AP human geography unit1
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
69 Terms
reference map
used for general info
thematic maps
show spatial aspects of info/phenomena
thematic map types
choropleth, dot map, proportional/graduated symbol, cartogram, isoline
cartographic scale
way the map communicates the ratio of its size to the size of what it represents
small-scale maps
larger area, little detail
large-scale maps
smaller area, more details
spatial patterns
location, direction, distance, elevation, distribution
absolute location
latitude, longitude coordinate
relative location
description of where sth is in relation to other things(connectivity, accessibility)
direction
describe where things are in relation to each other(NSEW)
absolute distance
measured in terms of ft, mi, m, km
relative distance
degree of nearness based on time/money, dependent on the mode of travel
elevation
distance of features above sea level, usually in ft, m.
distribution patterns
clustered/agglomerated, linear, dispersed, circular, geometric, random
distribution
the way phenomenon is spread out over an area
mercator projection
used for navigation: correct direction, land near pole appear larger
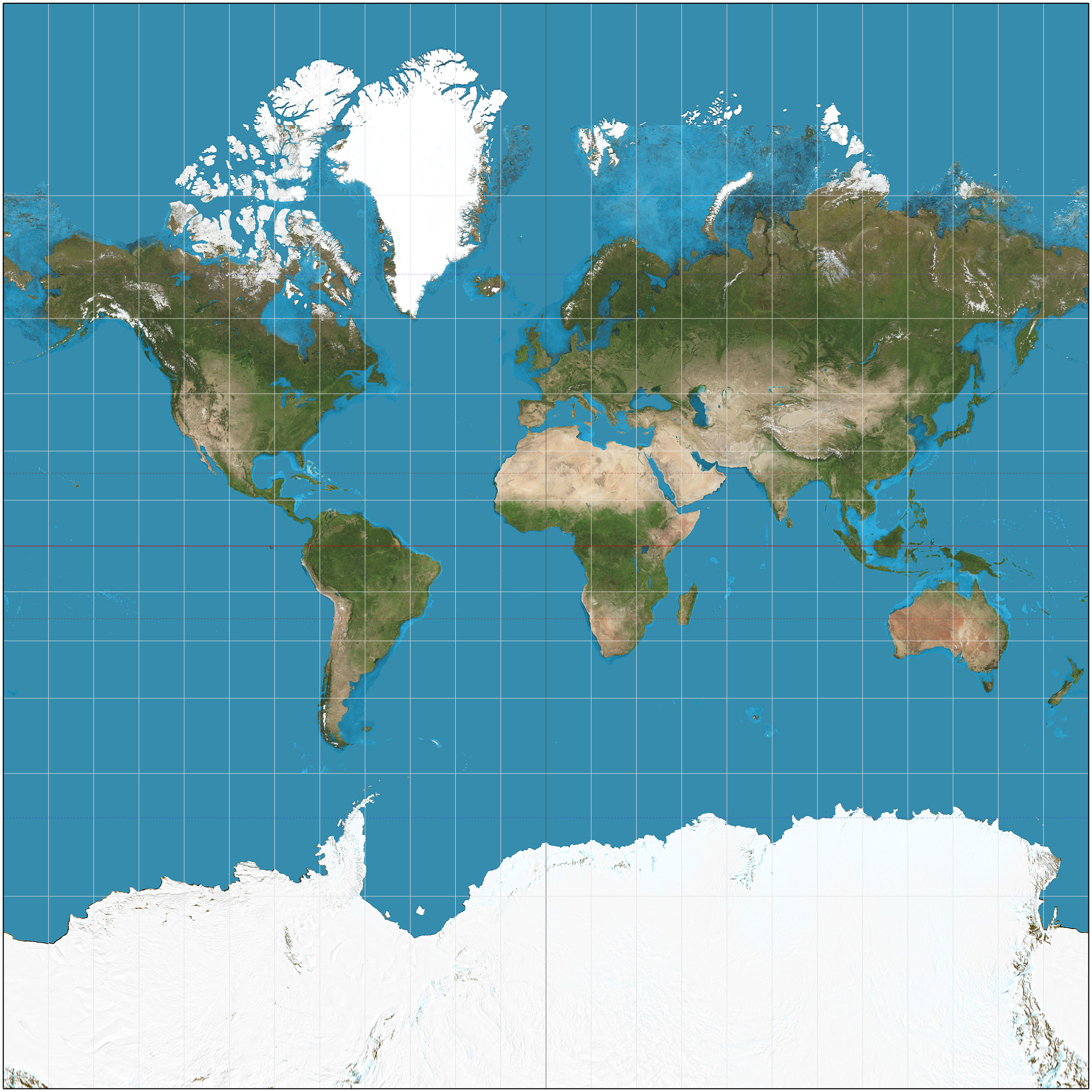
peters projection
correct spatial distributions related to area: accurate sizes, inaccurate shapes(especially near poles)
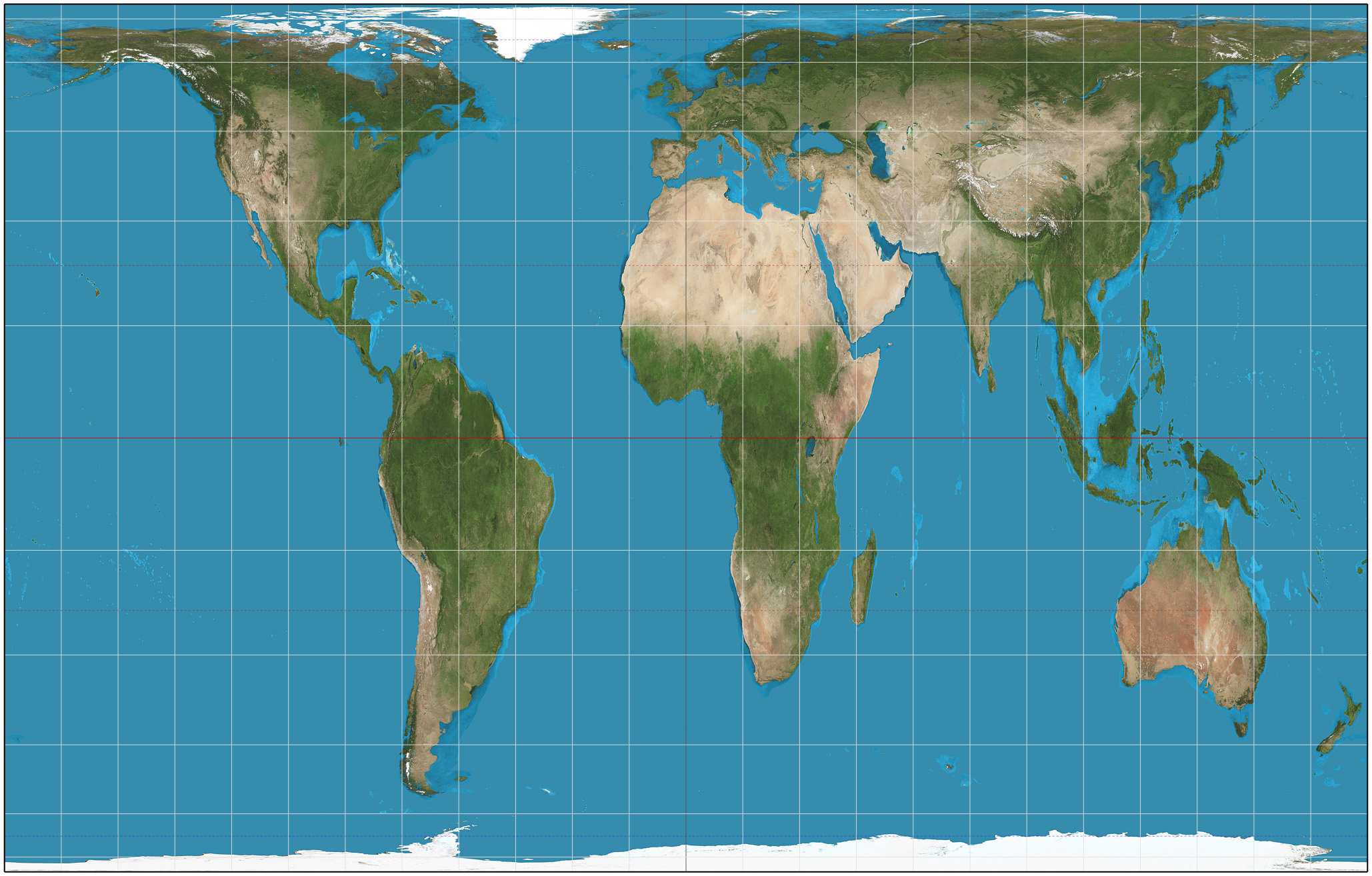
conic projection
general use in midlatitude countries: direction not constant
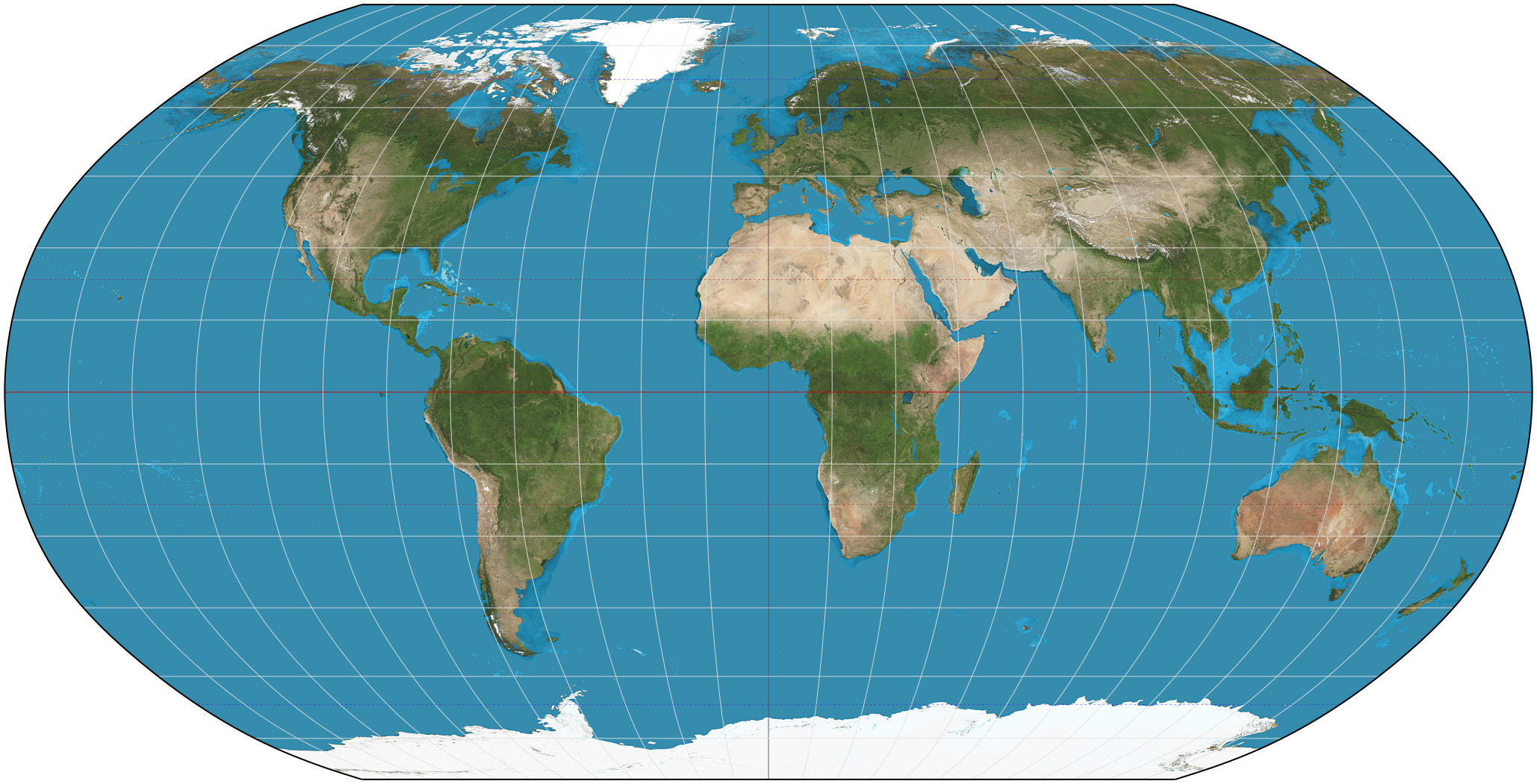
robinson projection
general use(classroom): all distorted slightly
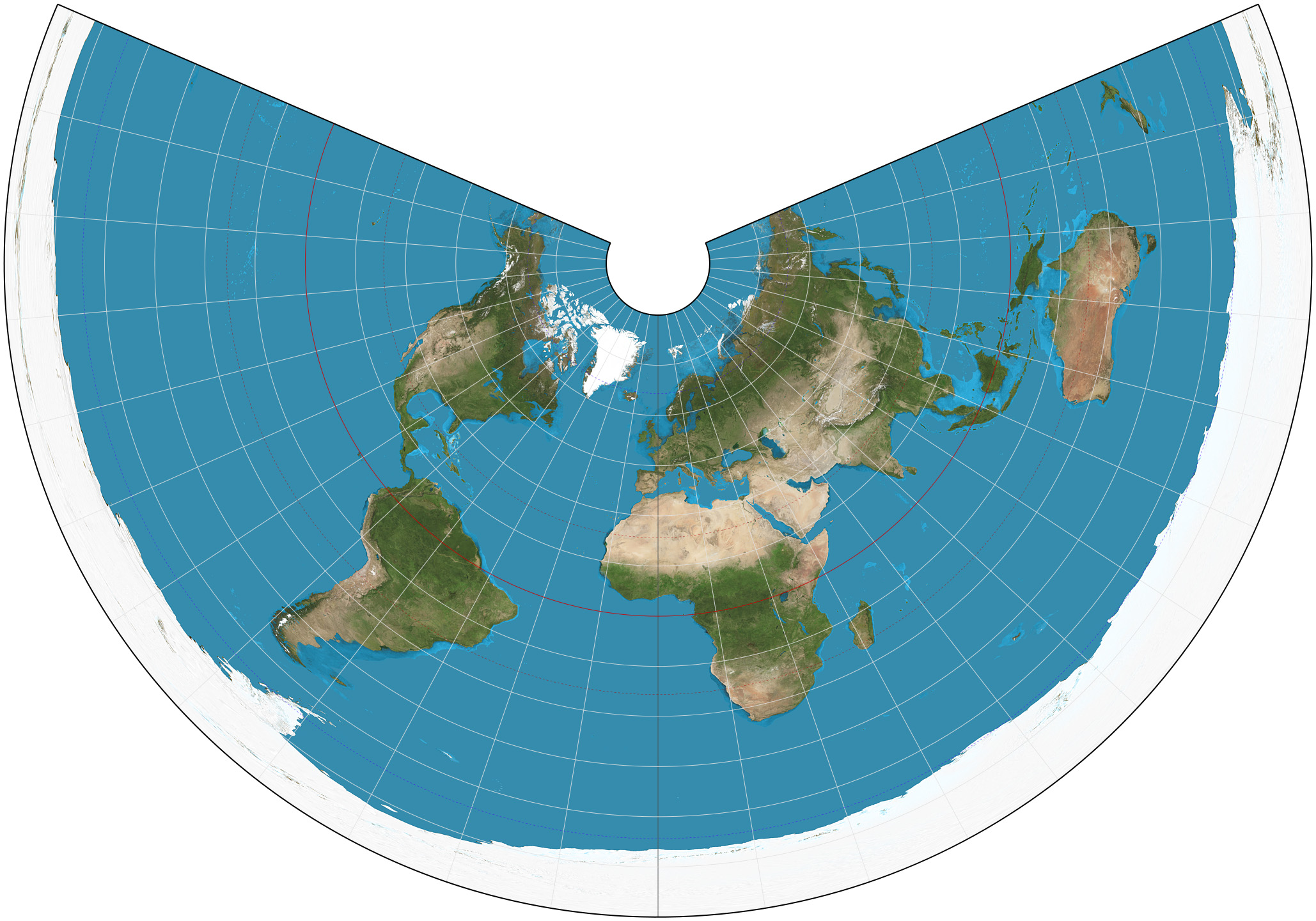
prime meridian
zero degrees longitude
choropleth
colors show numbers/amounts
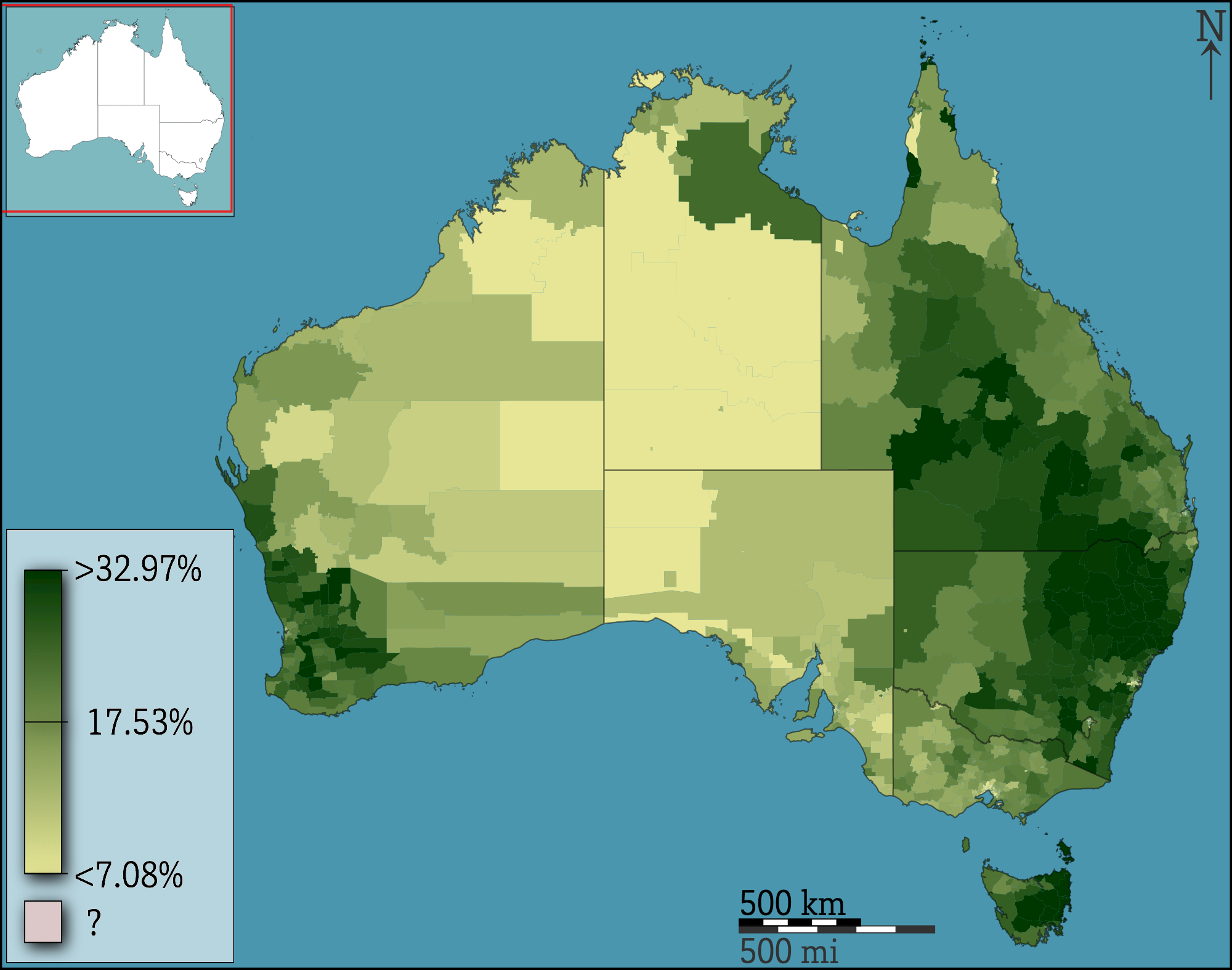
