3. Foodborne Illnesses: Gram negative pathogens
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
Salmonella
Part of entero bacteria
Genus: Salmonella
Two species: S. bongori and S. enterica
Subspecies: S. enterica subsp. enterica
Further subdivision into many serovars (which is not written in italic!!
e.g. Salmonella enterica ssp. enterica serovar Typhimurium
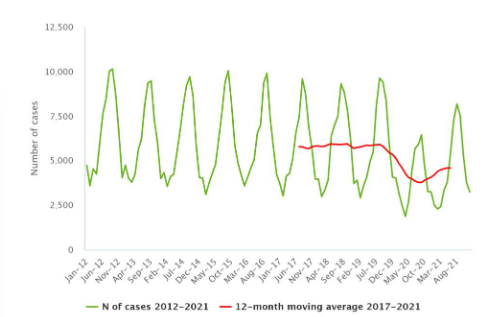
Seasonal trend for Salmonella cases
peak in summer, reason is not known
Average dip (red line) during covid, e.g. people did not go out to eat and larger focus on hygiene.
Characteristics of Salmonella
Gram negative, motile rod
Growth temperature: 5-47C
Awmin for growth: 0.93
Salmonella can survive for extended periods at even lower aw
Protection against gastric acid by food matrix
Symptoms of consuming Salmonella (Gastro-enteritis)
Symptoms:
Abdominal pain, nausea/vomting, diarrhoea
Incubation time: 8-72 hours
Duration: 3-7 days
D/R usually quite high, but sometimes low
Can even lead to arthritis
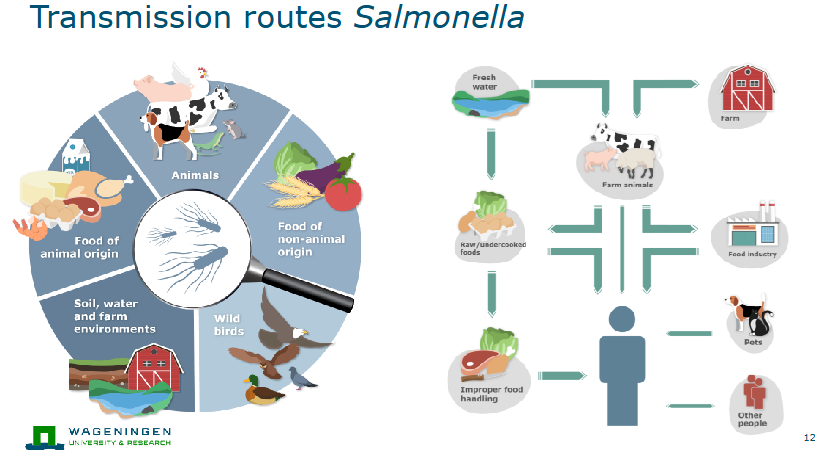
Transmisison routes Salmonella
Persistence of Salmonella
Salmonella can persist in food factories, e.g. as house flora on a machine that cuts pig carcasses
Salmonella can also persist in stables, in which production animals, such as broilers, are raised
Cleaning and disinfection does not necessarily solve the problem, darkling beetles can be a vector and bypass cleaning of broiler house
Preventative measures in supply chain
Prevention of infection at farm
Implement national control programmes
Hygiene measures, separate animals from outside
Salmonella-free feed and water
Vaccination
Limit spread of contamination
Compliance with microbiological criteria
Logistic slaughter
Hygiene design equipment
Good general hygiene in factory and retail
Proper heating and storage at reatail, catering, consumer’s
Characteristics of E. coli
Gram negative rod
Mesophile (8-45C)
Facultative anaerobe
Usually harmless inhabitant in intestines
Indicator-organism:
Hygiene production
Faecal contamination
Some types of E. coli can cause disease: e.g. E. coli O157:H7
Low D/R
No spores
Grows at low pH
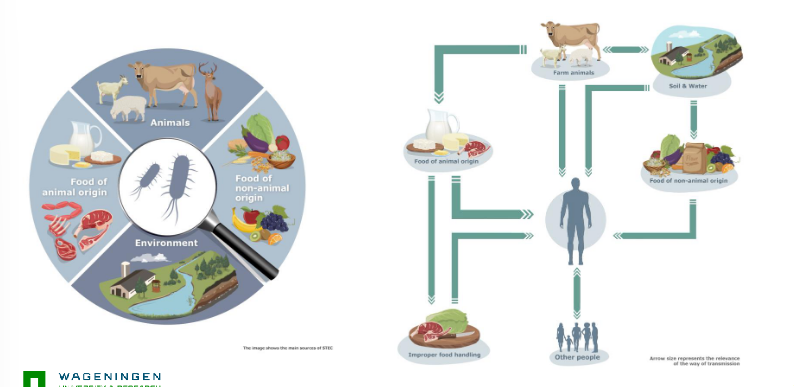
Transmission routes of E. coli
EHEC (E. coli O157:H7)
Toxin: produced in gut (shigatoxin)
Dose: 10-100 cells: low D/R
Symptom:
Bloody diarrhoea
Incubation time: 2-3 days (~21 days)
Complication in children and ederly: haemolytic uremic syndrome (HUS), leading cause acute renal failure
Hence this E. coli is studied a lot.
