Bio 2000 SJU - End of Chapter Multiple Choice Questions (Chapter 2-21)
1/199
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
200 Terms
_____________ make up the nucleus of an atom
A) Protons and electrons
B) Protons and neutrons
C) Protons, neutrons, and electrons
D) Neutrons and electrons
E) Electrons
B) Protons and neutrons
Living organisms are composed mainly of which atoms?
A) Calcium, hydrogen, nitrogen, and oxygen
B) Carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, and oxygen
C) Hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, and helium
D) Carbon, helium, nitrogen, and oxygen
E) Carbon, calcium, hydrogen and oxygen
B) Carbon, Hydrogen, nitrogen, and oxygen
Hydrogen bonds differ from covalent bonds in that
A) Covalent bonds can form between two atoms of any type, but hydrogen bonds form only between H and O
B) Covalent bonds involve sharing of electrons, and hydrogen bonds involve complete transfer of electrons
C) Covalent bond result from equal sharing of electrons, but hydrogen bonds involve unequal sharing of electrons
D) Covalent bonds involve sharing of electrons between atoms, but hydrogen bonds are the result of weak attractions between a hydrogen atom of a polar molecule and an electronegative atom of another polar molecule.
E) Covalent bonds are weak bonds that break easily, but hydrogen bonds are strong links between atoms that are not easily broken
D) Covalent bonds involve sharing of electrons between atoms, but hydrogen bonds are the result of weak attractions between a hydrogen atom of a polar molecule and an electronegative atom of another polar molecule.
Chemical reactions in living organisms...
A) May continue to completion if the products are removed
B) Often require a catalyst to speed them up
C) Are in many cases reversible
D) Occur in liquid environments, such as water
E) May exhibit all of the above
E) May exhibit all of the above
The sum of the atomic masses of all atoms of a molecule is its....
A) Atomic weight
B) Molarity
C) Molecular mass
D) Concentration
E) Molecular Formula
C) Molecular mass
On Earth, the natural abundance of carbon isotopes is as follows: 98.95% C-12, .63% C-13, .42% C-14. Calculate the average atomic mass of carbon
A) Exactly 12
B) 12.01
C) 12.04
D) 12.22
E) 36.04
B) 12.01
6 CO2 + 6H2O + light -> C6H12O6 + 6O2 is an example of a chemical reaction. What is occurring during this reaction?
A) Atoms are split and re-form as new molecules
B) Protons and neutrons are reorganized to form new structures
C) Substances are changed into other substances by the making or breaking of chemical bonds
D) Shells of atoms divide to transport protons to other atoms
E) Both A) and B) are occurring
C) Substances are changed into other substances by the making or breaking of chemical bonds
In their outermost electron shells, a carbon atom has four electrons and a hydrogen atom has one electron. Which of the following molecules would you predict to be stable?
A) CH
B) CH2
C) CH4
D) C2H6
E) Both C) and D)
E) Both C) and D)
The molecular mass of glucose is about 180g/mol. If 45g of glucose is dissolved in water to make a final volume of 0.5L, what is the molarity of the solution?
A) .125M
B) .25M
C) .5M
D) 1.0M
E) 2.0M
C) .5M
Let's suppose a solution of pure water at 25C contains OH- ions at a concentration of 10^-9 M. Calculate the pH of the solution
A) 3
B) 5
C) 7
D) 9
E) 11
B) 5
Which of the following is a common functional group found in organic molecules?
A) A hydrocarbon
B) A ketone
C) an isomer
D) A carbon atom
E) An oxygen atom
B) A ketone
The ability of carbon to form chains that serve as backbones for a variety of molecules is due to...
A) the ability of carbon atoms to form four covalent bonds
B) The ability of carbon to form ionic bonds with many different atoms
C) The abundance of carbon in the environment
D) the ability of carbon to form single, double, and even triple covalent bonds withy many different types of atoms
E) both A) and D)
E) both A) and D)
_____________ is a polysaccharide characterized by an unbranded linear structure linear structure and a high degree of hydrogen bonding between chains
A) Glucose
B) Starch
C) Wax
D) Cellulose
E) Glycogen
D) Cellulose
The monomers of proteins are _________________, and these are linked by polar covalent bonds commonly referred to as ____________ bonds.
A) nucleotides, peptide
B) Polypeptides, peptide
C) Dipeptides, amino
D) Amino acids, peptide
E) monosaccharides, glycosidic
D) Amino acids, peptide
A(n) ___________ is a portion of a protein with a particular structure and function.
A) peptide bond
B) domain
C) phospholipid
D) amino acid
E) monosaccharide
B) domain
Which of the following molecules is the most hydrophobic?
A) C3H7COOH
B) CH3OH
C) C2H6
D) C5H10O5
E) Both b and d are correct
C) C2H6
A polysaccharide is composed of 74 glucose molecules. How many chemical reactions would be needed to completely break down this polysaccharide into 74 individual glucose molecules?
A) 74 dehydration reactions
B) 73 dehydration reactions
C) 74 hydrolysis reactions
D) 73 hydrolysis reactions
E) Both A) and C) are correct
D) 73 hydrolysis reactions
Both safflower oil and butter contain fats. However, safflower oil is liquid at room temperature and butter is solid. Why?
