Intellectual Disability
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
mental retardation (MR)
term often used in schools and social service agencies
(outdated term)
*usually IQ driven
(below 70-75)
**disability must originate before age 18
intellectual disability (ID)
preferred term
(interchangeable with MR)
*still includes IQ cut-offs
**ALL will have developmental disability
developmental disability
defined by Developmental Disabilities Assistance and Bill of Rights Act (2000)
*NO IQ cut-off
**often used in context of IDEA eligibility
conditions associated with intellectual disability
- fetal alcohol syndrome
- down syndrome
- autism
- prader-willi syndrome
- cri du chat syndrome
- corenlia delange syndrome
- fragile X
- hurler syndrome
- lesch-nyhan syndrome
- ardt syndrome
- williams syndrome
- angelman syndrome
cri du chat syndrome
rare chromosomal disorder due to loss of material from 5p
- initially present with hypotonia
- facial abnormalities
- minor UE abnormalities
- scoliosis/congenital heart disease is common
*high pitched cry (like a kitten)
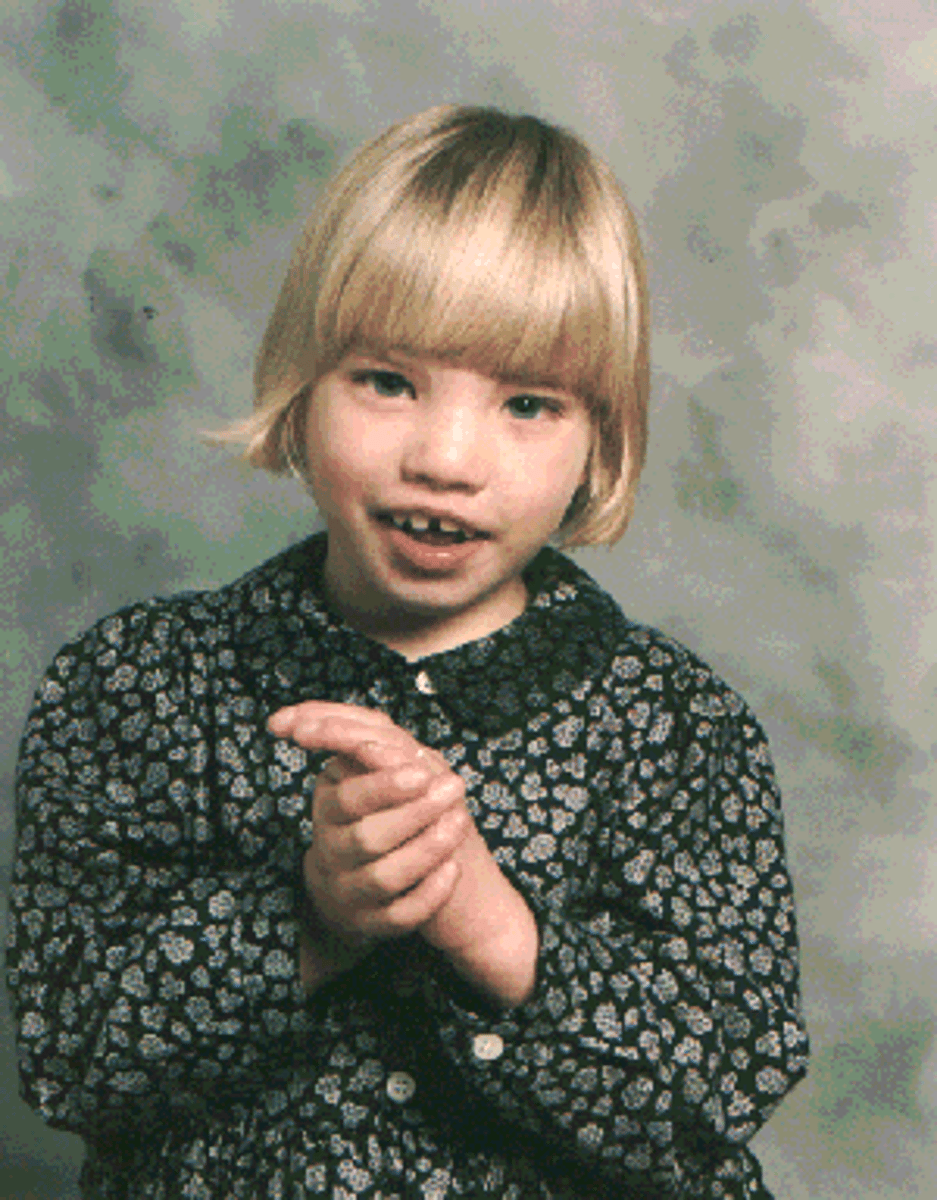

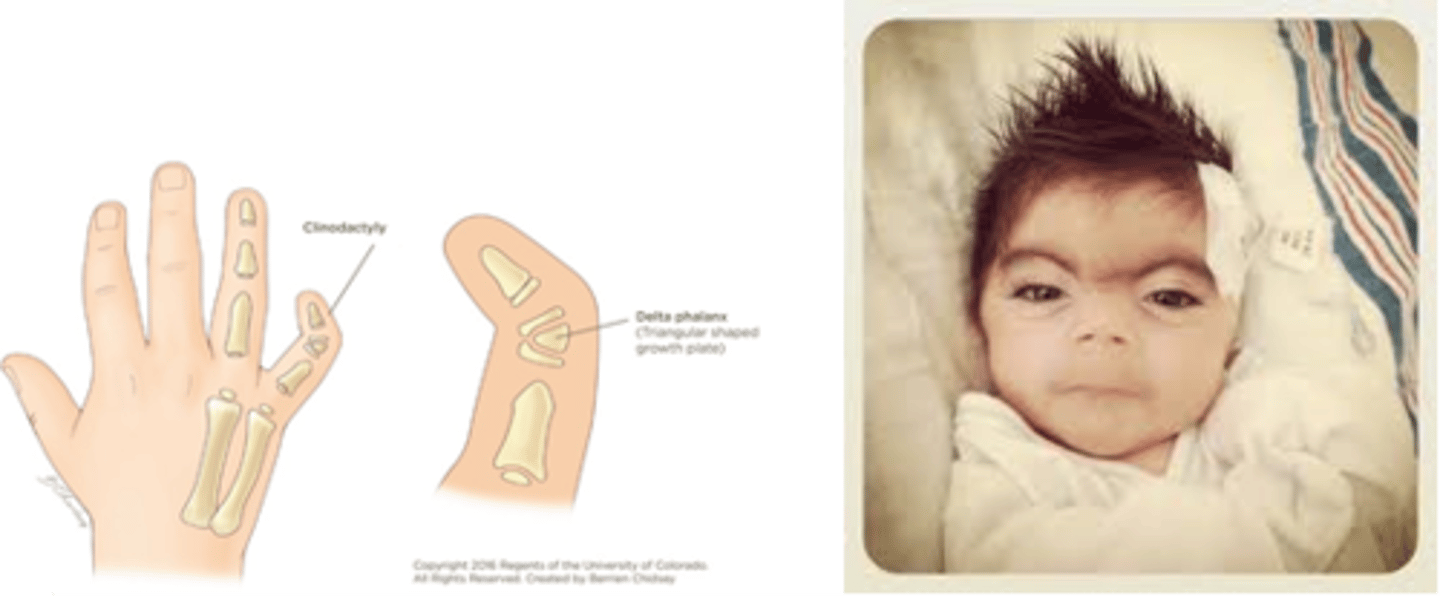
cornelia deLange syndrome
genetic mutation characterized by:
- limb abnormalities
- microcephaly
- severe growth retardation
- spasticity
- intention tremor
- seizures
- clinodactyly of the fifth fingers
- respiratory and GI problems, congenital heart disease
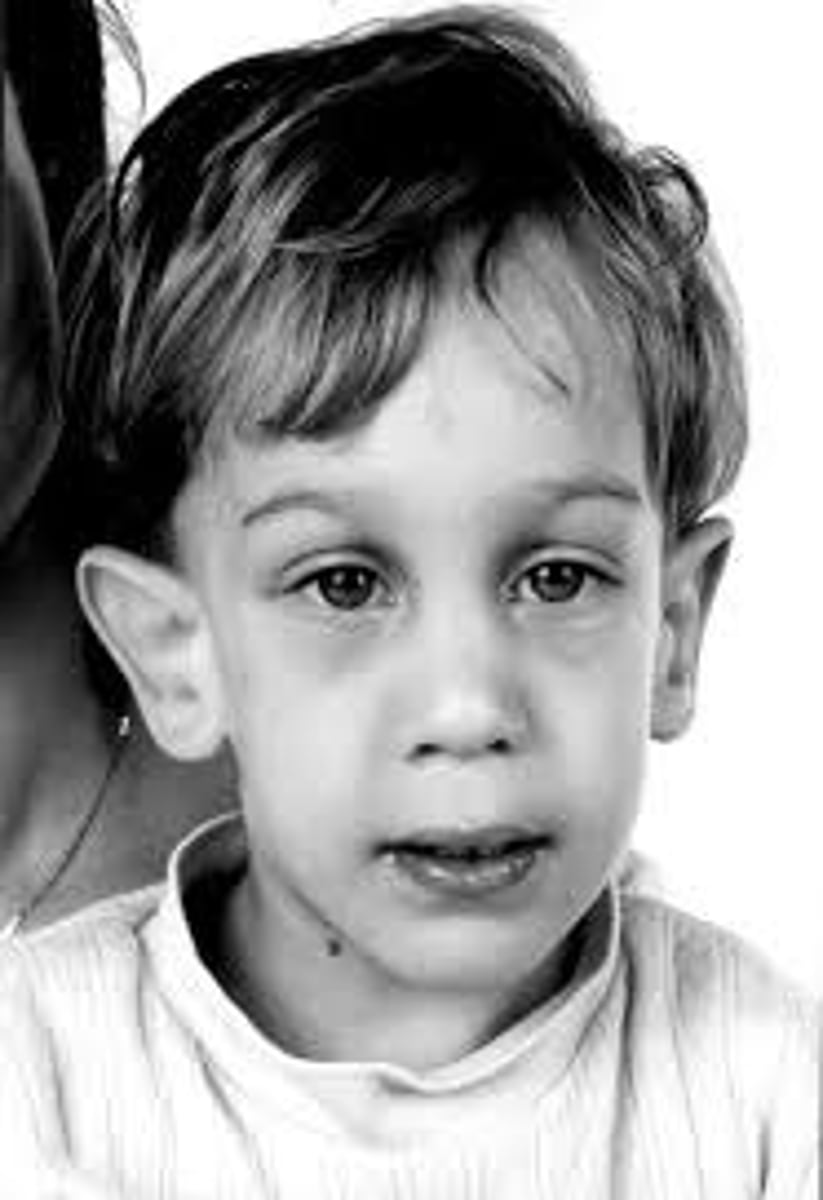
fragile x syndrome
most common form of inherited ID
genetic abnormality characterized by:
- poor coordination & motor planning
- tremor/ataxia
- ADD
- anxiety
- seizures
- connective tissue abnormalities