Hamburger disease

Prevention of E. coli

Characteristics Campylobacter
Gram negative, motile curved rod
Sometimes coccus (non-culturable, non-infective)
No spores
Thermotolerant types: C. jejuni, C. coli, C. lari
Growth temperature: 30-44 (Psychrotrophic, capable of growth at refrigeration temperatures down to 3)
Grows best with 3-5% oxygen (microaerophilic organism)
Sensitive to drying (chilling of meat), heating, some reduction below zero degrees (minimum pH for growth is 4.9)
Does not grow well in dry environments
Number 1 cause of bacterial foodborne infections in EU.
Symptoms of consuming Campylobacter
Diarrhoea, often belly cramps, fever and blood in faeces
Incubation time: 1-7 days (3d average)
Duration: up to 1 week
Low dose response (only 400 to 500 cells needed)
Sometimes sequela develop:
Reactive arthritis (joints)
Guillain Barre Syndrome (paralysis)
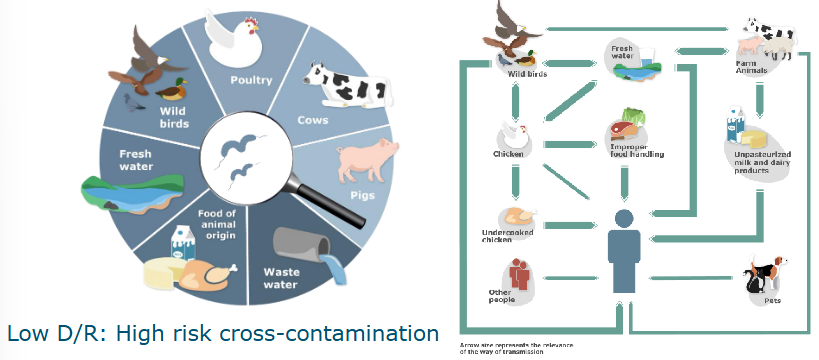
Transmission routes Campylobacter
Preventative measures for Campylobacter

Microbe found in rice
B. cereus d type, even when cooked can still be found in rice due to spores
Cl. perfringens
Can be found in spices and vegetables.
Where can you find norovirus?
Can be found in rice, spice, vegetables
E. coli in foods
Undercooked ground meat, raw milk, and fresh produce
Cattle are an important reservoir for O157:H7, contamination can occur during slaughter and processing.
Acidic foods can be dangerous too, E. coli can survive prolonged periods at low pH, especially under refrigeration.
In what foods is Salmonella found?
Foods of animal origin are the most frequently implicated, particularly poultry meat and eggs.
Eggs and egg products: especially raw or lightly cooked ones, were frequent vehicles in outbreaks
Poultry
Fresh produce
Campylobacter in foods
Common inhabitant of the gastrointestinal tract of warm-blooded animals, with poultry being the primary reservoir and most frequent source of human infection
Raw milk
Raw meat, raw vegetables, and water
E. coli ETEC
Common cause of travelers diarrhea & infant diarrhea
Symptom: watery diarrhea, dehydration and abdominal cramps
Produce heat labile and/or heat stable enterotoxins
E. coli (EIEC)
Causes dysentery-like illness
Symptoms: Resembles Shigella infections, includes fever, cramps, and watery to bloody diarrhea.