A) Safflower oil has more saturated fats than butter
B) Safflower oil has more unsaturated fats than butter
C) The fatty acid in safflower oil have more double bonds than those in butter
D) The fatty acids in safflower oil have fewer double bonds than those in butter
E) Both B) and C) are correct
E) Both b and c are correct
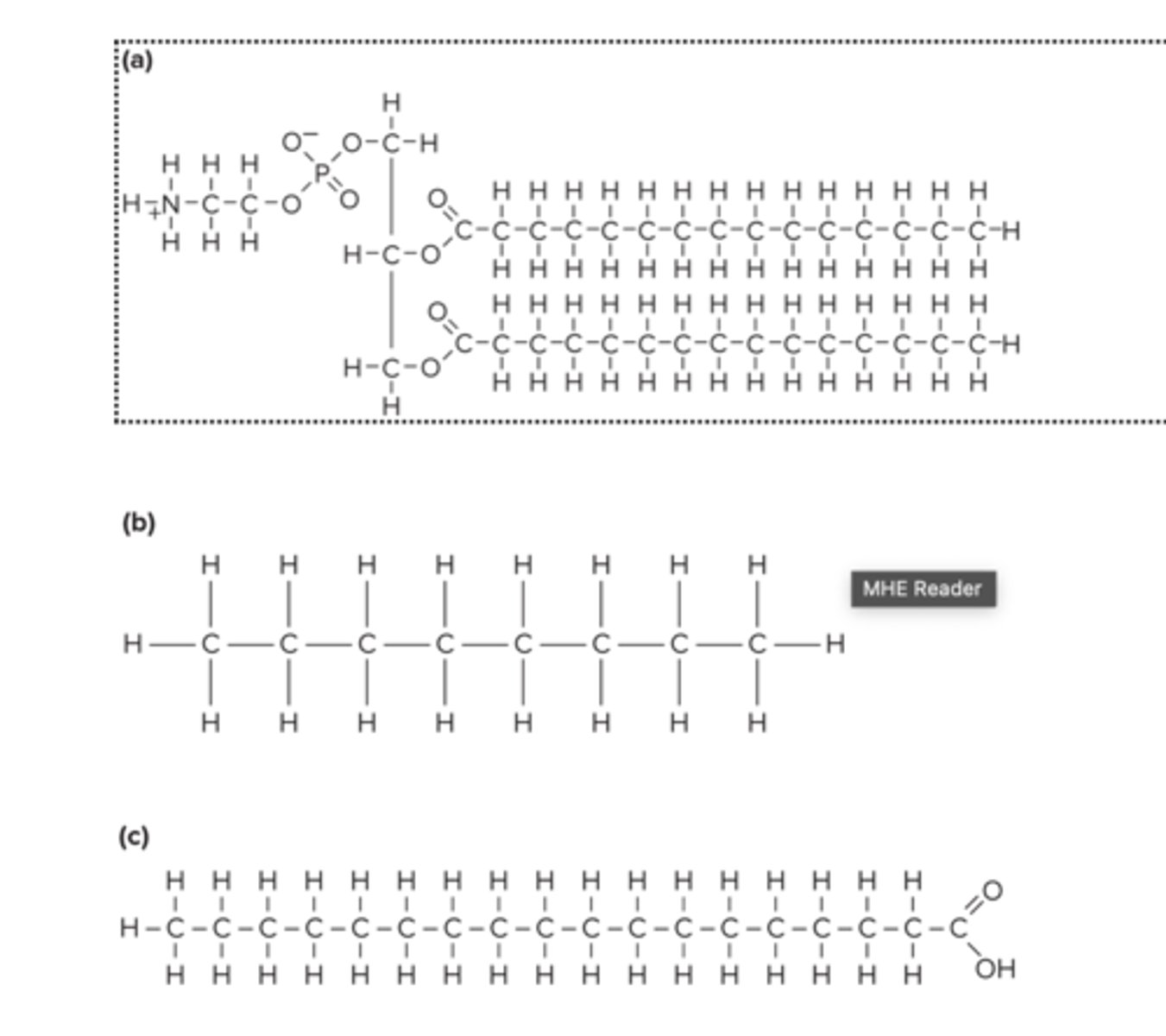
The structures of three molecules are shown below. Which of them is (are) amphipathic?
A) (a) only
B) (b) only
C) (c) only
D) (b) and (c)
E) (a) and (c)
E) (a) and (c)
In a DNA molecule, 30% of the bases are guanine (G). What percentage of the bases are adenine (A)?
A) 30%
B) 20%
C) 15%
D) 10%
E) none of the above
B) 20%
The cell theory states...
A) That all living things are composed of cells
B) That cells are the smallest units of living organisms
C) That new cells come from pre-existing cells by cell division
D) all of the above
E) A) and B) only
D) all of the above
When using microscopes, resolution is...
A) The ratio between the size of the image produced by the microscope and the actual size of the object
B) The degree to which a particular structure looks different from other structures around it
C) how well a structure takes up certain dyes
D) the ability to observe two nearby objects as being separated from each other
E) the degree to which the image is magnified
D) the ability to observe two nearby objects as being separated from each other
If a motor protein was held in place and a cytoskeletal filament was free to move, what type of motion would occur when the motor protein was active?