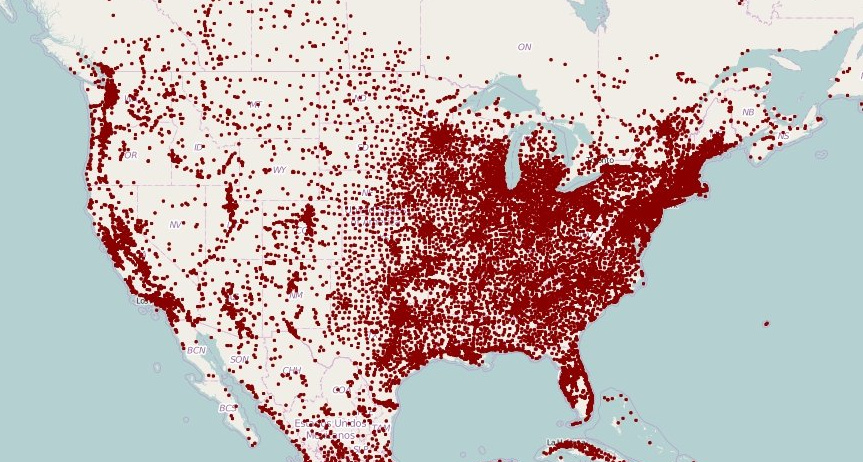
dot map
dots show how many things there are
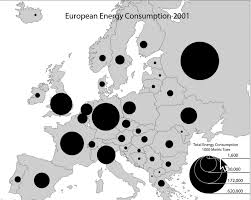
graduated/proportional symbol
symbols get bigger for more of sth
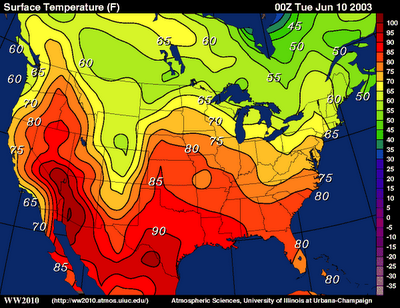
isoline map
lines connect places with the same value
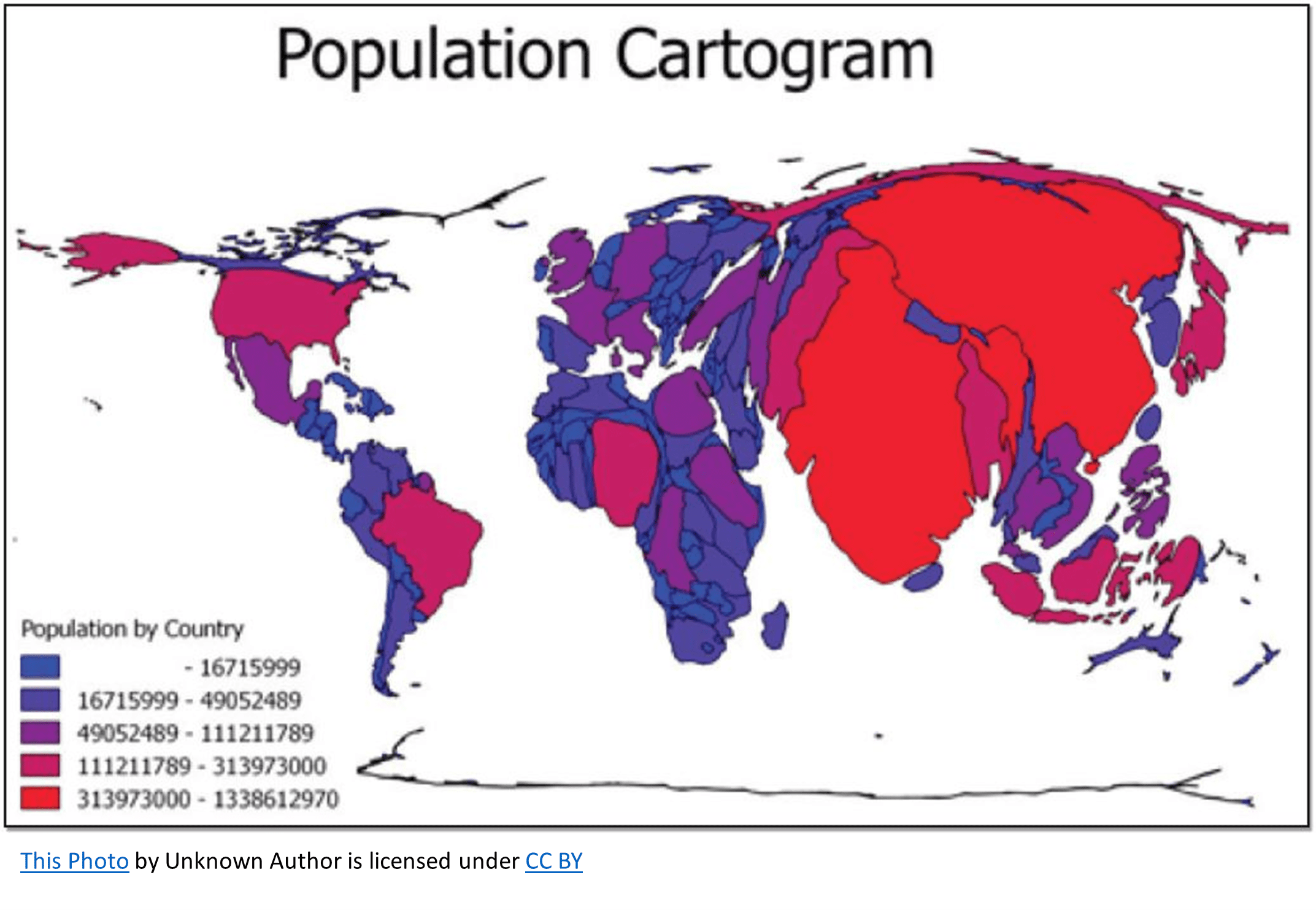
cartogram
map stretches/shrinks places based on data
field observation
traveling to somewhere to get firsthand info
spatial data
all info that can be tied to a specific location
remote sensing
satellites gather info and send to Earth; monitor environmental changes, assess spread of spatial phenomena
aerial geography
professional images captured from planes within the atmosphere
fieldwork
gather data on a location
geovisualizations
methods used to create visual representations of geospatial data
geovisualizations techs