Invade and multiply within colonic enterocytes, leading to cell destruction
E. coli (EPEC)
Primarily causes infant diarrhea in developing countries, leading to watery diarrhea, vomiting, and fever
Adheres intimately to epithelial cells, causing “attaching and effacing” lesions that disrupt microvilli and absorption
When do most E. coli infections happen?
Summer, people eat more ground beef and harder to keep below at temperature of 7C
Disease caused by Salmonella (Enteric fever)
Caused by host-adapted serotypes which are more invasive
Typhoid fever has an incubation period of 3 to 56 days (usually 10-20 days)
Invasive Salmonella enter the intestinal lining, move through the lymphatic system to the mesenteric lymph nodes, multiply inside macrophages, and spread through the body via the bloodstream.
Symptoms: slow onset of fever, headache, abdominal tenderness, and constipation.
Mortality rate is around 10-20%
Which two groups of people appear particularly susceptible to Campylobacter infections?
Young children
Young adults
(Platy)Helminths
Flatworms
Nematodes
Roundworms
Worms associated with foods
Animal parasites: need animal host to develop - therefore worms are only found in meat products
Life cycle: egg, intermediate stage(s), mature worm
Classified according to shape adult worm:
Flatworms: Trematodes and Cestodes
Roundworms: Nematodes
Do not grow in foods
The four most important worms, their hosts and the food vehicles.
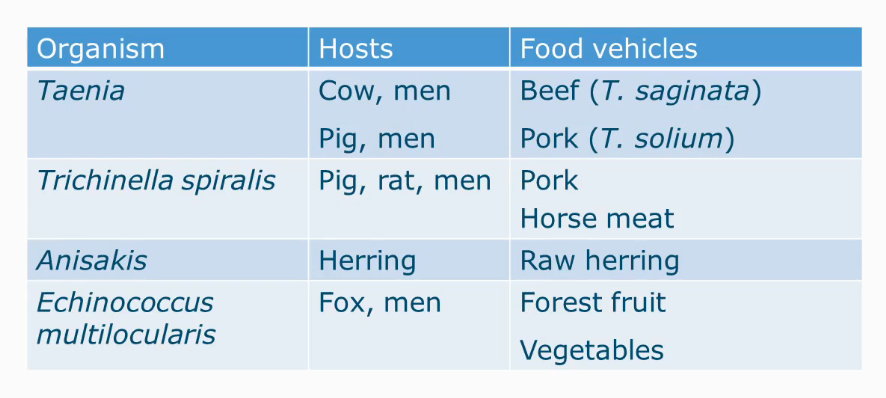
Transmission cycle Taenia solium
Pig tapeworm
Only in humans the larvae will mature, not in the food.
Similar cycle for T. safinata but instead it grows in beef.
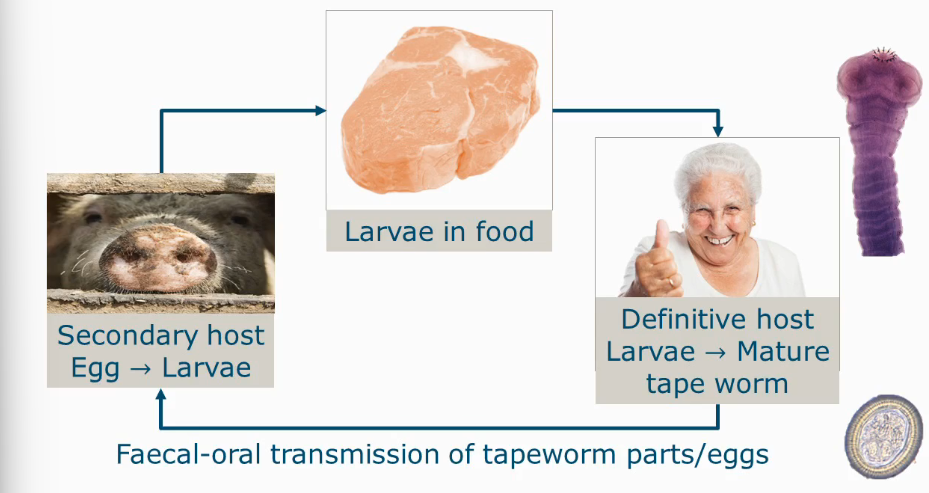
Human health effect Taenia
Mature tapeworm only develops in human hosts
4-12 m long (1000-2000 segments, proglottids)
Symptoms: asymptomatic, nausea, abdominal pain, weight loss, anemia
Effects more severe in young and immuno-compromised
Efficient drugs are available.
