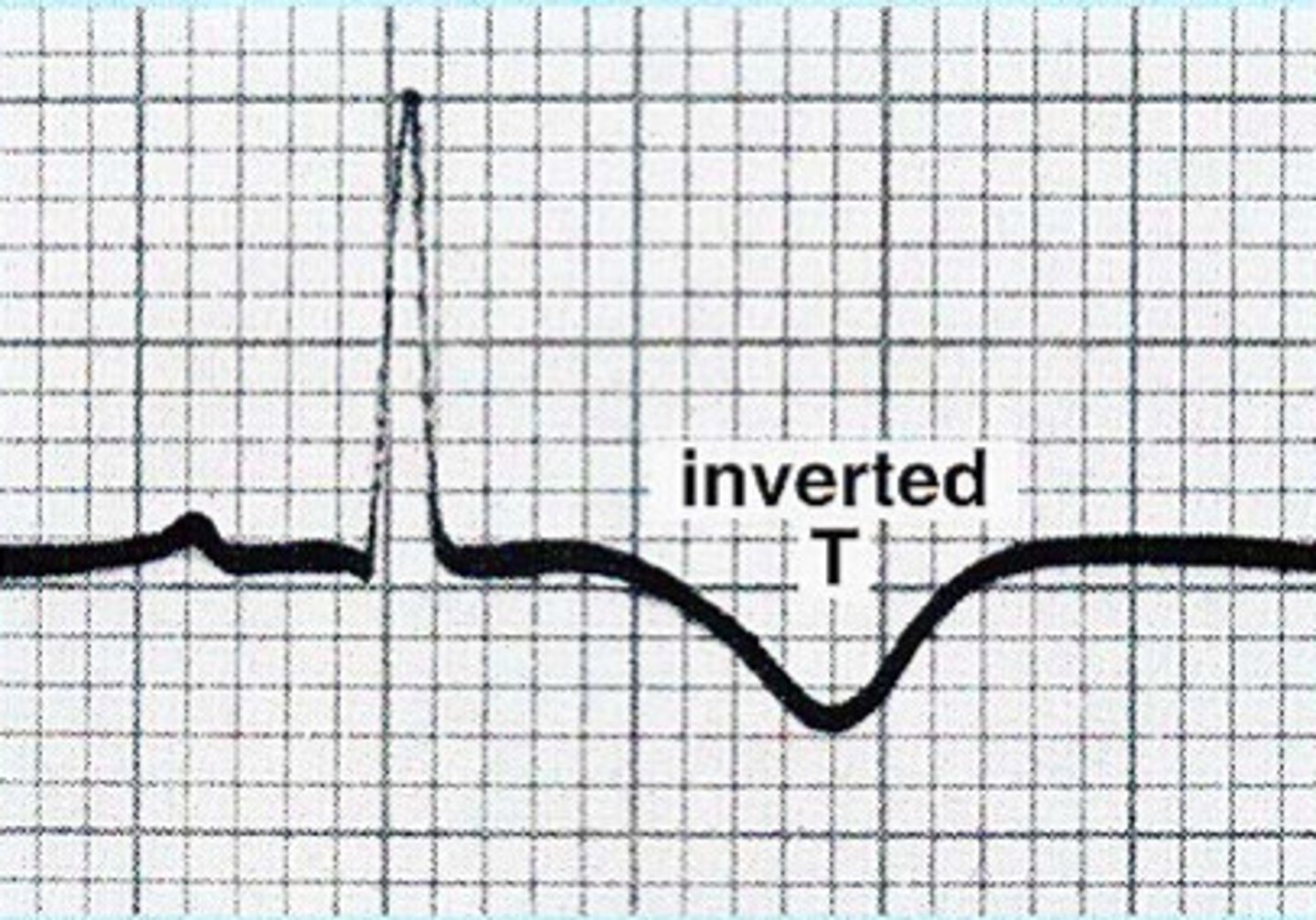
Ischemia
- T wave inversion
- Ischemia is caused by a decrease in oxygen to the myocardial tissue (hypoxia/diminished blood supply)
- can still save heart cells/reverse
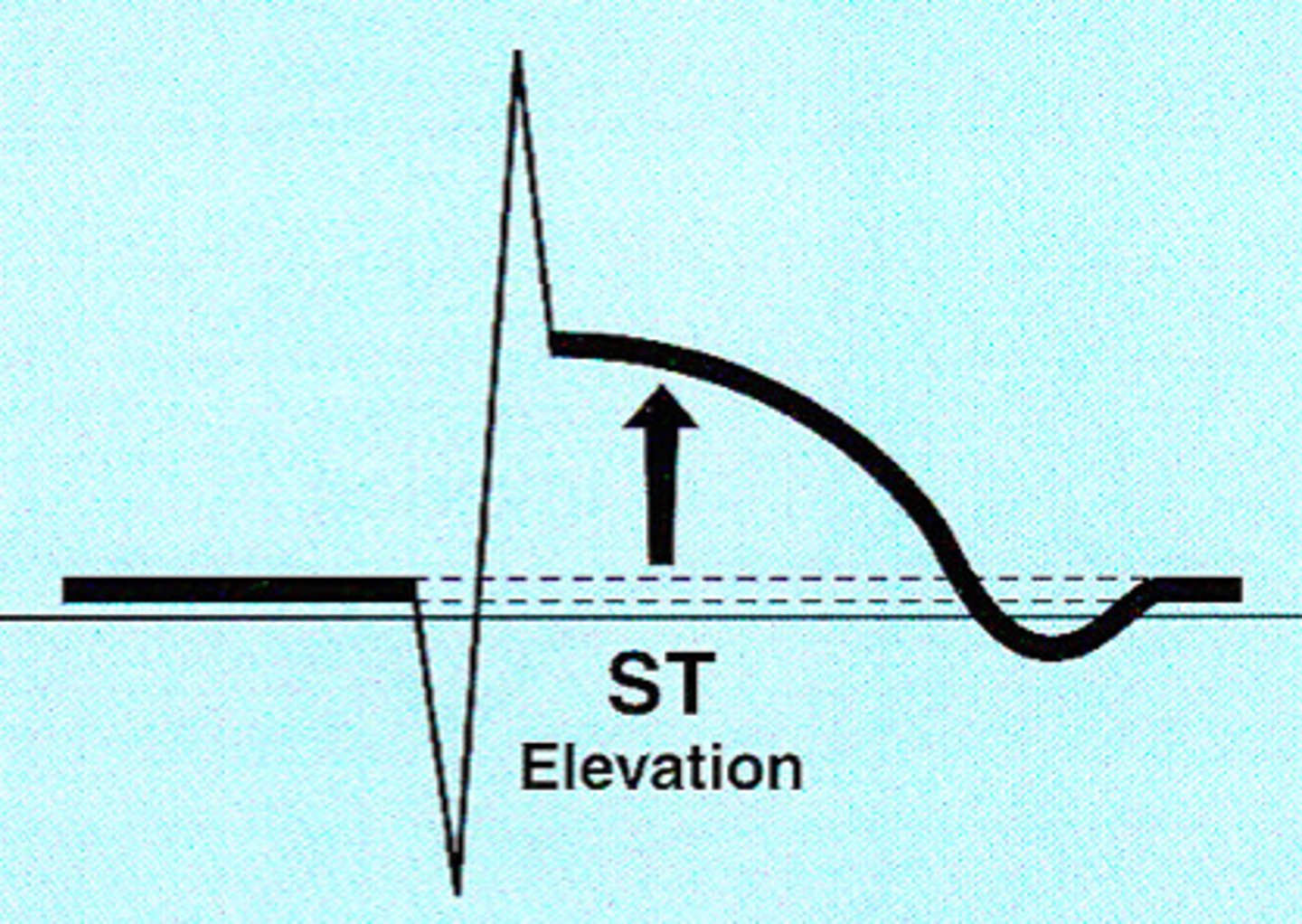
Injury
ST segment elevation (a sign of acute injury going on presently) (look for sad face)
- Injury indicates the acuteness of an infarct (acute or recent)
- can still save heart cells/reverse
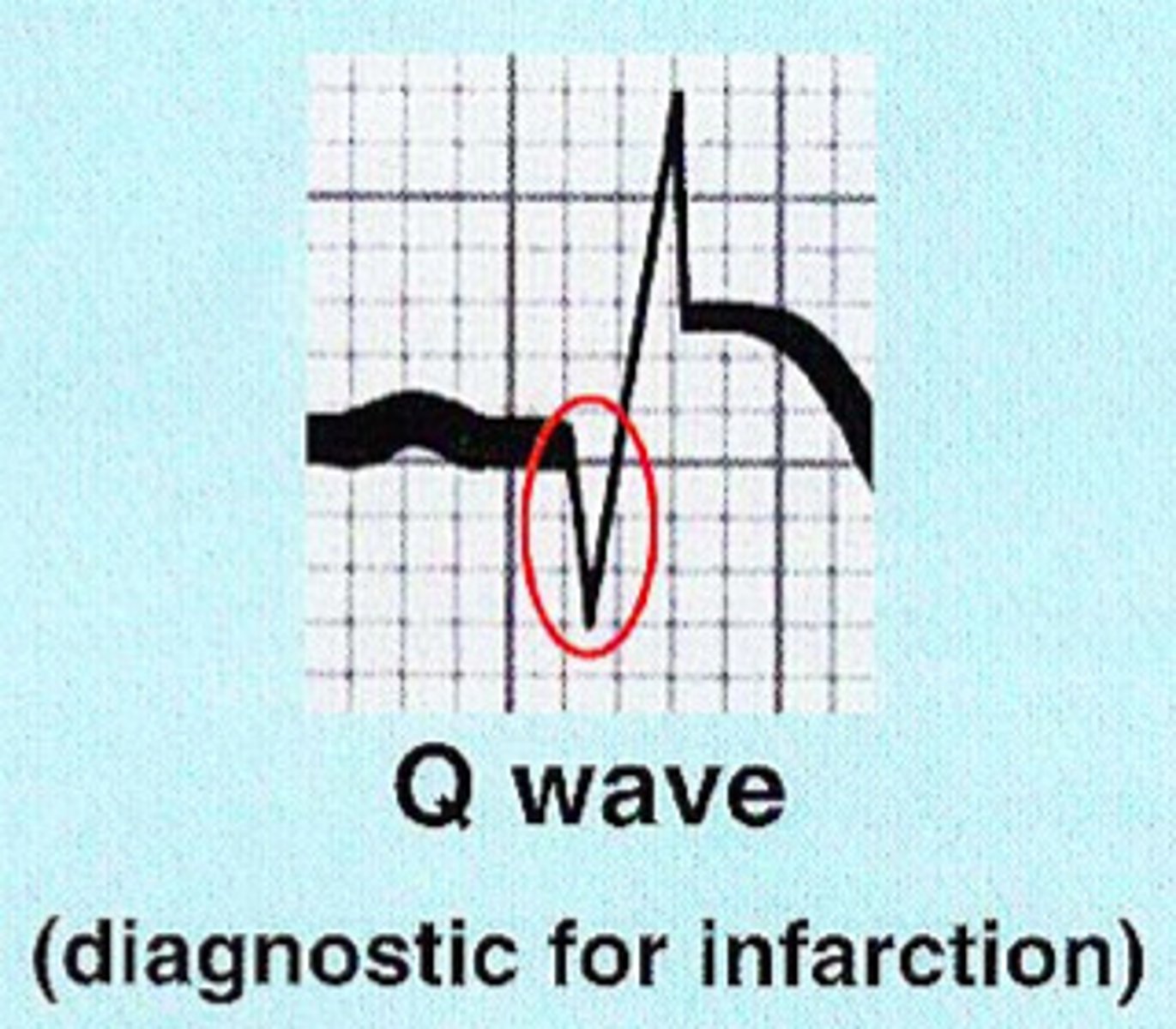
Necrosis
significant Q waves
(≥than 1 square wide or ≥1/3 amplitude)
- indicated by Q-waves which make the dx
- Infarction is completed, now dead tissue
(canNOT be reversed, permanent damage)
anterior wall
V1, V2, V3, V4
- occlusion of anterior descending coronary artery
Anteroseptal region
V1, V2
Inferior wall
II, III, aVF
- occlusion of right or left coronary artery
Lateral wall
I, aVL and V5, V6
- occlusion of circumflex artery
Posterior wall
since no post lead look in V1 for unusually large R wave
- occlusion of right coronary artery
Angina pectoris
...