A) The motor protein would walk along the filament
B) The filament would move
C) The filament would bend
D) All of the above would happen
E) Only B) and C) would happen
B) The filament would move
Each of the following is part of the endo-membrane system except
A) The nuclear envelope
B) The endoplasmic reticulum
C) The Golgi apparatus
D) lysosomes
E) mitochondria
E) mitochondria
the central vacuole in many plant cells is important for...
A) storage
B) photosynthesis
C) Structural support
D) all of the above
E) A) and C) only
E) A) and C) only
Using knowledge from cell biology, a fabric company wants to create a new material for the military that is able to bear high levels of tension. What cellular component(s) might be useful in this fabric?
A) elastin
B) collagen
C) microtubules
D) intermediate filaments
E) both B) and D)
E) both B) and D)
A spherical cell has a radius of 34um. What is its surface area/volume ratio?
A) .088
B) .12
C) 11.3
D) 55.7
E) 127
A) .088
A mutation arises in a gene that codes an enzyme called lysosomal acid hydrolase. The mutation changes an amino acid in the active site of the enzyme, so the enzyme doesn't function properly. What effect will this mutation have on lysosome function?
A) Vesicles from the Golgi will not be able to fuse with the lysosome
B) The lysosome will not be able to digest certain molecules
C) The overall structure of the lysosome will be altered
D) There will be no effect, since the lysosome is an organelle and not a single enzyme
E) Both A) and B) are correct
B) the lysosome will to be able to digest certain molecules
Let's suppose a mutant protein contains a sorting signal at its amino end that targets it cotranslationally to the ER as well as a sorting signal at its carboxyl end that targets it post-translationally to the mitochondria If you used fluorescence microscopy with a fluorescent dye that specifically stained this mutant protein, where would you expect to see most of the fluorescence?
A) in the cytosol
B) In the ER only
C) in the mitochondrion only
D) In both the ER and the mitochondrion
E) Equally in the cytosol, ER, and mitochondrion
B) in the ER only
Which of the following observations would not be considered evidence for the endosymbiosis theory?
A) Mitochondria and chloroplasts have genomes that resemble smaller versions of bacterial genomes
B) Mitochondria, chloroplasts, and bacteria all divide by binary fission
C) Mitochondria, chloroplasts, and bacteria all have ribosomes
D) Mitochondria, chloroplasts, and bacteria all have similar sizes and shapes
E) All of the above are considered evidence for the endosymbiosis theory
C) Mitochondria, chloroplasts and bacteria all have ribosomes
Which of the following statements best describes the chemical composition of biological membranes?
A) Biological membrane are bilayers of proteins with associated lipids and carbohydrates
B) Biological membranes are composes of two layers: one layer of phospholipids and one layer of proteins
C) Biological membrane are bilayers of phospholipids with associated proteins and carbohydrates
D) Biological membrane are composed of equal numbers of phospholipids, proteins, and carbohydrates
E) Biological membranes are composed of lipids with proteins attached to the outer surface
C) Biological membrane are bilayers of phospholipids with associated proteins and carbohydrates.
Which of the following events in a biological membrane would not be energetically favorable and there would not occur spontaneously?
A) The rotation of phospholipids
B) The lateral movement of phospholipids
C) The flip-flop of phospholipids to the opposite leaflet
D) The rotation of membrane proteins
E) The lateral movement of membrane proteins
C) The flip-flop of phospholipids to the opposite leaflet
Which of the following movements is not an example of passive transport?
A) The movement of water through aquaporins
B) the intercellular transport of molecules via channels
C) the transport of Na+ and K+ via Na+/K+- ATPase
D) the simple diffusion of CO2 through a phospholipid bilayer
E) All of the above are examples of passive transport
C) The transport of Na+ and K+ via Na+/k+- ATPase
What features of a membrane are major contributors to is selective permeability?
A) phospholipid bilayers
B) channels and transporters
C) glycolipids on the outer surface of the membrane
D) peripheral membrane proteins
E) both A) and B)
E) both A) and B)
Large particles can be brought into a cell by...
A) facilitated diffusion
B) active transport
C) phagocytosis
D) exocytosis
E) all of the above
C) phagocytosis
Let's suppose an insect, which doesn't maintain a constant body temperature, was exposed a shift in temperature from 60F to 80F. Which of the following types of membrane changes would be the most beneficial to help this animal cope with the temperature shift?
A) An increase in the number of double bonds in the non polar tails of phospholipids
B) An increase in the length of the non polar tails of phospholipids
C) A decrease in the amount of cholesterol in the membrane
D) A decrease in the amount of carbohydrate attached to membrane proteins
E) A decrease in the amount of carbohydrate attached to phospholipids
B) An increase in the length of the non polar tails of phospholipids
When placed in a solution of water, a human skin cells burst. Which of the following statements best explains why this happens?
A) The inside of the cell is hypertonic to the outside
B) The inside of the cell is hypotonic to the outside
C) The membrane contains transporters that allow the rapid movement of ions
D) The membrane contains channels that allow the rapid movement of ions
E) Both C) and D) are correct explanations
A) The inside of the cell is hypertonic to the outside
The solute concentration inside the cells of a plant is 0.3M; outside the cells, it is 0.2M. If you assume that the solutes do not readily cross the membrane, which of the following statements best describes what will happen?
