Psychology Unit Test
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
what is psychology?
psychology is the the study of the (individual) mind and behaviour, looking at thoughts, feelings, and actions across all stages of life.
goal of psych : describe, explain, predict, and influence behaviour.
one way psych can improve your life?
way : it helps you understand behaviours (yours and others)
why : by understanding behaviour, you can improve relationships, communicate better, and have more self-awareness.
psychology vs. psychiatry
psychology : focuses on studying and guiding behaviour, but are not medical doctors
psychiatrists : medical doctors who specialize in treating mental illnesses and prescribe medications.
schools of thought in psychology
psychoanalysis : unconscious urges and childhood experiences influence behaviour
behavioural psychology : focuses on behaviours learned from the environment
cognitive psychology : studies thinking, memory, and perception
humanistic psychology : emphasizes individual growth and self improvement
brief history of psychology
ancient greeks : thought personality came from bodily fluids (like blood)
hippocrates : connected emotions to the brain, not the heart
john locke : said the mind forms ideas based on senses
phrenology : 1800s practice of linking skull bumps to personality traits
modern psychology : began late 1800s with scientific methods (3 major branches : experimental, clinical, mental health psychology)
the brain vs. the mind
brain : the organ that controls body functions
mind : thoughts, feelings, and actions
freud and psychoanalysis
psychoanalysis : freud’s theory, early childhood shapes our unconscious mind, influencing behaviour and relationships. aims to unlock the unconscious to understand personality
freud’s theory of the mind (id, ego, superego)
id : pleasure principle (devil)
ego : reality (balance between id and superego)
superego : moral principle (right from wrong - angel)
conscious vs. unconscious mind
conscious mind : small, aware part we can see and control
unconscious mind : larger, hidden part storing thoughts, memories, and feelings we aren’t aware of
mind as an iceberg
iceberg diagram :
superego : conscious mind (above water)
ego : just below the line between conscious and unconscious mind (below surface)
id : unconscious mind (under water)
dreaming and type of dreams
REM : rem stands for rapid eye movement. it’s a phase of sleep that involves quick random movements of the eyes.
freud and jung studied dreams to understand the unconscious mind with different views of their meanings.
dream analysis
dreams can reveal hidden desires or concerns
freud saw dreams as hidden wishes from the ID that were hiding to avoid conflict with the superego.
manifest vs. latent content
manifest content : storyline you remember of a dream
latent content : meaning behind the dream
definition of personality
personality is a mix of thoughts, feelings, and actions making everyone unique.
introversion vs. extraversion
introversion : focus on internal interests, driven by isolation.
extraversion : focus on external interests, drives by social settings/interactions.
carl jung - 4 functional types
thinker (uses reason)
feeler (uses emotions)
sensor (uses all 5 senses)
intuitive (uses perception)
psychometrics and MBTI (myers briggs type indicator)
psychometrics uses test to analyze personality
MBTI expands jung’s groups into 16 personality types
hans eysenck & 2 dimensions
2 main dimensions of personality
extraversion-introversion : social or reserved
neuroticism : emotional stability
the big five
openness/close minded (independent vs. complying)
conscientiousness/unconscientiousness (organized vs. unorganized)
extraversion/introversion (outgoing vs. reserved)
agreeableness/disagreeableness (friendly vs. unkind)
neuroticism/balanced emotions (insecure vs. secure)
karen horney
a developmental psychologist who rejected freud’s focus on childhood sexual conflicts. She believed society and culture shaped women’s personalities and exposed bias against women in psychology
ivan pavlov
known for classical conditioning
dogs drooled when fed; later, they drooled at cues (lab coat)
experiment showed a neutral stimulus could trigger a response after pairing with a conditioned stimulus

classical conditioning
neutral stimulus: Becomes conditioned stimulus after pairing.
unconditioned stimulus : Naturally triggers response (plate of food).
unconditioned response : Natural response to unconditioned stimulus (e.g., salivation).
conditioned stimulus : Previously neutral, now triggers response.
conditioned response : Learned response to conditioned stimulus.
example (the office):
neutral/conditioned stimulus : Computer noise.
conditioned response : Expecting a mint.