(DDH, scoliosis, pes planus)
- mitral valve prolapse
- autism
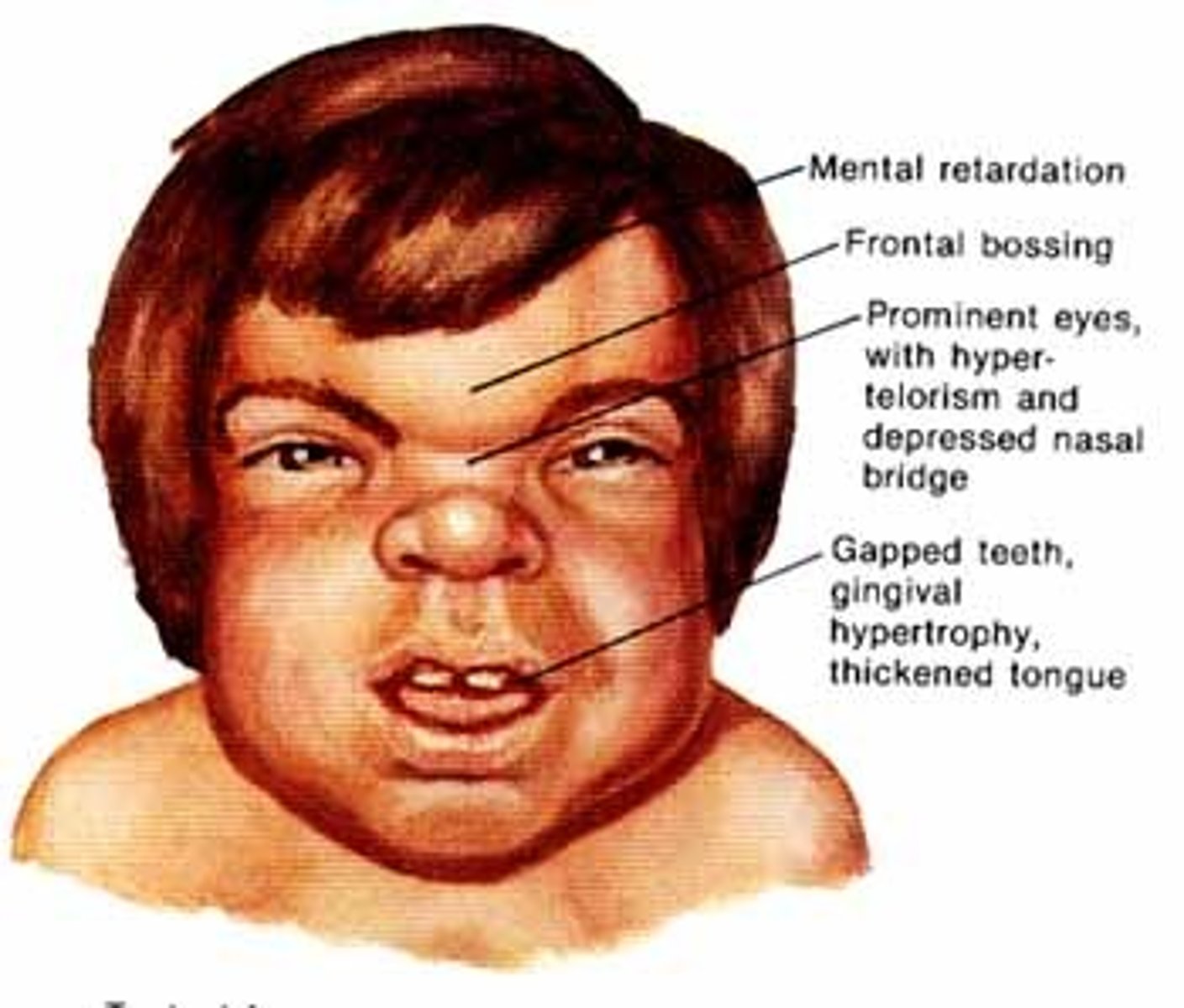
hurler syndrome
autosomal recessive storage disorder
(unable to break down long chains of sugar molecules)
CHARACTERIZED BY:
- hydrocephalus
- joint contractures
- visual defects
- kyphosis
- shallow acetabular and glenoid fossae
- cardiac deformities
(R ventricular hypertension common)
*death frequently due to cardiac failure
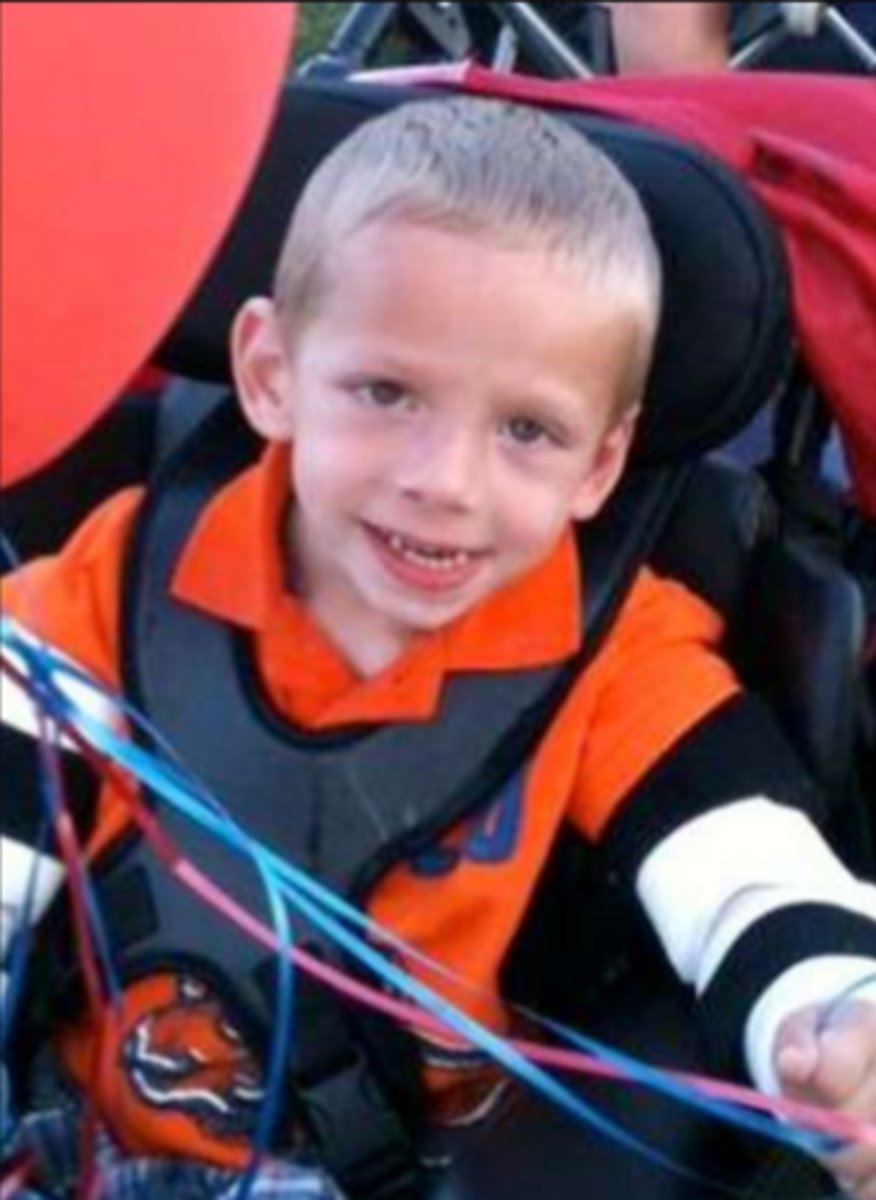
lesch-nyhan syndrome
genetic deficiency of the HPRT enzyme
CHARACTERIZED BY:
- spasticity
- chorea
- athetosis
- dystonia
- compulsive self-injurious behavior
(ex. extreme biting--> some have teeth pulled)
rett syndrome
caused by mutation in X chromosome
(almost always seen in GIRLS)
*often misdiagnosed as autism
CHARACTERIZED BY:
- deceleration of head growth
