OMIS 4300 Exam 1 - Woosley,
1/155
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
156 Terms
Product and Service Design
Aligns offerings with organizational strategy and goals.
Customer Needs
Requirements that drive product and service development.
Quality Goals
Standards set for product performance and reliability.
Cost Targets
Financial benchmarks for product development expenses.
Prototypes
Initial models used for testing product concepts.
Process Specifications
Guidelines for manufacturing based on product specs.
Inter-functional Collaboration
Teamwork across departments for effective design.
Market Opportunities
Potential areas for growth identified through analysis.
Economic Factors
Financial conditions influencing product design decisions.
Social and Demographic Factors
Trends affecting consumer preferences and behaviors.
Manufacturability
Ability to produce a product profitably.
Serviceability
Capability to maintain service at acceptable costs.
Quality Expectations
Standards set by customers and competitors.
Liability Issues
Legal responsibilities related to product safety.
Reverse Engineering
Analyzing competitor products for improvement insights.
Research and Development (R&D)
Efforts to innovate and enhance product knowledge.
Basic Research
Knowledge advancement without immediate commercial goals.
Applied Research
Research aimed at practical commercial applications.
Product Liability
Manufacturer's responsibility for product-related damages.
Uniform Commercial Code (UCC)
Legal framework ensuring product quality standards.
Sustainability
Resource use that protects ecological systems.
Life-Cycle Assessment (LCA)
Evaluates environmental impact throughout a product's life.
End-of-Life Programs
Strategies for managing products at their lifecycle's end.
Value Analysis
Cost-performance evaluation of product components.
3-Rs
Reduction, Reuse, and Recycling principles in design.
Global Warming
Increase in Earth's average temperature due to emissions.
Solid Waste Generation
Production of waste materials from products.
ISO 14000
Standards for environmental management and assessment.
Alternative Sources
Other materials or services that can replace current ones.
Remanufacturing
Refurbishing used products by replacing defective components.
Cost of Remanufactured Products
Sold for about 50% of new product cost.
Design for Disassembly (DFD)
Designing products for easy disassembly after use.
Recycling
Recovering materials for future use from products.
Cost Savings from Recycling
Reduces costs and addresses environmental concerns.
Design for Recycling (DFR)
Designing products to facilitate recovery of recyclable parts.
Standardization
Absence of variety in products or services produced.
Advantages of Standardization
Fewer parts, reduced costs, and improved quality control.
Disadvantages of Standardization
Less variety may decrease consumer appeal.
Mass Customization
Standardized goods with some degree of customization.
Delayed Differentiation
Postponing product completion until customer preferences are known.
Modular Design
Grouping components into easily replaceable modules.
Advantages of Modular Design
Easier repairs and lower training costs.
Disadvantages of Modular Design
Limited configurations and potential module scrapping.
Reliability
Ability to perform intended function under specified conditions.
Failure
When a product does not perform as intended.
Normal Operating Conditions
Conditions under which reliability is specified.
Robust Design
Products functioning over a broad range of conditions.
Ferrari Enzo
Example of a less robust automobile design.
Toyota Avalon
Example of a more robust automobile design.
Environmental Regulations
Laws requiring recyclability in products sold in the EU.
Supplier Suggestions
Recommendations from suppliers for product improvements.
Packaging Improvements
Enhancements to reduce costs or improve efficiency.
Combining Parts
Using multiple components together for efficiency.
Less Stringent Specifications
Relaxing requirements to save time or costs.