A) The plant cells will lose a lot of water, and the cells will crenate
B) The plant cells will lose a little water, and the cells will expand
C) The plant cells will take up a lot of water, and the cells will undergo osmotic lysis
D) The plant cells will take up a little water, and the plasma membrane of the cells will slightly push against the cell wall
E) Both A) and B) are correct
D) The plant cells will take up a little water, and the plasma membrane of the cells will slightly push against the cell wall
Artificial membrane vesicles that contain purified proteins can be created in a laboratory. Researchers can control the concentrations of ions and other solutes that are present on the inside and outside of these vesicles. Let's suppose that researchers prepared membrane vesicles with or without an H+/glucose symporter or an H+ pump that pumps H+ out of the vesicle. If the researchers then added glucose outside of the vesicles, under which of the following sets of conditions would you expect glucose to move against a gradient and accumulate inside the vesicles?
A) vesicles contain an H+/glucose symporter, and the pH inside is lower than outside
B) vesicles contain an H+/glucose symporter, and the pH outside is lower than inside
C) Vesicles contain an H+/glucose symporter, and the Na+ concentration inside is lower than outside
D) Vesicles contain an H+/symporter, and an H+ pump
E) Both B) and D) are correct
E) Both B) and D) are correct
Researchers have identified a drug that prevents coat proteins in eukaryotic cells from binding to each other. If you added the drug to a sample of cells, which of the following steps in receptor-mediated endocytosis or exocytosis would be inhibited?
A) The formation of vesicles at the plasma membrane during receptor-mediated endocytosis
B) the uncoating of vesicles during receptor-mediated endocytosis
C) fusion between a vesicle and a lysosome during receptor-mediated endocytosis
D) The formation of vesicles at the Golgi membrane during exocytosis
E) Both A) and D) would be inhibited
E) Both A) and D) would be inhibited
Reactions that release free energy are...
A) exergonic
B) Spontaneous
C) endergonic
D) Endothermic
E) Both A) and B)
E) Both A) and B)
Enzymes speed up reactions by
A) Providing chemical energy to fuel a reaction
B) lowering the activation energy necessary to initiate the reaction
C) Causing an endergonic reaction to become exergonic
D) Substituting for one of the reactants necessary for the reaction
E) Doing none of the above
B) lowering the activation energy necessary to initiate the reaction
When NADH is converted to NAD+ + H+, NADH has been
A) reduced
B) phosphorylated
C) oxidized
D) decarboxylated
E) methylated
C) Oxidized
Scientists identify proteins that use ATP as an energy source by...
A) Determining whether a protein function in anabolic or catabolic reactions
B) Determining if a protein has a known ATP-binding site
C) Predicting the free energy necessary for a protein to function
D) Determining if a protein has an ATP synthase subunit
E) doing all of the above
B) Determining if a protein has a known ATP-binding site
Which of the following is (are) key benefits of catabolic reactions?
A) Recycling of organic building blocks
B) breakdown of organic molecules to obtain energy
C) Synthesis of important polymers, such as polypeptides
D) All of the above
E) A) and B) only
E) A) and B) only
For the idealized reaction aA + bB ⇋ cC + dD , let's suppose that the ΔG value is positive. If the starting concentrations for A, B, C, and D are 1 M each, what would you predict will happen?
A) The forward reaction is favored
B) The reverse reaction is favored
C) The forward reaction is fast
D) The reverse reaction is fast
E) Both B) and D) are correct
B) The reverse reaction is favored
Reaction 1 is A + B ⇌ C + H2O. It is endergonic with ΔG = +4.6 kcal/mol.
Reaction 2 is ATP + H2O ⇌ ADP + Pi . It is exergonic with ΔG = -7.3 kcal/mol.
What is the overall free energy for the following coupled reaction A + B + ATP ⇌ ADP + Pi + C?
A) 0 kcal/mol
B) -2.7 kcal/mol
C) +2.7 kcal/mol
D) -11.9 kcal/mol
E) +11.9 kcal/mol
B) -2.7 kcal/mol
Succinate dehydrogenase is an enzyme that functions in the citric acid cycle to catalyze a reaction that converts succinate to fumarate. A molecule called malonate acts as an inhibitor of succinate dehydrogenase. The presence of malonate raises the Km for succinate but does not affect the Vmax of the reaction. Malonate ________
A) is a competitive inhibitor
B) is a non-competitive inhibitor
C) binds to the active site of the enzyme
D) binds to an allosteric site of the enzyme
E) Both A) and C) are correct
E) Both A) and C) are correct
Researchers analyzed a cell extract—a mixture of molecules isolated from cells—and studied a chemical reaction in which a carbohydrate was broken down into smaller molecules. When they added a protease to the cell extract, they discovered that the protease greatly inhibited the rate of the reaction. Based on this observation, you could conclude that the reaction is
A) Exergonic
B) Endergonic
C) Catalyzed by an enzyme
D) Catalyzed by a ribosome
E) Both B) and C) are true of this reaction
C) Catalyzed by an enzyme
A metabolic pathway consists of reaction that involve four enzymes. All four of these enzymes have similar affinities for their substrates (they have similar Km values). The Vmax values in nmol/min/mg enzyme for each enzyme is as follows: enzyme 1 = 77; enzyme 2 = 415; enzyme 3 = 21; enzyme 4 = 1278. Which of these enzymes would be the best target(s) for feedback inhibition?
