Animal Evolution
1/20
Earn XP
Description and Tags
From the Cambrian to the Cenozoic
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
How old is Earth?
Approximately 4.5 billion years.
What was life like during the Precambrian?
Dominated by microbial films and soft-bodied organisms; Ediacaran biota appeared around 580–560 MYA.
What happened during the Cambrian Explosion?
Rapid diversification of animal life; emergence of hard-bodied animals, apex predators, and unique forms like Opabinia and Hallucigenia.
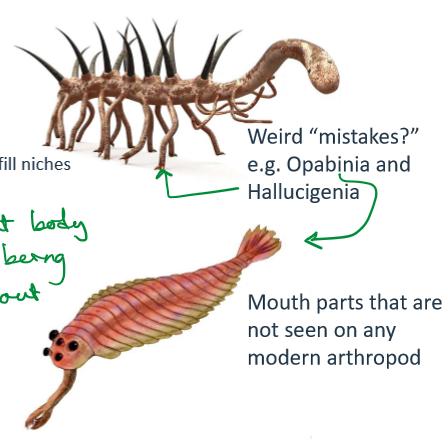
What caused the Cambrian Explosion?
Oxygenation, mass extinction of Ediacaran fauna, and predator-prey evolutionary arms races.
What characterized the Devonian period?
Rise of jawed fish like placoderms; development of fins, jaws, and early vertebrate features.
What is significant about lobe-finned fish (Sarcopterygians)?
They had limb-like fins and lungs, leading to the evolution of tetrapods.
Why did vertebrates move to land around 400–350 MYA?
To exploit new resources, despite challenges in support, locomotion, respiration, and reproduction.
What evidence challenges traditional views on land invasion?
Fossils like Acanthostega show limbs evolved before full terrestrial life.

What evolutionary innovation allowed full terrestrial reproduction?
The amniotic egg with a tough shell.
Which groups diverged from early amniotes?
Diapsids (reptiles and birds) and synapsids (mammals), distinguished by skull openings.
What are the two main dinosaur lineages?
Ornithischia (bird-hipped, herbivorous) and Saurischia (lizard-hipped, includes theropods and sauropods).
Which group evolved into birds?
Theropods (a subgroup of Saurischia), not Ornithischia despite their "bird-hipped" name.
What were key features of sauropods?
Enormous size, long necks, quadrupedal stance, and adaptation for high browsing.
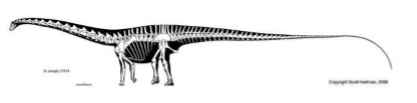
What defined theropods?
Bipedal carnivores with specialized hunting features; includes tyrannosaurs, spinosaurs, dromaeosaurs.
What links birds to theropods?
Shared features like feathers, wishbone, and modified wrist bones.
What are two main flight origin hypotheses?
Ground-up (cursorial) and tree-down (arboreal) models.
What caused the K-T extinction?
Likely a meteor impact triggering global climate change and volcanism.
Which species went extinct?
Non-avian dinosaurs, marine reptiles, ammonites, many birds and mammals.
Who survived?
Small mammals, amphibians, some fish, crocodiles, turtles, and a portion of birds.
What adaptations helped mammals survive the K-T extinction?
Small size, nocturnality, burrowing behavior, endothermy, fur, and specialized teeth.
What happened to mammals after the extinction?
Rapid adaptive radiation and diversification during the Cenozoic.