Product Life Stage Strategies
Approaches for managing different stages of product life.
Quality Function Deployment (QFD)
Integrates customer voice into product/service development.
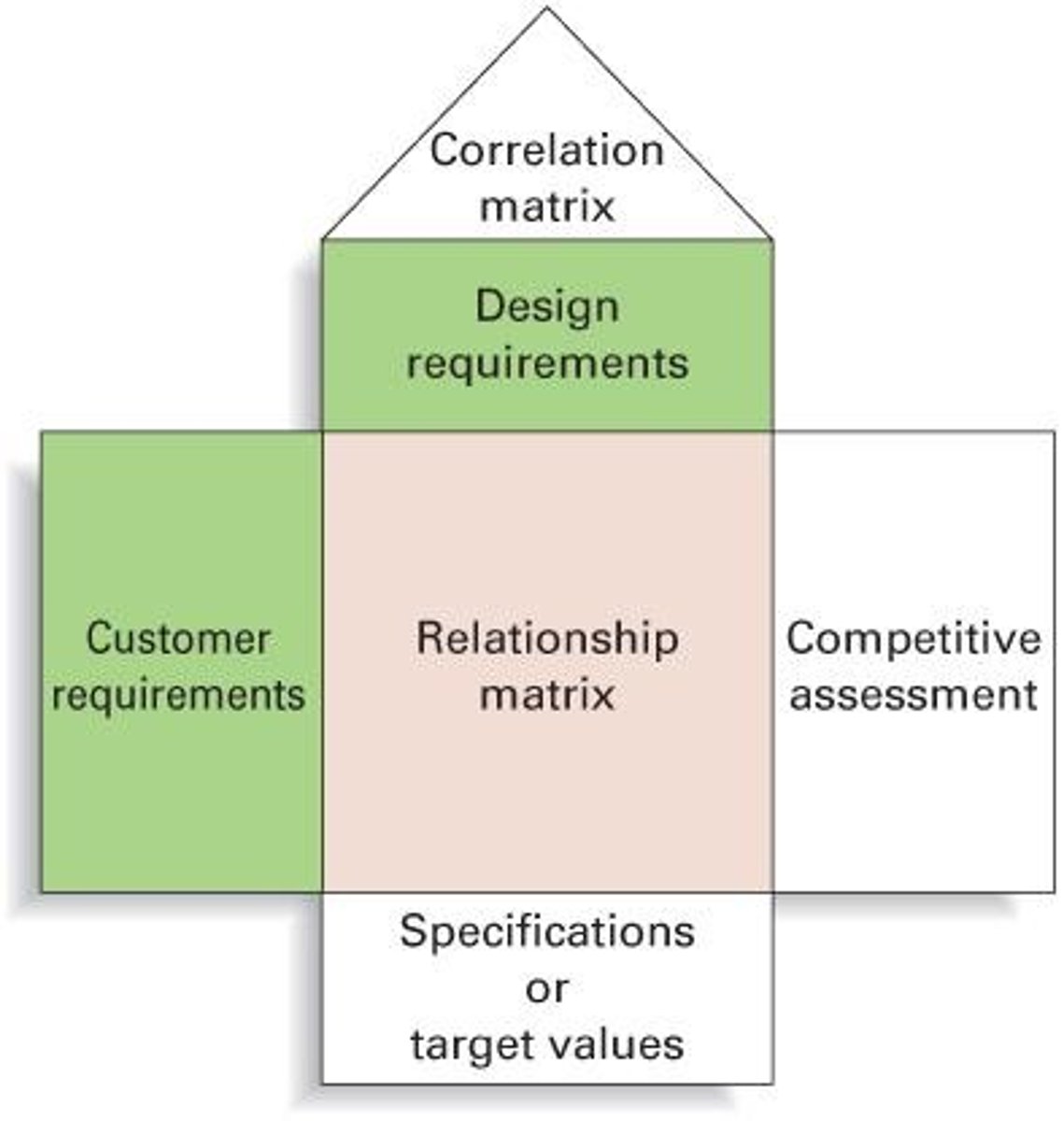
Voice of the Customer
Customer requirements influencing product/service design.
Customer Requirements
Factors ensuring customer satisfaction in development.
Listening to Customers
Central feature of Quality Function Deployment.
Kano Model
Framework categorizing customer satisfaction factors.
Basic Quality
Limited effect on satisfaction; dissatisfaction if absent.
Performance Quality
Satisfaction proportional to functionality and appeal.
Excitement Quality
Unexpected features causing customer excitement.
Phases in Design & Development
Steps from feasibility analysis to follow-up evaluation.
Feasibility Analysis
Assessment of project viability before development.
Prototype Development
Creating initial models for testing concepts.
Design Review
Evaluation of design before production begins.
Market Test
Trial phase to gauge product acceptance.
Product Introduction
Launching product into the market.
Follow-up Evaluation
Assessing product performance post-launch.
Concurrent Engineering
Integrating design and manufacturing early in process.
Cross-Functional Teams
Collaboration among various departmental personnel.
Production Requirements
Consideration of capabilities in design process.
Design for Manufacturing (DFM)
Designing products compatible with manufacturing capabilities.
Design for Assembly (DFA)
Focus on reducing parts and improving assembly.
Manufacturability
Ease of fabrication and assembly in production.
Component Commonality
Using similar parts across multiple products.
Service Delivery System
Facilities and processes for providing a service.
Product Bundle
Combination of goods and services for customers.
Service Package
Resources and features included in service delivery.
Service Design
Strategy determining service nature and target market.
Service Design Issues
Variation, customer contact, and involvement considerations.
Differences in Service and Product Design
Tangible products vs. intangible services.
Service Visibility
Services are highly visible to consumers.
Operations Strategy
Design strategies to achieve competitive advantage.
Operations
The part of a business organization that is responsible for producing goods or services.
Operations management
the management of systems or processes that create goods and/or provide services.
Goods
physical items that include raw materials, parts, subassemblies, and final products.
Services
activities that provide some combination of time, location, form or psychological value.
inputs; outputs
Value-added is the difference between the cost of __________ and the value or price of __________.
goods and services.
Product packages are a combination of ________.
more competitive.
Product packages can make a company _____________.
Supply Chain
a sequence of activities and organizations involved in producing and delivering a good or service.
Suppliers' suppliers > direct suppliers > producer > distributor > final customers
Supply Chain order
basic function of the business organization
Challenges of managing services
1.Jobs in services are often less structured than in manufacturing
2.Customer contact is generally much higher in services compared to manufacturing
3.In many services, worker skill levels are low compared to those of manufacturing employees
4.Services are adding many new workers in low-skill, entry-level positions
5.Employee turnover is high in services, especially in low-skill jobs
6.Input variability tends to be higher in many service environments than in manufacturing
7.Service performance can be adversely affected by many factors outside of the manager's control (e.g., employee and customer attitudes)
wasteful costly
Supply > Demand
Opportunity loos customer dissatisfaction
Supply < Demand
Ideal supply and demand
Supply = Demand
Process
one or more actions that transform inputs into outputs