b.f skinner
developed true behavioursim, focusing on observable behaviours not mental processes. he studied how rewards and punishments influence behaviour using rats and pigeons
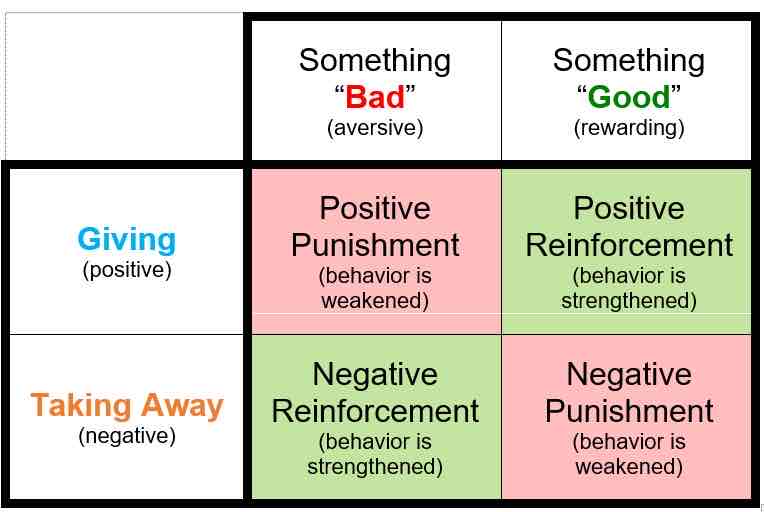
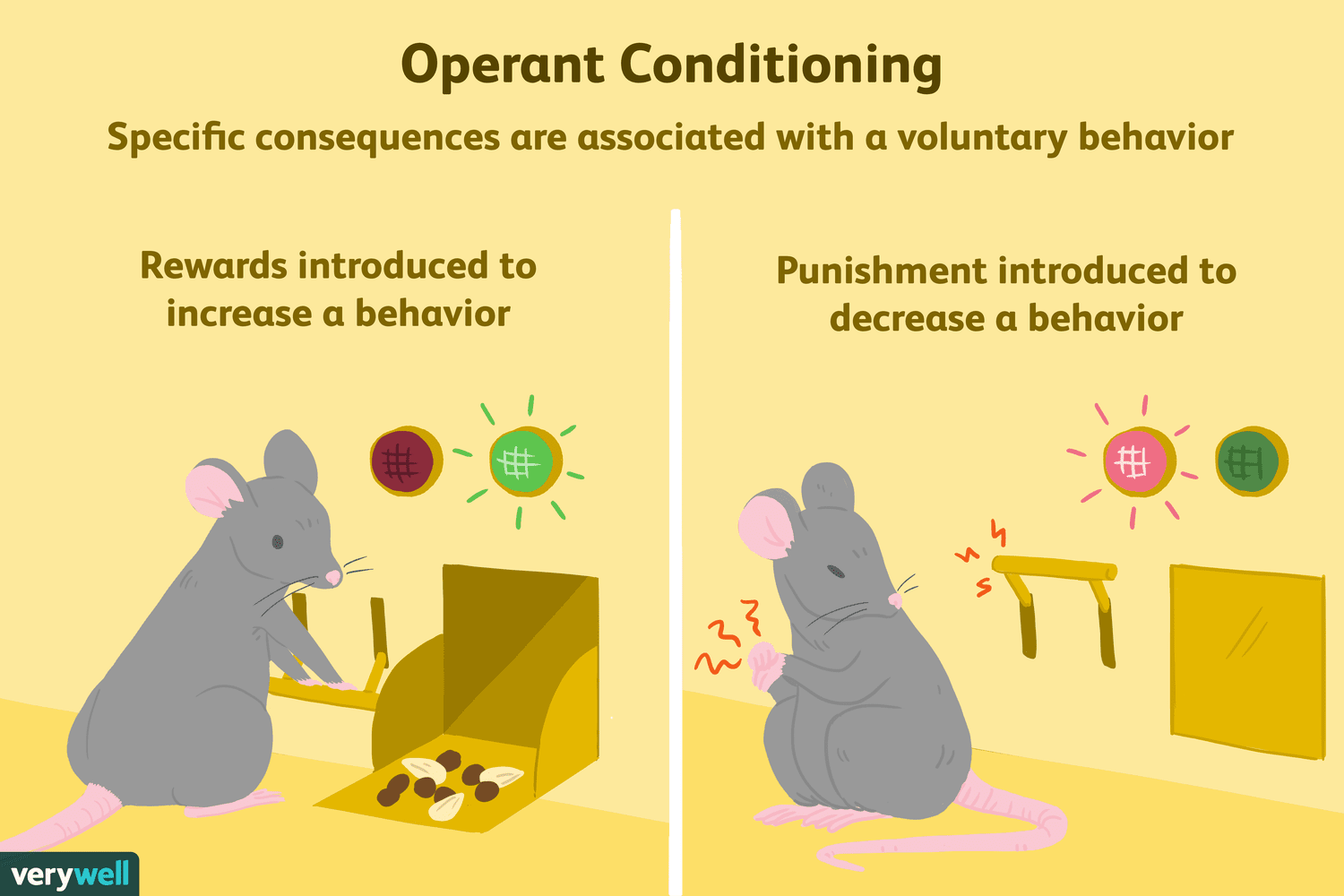
operant conditioning
operant conditioning is learning through rewards and punishments to shape behaviour.
humanism - abraham maslow
founder of humanistic psychology is known for hierarchy of needs, he studied self-actualizing people who reached their full potential and their peak experiences. each need must be met to move to the next level.
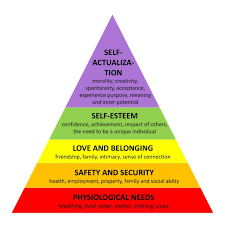
maslow’s theory
humans are driven by basic needs that build on each other
physiological needs : basics like food, water, and sleep
safety needs : feeling secure with shelter, money, and safety
love/belonging needs : friendships, family, scoail circles
esteem : self respect, feeling valued, gaining respect from others