- loss of skills after 6-18 months
- scoliosis
- growth failure
- hyperventilation and breath holding
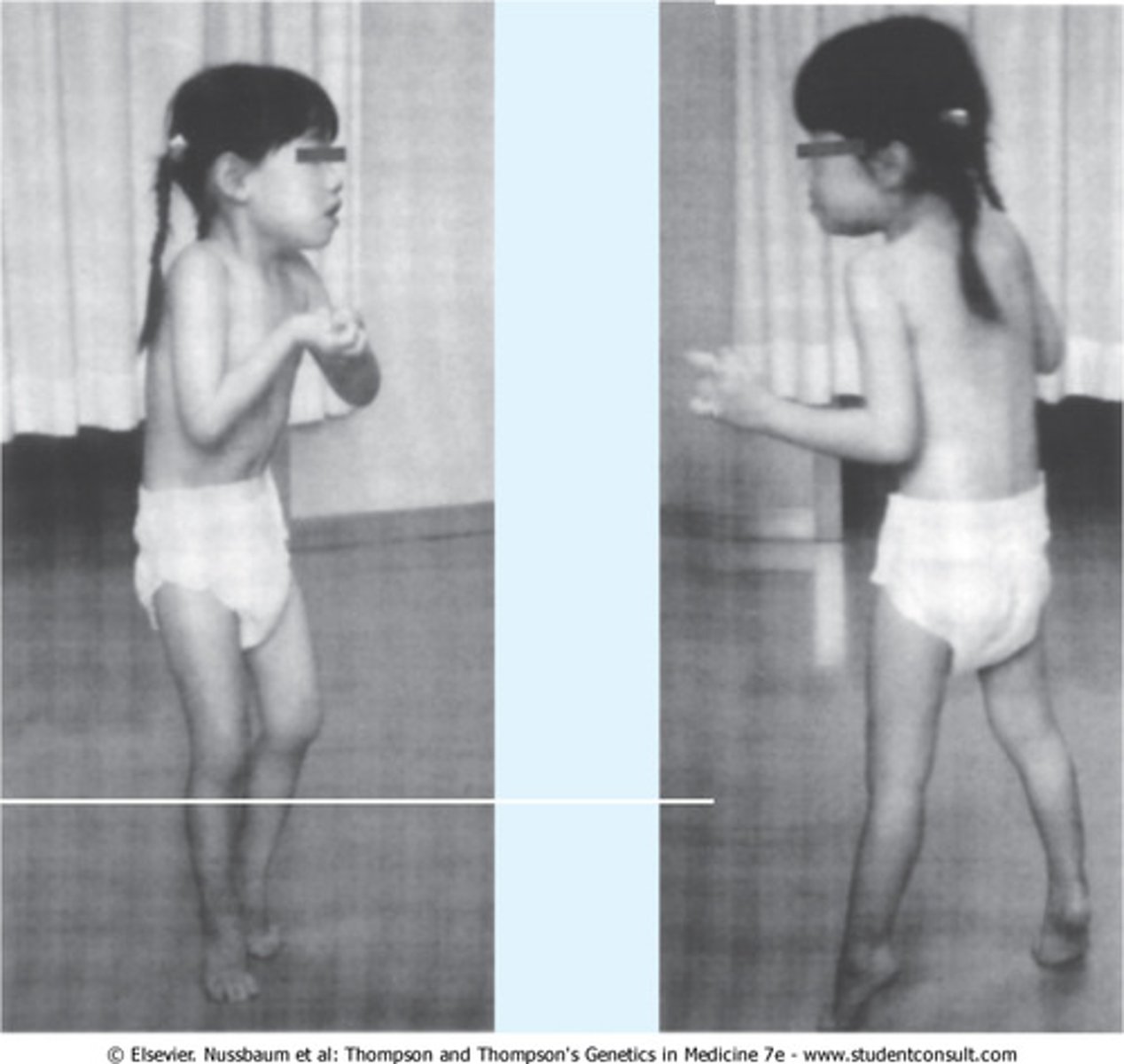
williams syndrome
mutation or deletion of the elastin gene at 7q11.23
CHARACTERIZED BY:
- hypersocialability
- mild neurologic dysfunction
- hypotonia
- cerebellar dysfunction
- facial abnormalities
- slow growth
- connective tissue abnormalities
- scoliosis/kyphosis
- aortic stenosis
- hypertension
- mitral valve prolapse
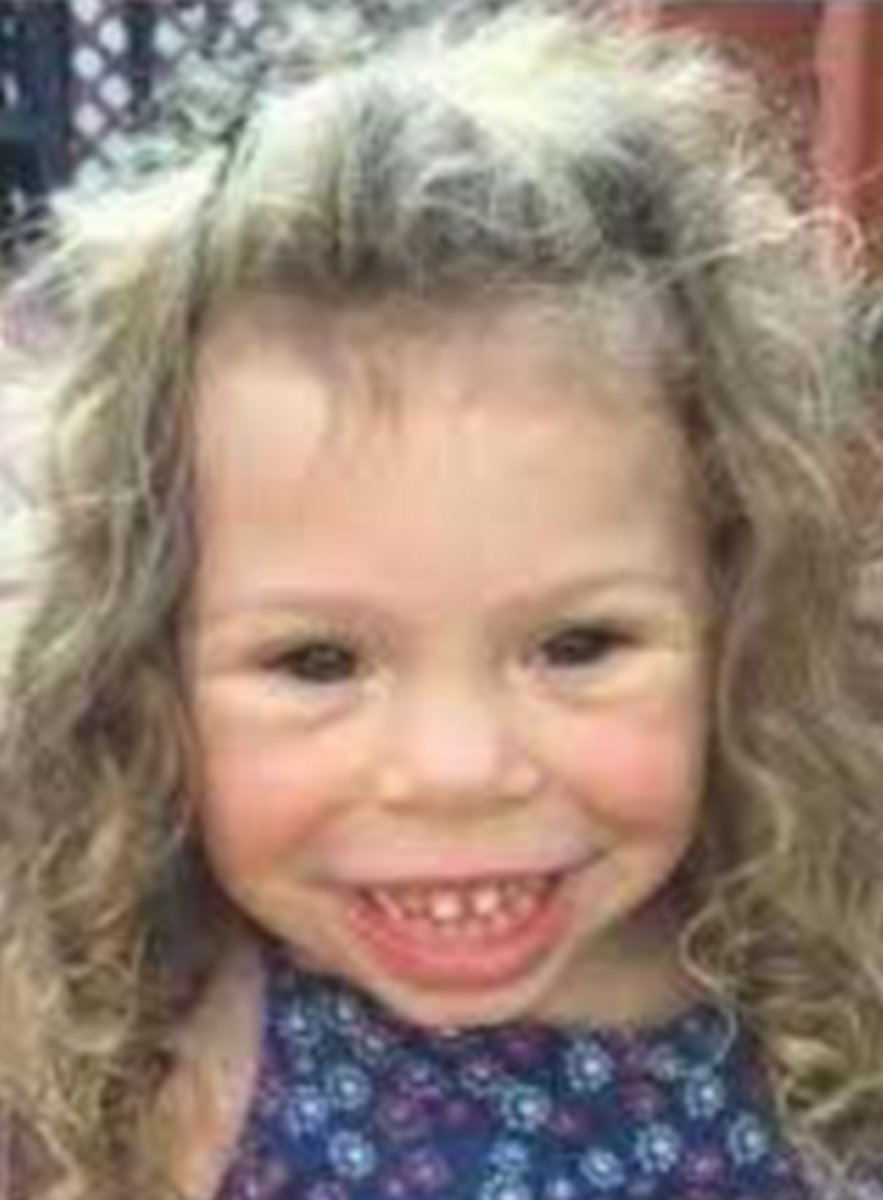

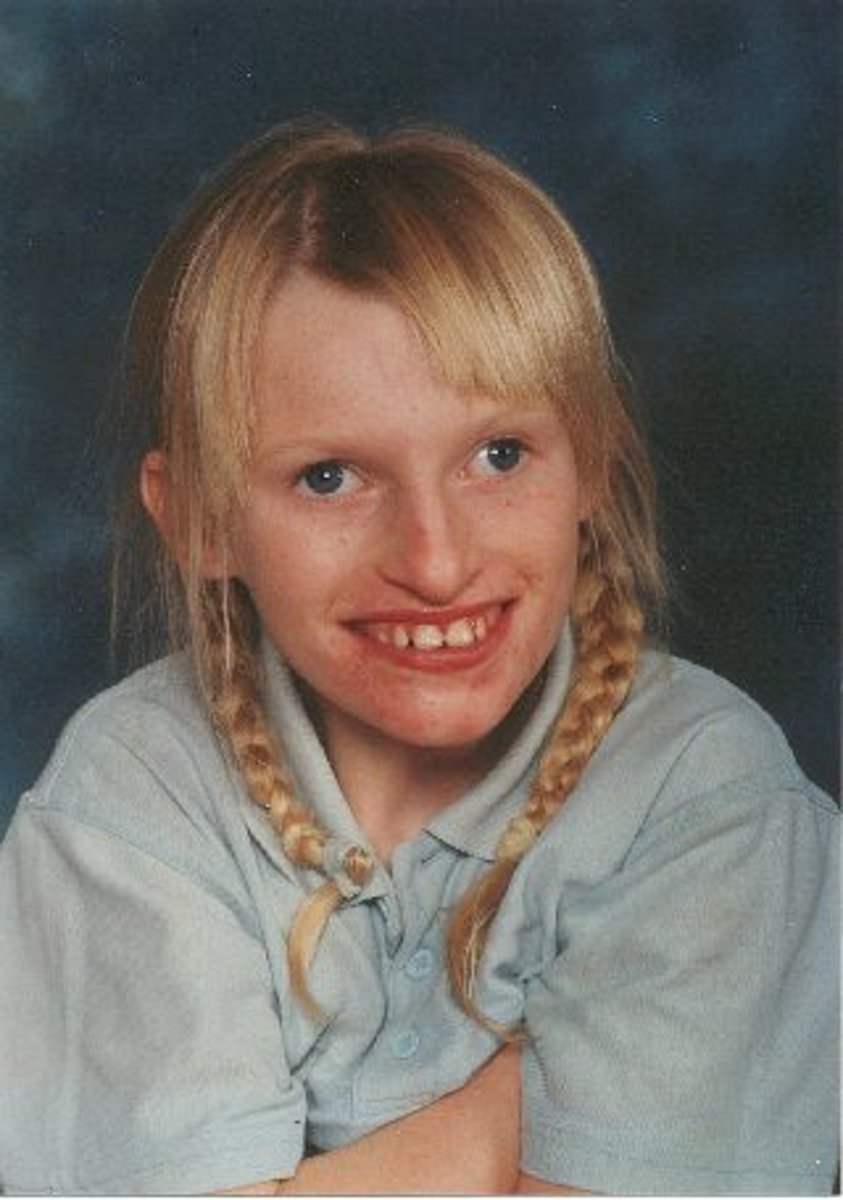
angelman syndrome
genetic disorder characterized by:
- hypotonicity
- seizures
- developmental delay
- ataxia/balance problems
- lack of speech
- behavior problems
*often fascinated by water
poor head control, poor trunk control, disinterest in movement
What are the 3 common early motor signs in children with ID?