A) Enzyme 1
B) Enzyme 2
C) Enzyme 3
D). Enzyme 4
E) Enzyme 1 and enzyme 4
C) Enzyme 3
The net products of glycolysis are
A) 6CO2, 4 ATP, and 2 NADH
B) 2 pyruvate, 2 ATP, and 2 NADH
C) 2 pyruvate, 4 ATP, and 2 NADH
D) 2 pyruvate, 2 GTP, and 2 CO2
E) 2 CO2, 2 ATP, and glucose
B) 2 pyruvate, 2 ATP, and 2 NADH
The ability to diagnose tumors using fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) is based on the phenomenon that most types of cancer cells exhibit higher levels of
A) glycolysis
B) pyruvate breakdown
C) Citric acid metabolism
D) oxidative phosphorylation
E) all of the above
A) glycolysis
Which organic molecule supplies a two-carbon group to start the citric acid cycle?
A) ATP
B) NADH
C) Acetyl CoA
D oxaloacetate
E) Both A) and B)
C) Acetyl CoA
The source of energy that directly drives the synthesis of ATP during oxidative phosphorylation is the
A) Oxidation of nADH
B) Oxidation of glucose
C) Oxidation of pyruvate
D) H+ electrochemical gradient
E) reduction of O2
D) H+ electrochemical gradient
When conditions in a muscle become anaerobic during strenuous exercise, why is it necessary to convert pyruvate to lactate?
A) to increase NADH and decrease NAD+
B) to decrease NADH and increase NAD+
C) to increase NADH and increase NAD+
D) to decrease NADH and decrease NAD+
E) to maintain the rate of oxidative phosphorylation
B) to decrease NADH and increase NAD+
Which of the following enzymes does not catalyze the removal of electrons from an organic molecule?
A) Isocitrate dehydrogenase
B) a-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase
C) succinyl-CoA synthetase
D) Succinate dehydrogenase
E) malate dehydrogenase
C) succinyl-CoA synthetase
In the experiment conducted by Yoshida and Kinosita regarding the rotation of ATP synthase, what was actually observed to be spinning?
A) The y(gamma) subunit that extends upward through the ring of the a (alpha) and B (beta) subunits
B) the ring of a and B subunits
C) the ring of c subunits that are found in the inner mitochondrial membrane
D) A fluorescently labeled actin filament
E) Both A) and B)
D) A fluorescently labeled actin filament
In the experiment of Racker and Stoeckenius, bacteriorhodopsin was oriented in such a way that it pumped H+ into a vesicle. Each vesicle actually contained many molecules of bacteriorhodopsin. How would the results of the experiment have been affected if 50% of the bacteriorhodopsin molecules pumped H+ into the vesicle and 50% pumped H+ out of the vesicles?
A) The same amount of ATP would be made in the presence of light, and no ATP would be made in the dark
B) More ATP would be made in the presence of light, and no ATP would be made in the dark
C) No ATP would be made in the presence of light, and no ATP would be made in the dark
D) No ATP would be made in the presence of light, but some ATP would be made in the dark
E) Some ATP would be made in the presence of light, and some ATP would be made in the dark
C) No ATP would be made in the presence of light, and no ATP would be made in the dark
An insecticide called rotenone inhibits NADH dehydrogenase, which is evolved in the first step of the electron transport chain (ETC). Rotenone blocks the ability of NADH dehydrogenase to accept electrons from NADH and thereby inhibits ATP synthesis. What is the mechanism by which rotenone inhibits ATP synthesis?
A) Rotenone prevents the synthesis of O2
B) Rotenone inhibits the formation of an H+ electrochemical gradient
C) Rotenone directly inhibits the functioning of ATP synthase
D) Rotenone prevents FADH2 from donating electrons to the ETC
E) Rotenone prevents the reduction of NAD+ to NADH
B) Rotenone inhibits the formation of an H+ electrochemical gradient
Certain drugs act as ionophores that cause the mitochondrial membrane to be highly permeable to H+. How would such drugs affect oxidative phosphorylation?
A) Movement of electrons down the ETC would be inhibited
B) ATP synthesis would be inhibited
C) ATP synthesis would be unaffected
D) ATP synthesis would be stimulated
E) Both A) and B) are correct
B) ATP synthesis would be inhibited
IN PSII, P680 differs from the pigment molecules of the light-harvesting complex in that it...
