Geography coasts
1/82
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
83 Terms
Discordant coastline can also be referred to as?
atlantic coastlines
Concordant coastline can become what types of coastlines?
Haff and Dalmatian coasts
Example of a concordant coastline in UK
Lulworth cove on the Jurassic coast
Harder rock in Lulworth cove
Portland limestone
Softer rock in Lulworth cove
Wealden clay
How was the Dalmatian coast in Croatia formed
through tectonic forces and sea level rise
(that caused the submergence of land and the formation of a series of islands and coastal inlets.)
(folding of the plate caused anticlines and syclines (when it folds the land upwards and downwards, respectively —— to ~~~ the up hump is anticline and down dip is sycline)
on the adriatic sea
from the collision of the African and eurasian plates 50 million years ago
where is a haff coastline?
southern baltic coast
deposition produces unconsolidated (loosely arranged not cemented together like sand etc) geological structures parallel to the coastline
Nerman Haff - from Russia to Lithuania
(just a spit turning into a bar on a large scale really)
what type of coastline is the Jurassic coast?
East = discordant
south = concordant
Name coastal erosion processes
Hydraulic action
Abrasion
Attrition
Corrasion
Name the transportational processes
Traction (rolling rocks along the bottom)
Saltation (skipping rocks along bottom)
Suspension
Solution
strata
layers of rock also known as beds
bedding planes
horizontal cracks/lines between the different strata
(surface that separates one strata and another)
created by the pauses in rock formation
joints
vertical cracks in the rock caused by tectonic movement or contraction

Folds
the result of pressure during tectonic movement causing the rock strata to fold

Faults
the result of stress or pressure on the rock causing to fracture


Dip
The angle of the rock strata
Sub-aerial processes
weathering
mechanical (physical)
chemical
biological
mass movement
sliding (mudslide or landslide)
slumping
rockfall
Mechanical (physical) weathering examples
Thermal expansion(heating and cooling of the rock in general)
frost weathering/wedging (water seeps into cracks then expands when it turns into ice over night)
Salt weathering. (salt water gets in rock, water evaporates leaving salt crystals behind (accumulates adding more pressure))
exfoliation (curved plates of rock are stripped from rock below)

By how much does water expand when frozen/turned to ice?
by 10%
Chemical weathering
bodily fluids from animals (feces and urine)
solution/carbonation (slightly acidic carbonic rain it reacts with the calcium carbonate - affects rocks like limestone and chalk)
Oxidation (when rocks are broken down by oxygen and water.)
Hydrolisis (chemical breakdown of a substance when combined with water)
Biological weathering examples
animals burrowing in the ground
Plant roots weakening the rock
humans eroding it by walking all over it
mass movement
when rocks and loose material shift down slopes. This happens when gravity overcomes the force supporting the material.
Where permeable rock over lies impermeable rock, the permeable rock is vulnerable to mass movement because the additional weight and lubrication the water creates leads to instability
Difference between sliding, slumping and rockfall
Slides - rock moves in a straight line
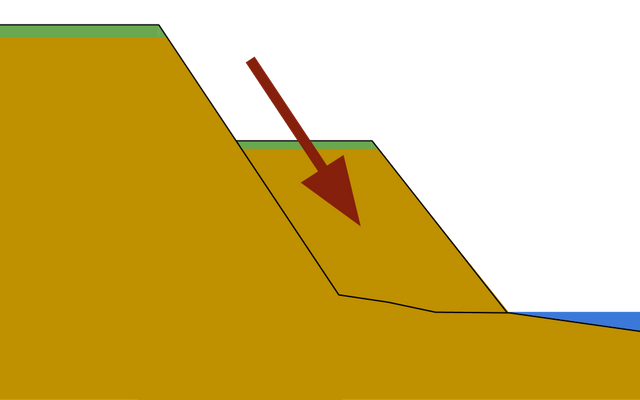
Slumps are when material moves down a slope with a rotation. (cliff gets saturated with water and base is eroding (maybe wave cut notch)and slumps
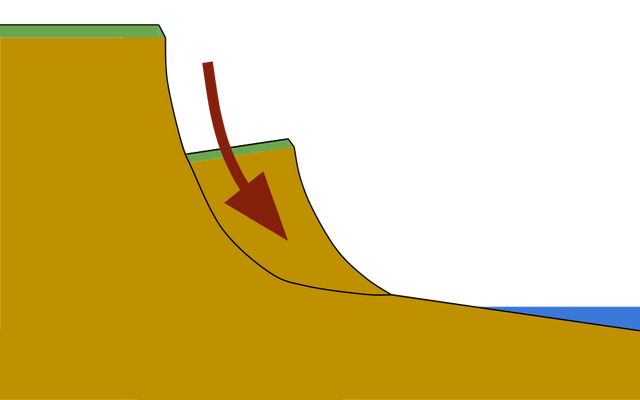

Rock falls are when material breaks apart because of erosion and weathering and then rolls down a slope.