assessment of intellect in children
- Stanford-Binet Intelligence Scale IV
(used to identify giftedness)
- Weschler Intelligence Scale for Children III (WISC)
- The Columbia Mental Maturity Scale
(designed specifically for children w/ CP - NO oral response)
infant assessment is unreliable
- developmental assessments
- poor predictors on intelligence
*Fagan Test of Infant Intelligence*
low IQ expected skills
important for PROGNOSIS
REFER TO IMAGE
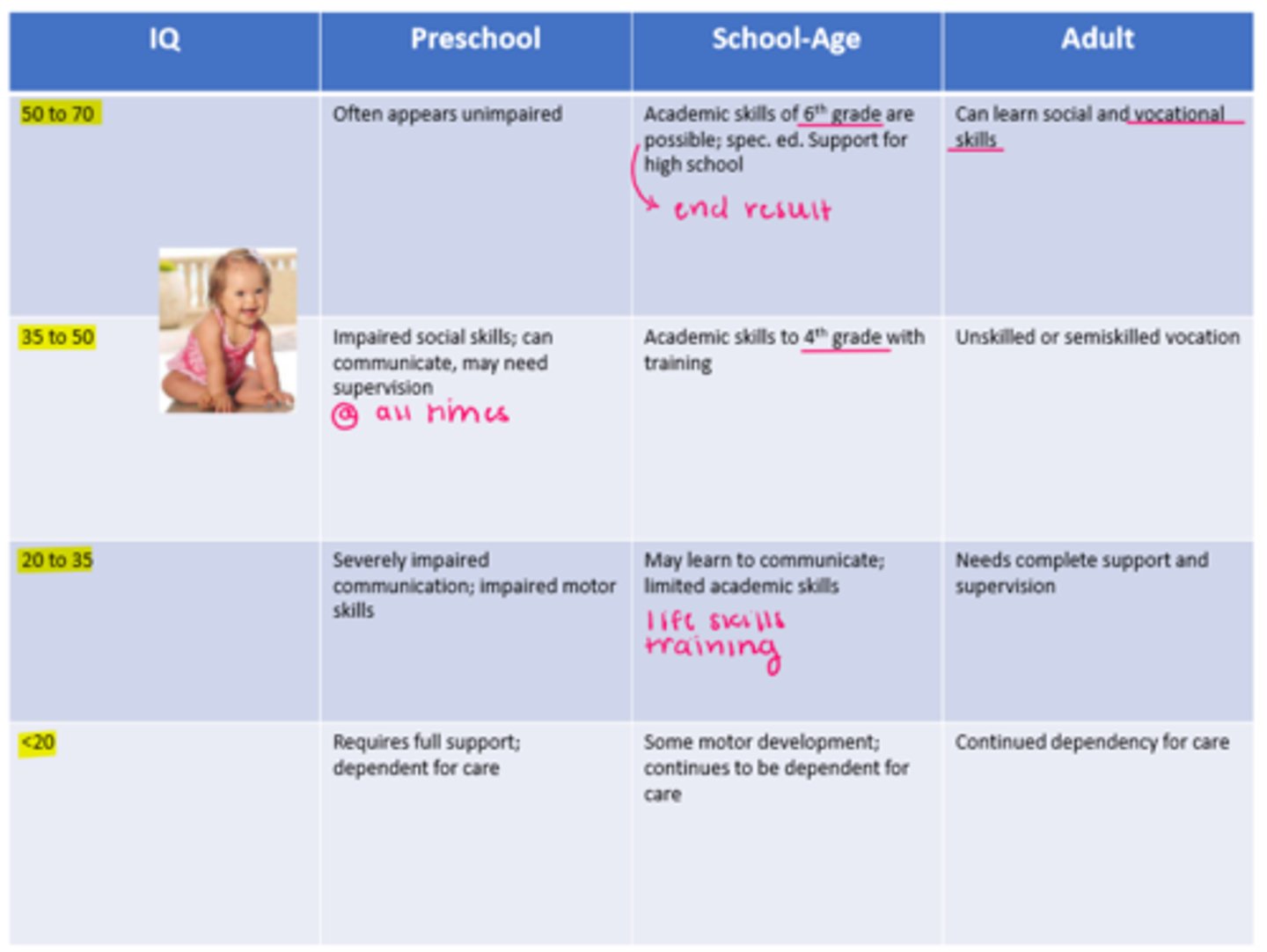
variety
PT goals can encompass a wide range of skills from expectations of typical development at a slower pace to physical support for posture and mobility (AD use)

establishing goals
Normalization vs Compensation
1. bottom up approach
- identify strengths & weaknesses
- determine goal
- intervention plan and strategies
- assessment
