NVCC ECO 202 Midterm
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
80 Terms
The basic difference between macroeconomics and microeconomics is that:
microeconomics is concerned with the trees (individual markets) while macroeconomics is concerned with the forest (aggregate markets)
macroeconomics is concerned with generalization while microeconomics is concerned with specialization
macroeconomics is concerned with groups of individuals while microeconomics is concerned
with single countries
microeconomics looks at the forest (aggregate markets) while macroeconomics looks at the
trees (individual markets)
microeconomics is concerned with the trees (individual markets) while macroeconomics is concerned with the forest (aggregate markets)
Specialization:
leads to greater self-sufficiency.
is always the result of an inefficient use of resources
can lead to an increase in overall production.
allows workers to develop skills by working on a large number of tasks
can lead to an increase in overall production
In a _______________________, most economic decisions about what to produce, how to produce it, and for whom to produce it are made by buyers and sellers.
market-oriented economy
macroeconomy
microeconomy
command economy
market-oriented economy
The circular flow diagram of economic activity is a model of the:
role of unions and government in the economy. flow of goods, services, and payments between households and firms.
influence of government on business behavior.
interaction among taxes, prices, and profits.
flow of goods, services, and payments between households and firms.
Which of the following best describes a fiscal policy tool?
financial capital markets
household spending
bank lending
government spending
government spending
Which of the following best describes a monetary policy tool?
household savings
taxes
interest rates
government spending
interest rates
In a command economy, the __________ either makes most economic decisions
itself or at least strongly influences how the decisions are made.
market
firm
business sector
government
government
In the ____________, households work and receive payment from firms.
savings market
financial investment market
financial capital market
labor market
labor market
Which of the following is most likely a topic of discussion in macroeconomics?
a decrease in the unemployment rate
an increase in the wage rate paid to automobile workers
an increase in the price of a hamburger
a decrease in the production of DVD players by a consumer electronics company
a decrease in the unemployment rate
Which of the following statements most likely lies within the realm of microeconomics?
A rapid acceleration of the supply of money may create inflation.
Unemployment rises during a recession and falls during an expansion.
An increase in government spending will increase the aggregate demand for goods and
services in the economy.
An increase in labor costs will increase the additional cost of producing another bus.
An increase in labor costs will increase the additional cost of producing another bus.
Philosophers draw a distinction between positive statements, which describe the world as it is, and ___________________s, which describe how the world should be.
budget constraint
normative statement
trade-off
opportunity cost
normative statement
Attending college is a case where the ________________ exceeds the monetary cost.
marginal analysis
budget constraint
marginal utility
opportunity cost
opportunity cost
As depicted in _________________________________, it is necessary to give up some of one good to gain more of the other good.
scarcity
utility
allocative efficiency
the production possibilities frontier
the production possibilities frontier
Why is there scarcity?
Because human wants are limited.
Because theory dictates it.
Because our unlimited wants exceed our limited resources.
Because the opportunity set determines this.
Because our unlimited wants exceed our limited resources.
"If I didn't have class tonight, I would save the $4 campus parking fee and spend
four hours at work where I earn $10 per hour." The opportunity cost of attending
class this evening is:
$4
$40
$0
$44
$44
As a person receives more of a good, the _______________ from each additional unit of the good declines.
marginal utility
sunk costs
budget constraint
utility
marginal utility
Which of the following would most likely shift the production possibilities curve
inward?
technological progress
a decrease in the average number of hours worked per week as the labor force chooses to
enjoy more leisure time
an increase in the production of capital goods
an increase in the number of hours factories are in use
a decrease in the average number of hours worked per week as the labor force chooses to
Economists refer to this pattern, the ___________________________________,
which means that as a person receives more of a good, the additional or marginal
utility from each additional unit of the good declines.
law of diminishing marginal utility
law of increasing marginal utility
law of trade-offs
production possibilities frontier
law of diminishing marginal utility
Philosophers draw a distinction between ___________________, which describe the world as it is, and normative statements, which describe how the world should be.
utilitarianism
negative statements
tradeoffs
positive statements
positive statements
The model that economists use for illustrating the process of individual choice in a
situation of scarcity is the _________________, sometimes also called the
opportunity set, a diagram that shows what choices are possible.
income cap
consumption set
original budget
budget constraint
budget constraint
The slope of the production possibility frontier is determined by the _________ of expanding production of one good, measured by how much of the other good would be lost.
relative advantage
specialization
absolute advantage
opportunity cost
opportunity cost
When one nation can produce a product at lower cost relative to another nation, it is said to have a(n)____________________in producing that product.
absolute advantage
relative advantage
production efficiency
economy of scale
relative advantage/comparative advantage
Which of the following is true?