Transmission cycle Trichinella spiralis
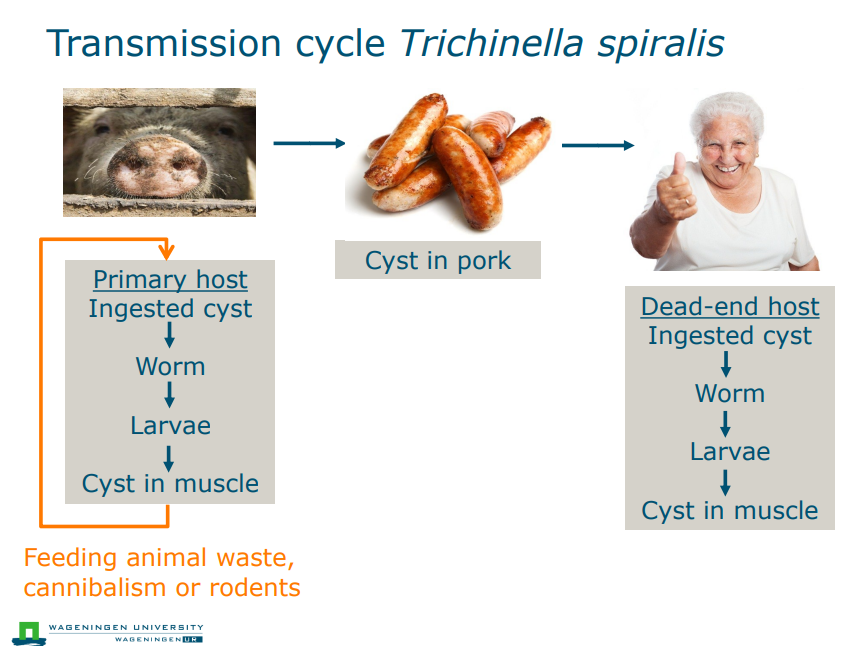
Trichinellosis
Roundworm
caused by consumption of Trichinella spiralis
Encysted larvae released in stomach
Larvae mature to adult worm (3-4 mm) in intestine
Female worm releases larvae
Larvae invading intestinal mucosa, causing symptoms
Incubation time: few days - month
Symptoms: abdominal pain, nausea, diarrhoea
Larvae invade and encyst in muscle tissue
Symptoms: muscle pain, fever
Efficacy of drugs uncertain
Contamination cycle of Echinococcus multilocularis
fox tapeworm
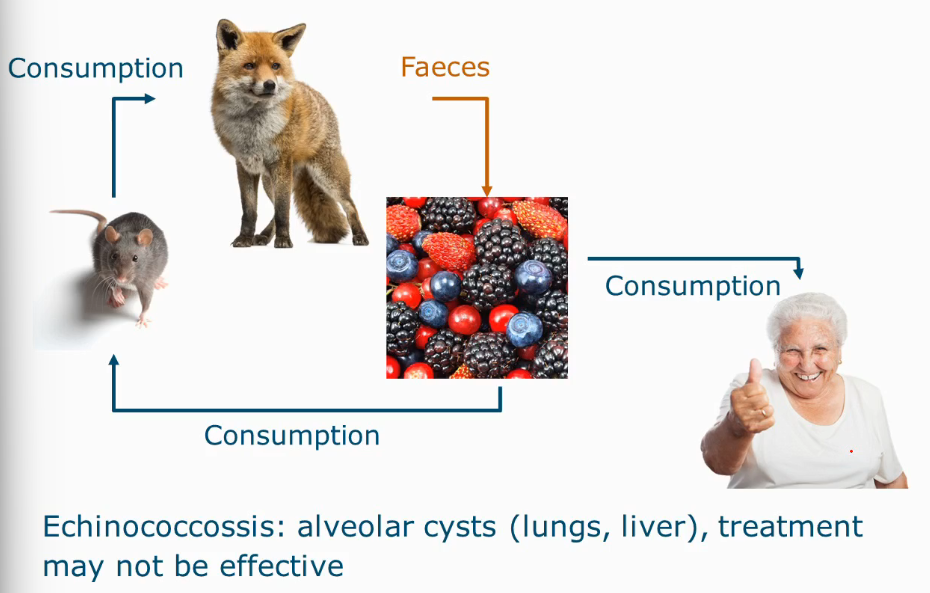
Echinococcossis
Disease caused by consumption of Echinococcus multilocularis
Which is a parasite found in foxes
Alveolar cysts (lungs, liver), treatment may not be effective.