A) is a carotenoid
B) absorbs light energy and transfers that energy to other molecules without the transfer of electrons
C) Transfers an excited electron to the primary electron acceptor
D) transfers an electron to O2
E) acts like ATP synthase to produce ATP
C) Transfers an excited electron to the primary electron acceptor
During linear electron flow, the high-energy electron from P680
A) eventually moves to NADP+
B) becomes incorporated into water molecules
C) is pumped into the thylakoid space to drive ATP production
D) provides the energy necessary to split water molecules
E) falls back to the low-energy state in photosystem II
A) eventually moves to NADP+
The NADPH produced during light reactions is used during
A) the carbon fixation phase, which corporates carbon dioxide into an organic molecule in the Calvin cycle
B) the reduction and carbohydrate production phase in the Calvin cycle
C) the regeneration of RuBP in the Calvin cycle
D) all of the above
E) A) and B) only
B) the reduction and carbohydrate production phase in the Calvin cycle
The majority of the G3P produced during the reduction and carbohydrate production phase is used to make
a) glucose
B) ATP
C) RuBP so that the cycle can continue
D) rubisco
E) all of the above
C) RuBP so that the cycle can continue
Photorespiration is minimized in C4 plants because
A) these plants separate the formation of a four-carbon molecule from the rest of the Calvin cycle in different cells
B) These plants carry out only anaerobic respiration
C) The enzyme PEP carboxylase functions to maintain high CO2 concentrations in the bundle-sheath cells
D) all of the above
E) A) and C) only
E) A) and C) only
O-18 is a rare and stable isotope of oxygen. Let's suppose you can expose plants to the following oxygen containing compounds in which the oxygen atoms are in the form of O-18. Which of these compounds would result in the production of O2 containing O-18?
A) CO2
B) glucose
C) H2O
D) CO
E) both A) and C)
C) H2O
Herbicides, such as atrazine, are thought to inhibit plant growth by blocking the ability of Qb to accept electrons from QA. Atrazine would be expected to inhibit the production of
A) NADPH
B) an H+ electrochemical gradient across the thylakoid membrane
C) ATP
D) all of the above
E) A) and C) only
D) all of the above
Paraquat is an herbicide that competes with Fd (Ferredoxin) for the electrons that are released from PSI after it is struck by light. In other words, paraquat can accept electrons from PSI. Paraquat would be expected to greatly inhibit the production of
A) NADPH
B) Oxygen
C) ATP
D) all of the above
E) A) and C) only
A) NADPH
The Calvin cycle is completed one time of reach molecule of carbon dioxide that enters the cycle. How many times must the Calvin cycle be completed to produce two glucose molecules?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 12
D) 24
E) 48
C) 12
As in the experiment by Calvin and coworkers, 14C-labeled carbon dioxide was added to a liquid medium containing algae. In which organic molecule did the C-14 label first appear?
A) 3-phosphoglycerate
B) glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate
C) ribulose bisphosphate
D) 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate
E) glucose
A) 3-phosphoglycerate
An agent that allows a cell to respond to changes in its environment is termed
A) A cell surface receptor
B) An intracellular receptor
C) A structural protein
D) a signal
E) A cellular response
D) a signal
When a cell secretes signaling molecules that bind to receptors on neighboring cells as well as on the cell itself, this is called ________ signaling
A) direct intercellular
B) contact-dependent
C) autocrine
D) paracrine
E) endocrine
C) autocrine
Which of the following is not an example of a cell surface receptor?
A) An enzyme-linked receptor
B) A G-protein-coupled receptor
C) a ligand-gated ion channel
D) the estrogen receptor
E) All of the above are cell surface receptors
D) the estrogen receptor
The EGF receptor functions as
A) A receptor tyrosine kinase
B) A G-protein-coupled receptor
C) a ligand-gated ion channel
D) a transcription factor
E) none of the above
A) A receptor tyrosine kinase
Apoptosis is the process of
A) cell migration
B) cell signaling
C) signal transduction
D) Signal amplification
E) programmed cell death
E) programmed cell death
After you eat a meal, a rise in glucose levels in the blood triggers the pancreas to release insulin into the bloodstream. The insulin then travels through the bloodstream and binds to receptors on the surface of adipose and skeletal muscle cells. Binding of insulin to cells' insulin receptors leads to a cellular response in which those cells are better able to take up glucose. This form of cell signaling is an example of
A) autocrine signaling
B) paracrine signaling
C) endocrine signaling
D) direct intercellular signaling
E) contact-dependent signaling
C) endocrine signaling
The binding of a substrate to an enzyme is analogous to the fitting of a key into a lock. Similarly, this analogy can be applied to a receptor. After a key is inserted in a keyhole, the turning of the key causes the lock to become unlocked. With regard to a receptor, the event of the lock becoming unlocked is analogous to
A) The cellular response that occurs after receptor activation
B) the binding of a signaling molecule to a receptor
C) the activation of a signal transduction pathway that occurs after receptor activation
D) The conformation change in the receptor after it binds to a signaling molecule
E) Both A) and C)
D) The conformation change in the receptor after it binds to a signaling molecule
A receptor has a Kd for its ligand equal to 50nM. This receptor
A) has a higher affinity for its ligand compared to a receptor with a Kd of 100nM
B) has a higher affinity for its ligand compared to a receptor with a Kd of 10nM
C) will be mostly bound by its ligand when the ligand concentration is 100nM
D) must be an intracellular receptor
E) Both A) and C) are correct
E) Both A) and C) are correct
Certain anticancer drugs are effective because they inhibit signal transduction pathways that are activated by growth factors. Which of the following would not be a good target for such a drug
A) An enzyme-linked receptor, such as the EGF receptor
B) A G-protein-coupled receptor
C) Ras
D) A protein kinase within a protein kinase cascade
E) A relay protein that activates Ras
B) A G-protein-coupled receptor
A mutation in the gene that codes the a subunit of a G protein causes the a subunit to bind more tightly to the b/y dimer. Predict the effects of this mutation of the ability of the G-protein-coupled receptor to activate the signal transduction pathway and to promote a cellular response.