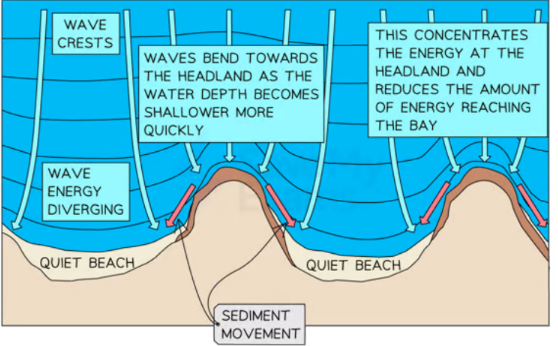
Wave refraction and how it affects the coastline
waves bend as they hit the coastline at an angle, causing uneven distribution of energy and significantly influencing coastal shaping through erosion and deposition
How can mineral composition affect erosion?
Some minerals are more reactive than others which affects the rate of chemical weathering
Examples:
Quartz (inert) not reactive so chemical erosion is slower
Calcite is very reactive so erodes much quicker
How are sedimentary rocks formed?
formed from compaction and cementation of sediment called lithification
Examples of sedimentary rock
shales, sandstone and limestone
Properties of sedimentary rocks
erode and weather more rapidly
form in layers
have weak bedding planes
they are clastic
meaning they are made of clasts (sediment particles)
heavily jointed
often have many bedding planes and fractures
How are metamorphic rocks formed?
Sedimentary and igneous rocks are altered through heat and pressure but do not melt in the process
Examples of metamorphic rocks
slate and marble
Properties of metamorphic rocks
crystalline structure
often folded and faulted
more resistant the sedimentary
crystals have parallel arrangement (foliation) which means they are weaker than igneous
How are igneous rocks formed
molten rock from volcanoes cools and hardens
Examples of igneous rocks
granite and basalt
properties of igneous rocks
most resistant
can be categorized into 2 types
intrusive - form within the ground, cool slowly and have large course crystals
extrusive - form on the earths surface, cools quickly, forms smaller crystals
has interlocking crystals
making it harder than metamorphic
fewer joints and weaknesses than other rocks
what is differential erosion?
changing/differing rates of erosion along a coastline
the whole coastline doesn’t erode at the same rate
headlands and bays are an example
bay erodes quicker than the headland
How can differential erosion affect coasts lines?
leads to headlands and bays on discordant coastlines
alternating strata can create a cliff profile where they more resistant rock juts out
alternating permeability
permeable is on the top can be at risk of mass movement because of added weight and lubrication
role of vegetation in coastal stability
plant roots bind sand/soil together reducing the impact of erosion
reduces wind speeds (which reduces erosion)
dead plant life left on sand can eventually lead to the formation of soil
why is vegetation often sparse in coastal environments?
saline water
evaporation of water causes increase in salinity
high wind speeds
lack of shade
lack of nutrients
“free draining sediment” - water is not retained
what are pioneer species?
the first plants to grow in the harsh coastal conditions, paving the way for other plants which are less able to survive in these conditions
help stabilize sediment
add organic matter
increase shade
trap more sediment
what are common pioneer species?
marram grass, sea rocket, and glassworts
What is dynamic equilibrium in coasts
balance between inputs and outputs of energy and material
also be thought of as longer term changes such as sea level - affects the balances
you could factor in more local changes such as low and high tide, weather conditions vary wave energy etc
rate of sea level rise according to NASA and satellite technology
3.4 mm a year
How does dip of strata affect erosion?