Unstable angina
...
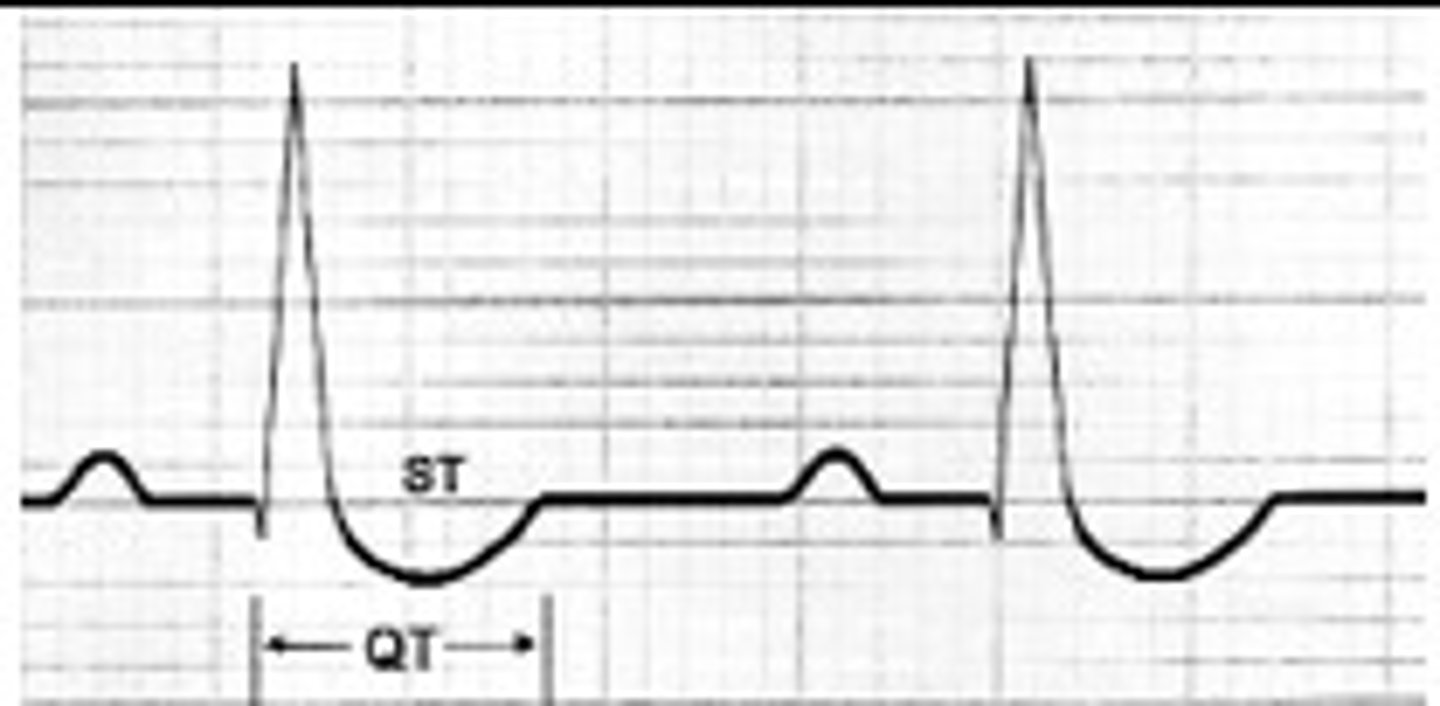
Digitalis Effect
- shortened QT interval
- characteristic down-sloping ST depression (SCOOPING ST seg)
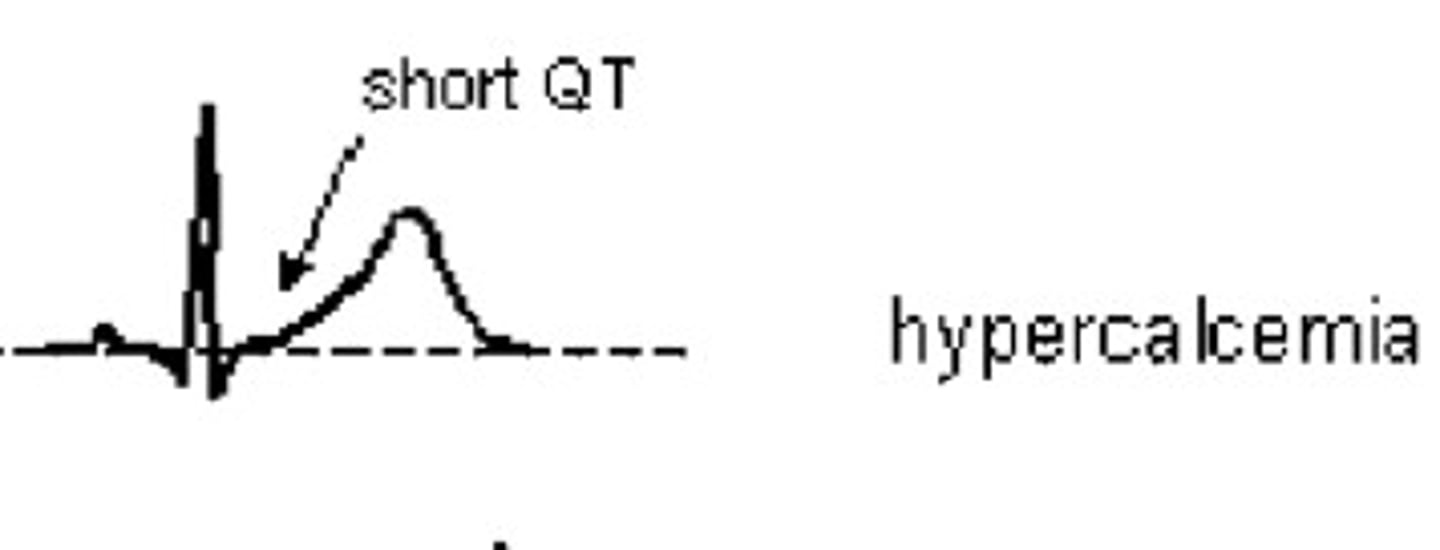
Hypercalcemia
Short/absent QT segment
(tooo healthy --> short QT (skinny))
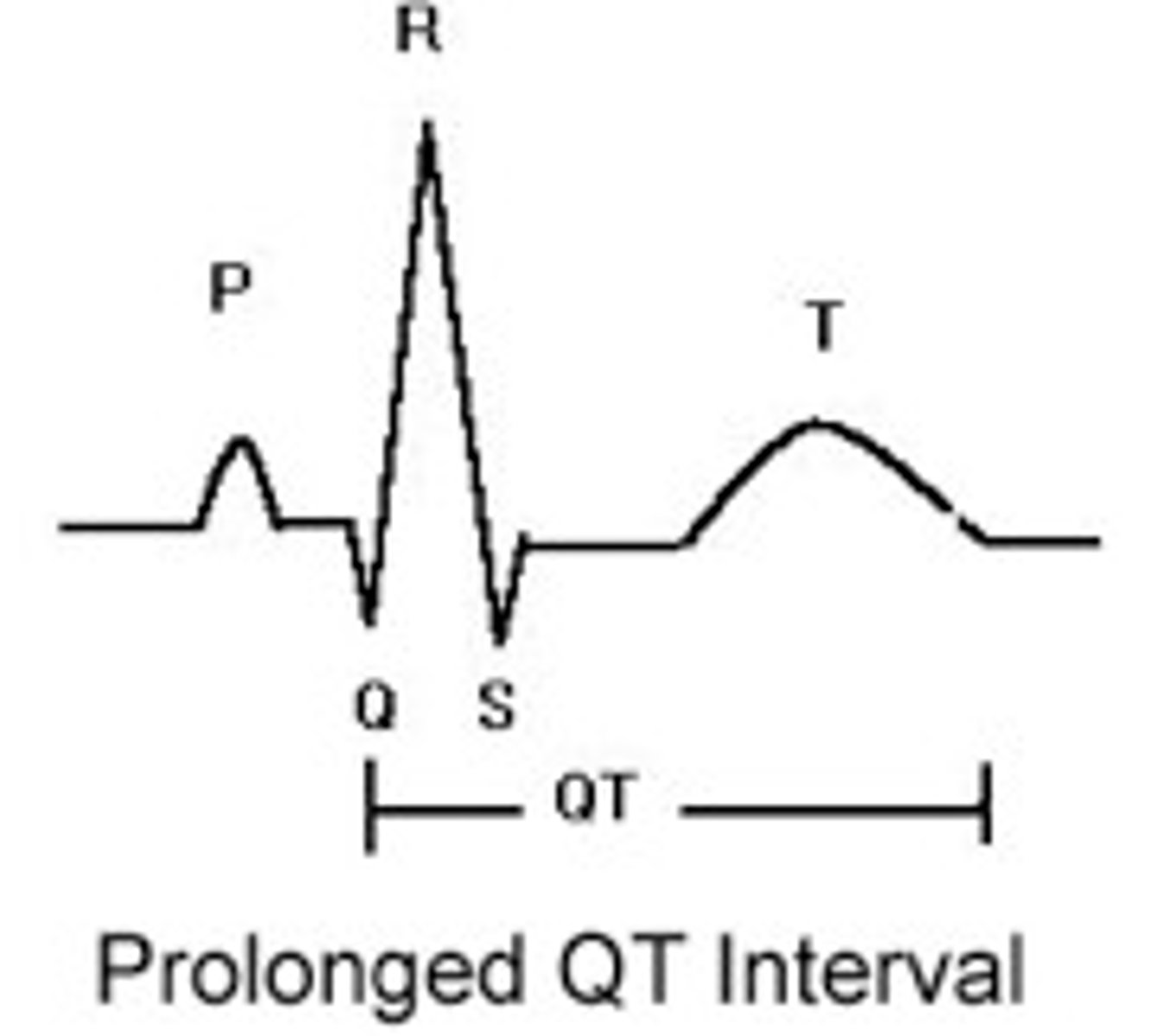
Hypocalcemia
