Cardiac Tumors and Masses
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
Cardiac tumors
Abnormal growths in the heart or heart valves.
Classified as benign or malignant.
Most are benign, but they can cause problems due to size and location.
Small pieces may break off into the bloodstream and embolize.
Sporadic
Familial
Part of another health condition
What are the causes of cardiac tumors (3)?
Sporadic
Most common form.
Result of cell overgrowth that either starts in the heart or moves to the heart.
Familial
Small percentage of cardiac tumors are due to a genetic component.
Family history of the condition.
NAME syndrome
LAMB syndrome
Carney syndrome
What are some of the other conditions that cardiac tumors can be apart of (3)?
NAME syndrome
Nevi
Atrial myxoma
Myxoid neurofibroma
Ephelides
LAMB syndrome
Lentigines
Atrial myoxoma
Mucocutaneous myxomas
Blue nevi
Carney syndrome
Autosomal dominant syndrome associated with spotty pigmentation of the skin, endocrinopathy, and endocrine and nonendocrine tumors.
Primary tumors
Begin growing in the heart and stay there.
Secondary tumors
Do not start in the heart.
Move to the heart from other parts of the body.
Most often begin in the lungs, breast, stomach, kidneys, liver, and colon.
Secondary
Which are more common, primary or secondary tumors?
Myxoma
Most common adult primary benign tumor.
75% occur in the right atrium.
Most often arise from the fossa ovalis.
Mobile, lobular mass.
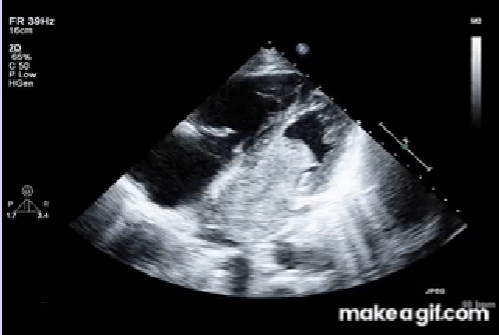
Fossa ovalis of the IVS
Myxomas most often arise from the ____.
Myxoma
Irregular shape with protruding “fronds” of tissue or grape cluster.
Heterogenous - areas of necrosis and hemorrhage.
Usually solitary; multiple if from familial syndromes.
May become quite large and cause hemodynamic obstruction.
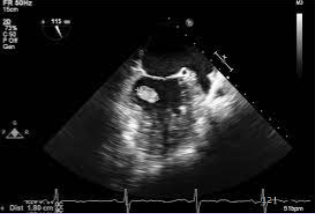
Papillary fibroelastoma
Second most common primary benign tumor of the heart.
Arises on valvular tissue.
Found on the downstream side of the valve - LV side of the MV or aorta side of the AV.
Usually no clinical significance other than possibility of thrombus and emboli.
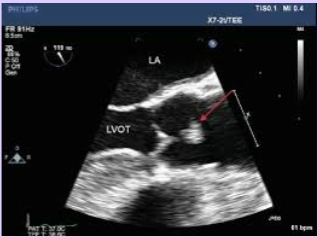
Valvular vegetation
A papillary fibroelastoma may mimic the appearance of a ___.
Papillary fibroelastoma - downstream (below valve)
Vegitation - upstream (above valve)
How can you differentiate a vegetation from a papillary fibroelastoma?
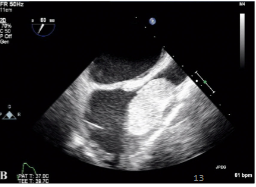
Lipoma
Benign, fatty tumor that grows within the heart muscle or pericardium.
Usually solitary.
Most commonly found in LV, RA, and IAS.
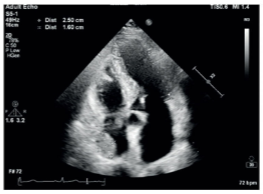
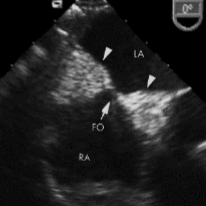
Lipomatous hypertrophy of IAS
Normal variant of the heart muscle that can be mistaken for a tumor.
Superior and inferior fatty portions of the IAS sparing the fossa ovalis region.
“Dumbbell” appearance
Dumbbell
Lipomatous hypertrophy of the IAS has a characteristic ___ appearance.
Cardiac hemangiomas
A benign tumor of the heart that is made up of blood vessels.
Occur in any chamber, but are usually found in the RA.
On echo, demonstrate complex echogenicity with cystic and solid areas mixed with calcifications.
Cavernous hemangioma
Capillary hemangioma
Arteriovenous hemangioma
What are the three compositions of cardiac hemangiomas?
