AP Photosynthesis
1/20
Earn XP
Description and Tags
https://quizlet.com/965406234/ap-photosynthesis-flash-cards/
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
where does ps occur?
plants, some protists, some bacteria -> tree (ex) -> leaf -> mesophyll cell -> chloroplast
source of energy in photosynthesis
the Sun
What happens during the light rxns?
light + H2O -> NADPH & 2ATP on the thylakoid membrane
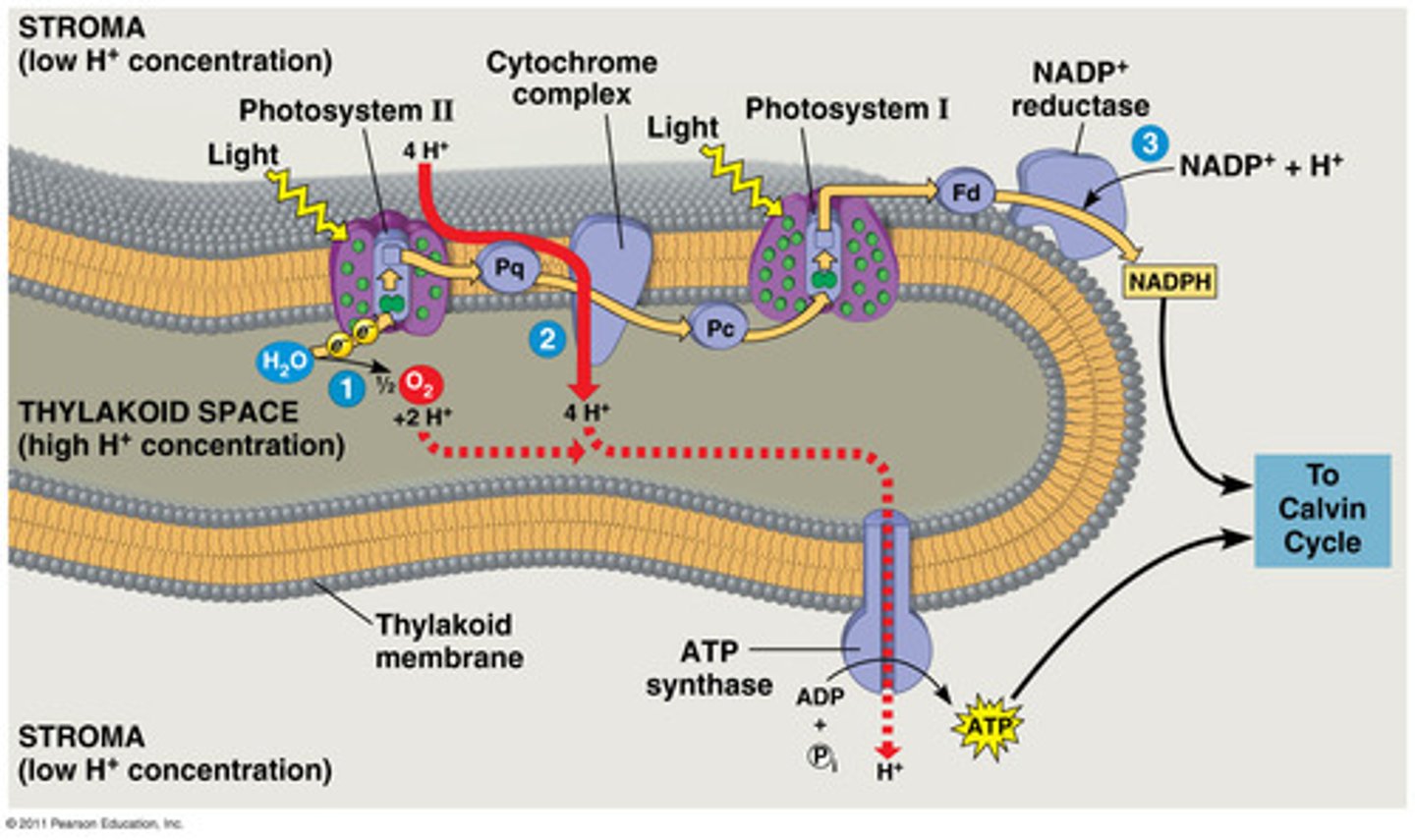
LR Step 1A: light
the sunlight hits chlorophyll a, chlorophyll b, and carotenoids in photosystems 1 & 2
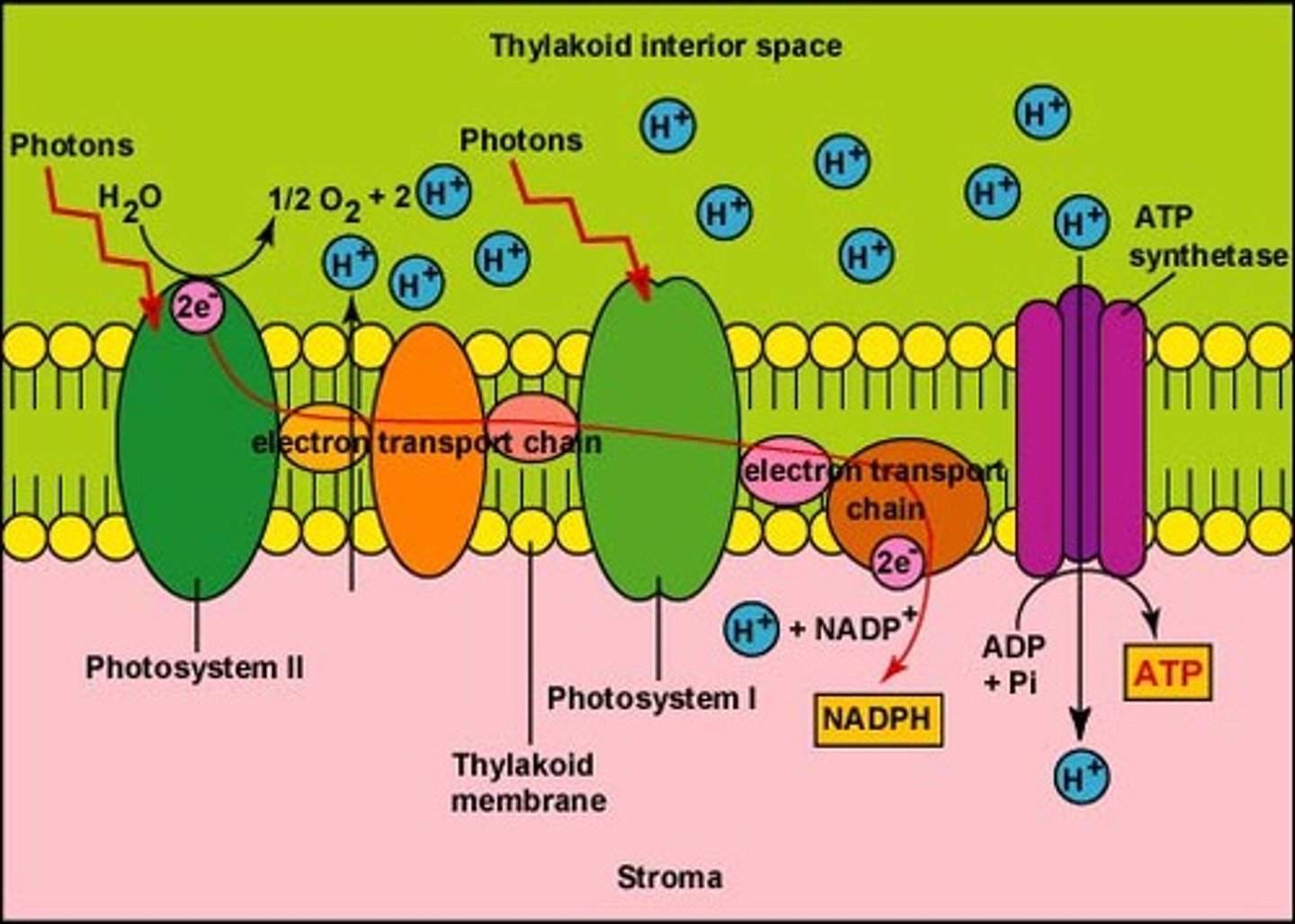
LR Step 1B: H2O
WSE (water splitting enzyme) splits a water molecule into 2 H+, 1 O-, and 2 e-
LR 1B: H+