Horizontal -
near perfect vertical cliff profile
notches reflecting weathering
small scale mass movement of strata that are jointed or more easily eroded
High angle seaward dip \\~
sloping low angled profile
vulnerable to rock slides
Low angle seaward dip |\~
steep profile
may create overhanging rock
frequent small scale mass movement
major cliff collapse when overhanging is unsustainable from undercutting
landward dip
steep profile
gravity pulls loosened blocks into place
very stable
few rockfalls
Fancy name for plant succession in a sandy environment
psammosere
Fancy words to describe plants that colonize sand dunes
xerophytic (can withstand dry/arid and sandy conditions)
halophytic (can withstand high salinity)
Maximum height of a embryo dune
1m
fore dunes
embryo dunes in front of it protect from winds
allows other species to grow like marram grass
the grass then stabilizes the dune with its root system
the organic matter from the plants make it more hospitable for future plants
micro climate forms in dune slack (dip between dunes)
“ small-scale variation in weather conditions, like temperature or wind”
Maximum height for fore dunes
5m
yellow dunes
initially yellow (sand) but slowly darken as organic material is added to soil
marram still dominates vegetation but more delicate flowers and bugs can be found in the dune slacks around it
20% of the dune is exposed
in earlier stages 80% of it is exposed so significant difference in coverage
Maximum height of a yellow dune
8m
grey dunes
more stable
good range of biodiversity
only 10% of sand exposed
soil acidity increases (good thing as salt is alkaline) and water content due to humus (type of good soil from decomposed organisms) being added
shrubs and bushes appear eg gorse
Height of grey dune
8-10m
mature dunes
oldest and most stable
several hundred meters from the shoreline
soil can support a variety of flora eg oak trees
climax vegetation and climax community stage
the final, relatively stable stage of ecological succession in a particular environment
fancy word for succession in salt
halosere
what is succession?
the process by which the mix of species and habitat in an area changes over time
why do salt marshes often develop by estuarine areas
steady supply of sediment from the river
shelter from strong waves
what happens when salt water and fresh water in estuarine environments mix
causes flocculation where clay particles stick together
these clay particles then sink causing sediment to build up
Salt marsh succession
sediment builds up and is covered less and less by the tide at a time
this allows other plants such as cord grass to colonise
the height of sediment increases until it is only covered by the highest tides
more plants colonize such as
sea lavender
sea thrift
saline levels decrease allowing more and different plants to colonise
this continues until the climax community is achieved
EXAMPLE - Dawlish warren
what happens in estuarine areas when algae colonises the sediment
binds sediment together
increases organic matter
traps more sediment
what is a climax community
the final, stable stage of ecological succession in a particular area, reached when the ecosystem has reached its full potential in terms of species diversity and complexity
what is the main source of energy on coasts
waves
(friction between wind and surface of water transfers energy from the wind to the water)
why does wind occur?
rotation of the earth
differences in atmospheric pressure (when different parcels of air are heated by the sun)
factors that affect how much energy a wave has
Fetch
the distance of open water the wind blows over
Strength
How forceful the wind is
determined by the pressure difference in the air
Duration
how long the wind has been blowing
wave height
height from peak to trough
wave length
distance from crest to crest
wave frequency
number of waves which pass a specific point over a given time
what is beach morphology
the geological structure, shape or form of a feature
what % of the population live within 100km of the coast? (about 2.5 billion people)
40%
How do waves affect beach morphology?
steeper profile in the summer
because there are more constructive waves
gentler in winter
destructive waves more often so even out the profile
storm berms may appear in the winter
destructive storm waves carry larger sediment further up the beach than normal
Winter beaches may have more variation in sizes of sediment
what is terminal groyne syndrome
Beyond the last groyne the beach is starved of sediment so is more vulnerable to erosion.