A) This mutation would not affect that activation of the signal transduction pathway or the cellular repsonse
B) This mutation would enhance the activation of the signal transduction pathway and enhance the cellular response
C) This mutation would enhance the activation of the signal transduction pathway and inhibit the cellular response
D) This mutation would inhibit the activation of the signal transduction pathway and inhibit the cellular response
E) This mutation would inhibit the activation of the signal transduction pathway and enhance the cellular response
D) This mutation would inhibit the activation o fate signal transduction pathway and inhibit the cellular response
The function of the extracellular matrix (ECM) in animals is
A) to provide strength
B) to provide structural support
C) to organize cells and other body parts
D) cell signaling
E) All of the above
E) All of the above
The protein found in the ECM of animals that provides strength and resistance to tearing when stretched is
A) elastin
B) cellulose
C) collagen
D) laminin
E) fibronectin
C) collagen
The polysaccharide that forms the hard outer covering of many invertebrates is
A) collagen
B) chitin
C) chondroitin sulfate
D) pectin
E) cellulose
B) Chitin
The extension sequences found in procollagen polypeptides
A) cause procollagen to be synthesized into the ER lumen
B) cause procollagen to form a triple helix
C) prevent procollagen from forming large collagen fibers
D) cause procollagen to be secreted from the cell
E) do both B) and C)
E) do both B) and C)
The dilated state of plasmodesmata allows the passage of
A) Water
B) ions
C) small molecules
D) macromolecules and viruses
E) all of the above
E) all of the above
A strain of mice carries a mutation that decreases the amounts of glycosaminoglycans and proteoglycans that are found in the extracellular matrix in skin tissue. If you took samples of skin tissue from mice of this mutant strain and allayed their properties, what difference(s) would you expect to observe compared to the skin tissue samples from a normal strain of mice?
A) The tissue from the mutant mice would rip apart more easily; it would have less tensile strength
B) The ECM in the tissue from the mutant mice would not have as many connections to skin cells
C) The tissue from the mutant mice would be more easily compressed
D) All of the above would be observed
E) Only A) and B) would be observed
C) The tissue from the mutant mice would be more easily compressed
Let's suppose that a mutant form of procollagen contains the signal peptide that causes the polypeptide to be synthesized into the ER lumen, but it lacks the extension sequences. What would you predict to be the effects of this mutation on the synthesis, secretion, and/or assembly of collagen?
A) The mutant procollagen would behave normally; collagen fibers would assemble extracellularly
B) The mutant pro collagen would enter the ER lumen but it could not assemble into a collagen protein with three subunits and cold not assemble into collagen fibers
C) The mutant pro collagen would enter the ER lumen; collagen proteins with three subunits and collagen fibers would assemble in the ER lumen and then be secreted
D) The mutant pro collagen would enter the ER lumen; collagen proteins with three subunits and collagen fibers would assemble in the ER lumen by the fibers would be too large to be secreted.
B) The mutant pro collagen would enter the ER lumen but it could not assemble into a collagen protein with three subunits and cold not assemble into collagen fibers
the gap junctions of animal cells differ from the plasmodesmata of plant cells in that
A) gap junction serve as communicating junctions and plasmodesmata serve as anchoring junctions
B) gap junction prevent extracellular material from moving between adjacent cells but plasmodesmata do not
C) gap junction allow direct exchange of cellular material between cells but plasmodesmata cannot allow that type of exchange
D) Gap junctions are formed by specialized proteins that form channels through the membrane of adjacent cells and plasmodesmata are formed by connecting the plasma membranes of adjacent cells
E) All of the above are correct
D) Gap junctions are formed by specialized proteins that form channels through the membrane of adjacent cells and plasmodesmata are formed by connecting the plasma membranes of adjacent cells
Some mutations that promote cancer exert their effects by enhancing metastasis, which is the movement of cells from their proper location to other regions of the body. For example, during metastasis, lung tumor cells may leave the lung and travel to other parts of the body via the bloodstream. Which of the following type(s) of mutation would you predict to promote metastasis?
A) A mutation that causes the over expression of cadherin
B) A mutation that inactivates cadherin
C) A mutation that causes the over expression of integrin
D) A mutation that inactivates integrin
E) Both B) and D)
E) Both B) and D)
Which of the following is not a correct statement comparing plant tissues and animal tissues?
A) Nervous tissue of animals plays the same role as vascular tissue in plants
B) The dermal tissue of plants is similar to epithelial tissue of animals in that both provide a covering for the organism
C) The epithelial tissue of animals and the dermal tissue of plants have special characteristics that limit the movement of material between cell layers
D) The ground tissue of plants and the connective tissue of animals provide structural support for the organism
E) The ground tissue of plants and the connective tissue of animal have large amounts of extracellular material (that is, thick cell walls in plants and large amounts of ECM in animals).
A) Nervous tissue of animals plays the same role as vascular tissue in plants
what component(s) of a nucleotide is (are) always different when comparing nucleotides in a DNA strand to those in an RNA strand?