builds up the concentration gradient bc it can't pass thru the plasma membrane bc it is an ion
they pass thru ATP synthase once the gradient starts pushing them thru. as they pass thru, the protein spins, generating rotational energy that helps it snap ADP & P together to make ATP
LR 1B: O-
waits for another H2O molecule to split and then they bond, forming O2 and then they can leave thru the plasma mebrane
LR 1C: 2 e-
the e- replace the ones lost by the pigments in PS II
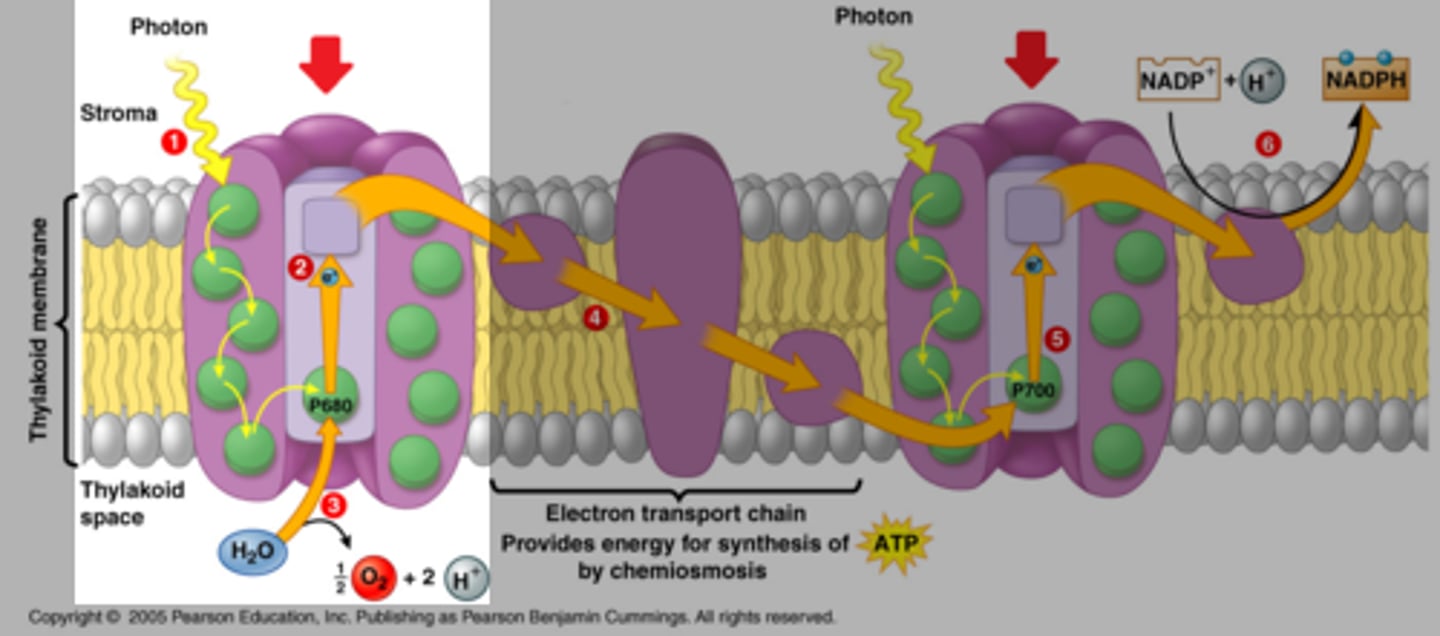
LR Step 2
the energy makes the pigments the light hits vibrate, causing others around them to vibrate as well. they pass 2 e- to the next pigment along with the energy
LR Step 3
Eventually, the e- and energy reaches a special pair of chlorophyll a molecules, which pass the e- to the primary e- acceptor
LR Step 4: ETC
The e- in PS II's PEA go thru the e- transport chain. first going to plastoquinone (Pq), then cytochrome B6F, then plastocyanin (Pc).
LR Step 5A: back to PS I
the e- in PS I go to ferrodoxin (Fd) and then to ferrodoxin-NADP+ reductase (FNR), which adds 2 e- to NADP+ so it can bond with 2H+, creating NADPH with an H+ byproduct.
LR Step 5B: after the ETC
the e- replace the missing e- in PS I
LR Step 6
NADPH and ATP go to the cc

What happens during the CC?
3CO2 + 9ATP + 6NADPH -> 1 G3P
This process happens twice and the 2 G3P combine to make a glucose.