A nation cannot have a comparative advantage in the production of every good.
A nation cannot have an absolute advantage in the production of every good.
A nation can have a comparative advantage in the production of a good only if it also has an
absolute advantage.
A nation can have a comparative advantage in the production of every good, but not an absolute advantage.
A nation cannot have an comparative advantage in the production of every good.
The underlying reason why trade benefits both sides of a trading arrangement is
rooted in the concept of
specialization
opportunity cost
maximum production
absolute advantage
opportunity cost
According to international trade theory, a country should:
import goods in which it has an absolute advantage
import goods in which it has an absolute disadvantage
import goods in which it has a comparative disadvantage
export goods in which it has an absolute advantage
import goods in which it has a comparative disadvantage
Jethro has a(n) ____________________ in all aspects of camping: he is faster at
carrying a backpack, gathering firewood, paddling a canoe, setting up tents,
making a meal, and washing up.
absolute advantage
comparative advantage
relative advantage
opportunity cost
absolute advantage
Say that Alland can produce 32 units of food per person per year or 16 units of clothing per person per year, but Georgeland can produce 16 units of food per year or 8 units of clothing. Which of the following is true?
Alland has an absolute advantage, but not comparative advantage, in producing food
Georgeland has a comparative advantage, but not an absolute advantage, in producing
clothing
Georgeland has both a comparative and absolute advantage in producing clothing
Alland has a comparative advantage, but not an absolute advantage, in producing food
Alland has an absolute advantage, but not comparative advantage, in producing food
Intra-industry trade between similar trading partners allows the gains from
________________ that arise when firms and workers specialize in the production
of a certain product.
creating the value chain
learning and innovation
relative advantage
comparative advantage
learning and innovation
Trade allows each country to take advantage of ______________ in the other country.
economies of scale
specialization
worker productivity
lower opportunity costs
lower opportunity costs
Some nations that seek to produce all of their own needs face the problem that:
the opportunity cost of producing some of their own goods is lower than that of trading with others for them
they can deplete their natural resources as a result
some industries are too small to be efficient if restricted to their domestic markets alone
they will not be able to satisfy the wants of all of their citizens
some industries are too small to be efficient if restricted to their domestic markets alone
The downward slope of the demand curve again illustrates the pattern that as _____________ rises, ______________ decreases.
quantity supplied, quantity demanded
price, quantity supplied
price, quantity demanded
quantity demanded, price
price, quantity demanded
Any given demand or supply curve is based on the ceteris paribus assumption that _________________________.
what is true for the individual is not necessarily true for the whole
all else is held equal
everything is variable
no one knows which variables will change and which will remain constant
all else is held equal
When economists talk about supply, they are referring to a relationship between price received for each unit sold and the ________________
market price
demand schedule
demand curve
quantity supplied
quantity supplied
The demand schedule for a good:
indicates the quantity that people will buy at the prevailing price.
is determined primarily by the cost of producing the good.
indicates the quantities that suppliers will sell at various market prices.
indicates the quantities that will be purchased at alternative market prices.
indicates the quantity that people will buy at the prevailing price
When quantity demanded decreases in response to a change in price:
there is a movement up along the demand curve.
there is a movement down along the demand curve.
the demand curve shifts to the right.
the demand curve shifts to the left.
there is a movement down along the demand curve.
The _________ is the only price where quantity demanded is equal to quantity supplied.
equilibrium price
vertical axis intercept
market price
horizontal axis intercept
equilibrium
If new manufacturers enter the computer industry, then (ceteris paribus):
some established manufacturers must exit the industry.
the supply curve shifts to the left.
the demand curve shifts to the left.
the supply curve shifts to the right
the supply curve shifts to the right
If a firm faces _____________________, while the prices for the output the firm produces remain unchanged, a firm's profits will increase.
higher demand
lower costs of production
a shift in demand
equilibrium
lower costs of production
___________________ are enacted when discontented sellers, feeling that prices are too low, appeal to legislators to keep prices from falling.