Fish parasites
Anisakis: herring worm
Symtpoms: abdominal pain
Therefore all freshly caught fish, has to be frozen for 24h at -18C which kills the worms
This makes it safe to eat the fish raw.
Preventative measures against worms
Examination of slaughter animals before and after slaughter
Multiple spots of parasites → rejection
Local contamination → approval after treatment
Severe cold treatment of contaminated fish or meat, e.g. Taenia saginata, -18C, 10 days in calf meat
Educate consumers: adequate heating of food before consumption, wash (wild) berries
Characteristics of protozoa
Unicellular eukaryotic organisms
Do not grow outside host
Organism itself vulnerable to environmental stresses e.g. low pH
Resistant structure: cysts and oocysts
Low dose response relation
Most relevant protozoa, host and sources
Greedy Lions Eat HoneyCombs, Prowl Through Grass
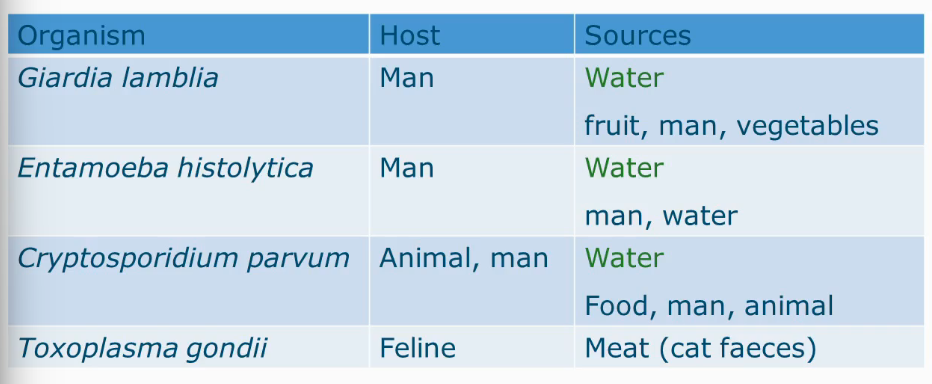
Giardia lamblia
Protozoa
Cysts survive in water
Gastric juices help to release trophozoites
Symptoms giardiasis: diarrhea, abdominal cramps, nausea
Food sources: salads, fruits washed with contaminated water
Chlorination of water not very effective
Treatment with drugs available.
Entmoeba histolytica
Protozoa
Transmission via water similar to Giardia
Amoebic dysentery
Invading the intestinal wall
Spread of trophozoites from the intestine via the bloodstream
Amoebic liver abscess
Effective drugs available.
Cryptosporidium parvum
Protozoa
Transmission oocysts through water
Especially affecting susceptible people (“aids defining illness”): diarrhoea
Cause of outbreaks:
Drinking water USA
Salad outbreaks (washed with contaminated water)
Lesson for companies (include in HACCP plan)
Chlorine resistant
Measures: Boil water 1 min
Toxoplasma gondii
protozoa
produces oocysts and tissue cysts
Cat plays central role, growth circle happens in cat.