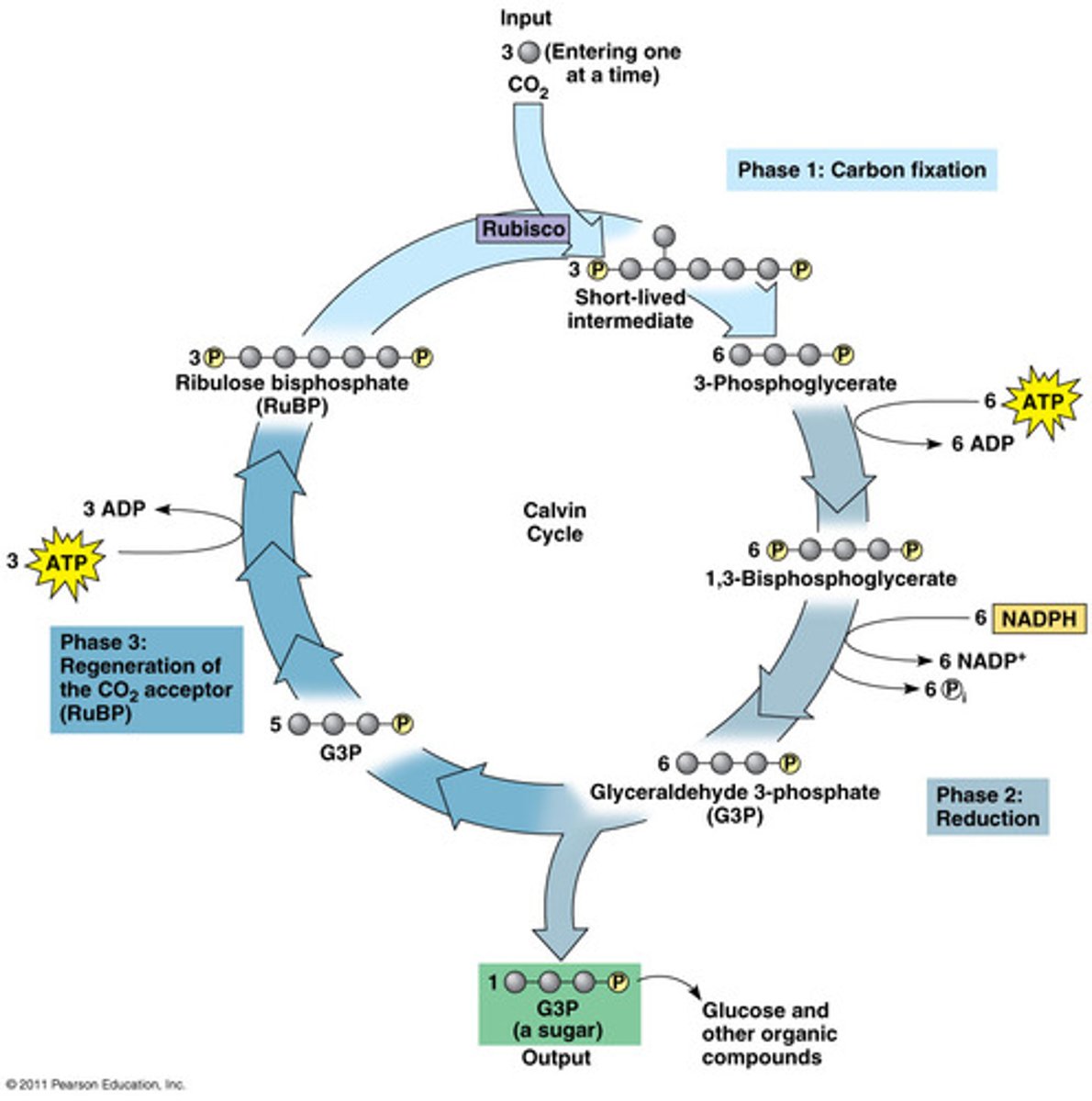
1 (CC)
RuBisCO combines 3 CO2 (1 C each) with 3 RuBP (5 C each) to make 3 unstable intermediates (6 C each)

2 (CC)
the unstable intermediates break in half, turning into 6 PGA (3 C each)

3 (CC)
6 PGA turns into 6 G3P (3 C each) after being phosphorylated by 6 ATP and reduced by 6 NADPH (12 e-)

4 (CC)
1 G3P molecule leaves the cycle

5 (CC)
the remaining 5 G3P molecules are phosphorylated by 3 ATPs, making 5 RuBP molecules, restarting the cycle
6 (CC)
the cycle happens again and the two G3P molecules combine to make a glucose (6 C)