Earth-Moon-Sun Earth and Space Science
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
Northern Hemisphere
The half of the earth north of the equator
Waxing Gibbous
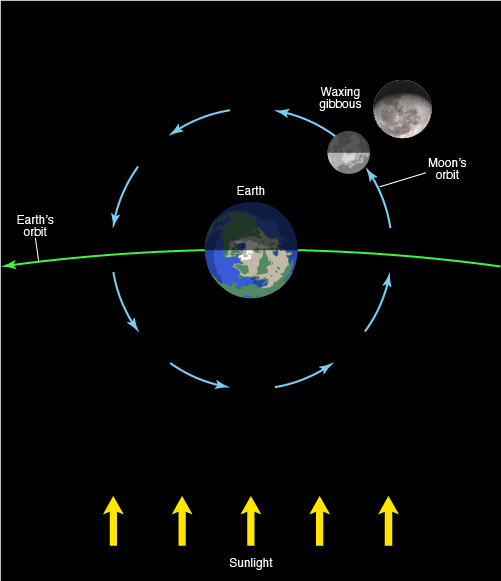
the phase during which the illuminated side of the moon is increasing, and more than half the face of the moon is illuminated as seen from Earth
Meteorological Seasons
groupings of three months based on common climate conditions; meteorological seasons start at the beginning of the months that contain solstices or equinoxes
First Quarter

the phase during which the moon has traveled one-quarter of the way around the Earth. To observers on the Earth, it appears to be half-illuminated.
Autumnal Equinox
a day all latitudes have equal day and night, marking the beginning of fall; occurs around September 23 in the Northern Hemisphere and around March 21 in the Southern Hemisphere
Spring Equinox
a day all latitudes have equal day and night, marking the beginning of the transition from winter to summer; occurs around March 21 in the Northern Hemisphere and around September 23 in the Southern Hemisphere
Spring Tide