GPS, remote sensing, GIS, smartphone&computer apps
global positioning system(GPS)
record receivers’ exact locations using multiple satellites; locating borders precisely, navigation, mapping lines/points
geographic information system (GIS)
computer system store, analyze, display info from multiple maps; LAYERS; urban planning, crime mapping, environmental monitoring
smartphone&computer applications
apps gather&store&use locational data; suggest locations(food, stores…) tracing disease
community-based solution
create buy-in from local residents, more likely to be locally accepted
spatial concepts
location, place, distance&time, patterns&distribution; the way in which different phenomena are organized in space
space
theoretical concept that geographers use to describe the geometric surface of the Earth
place
the way human s modify a particular space in ways that reflects who they are; site&situation
flow
patterns of connection between 2 places
distance decay(friction of distance)
further apart 2 things are, less connected they will be
outdated, due to globalization
site
characteristics at the immediate location
situation
location of a place relative to its surroundings and its connectivity to other places
toponyms
name of the place; e.g. Lake city
time-space compression
decreased distance between 2 places measured by the time/cost it requires to travel between them
spatial interaction
contact, movement, flow of things between locations
spatial association
matching patterns of distribution; indicate that phenomena may be related/associated with one another
natural resources
items that occur in the nature that people can use
types of natural resources
renewable&non-renewable
renewable natural resources