Holderness coast
soft boulder clay (deposited 18,000 years ago) is one of the fastest eroding coastlines in europe
2m of erosion a year!
23 towns/villages have already been lost
61km from Flamborough to spurn point
strong prevailing winds
narrow beaches offer little protection from strong destructive waves
Yorkshire - east england
Management
overall - do nothing approach/ managed retreat
sea defences can further erode the coast further down
Terminal groyne syndrome - groynes are trapping sediment and leading areas down drift deprived of sediment eg Hornsea is depriving Mappleton of sediment and Mappleton is depriving Great Cowden of sediment with their groynes leading to increased erosion
what is lithology
study of properties of rock
what is geology
study of how rocks are arranged
Longshore drift
main process of deposition and transportation along the coast
influenced by prevailing wind making waves approach at an angle
backwash carries sediment down the beach at a 90 degree angle T
Currents
surface currents are formed mainly by wind
deep water currents are caused in differences in densities between hot and cold water (also called thermohaline circulation)
salinity differences as well
Happisburgh
North Norfolk
1,400 residents
600 properties
sands and gravels and laminated silts and clays. (softer)
average rate of erosion 1.7m a year
groynes in 1959 and rock armor throughout the years
2002 4,000 tonnes armor
2007 1000 tonnes more
then In 2015 9000 tonnes of rock armor were re-aligned
Problem with rock armor is its susceptible to mass movement
1996 managed retreat was chosen
it would cost £15 million to protect Happisburgh but it is not worth the land its protecting
would have an impact on the wider coastal management plan.
Happisburgh would end up as a promontory (headland), blocking longshore drift and causing further erosion downdrift.
council was given £3 million to buy 'unsellable' houses near cliffs at 40% price to create a buffer zone, relocate public toilets and emergency rock armor
Locals Not happy at all created a group in 1998 called the "Coastal Concern Action Group"
Why does Happisburgh and Holderness have such strong destructive waves?
The north sea is narrowing closer to the English channel so there is lots of energy in such a small corner, more swell, as it turns from north sea to the Atlantic
long fetch
Bangladesh flood risk
convergence of three major rivers
50% of the country has an elevation of 10m or less above sea level
20 million people live less than 1 m above sea level
Cyclones regularly cause storm surges
monsoon rains increase amount of flood water
bay of bengal there are hundreds of small islands made from unconsolidated material
highly unstable and susceptible to flooding
8,000 Km³ will be lost if sea level rises by 0.3 m from its current level
more at risk as are removing mangrove forests for farmland
40% of all recorded storm surges have occurred in Bangladesh
shortages of rice and vegetables causing malnutrition
Farmland has been contaminated with salt water
human interference mangroves
The Sundarbans Reserve Forest (SRF) - largest mangrove forest in the world
Natural coastal defence
They are now at risk of disappearing entirely within the next 100 years
pond shrimp aquaculture, one of the main causes of mangrove loss
inked to as much as 38% of global mangrove deforestation
mangrove forests can store up to 4 times the amount of carbon as tropical forests
71% of bangladesh’s mangrove forest coastline is now retreating by as mush as 200m a year
Globally ½ of the mangrove trees have been lost since the mid twentieth century
Name of the largest mangrove forest
The Sundarbans Reserve Forest (SRF)
Chittagong Bangladesh management
2012 created “ Coastal Climate Resilient Infrastructure Project”
make coastal areas more resilient
funding from asian development bank
US$154.1 million
aims to help people, economy and environment (multi-pronged approach)
Locally organised and run projects, ensuring greater local engagement
building coastal embankments lined with halophytic vegetation
raising the levels of the roads and making them more durable
upgrade 25 cyclone shelters and improve acces
upgrade 37 boat landing stages
designed to cope with flood water
fishermen’s boats and livelihoods aren’t too damaged by storms
education programs
improving water supply pipelines
creating sewage and sanitation networks that are protected from floodwater
Erosion bangladesh coastline
Bangladesh average erosion 17-22 meters per year some areas its up to 120m a year!