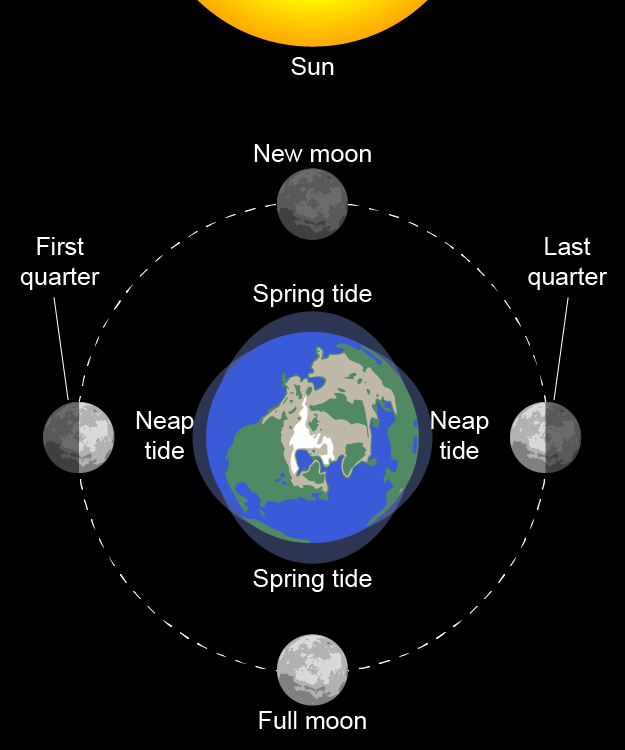
greater tidal effects due to the sun, moon, and Earth being aligned
Lunar Eclipse
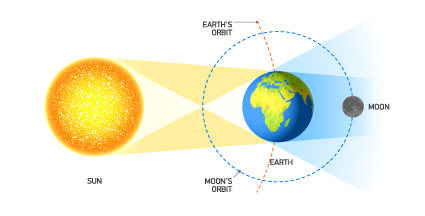
an event in which the moon's surface is obscured or darkened by Earth's shadow
Waning Gibbous
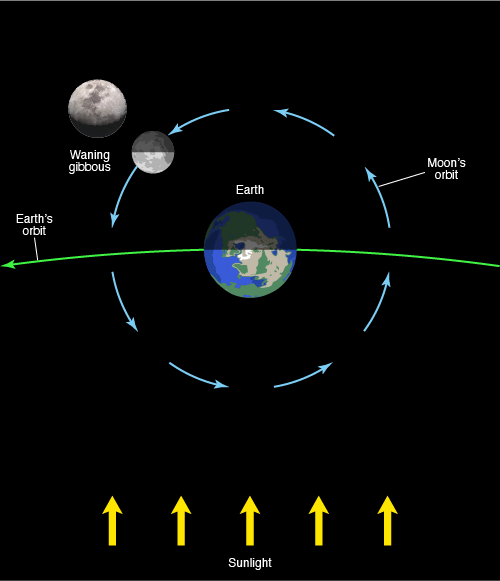
the phase during which the illuminated side of the moon is decreasing, but more than half the face of the moon is illuminated as seen from Earth
June Solstice
the day of longest daylight in the Northern Hemisphere (summer solstice) and shortest daylight of the year in the Southern Hemisphere (winter solstice); occurs around June 21
Fall (Autumn)
transition season between summer and winter that begins with equal daytime and nighttime hours (fall equinox) and ends with the shortest daylight hours (winter solstice)
Third Quarter
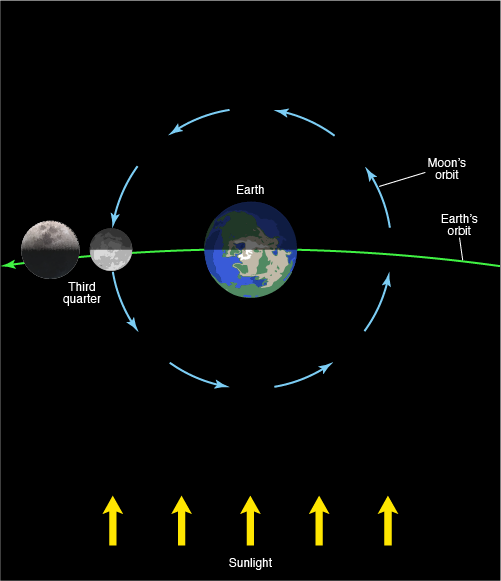
the phase during which the moon has traveled three-quarters of the way around the Earth. To observers on the Earth, it appears to be half-illuminated.
Lunar Cycle / Phase of the Moon
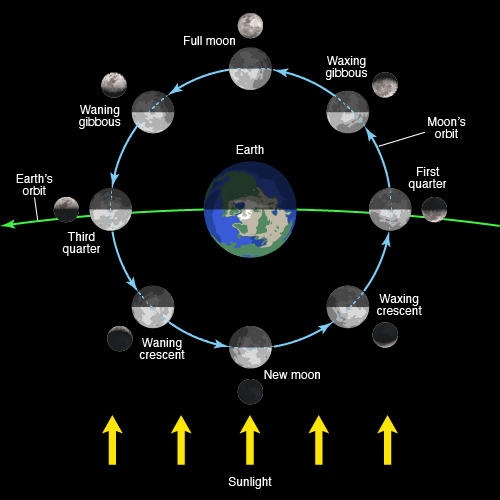
the appearance of the surface of the moon as seen on earth
Example.
