EXERCISE 3 | FREE FALL AND PROJECTILE MOTION
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
9 Terms
Displacement
the change in the initial and final position. (independent of path taken. Do not confuse with distance covered)
Velocity
defined as the change in position over change in time. The expression for the
average ***** is given by
Acceleration
is defined as the change in velocity over change in time.
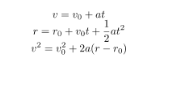
uniformly accelerated rectilinear motion (UARM) 3 types
Projectile
- any body that is given an initial velocity and then follows a path determined entirely by
the effects of gravitational acceleration.
trajectory
- the path of a projectile is called its *****.
Free falling bodies are
objects that are falling under the influence of the Earth’s
gravitational attraction
Motion along x-axis
can be derived from the fact that the acceleration along the
x-axis is zero. From the kinematic equations, we can derive the following
expression by setting .
Motion along y-axis
can be derived by setting , i.e., there is a constant
vertical acceleration along the y-axis