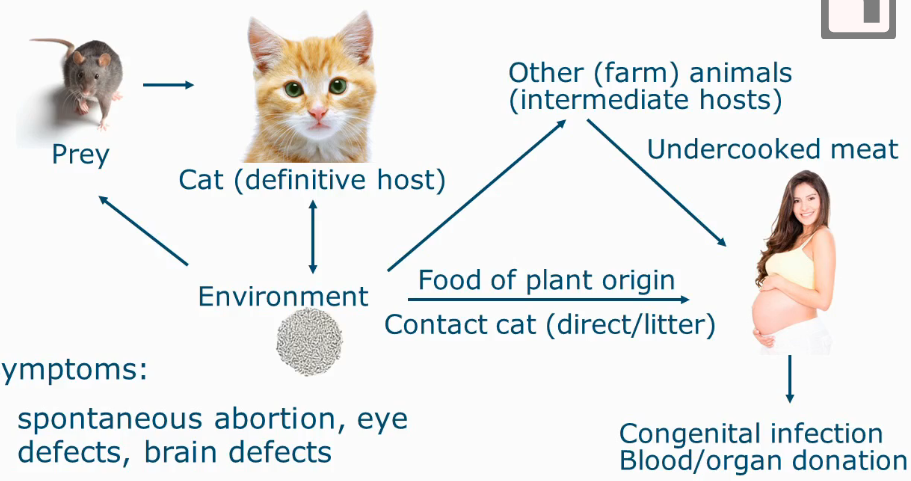
Symptoms of Toxoplasma gondii
Spontaneous abortion, eye defects, brain defects
Changes in behaviour
Asymptomatic
Lifecycle Giardia lamblia
Consumption of water or foods
Ingest cysts in intestine
Flagellate trophozoite (The active, movile form of a protozoa)
Multiplication in intestine
Cysts
Faeces
Contamination of water or food
Cycle repeats
Toxigenic algae
Toxigenic algae
e.g. dinoflagellates, diatoms, cyanobacteria
These produce fycotoxins (cyanotoxins)
Accumulation of toxin by:
Filter-feeding shellfish (mussels, clams)
Food webs fish
Toxin undetectable by naked eye and generally unaffected by cooking
Types of intoxications by shellfish and their effects
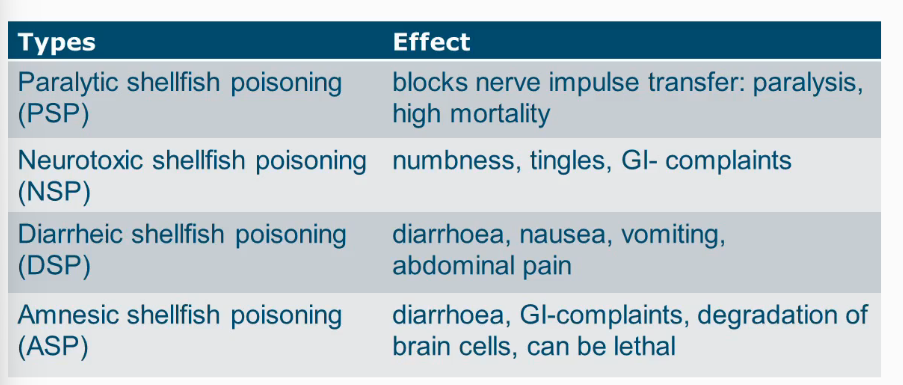
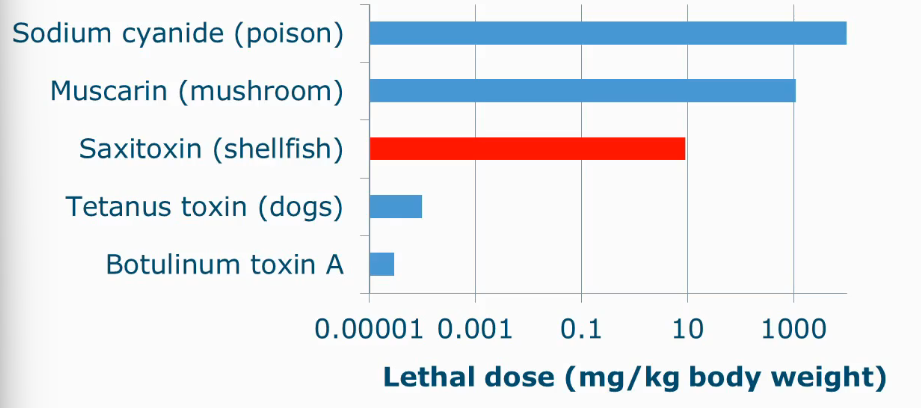
How toxic are toxins from algae?
Very toxic!! and lethal

Ciguatera intoxication
When fish eat the dinoflagellates (= algae) and produce ciguatera toxin that is found in algae
Accumulation of toxin in the fish, but does not make the fish sick
Humans can eat these fish and get sick
Symptoms comparable to neurotoxic shellfish poisoning: vomiting, diarrhoea, neurological effects.