Cavernous hemangioma
Cardiac hemangioma composition.
Composed of multiple thin-walled ectatic vessels.
Capillary hemangioma
Cardiac hemangioma composition.
Composed of multiple smaller capillary like vessels.
Arteriovenous hemangioma
Cardiac hemangioma composition.
Composed of thick-walled dysplastic arteries, capillaries, and vein like vessels.
Intramural cardiac hemangioma
Poorly circumscribed lesions that are hemorrhagic and congested.
Endocardial cardiac hemangioma
Well-circumscribed lesions that are variably myxoid (clear, mucous substance).
Rhabdomyoma
Benign tumor of striated muscle.
Most common primary cardiac tumor in children.
Multiple in 90% of cases, but can be isolated.
Most frequently arise in the ventricular myocardium.
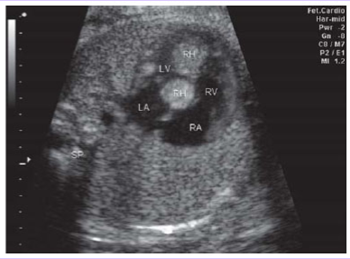
Tuberous sclerosis
Rhabdomyomas are frequently associated with ___.
Ventricular myocardium
Rhabdomyomas most frequently arise in the ___.
Can also be found in the atria, epicardial surface, or cavo-atrial junction.
Tuberous sclerosis
Autosomal dominant-inherited or sporadically occurring disorder characterized by widespread hamartomas that variably involve the brain, kidneys, heart, skin, and other organs.
Classic clinical triad: mental retardation, epilepsy, and facial angiofibromas
Associated with rhabdomyomas.
Well-circumscribed, homogenous, hyperechoic mass
Small, multiple lesions - may appear as thickened myocardium
Sonographic appearance of rhabdomyomas (2).
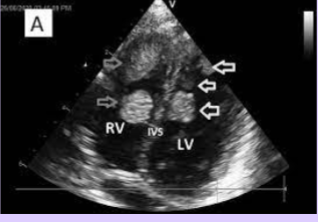
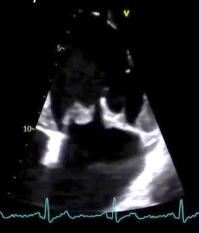
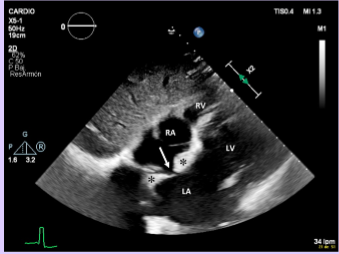
Rhabdomyoma
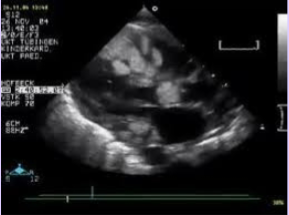
What is seen in this TTE?
Cardiac fibroma
Second most common benign cardiac tumor in children and infants.
Located in the myocardium - usually in the ventricle (at the septum.
Firm or rubbery and don’t demonstrate hemorrhage or necrosis. Very large, sometimes exceeding 10 cm in diameter.
Calcifications; usually solitary. Can regress with age.
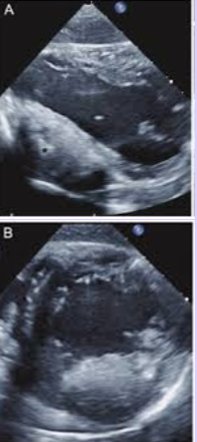
Fibromas have calcifications
How can rhabdomyomas be distinguished from fibromas?
Myxoma
Papillary fibroelastoma
Cardiac lipoma
Cardiac hemangioma
Rhabdomyoma
Cardiac fibroma
What are the primary benign tumors (6)?
Sarcomas
What are the most common types of malignant primary cardiac tumors?
Malignant primary cardiac tumors
Rare
Most common - sarcomas
Primary cardiac lymphoma
Sarcomas
Aggressive tumors that spread rapidly.
Characterized by rapid growth.
Low survival rate due to: hemodynamic compromise, local invasion, and distant mets.
RA
Pericardium
Sarcomas commonly involve the ___ and ___.
Right sided failure
Pericardial disease
Vena cava obstruction
Right-sided involvement of sarcomas causes ___(3).
Myxomas
When sarcomas occur on the left side, they can be mistaken for ___.
Cardiac metastases
More common than primary tumors.
Almost always occur in the setting of widespread primary disease.
Reach the heart via the bloodstream, lymphatics, direct invasion or venous extension of the heart.