A) Phosphate group
B) pentose sugar
C) base
D) both B) and C)
E) A), B), and C)
B) pentose sugar
Which of the following statements about the process of DNA replication is true?
A) New DNA molecules are composed of two completely new strands
B) New DNA molecules are composed of one strand form the old molecule and one new stand
C) New DNA molecules are composed of strands that are a mixture of sections from the old molecule and section that are new
D) None of the above is correct
B) New DNA molecules are composed of one strand form the old molecule and one new stand
The difference in the synthesis of the leading and lagging strands is the result of which of the following?
A) DNA polymerase replicates only the leading strand
B) The two template strands are antiparallel, and DNA polymerase makes DNA only in the 5' to 3' direction
C) The lagging strand is the result of DNA breakage due to UV light
D) the cell does not contain enough nucleotides to make two complete strands
B) The two template strands are antiparallel, and DNA polymerase makes DNA only in the 5' to 3' direction
The protein that separates DNA strands at the replication fork is
A) DNA polymerase
B) DNA ligase
C) DNA topoisomerase
D) DNA helicase
E) DNA primase
D) DNA helicase
Which of the following statements about euchromatin is false?
A) It is generally located closer to the center of the cell nucleus than heterochromatin is
B) It carries genes that can be transcribed
C) It is more compact than heterochromatin
D) It contains topologically associated domains (TADs)
E) All of the above are true
C) It is more compact than heterochromatin
You have analyzed that base composition of the genetic material in a virus and found the following; 32% adenine, 17% thymine, 18% guanine, and 33% cytosine. From this analysis, which of the following is the most likely structure of the viral genome?
A) single-stranded DNA
B) Double-stranded DNA
C) Single-stranded RNA
D) Double-stranded RNA
E) Either A) or B)
A) single-stranded DNA
Which of the following equations would be appropriate when considering DNA base composition?
A) %A + %T = %G + %C
B). %A= %G
C) %A = %G = %T = %C
D) %A + %G = %T + %C
E) %T= %C
D) %A + %G = %T + %C
If the sequences of a segment of DNA strand is 5'-CGCAACTAC-3', what is the correct sequence for the opposite strand?
A) 5'-GCGTTGATG-3'
B) 3'-ATACCAGCA-5'
C) 5'-ATACCAGCA-3'
D) 3'-GCGTTGATG-5'
E) 5'-CGCAACTAC-3'
D) 3'-GCGTTGATG-5'
What would be the expected results for the Meselson and Stahl experiment after five generations (that is, five cell divisions)? Note: Generation zero has all heavy DNA, and all subsequent generations use light nitrogen to make new DNA strands
A) 1/8 heavy, 7/8 light
B) 1/16 heavy, 15/16 light
C) 1/32 heavy, 31/32 light
D) 1/16 half-heavy, 15/16 light
E) 1/32 half-heavy, 31/32 light
D) 1/16 half-heavy, 15/16 light
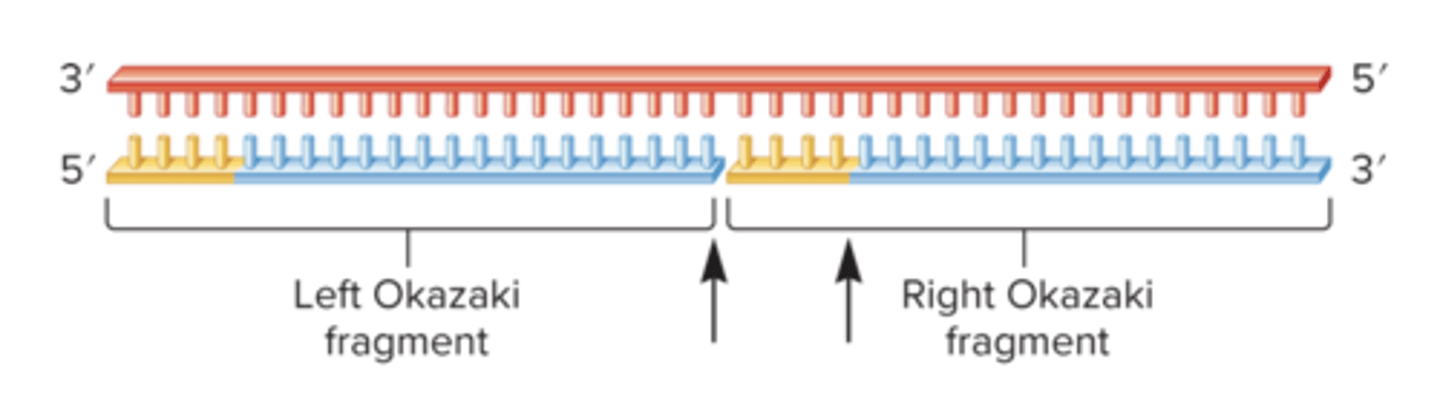
This drawing shows the synthesis of the lagging strand. The top strand is the template DNA
With regard to this drawing, which of the following statement is/are true?
A) DNA Polyermase I is responsible for synthesizing the blue DNA
B) DNA polymerase I removes the yellow primers
C) DNA Polymerase III removes the yellow primers
D) DNA polymerase III fills in the DNA after the primers are removed
E) Both A) and B) are true
B) DNA polymerase I removes the yellow primers