(not healthy (not taking vit like Ca++) so look like a hipo which is large -> long QT)
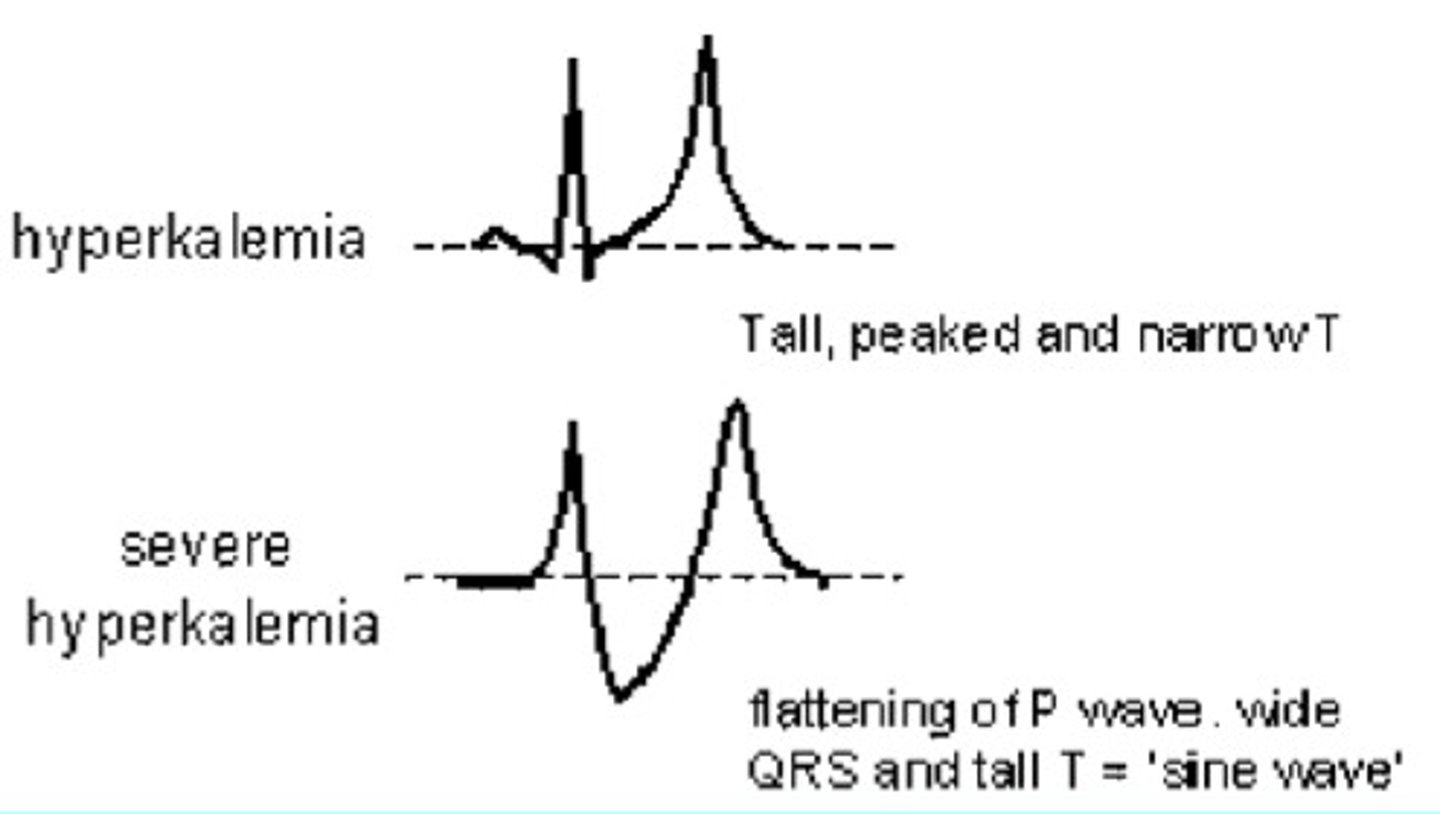
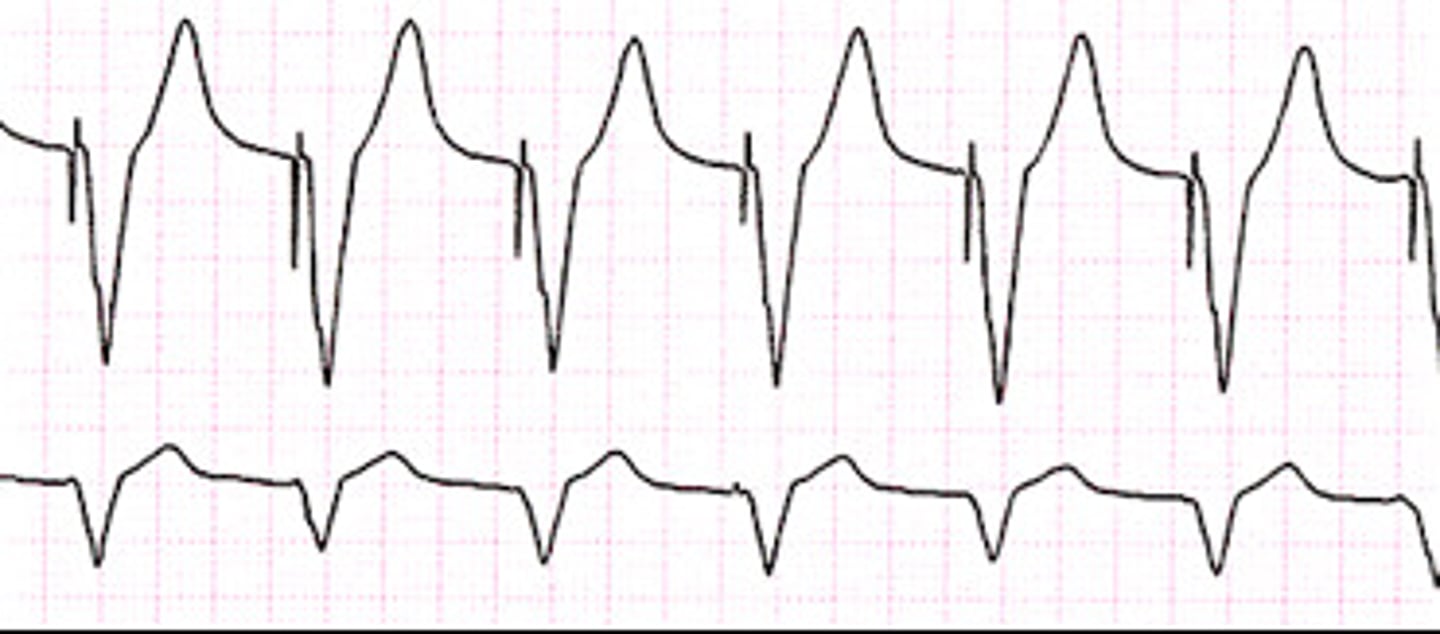
Hyperkalemia
tall, peaked and narrow T
severe --> flattening of P wave, wide QRS, and tall T='sine wave'
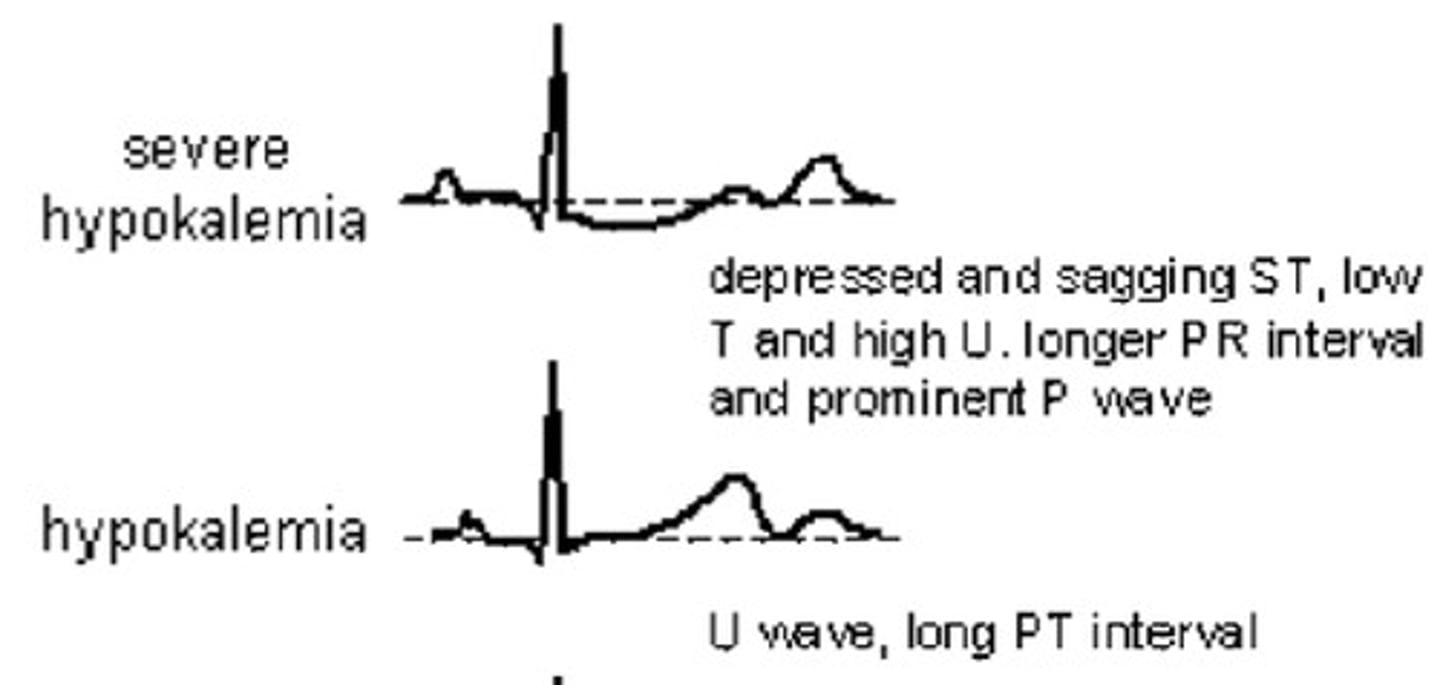
Hypokalemia
- flat T present
- depressed ST seg