Price ceilings
Price floors
Subsidies
Rent controls
Price floors
Price ceilings and price floors:
shift demand and supply curves and therefore have no effect on the rationing function of prices.
make the rationing function of free markets more efficient.
interfere with the rationing function of prices.
cause surpluses and shortages respectively.
make the rationing function of free markets more efficient.
The price elasticity of demand measures the:
responsiveness of price to a change in quantity demanded.
responsiveness of quantity demanded to a change in income.
responsiveness of quantity demanded to a change in quantity supplied.
responsiveness of quantity demanded to a change in price.
responsiveness of quantity demanded to a change in price.
Price elasticity of demand is defined as:
the slope of the demand curve divided by the price.
the percentage change in price divided by the percentage change in quantity demanded.
the slope of the demand curve.
the percentage change in quantity demanded divided by the percentage change in price.
the percentage change in quantity demanded divided by the percentage change in price.
Demand is said to be ___________ when the quantity demanded is very responsive to changes in price.
elastic
independent
inelastic
unit elastic
elastic
Demand is said to be _____________ when the quantity demanded is not very responsive to changes in price.
A. independent
B. inelastic
C. unit elastic
D. elastic
inelastic
Demand is said to be __________ when the quantity demanded changes at the same proportion as the price.
A. elastic
B. unit elastic
C. inelastic
D. independent
unit elastic
The elasticity of demand is defined as the percentage change in quantity demanded divided by the percentage change in __________.
A. quantity supplied
B. the slope of the demand curve
C. price
D. the slope in the supply curve
price
Billy Bob's Barber Shop knows that a 5 percent increase in the price of their haircuts results in a 15 percent decrease in the number of haircuts purchased. What is the elasticity of demand facing Billy Bob's Barber Shop?
A. 0.15
B. 3.0
C. 0.10
D. 0.05
3.0
If the demand curve is perfectly elastic, then an increase in supply will:
A. decrease the price but result in no change in the quantity exchanged.
B. increase the quantity exchanged but result in no change in the price.
C. increase the price but result in no change in the quantity exchanged.
D. increase both the price and the quantity exchanged.
increase the quantity exchanged but result in no change in the price.
13. A price cut will increase the total revenue a firm receives if the demand for its product is:
A. unit inelastic.
B. unit elastic.
C. inelastic.
D. elastic.
elastic
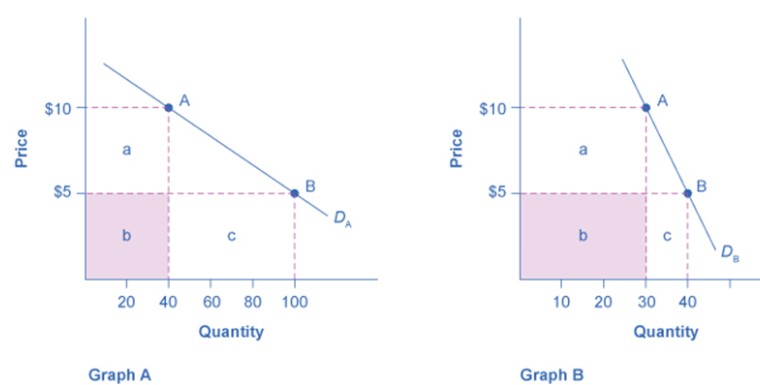
Refer to Figure 5-1. With reference to Graph A, at a price of $10, total revenue equals:
A. $1,000.
B. $500.
C. $400.
D. $200.
$400
The term _________________ refers to the additional utility provided by one additional unit of consumption.
Giffen utility
marginal utility
added utility
utility
marginal utility
The ________________ arises when a price changes because consumers have an incentive to consume less of the good with a relatively higher price and more of the good with a relatively lower price.
A. income effect
B. substitution effect
C. backward-bending supply curve
D. preferences effect
substitution effect
The term ___________________ is used to describe the common pattern whereby each marginal unit of a consumed good provides less of an addition to utility than the previous unit.
A. diminishing marginal utility
B. marginal utility pattern
C. marginal income utility
D. decreasing marginal utility
diminishing marginal utility
The term _____________ describes a situation where a ________________ causes a reduction in the buying power of income, even though actual income has not changed.
A. substitution effect; lower price
B. intertemporal budget; higher price
C. income effect; higher price
D. intertemporal budget; lower price
income effect; higher price
Marginal utility can:
A. be positive or negative, but not zero
B. decrease, but not become negative
C. be positive, negative, or zero
D. increase positively, but not negatively
be positive, negative, or zero
Jay and Jen are married with two children. They are preparing a household budget for the coming year. Based on statistical information for American households, approximately what portion of this family's annual consumption will most likely be budgeted for food and vehicle expenses?