self-actualization : creativity, acceptance, reaching full potential
logotherapy
logotherapy, a therapy helping people find meaning in life. focuses on the future and finding purpose to endure hardships
cognitive psychology
cognition : mental process of acquiring knowledge
albert bandura
a canadian psychologist apart of the “cognitive revolution” helped move psychology beyond behaviourism. he questioned why the same situation causes different responses in people. he developed social cognitive theory, which consideres motivation, environment, and behaviour and belived people learn by watching others.
bobo doll experiment
bobo doll experiment : was created to see if banduras assumptions were correct :
tested if people learn by watching and imitating others
children watched a video of an adult being aggressive towards a bobo doll
afterward they played with both aggressive and non-agreesive toys
results :
children who saw the video were aggressive and choose aggressive toys
children who didn’t see the video were less aggressive and avoided aggressive toys
understanding the brain
brain connections :
the nervous system is made up of neurons, special cells that receive, process, and send information using electrical and chemical signals called synapses
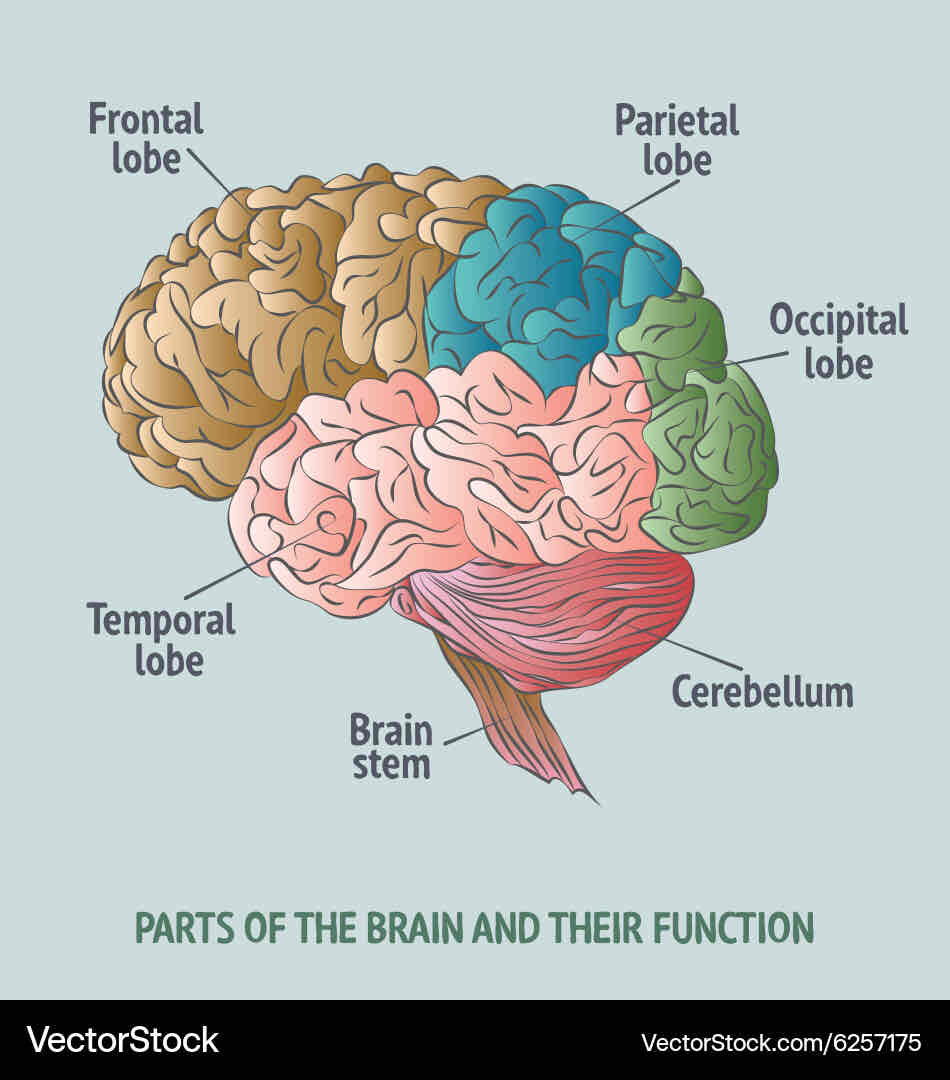
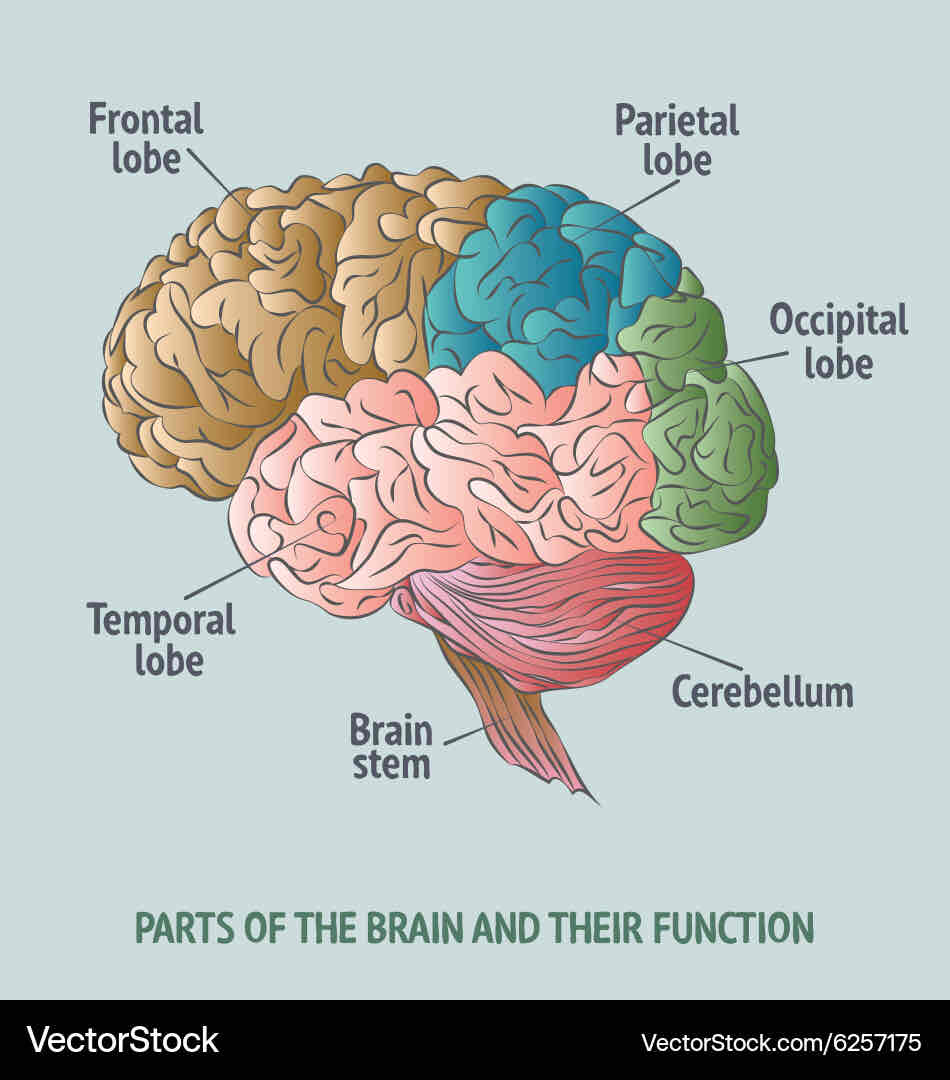
brain hemispheres
left side : controls right side of the body; focuses on words, logic, facts, and math
right side : controls left side of the body;focuses on imagination, intuition, arts, and rhythm
henry molaison (h.m.)
h.m. was a patient under Dr. William Scoville who believed that removing henry’s hippocampus would treat his epileptic seizures
perception and sensation
our brain constantly takes in what our eyes see and interprets it to understand. perception is the process of organizing and making sense of these sensations, helping the brain work efficiently
developmental psychology - sigmud freud’s psycho sexual stages of development