- U wave to prominent U wave
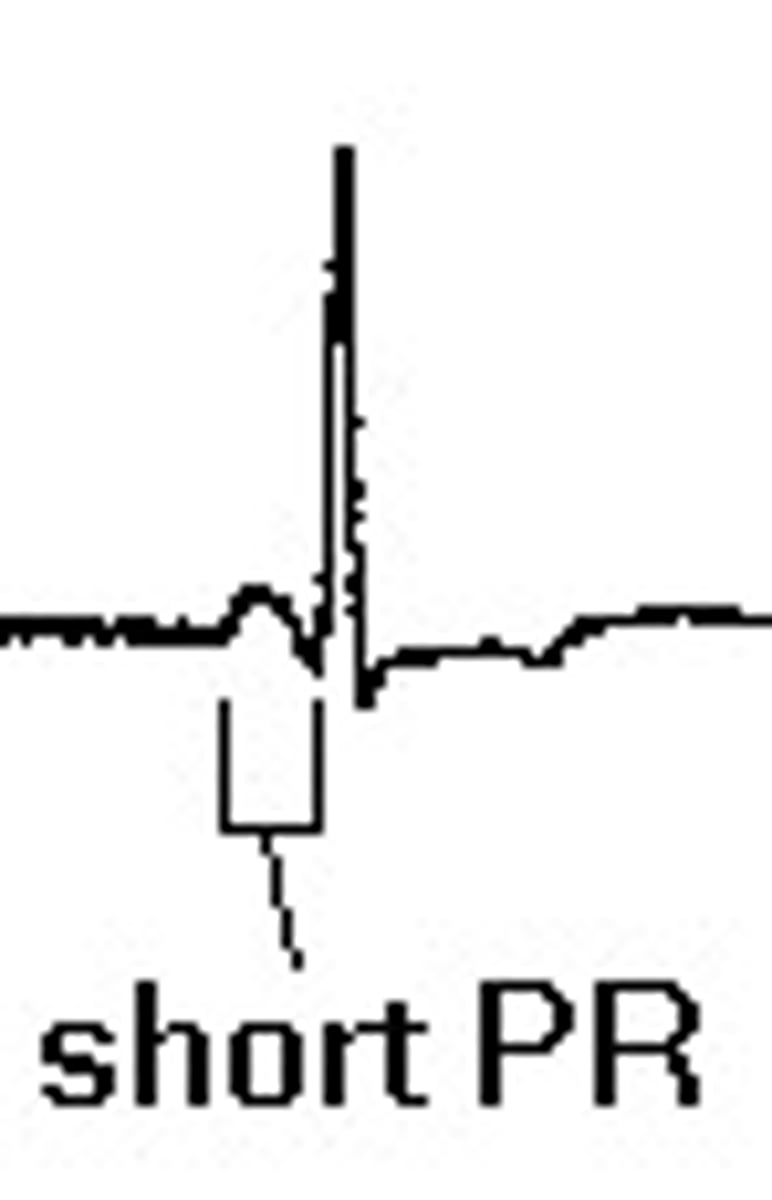
Lown-Ganong-Levine Syndrome
AV node by passed, so short PRI
P adjacent to QRS

Pacemakers
pacemaker spike (may be small; sometimes missed)
- not supraventricular so wide QRS
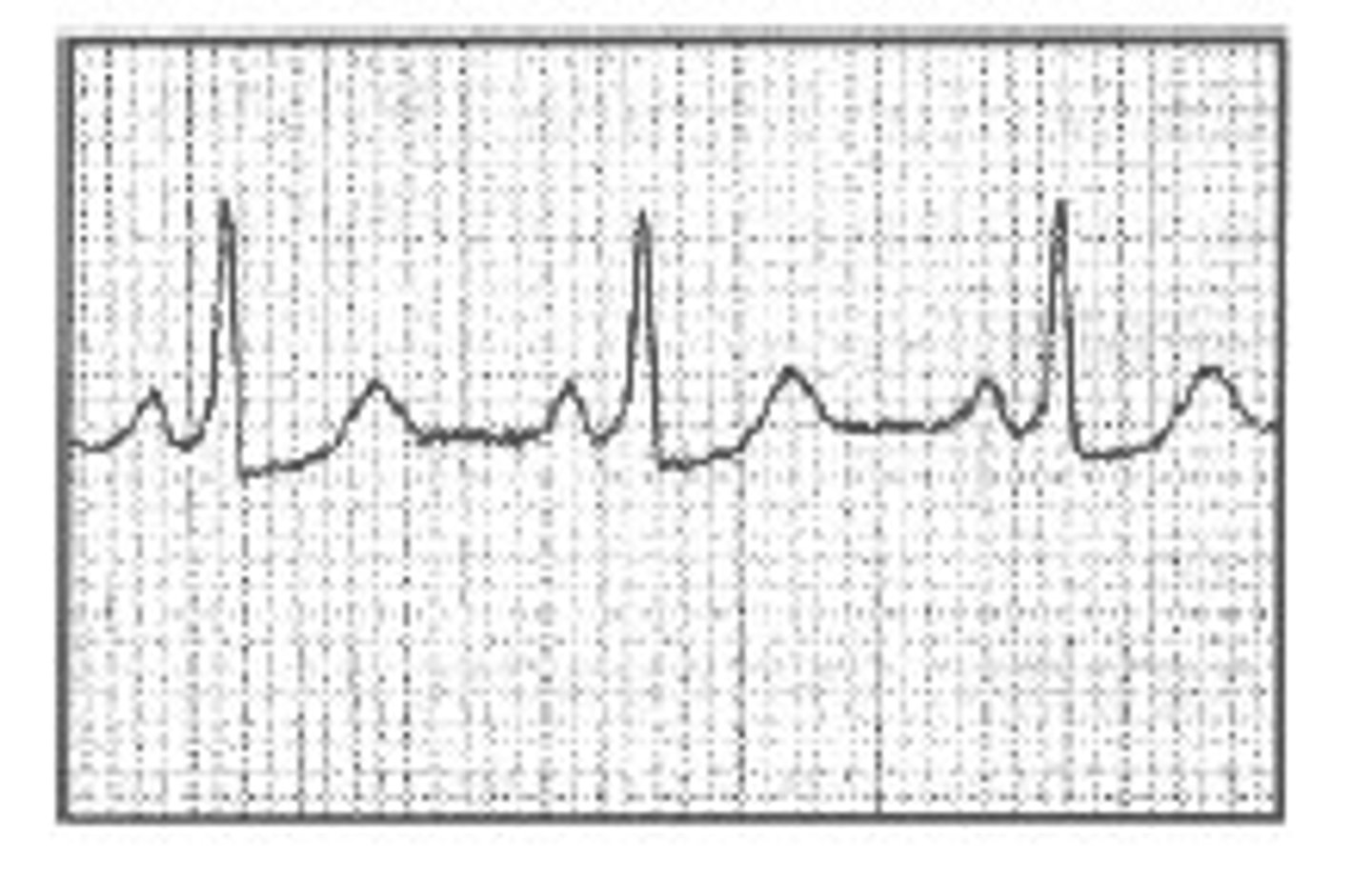
Pericarditis
ST segment elevated in ALL leads