(NORMALIZATION)
2. top down approach
- desired outcome (goal)
- identify obstacles & strengths
- strategies to bypass obstacles and to improve performance
- intervention plan
- assessment
(COMPENSATION)

common learning characteristics (intellectual impairments)
1. capability to learn a fewer number of things
- careful selection of high value skills
- TEAM APPROACH BEST
2. need for greater number of repetitions
- routines-based mindset
(increase frequency)
3. greater difficulty generalizing skills
- need to practice skills in context
(ex. specific stairwell at school)
4. greater difficulty maintaining skills not practiced
- increase number of reps
(imbed practice in daily routine)
5. slower response times
- consider speed & frequency of cuing
(SLOW DOWN)
6. limited repertoire of responses
- be "ok" w/ lack of variability & variation
*adapt environment to person, NOT person to environment
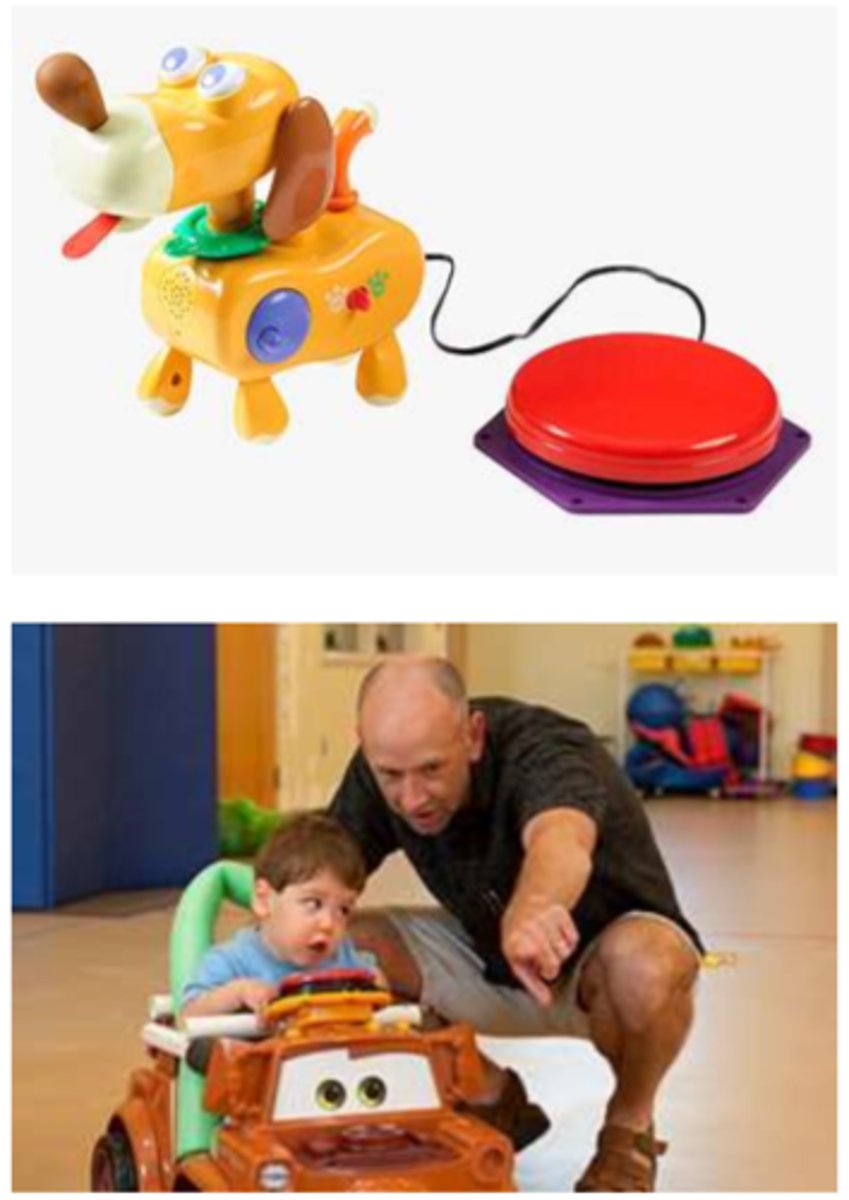
assistive technology
CONSIDER:
- early switch introduction
- adaptive equipment & developmental planning model
- compensation vs normalization

ADHD (Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder)
persistent pattern of inattention and/or hyperactivity impulsivity
- present before 7 y/o
- impairments in at least two settings
- clear evidence of interference with social, academic or occupational functioning
RULE OUT--> Pervasive Developmental Disorder, Schizophrenia, or other Psychotic Disorder
SUBTYPES:
- inattentive type
(focus issues)
- hyperactive-impulsive type
(physical manifestations)
- combined type
(most common)
inattentive type, hyperactive-impulsive type, combined type
What are the 3 subtypes of ADHD?