A. one-fourth
B. one-third
C. one-quarter
D. two-third
one-third
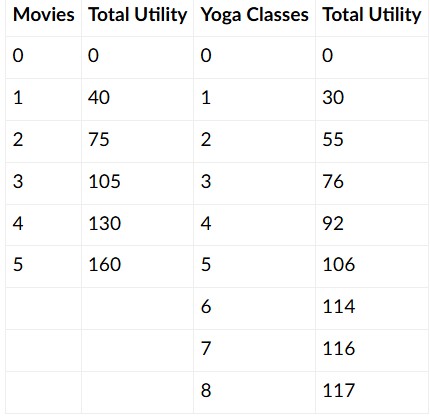
Kim has $24 per week in her entertainment budget. She splits her time between going to the movies and yoga classes. Each movie costs $8 while each yoga class costs $3. The total utility from each of these activities is set out in the table below. What is Kim's total utility maximizing point?
1 movie, 5 yoga classes
3 movies, 0 yoga classes
0 movies, 8 yoga classes
2 movies, 2 yoga classes
1 movie, 5 yoga classes
Which of the following is considered to be a tell-tale signal that the point with the highest total utility has been found?
A. the marginal utility per dollar is the same for both goods
B. the marginal utility per dollar is controlled by trade-offs
C. the quantities demanded change so total utility rises
D. the demand curves are flatter reducing quantity
the marginal utility per dollar is the same for both goods
For lunch, Maria eats only salads or vegetarian burgers. Her weekly food budget is $36. Each salad costs $6 and each vegetarian burger costs $3. When deciding how much of each good to buy, Maria knows that 2 salads and 4 vegetarian burgers will give her a utility of 8. Maria's utility-maximizing point is:
A. 6 salads, 1 vegetarian burger
B. 4 salads, 6 vegetarian burgers
C. 3 salads, 6 vegetarian burgers
D. 2 salads, 8 vegetarian burgers
3 salads, 6 vegetarian burgers
Substitution and income effects of a change in price of a good may be used to explain the:
A. direct relationship between price and quantity purchased.
B. inverse relationship between price and quantity demanded.
C. direct relationship between price and quantity supplied.
D. direct relationship between income and demand.
direct relationship between income and demand
A firm's ___________ consists of expenditures that must be made before production starts that typically, over the short run, _______________ regardless of the level of production.
fixed costs; are consistently changing,
variable costs; do not change,
fixed costs; do not change,
variable costs; are constantly changing,
fixed costs; do not change,
____________________________ occur when the marginal gain in output diminishes as each additional unit of input is added.
A. Diminishing variable returns
B. Diminishing average returns
C. Diminishing marginal returns
D. Diminishing marginal costs
Diminishing marginal returns
The term "constant returns to scale" describes a situation where
A. expanding all inputs does not change the average cost of production.
B. a larger-scale firm can produce at a lower cost than a smaller-scale firm.
C. expanding all inputs changes the average cost of production.
D. the quantity of output rises and the average cost of production falls.
expanding all inputs does not change the average cost of production.
______________ include all of the costs of production that increase with the quantity produced.
A. Fixed costs
B. Variable costs
C. Average costs
D. Average variable costs
Variable costs
If a firm is experiencing _____________________, then as the quantity of output rises, the average cost of production rises.
A. decreasing returns to scale
B. consent returns to scale
C. economies of scale
D. increasing returns to scale
decreasing returns to scale
I'MaPizzaCo. produces and sells specialty pizzas. Last year, it produced 8,000 mushroom, sausage and spinach pizzas and sold each one for $8. To produce these 8,000 specialty pizzas, the company incurred variable costs of $24,000 and a total cost of $40,000. I'MaPizzaCo's average fixed cost to produce 8,000 specialty pizzas was
A. $3.00
B. $2.00
C. $1.80
D. $1.60
$2.00
The marginal cost curve is generally ______________, because diminishing marginal returns implies that additional units are ________________________.
A. downward-sloping; more costly to produce
B. upward-sloping; more costly to produce
C. downward-sloping; less costly to produce
D. upward-sloping; less costly to produce
upward-sloping; more costly to produce
Whatever the firm's quantity of production, _____________ must exceed total costs if it is to earn a profit.