libido : stages of early development based on sexual instincts (known as the ID)
oral : birth to 18 months
anal : 18 months to 3 years
phallic : 3 to 6 years
latent : 6 years to puberty
genital : puberty onward
fixation
freud said if we focus too much on one stage of development, we can become fixated from too little or too much satisfaction which could lead to mental illness
jean piaget’s stages of cognitive development
sensorimotor : birth to 2 years
preoperational : 2 to 6 years
concrete operational : 7 to 11 years
formal operational : 12 years to adulthood
object permanence
a child’s ability to know that objects srill exist even when they can’t be seen or heard
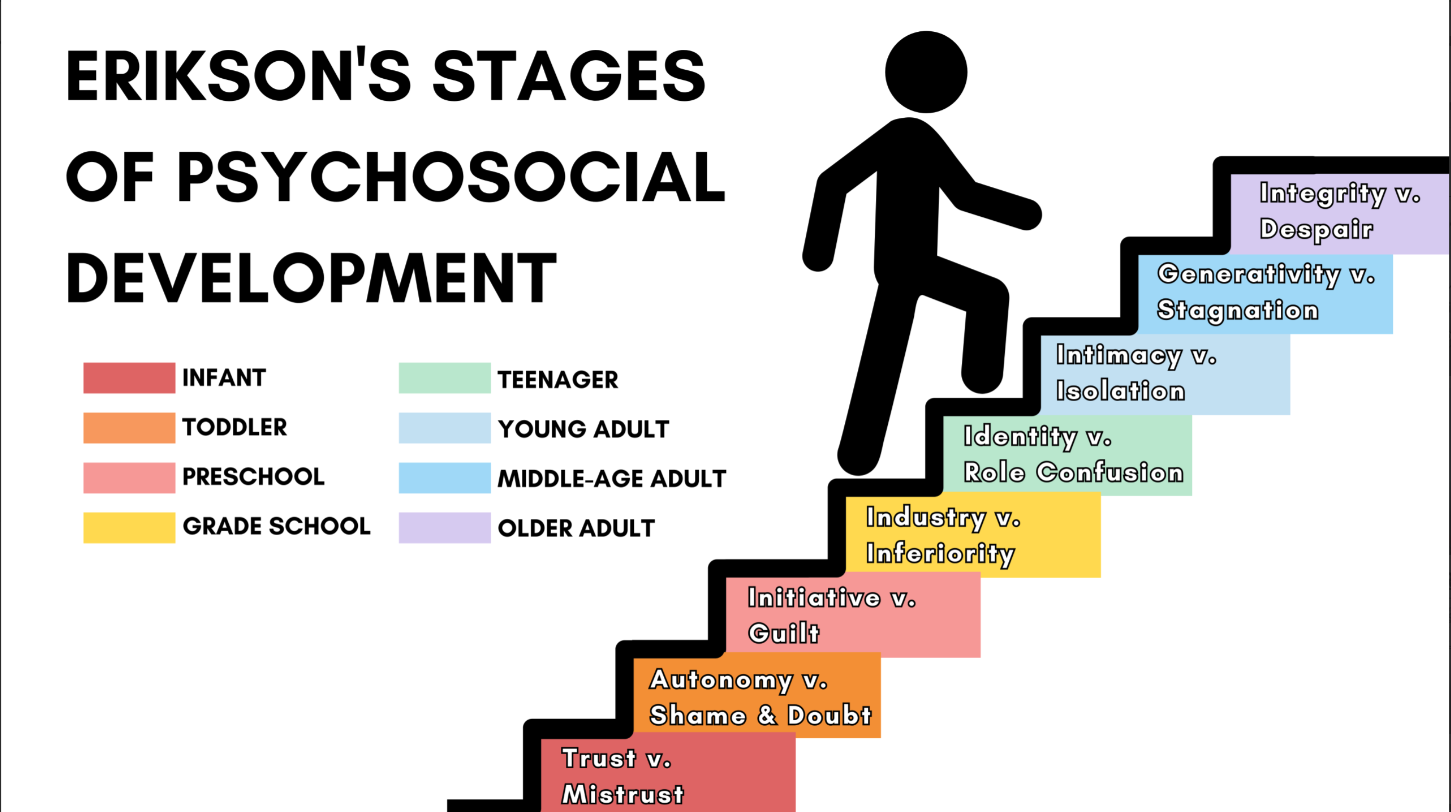
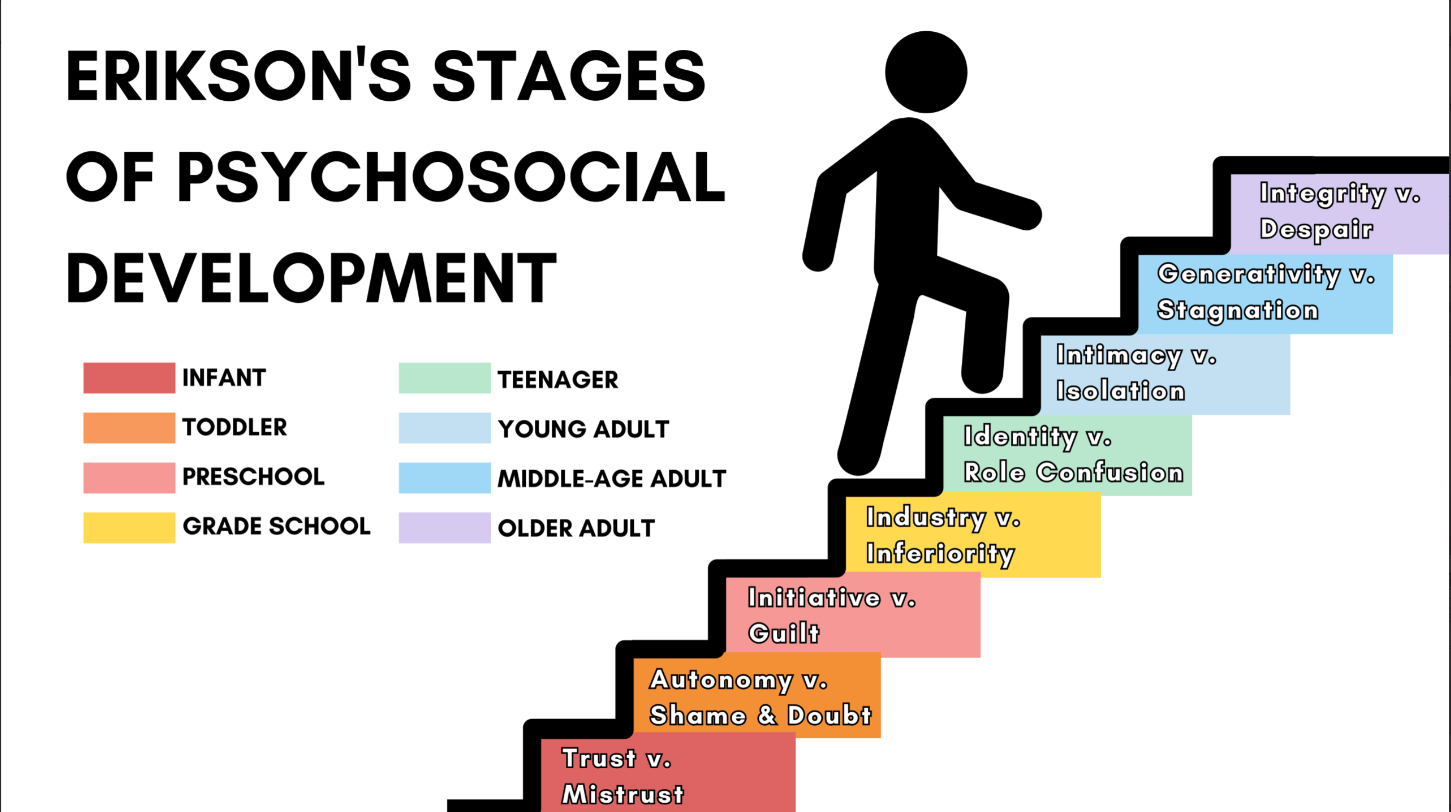
erik erickson’s stages of psychosocial development
personality develops in a set order from infancy to adulthood. at each stage there is a crisis that can have either a positive or negative impact on personality development.
mary ainsworth and the strange situation experiment