ADHD PT implications
- fidgeting should NOT be discouraged or punished
- regular physical activity can reduce the symptoms of ADHD
- meditation/yoga may help with focusing
*link btwn ADHD, sensory overresponsivity, anxiety disorder
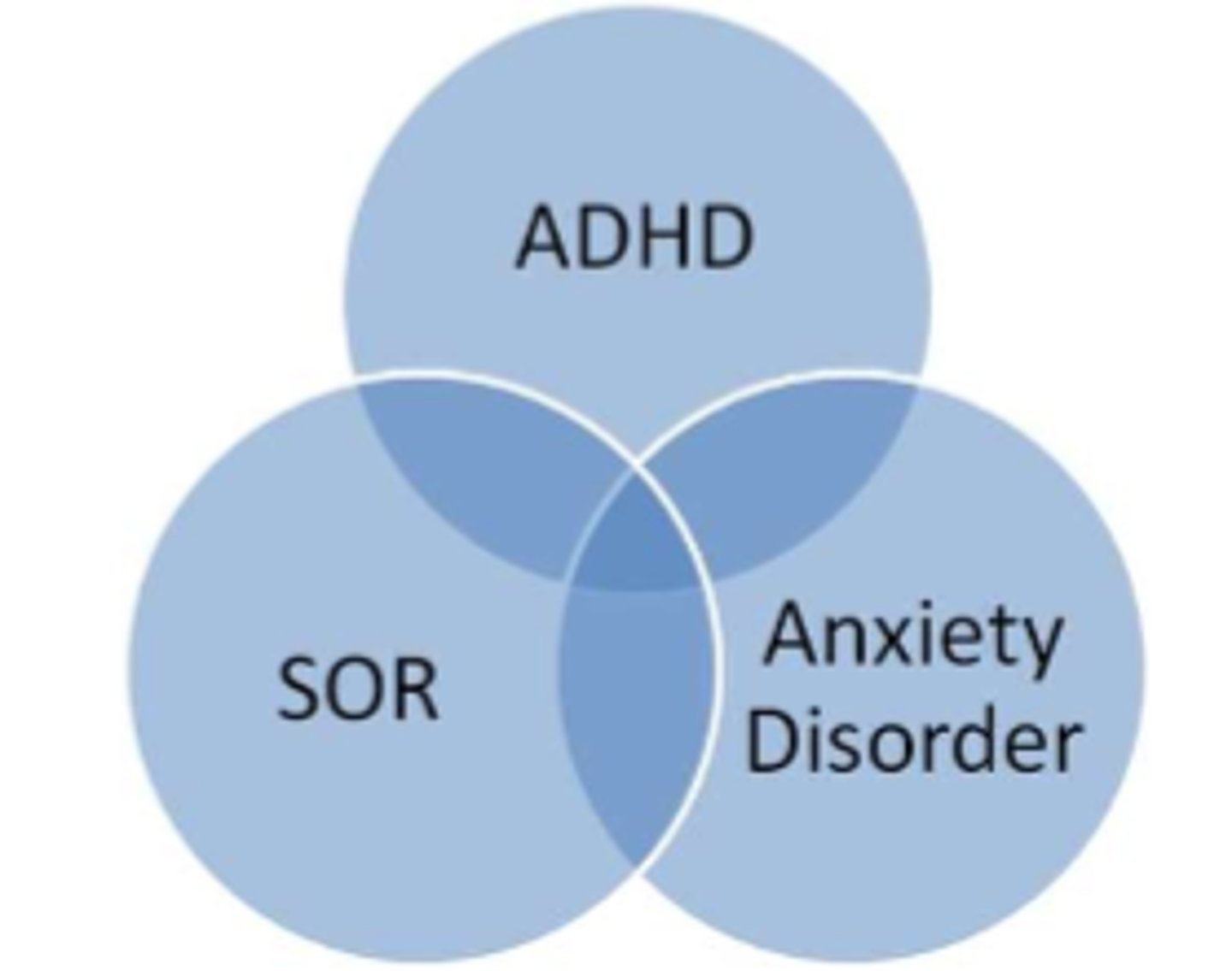
identifying PT need
1. norm-referenced tests
- help to identify
- must include "high level" balance and coordination tasks (BOT-2)
- program eligibility requirements
(older age = greater delay needed)
2. school-based therapy
- building relationships w/ teachers