Full Moon
Earth's Tilt
Earth is tilted 23.5o, which causes Earth's seasons
Low Tide
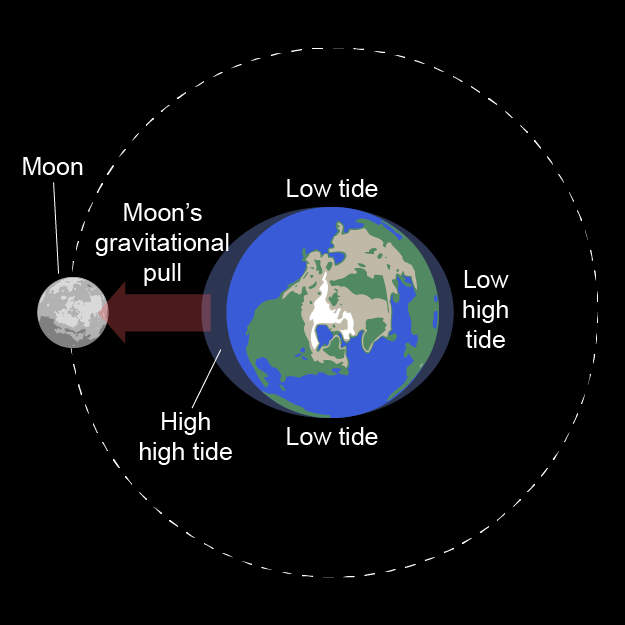
lower water levels due to being out of line with the gravity of the moon and sun
Fall Equinox
a day all latitudes have equal day and night, marking the beginning of the transition from summer to winter; occurs around September 23 in the Northern Hemisphere and around March 21 in the Southern Hemisphere
September Equinox
a day all latitudes have equal day and night, occurring around September 23; also known as the fall or autumnal equinox in the Northern Hemisphere
Full Moon
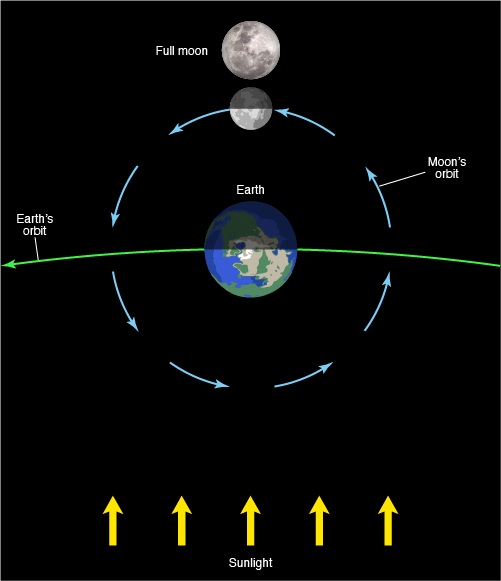
the phase during which the moon has traveled halfway around the Earth. To observers on the Earth, it appears to be fully illuminated.
Waning Crescent
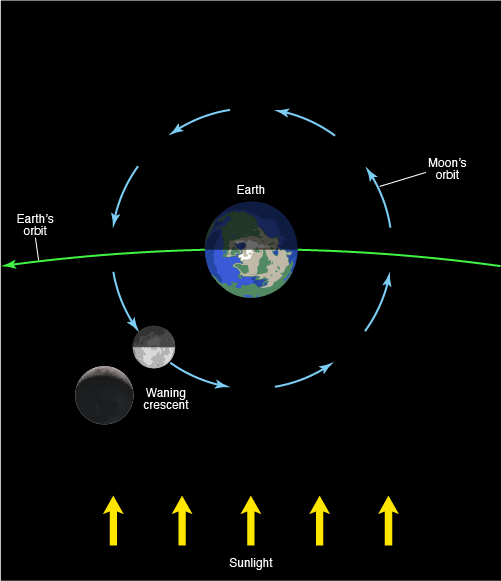
the phase during which the illuminated portion of the moon is decreasing, and less than half the moon's face is illuminated as seen from Earth
Summer Solstice
the day of longest daylight; occurs around June 21 in the Northern Hemisphere and December 22 in the Southern Hemisphere
Spring
transition season between winter and summer that begins with equal daytime and nighttime hours (spring equinox) and ends with the longest daylight hours (summer solstice)
Bulges

areas on the earth in line with the moon's gravity which have a larger amount of water
Rotate
when a planet spins about its axis
Neap Tide

lesser tidal effects due to the sun and moon pulling on the earth from different directions
New Moon
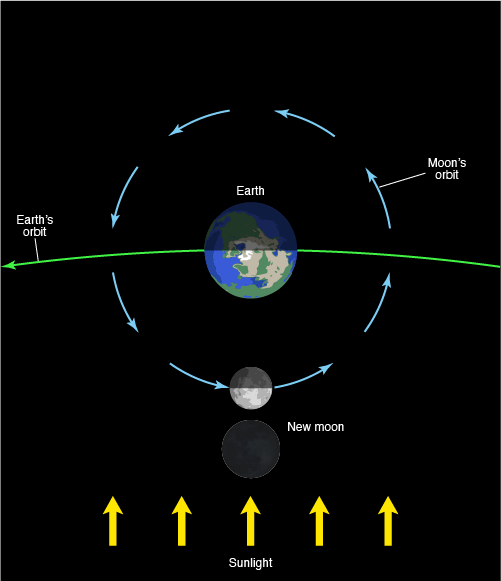
the phase during which the moon starts the cycle around the Earth. The moon is between the Sun and the Earth. To observers on the Earth, it appears to be unlit.