mary ainsworth is known for her work on emotional attachment and attachment theory, focusing on relationships, especially between children and parents. her “strange situation” experiment showed how attachment affects behaviour and became a standard test at for studying infants.
attachment types
secure (70%) : children trust caregivers, feel upset when separated, and happy when reunited
resistant (10%) : children get very upset when parents leave, less common
avoidant (20%) : children show no preference between caregiver and stranger, sign of neglect or abuse
disorganized : children appears confused, dazed, or disoriented
nature versus nurture
heredity factors : refers to physical traits and aspects of personality passed down from relatives (nature = biology/DNA)
edith experiment (1950s) : aaron stern tried to prove that the right environment could create a genius. he used his daughter, playing classical music and showing her flash cards
mental health and behaviours
psychopathology : the study of mental disorders and mental illnesses
psycho : mind
pathos : illness or disease
ology : study
psychotic disorders vs. neurotic disorders
neurotic disorders : mild mental disorders with specific symptoms but no loss of reality. causes include; biological, psychological, and economic factors.
psychotic disorders : severe mental illness with loss of reality and difficulty connecting with others, leading to social problems. causes include; genetics, biochemistry, and environmental
phobias
an extreme irrational fear of something. specific phobias are a type of anxiety disorder where exposure to the feared object or situation causes extreme anxiety or panic attacks.
types of phobias
agoraphobia : fear of public places where you might feel trapped or embarrassed
social phobia : fear of being judged or watched by others
specific phobias : fear of specific things or situations like animals/insects, blood/injury, situations (driving, crowds), natural environments/heights, water