wind, solar, biomass, water
non-renewable natural resources
fossil fuels, minerals, underground fresh water
sustainability
trying to use resources now in ways that allow their use in future while minimizing negative impacts on the environment
land use
how land is utilized, modified, organized by people
built environment
physical artifacts people have created and that form part of the landscape
cultural landscape
highlighting how communities adapt their surroundings to meet their needs
cultural ecology
study of how human adapt to the environment
environmental determinism
landforms and climates are the most powerful forces shaping human behavior and societal development while ignoring the influence of culture
environmental possibilism
acknowledges limits on the effects of the natural environment and focuses more on the role that human culture plays
geographic scale/relative scale
global, worldly regional, national, national regional, local
global
entire world
worldly regional
multiple countries of the world
national
one country
national regional
a portion of a country/regions within a country
local
a province, state, city, or neighborhood
aggregation
data organized into different scales; more easily mapped/organized
types of regions
formal/uniform/homogenous, functional/nodal, perceptual/vernacular
formal/uniform/homogenous regions
linked by common traits, tend to have clear boundaries which separate them from other regions
functional/nodal regions
shared functions, tend to have reasonably clear borders, but not always(some central location or node around which that shared activity is carried out)
perceptual/vernacular regions
defined by people’s shared beliefs and feelings about themselves, borders are relatively vague