Pericardium
Myocardium
Endocardium and valves - rare
What are the locations of cardiac metastases (3)?
Pericardium
What is the most common site of cardiac metastases?
Melanoma
Leukemia
Germ cell carcinoma
What cancers most commonly metastases to the heart (3)?
LV thrombus
Most common form of intracardiac thrombus due to impaired LV function.
Rarely occur in patients with preserved LV function.
Commonly found in the apex.
High risk for thromboembolic events, particularly stroke.
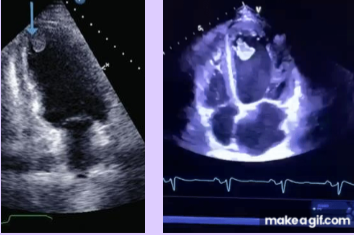
Acute MI
LVEF <40%
Previous MI with apical aneurysm
CM with LVEF <20%
What conditions that impair LV function lead to LV thrombus (4)?
CM with LVEF <20%
Patients with ____ causing impaired LV function are most likely to develop an LV thrombus.
Mural
Protruding
Mobile
What are the three types of LV thrombus (3)?
Mural thrombus
Only one surface is exposed to blood pool; other sides connected to cardiac wall.
Incidence for embolization and thromboembolic event is lowest.
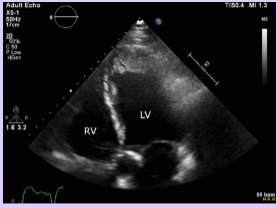
Protruding thrombus
More than one surface of the thrombus is exposed to the blood pool.
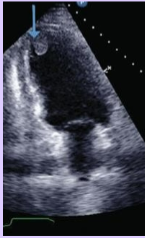
Mobile thrombus
Independent motion of part or whole thrombus.
Incidence for embolization and thromboembolic event is highest.
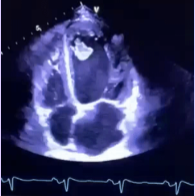
Clear endocardial border delineation
Contrast - will still be seen with contrast
Echo requirements for LV thrombus detection (2).
Left atrial appendage thrombus
Caused by stasis of blood within the cavity.
Most common location for atrial thrombus.
Often not seen with TTE; TEE used in patients with CVA.
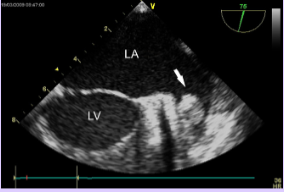
Left atrial appendage
What is the most common location for an atrial thrombus?
Shape of the cavity
Atrial arrhythmias (afib or a flutter)
Increased LV filling pressures, which decrease LA contractility
LAA thrombus formation is caused by stasis of blood in the cavity, which can be due to ___(3).
Right heart thrombus
Relatively common.
Associated with pulmonary embolism.
Better seen on TEE than TTE, due to increased visualization of the SVC and IVC.
RV dilation and dysfunction
PFO
What conditions increase the risk for a right heart thrombus (2)?
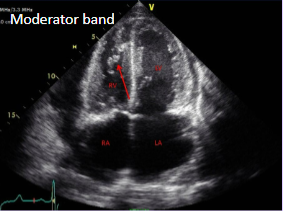
Moderator band
Muscular structure located in the right ventricle of the heart.
Can be mistaken for a right heart thrombus.
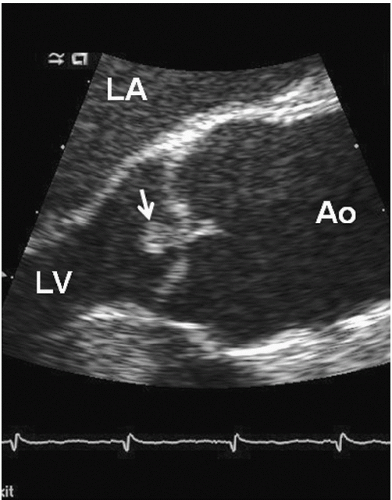
Nodules of Arantius
Small, fibrous thickening on the free edges of semilunar valves.
Typically seen on the aortic valve.
Can be mistaken for a mass.
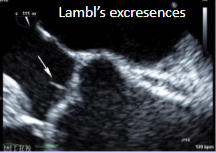
Lambl excrescences (valvular strands)
Small, filiform, fibrous strands at coaptation sites.
Typically seen on the aortic valve.
Can be mistaken for a mass.
Redundant chordae
An excess of the chordae tendineae that attach the MV to the papillary muscles.
Can be mistaken for a mass.
Myxomatous mitral valve
Degenerative thickening of the MV leaflets.
Can be mistaken for a mass.