A. marginal costs
B. average costs
C. total revenue
D. variable costs
total revenue
In order to determine ____________, the firm's total costs must be divided by the quantity of its output.
A. diminishing marginal returns
B. fixed costs
C. variable cost
D. average cost
average cost
In microeconomics, the term ___________________ is synonymous with decreasing returns of scale.
A. monopoly
B. economies of scale
C. diminishing returns
D. diseconomies of scale
diseconomies of scale
The term _______________ refers to a firm operating in a perfectly competitive
market that must take the prevailing market price for its product.
trend setter
price taker
price setter
business entity
price taker
In economics, the term "shutdown point" refers to the point where the
A. marginal cost curve crosses the total revenue curve.
B. average variable cost curve crosses the total revenue curve.
C. average variable cost curve crosses the marginal cost curve.
D. marginal cost curve crosses the average variable cost curve
marginal cost curve crosses the average variable cost curve
It is said that in a perfectly competitive market, raising the price of a firm's product from the prevailing market price of $179.00 to $199.00, ____________________.
A. will likely cause the firm to reach its shutdown point immediately
B. will cause the firm to recover some of its opportunity costs
C. could likely result in a notable loss of sales to competitors
D. is a sure sign the firm is raising the given price in the market
could likely result in a notable loss of sales to competitors
In the _________, the perfectly competitive firm will seek out ________________________ .
A. long run; the quantity of output where profits are highest
B. short run; profits by ignoring the concept of total cost analysis
C. short run; the quantity of output where profits are highest
D. long run; methods to reduce production and shut down
short run; the quantity of output where profits are highest
In the ________, the perfectly competitive firm will react to profits by __________________________ .
A. short run; increasing quality of products
B. long run; tailoring their quality controls
C. short run; reducing its labor inputs
D. long run; increasing its production
long run; increasing its production
Firms operating in a market situation that creates ___________________, sell their product in a market with other firms who produce identical or extremely similar products.
A. a perfect monopoly
B. perfect competition
C. an oligopoly
D. a free-market
perfect competition
In the ________, the perfectly competitive firm will react to losses by __________________________ .
A. short run; reducing production or shutting down
B. long run; reducing production or shutting down
C. short run; increasing physical inputs
D. long run; increasing capital inputs
long run; reducing production or shutting down
In a free market economy, firms operating in a perfectly competitive industry are said to have only one major choice to make. Which of the following correctly sets out that choice?
A. what quantity to produce
B. what price to charge
C. what quantity of labor is needed
D. what quality to produce
what quantity to produce
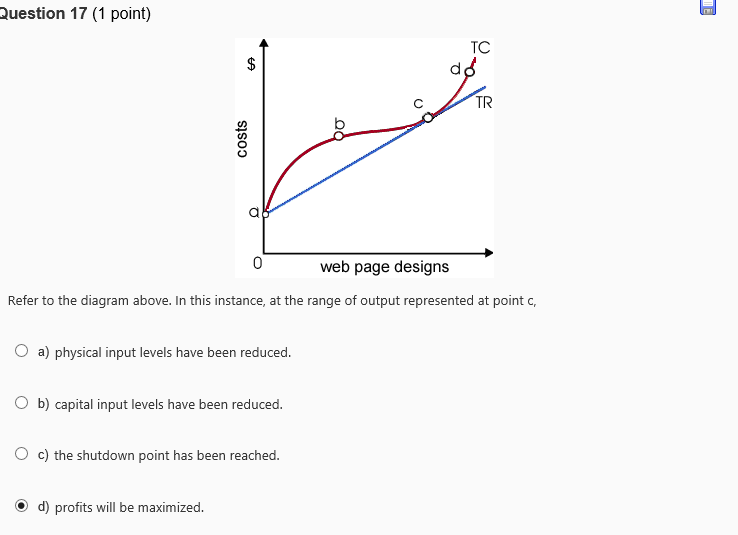
Refer to the diagram. In this instance, at the range of output represented at point c,
the shutdown point has been reached.
capital input levels have been reduced.
profits will be maximized.
physical input levels have been reduced.
profits will be maximized.
If a competitive firm experiences a shift in costs of production that decreases marginal costs at all levels of output,
A. expanding output levels at any given price will be profitable.
B. producing less at any market price will off-set marginal cost .
C. the firm's marginal cost curve will shift to the left.
D. the firm's demand curve will also shift to the left.
expanding output levels at any given price will be profitable.