T wave: may be elevated off the baseline
Pulmonary embolus
(S1 Q3 T3)
Lead I: wide S
Lead II: ST depression
Lead III: large Q and Inverted T
V1-V4: inverted T waves
Acute right BBB
Wolf-Parkinsons-White
- P wave is immediately followed by short delta wave
- slurred upstroke on wide QRS w/ short or no PRI
- common condition can lead to parox tachy
(ppl born w/ extra fibers)
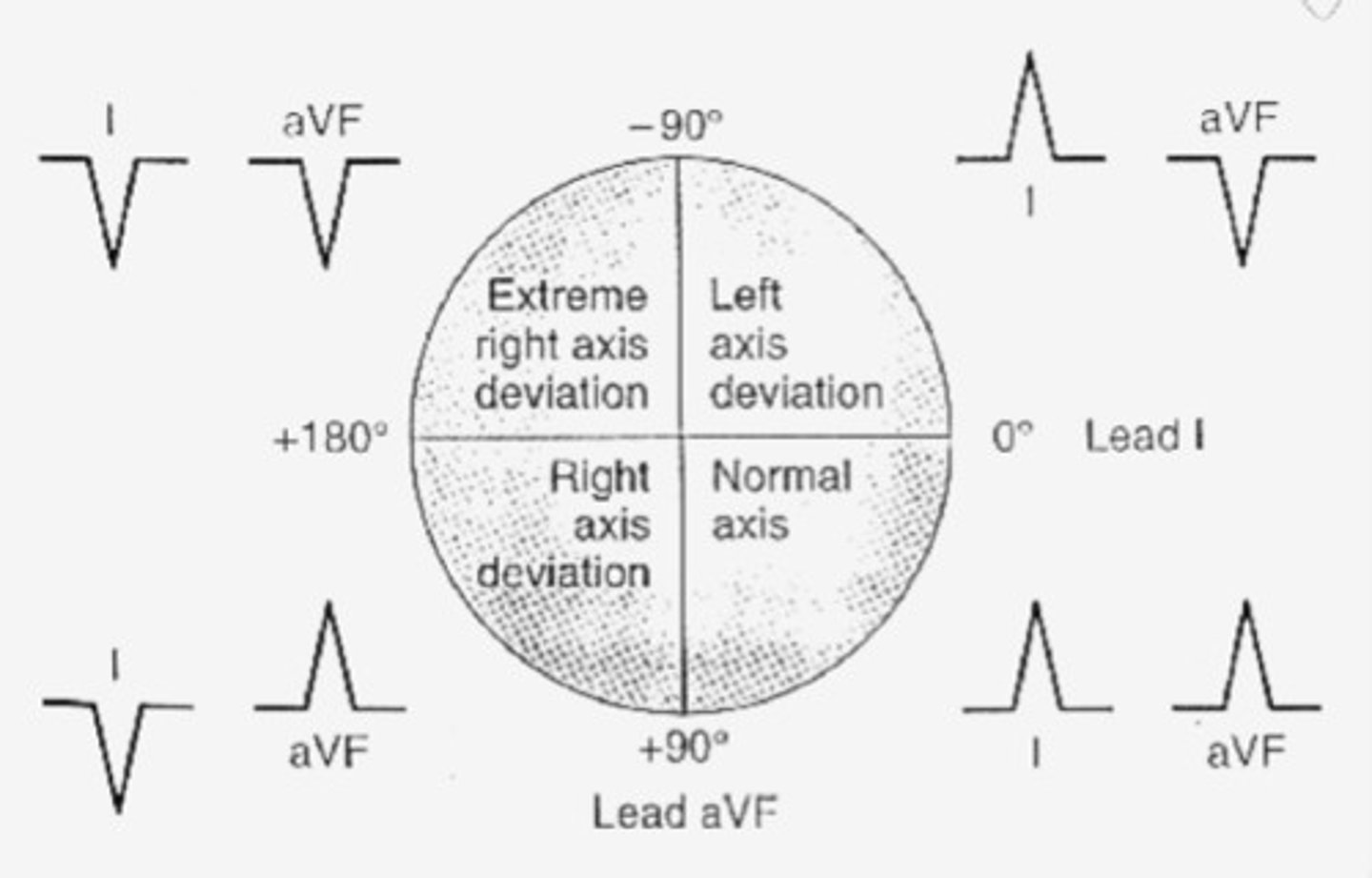
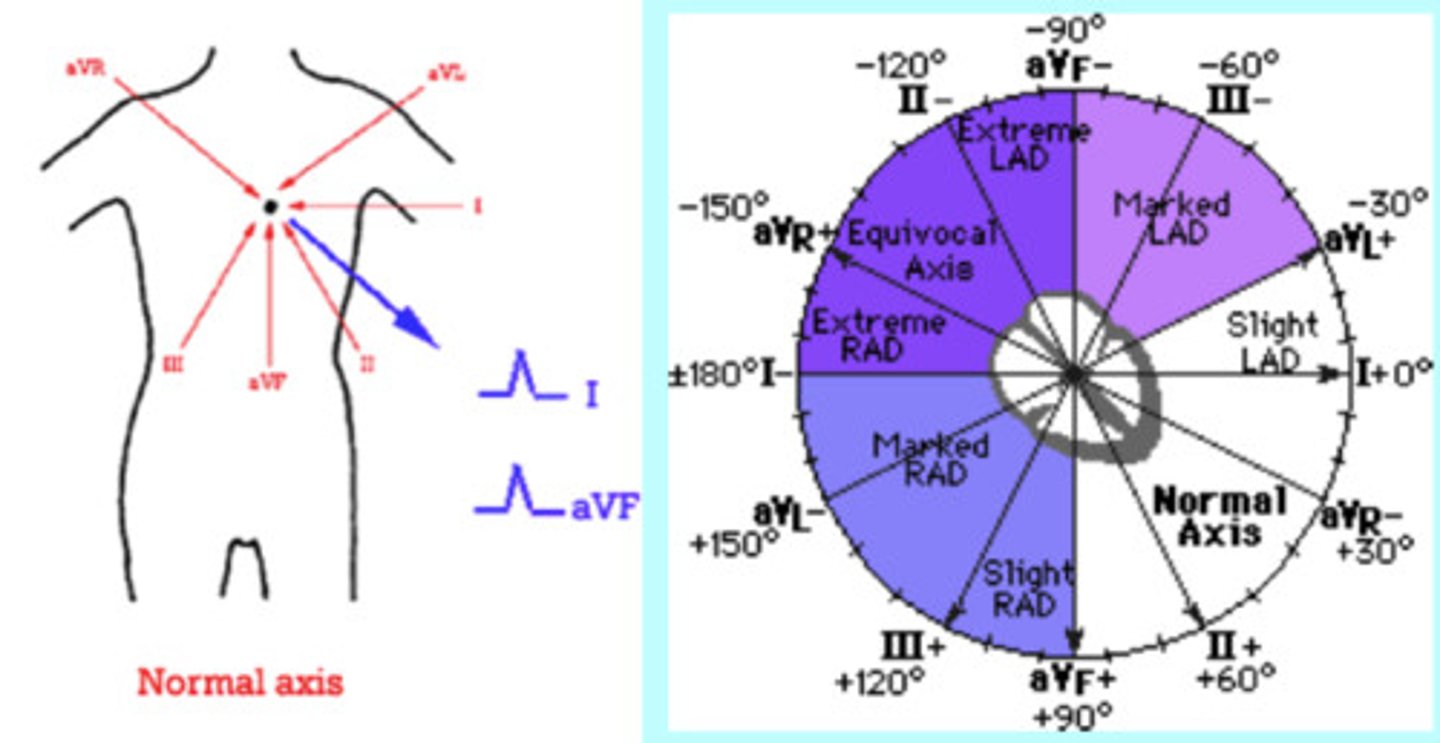
Axis
Refers to the direction of movement of depolarization
- Look in leads I and AVF
- I-left, AVF-right
Thumbs:
- both up = Normal axis
- both down = Extreme right axis deviation
- Lup/Rdown = Left axis deviation
- Rup/Ldown = Right axis deviation
- Specific axis degrees: determine type of deviation, choose most iso-electric line and go to that line on the circle chart. Go 90 degrees into the good quadrant (the one you know you're in) and that will tell you the exact degrees.
Axis pic
Wide QRS
Vtach, PVC, 3o AV block, BBB
Rate 40's
3o AV block, 2o AV block type II, or ventricular rhythm