Astronomical Seasons
seasons beginning on the date of each solstice or equinox; astronomical summer starts on the summer solstice around June 21
Winter Solstice
the day of the shortest daylight; occurs around December 22 in the Northern Hemisphere and June 21 in the Southern Hemisphere
Daylight Saving Time
the practice of setting clocks forward one hour during the summer months
Revolve
when a planet moves about another object; Earth revolves around the Sun, and the moon revolves around Earth
Tides

rising and falling sea levels due to the sun's and moon's gravity and the rotation of the earth
Time Zones
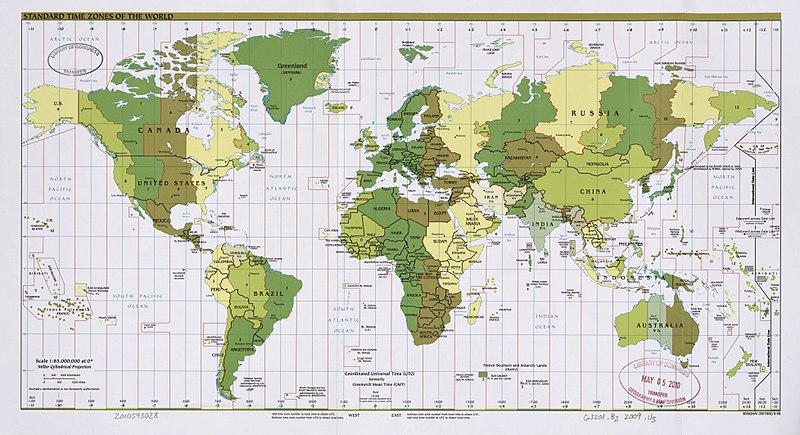
a region of the earth which observes a uniform standard time; there are around 37 time zones, depending on daylight saving time
Example.
Nepal Standard Time
Winter
coldest season; begins with the shortest daylight hours (winter solstice) and ends with equal daytime and nighttime hours (spring equinox)
Summer
warmest season; begins with the longest daylight hours (summer solstice) and ends with equal daytime and nighttime hours (fall equinox)
Waxing Crescent
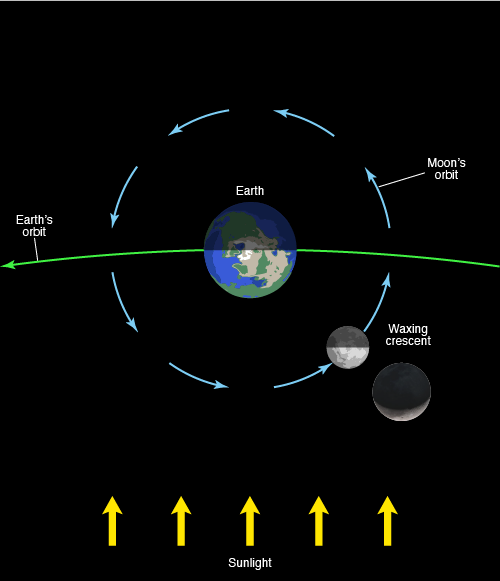
the phase during which the illuminated side of the moon is increasing, but less than half the face of the moon is illuminated as seen from Earth
High Tide

higher water levels due to the gravity of the moon and sun
Vernal Equinox
a day all latitudes have equal day and night, marking the beginning of spring; occurs around March 21 in the Northern Hemisphere and around September 23 in the Southern Hemisphere
Solar Eclipse
Term definition.
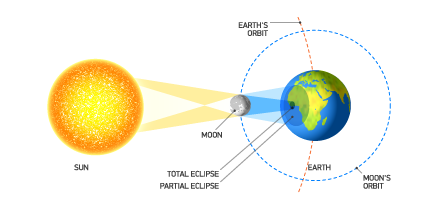
an event in which the sun's surface is obscured or darkened by the moon
December Solstice
the day of the shortest daylight of the year in the Northern Hemisphere (winter solstice) and the longest daylight of the year in the Southern Hemisphere (summer solstice); occurs around December 22
March Equinox
a day all latitudes have equal day and night occurring around March 21; known as the spring or vernal equinox in the Northern Hemisphere