Hearing Science Exam Two
1/276
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
277 Terms
What are the four middle ear contributions to hearing?
Impedance Polarization Function
Ventilation and Pressurization Protection and Distortion Reduction
What is each middle ear contribution designed to do?
solve a problem
What problem is the middle ear polarization function trying to solve?
how to allow for motion of the cochlear liquids inside closed capsule (if no fluid motion then no travelling wave)
What is the solution for middle ear polarization function?
two windows to the inner ear, with mechanical stimulation at the oval window
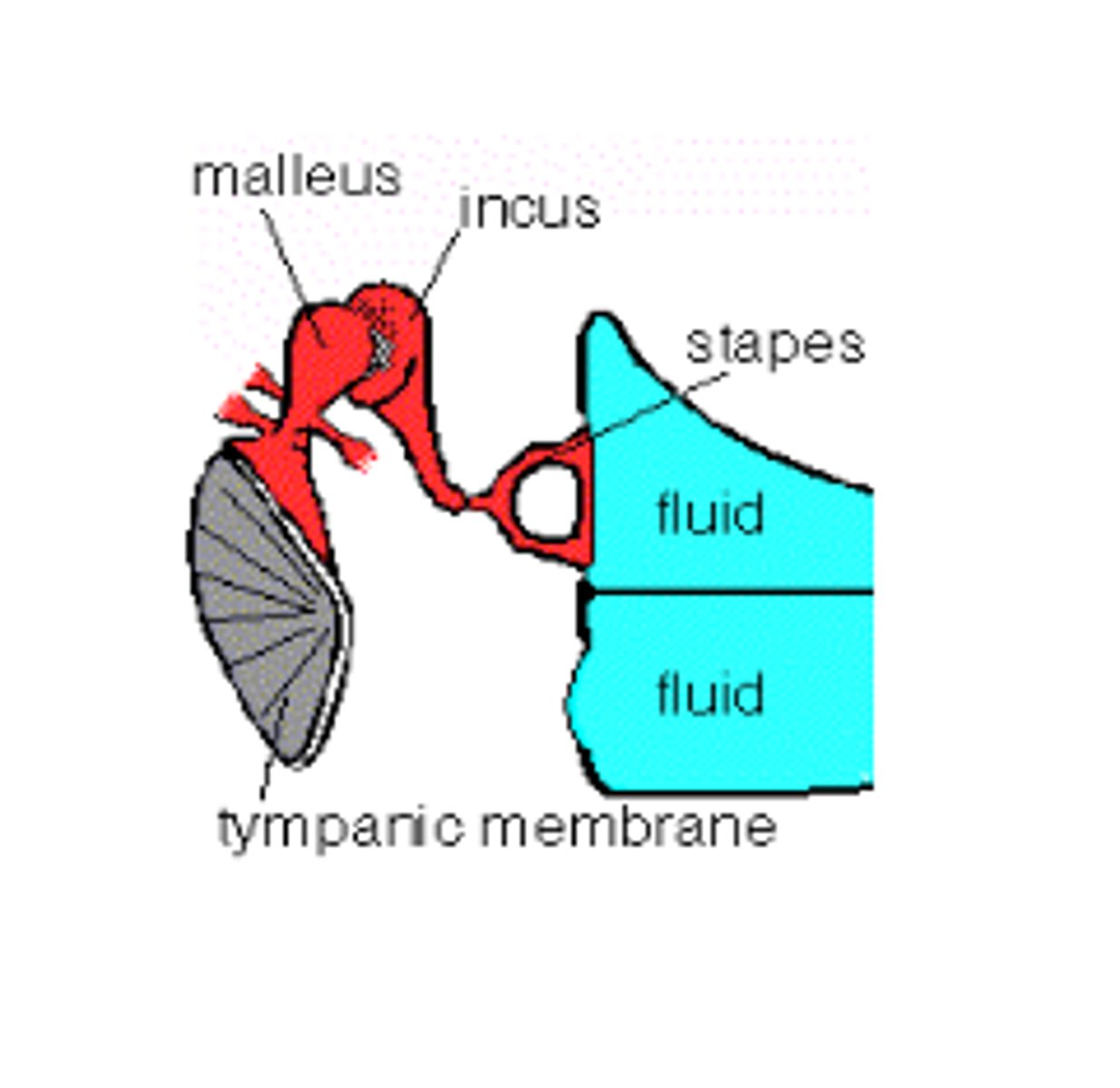
What does the round window do?
the round window reciprocates response
-reciprocating allows for displacement of cochlear
liquids, causing wave action
Middle Ear Polarization Function
reciprocating action between the oval window (stimulated by rocking motion of footplate of stapes) and round window (uncovered membrane below the oval window)
What problem is the middle ear ventilation and pressurization trying to solve?
tympanic cavity is closed (air-filled cavity)
What is the solution for middle ear ventilation and pressurization?
periodically open the airway via the eustachian tube
When does the eustachian tube open to allow for an open airway?
during swallowing, yawning, and chewing
-both tensor veli pallatini and levator veli palatini muscles are used
-opening at torus tubarious in nasopharynx
-place TM in proper postition
-prevents unhygienic environment
What muscles are used during swallowing, yawning, and chewing?
tensor veli palatini and levator veli palatini muscles
Eponym
a proper noun (a person's name) that has become the name of a thing
Who is Bartolommeo Eustachio?
he discovered the tube that connects the middle ear to the nasopharynx in 1561
-Italian anatomist
Eustachian Dysfunction
the inability to equalize middle ear and atmospheric pressure is an important factor in the pathogenesis of middle ear disease
Pathogenesis
mechanism that causes disease
What does eustachian tube dysfunction lead to?
lack of middle ear aeration
What does a lack of middle ear aeration cause?
-Tympanic membrane retraction
-Chronic otitis media (chronic ear infections)
-Hearing loss with language delay in children
-Chronic tympanic membrane perforations
-Cholesteatoma
Cholesteatoma
an abnormal skin
growth in the middle ear, if allowed to
increase in size it may destroy the ossicular chain, and in rare cases it may also result in a permanent hearing loss, dizziness, and facial muscle paralysis
What problem is the middle ear protection and distortion reduction trying to solve?
protect inner ear from mechanical over-stimulation
What is the solution for middle ear protection and distortion reduction?
increase of ossicular chain in order to reduce the low-frequency sound intensity that reaches the cochlea
What mechanism is used for middle ear protection and distortion control function?
the acoustic reflex
Acoustic Reflex
stimulated by eating, talking, yelling, other vocalizations, and exposure to high level sounds
-primarily, the stapedius muscle is contracted which stiffens the ossicular chain and reduces the sound reaching the cochlea
Acoustic Reflex Pathway
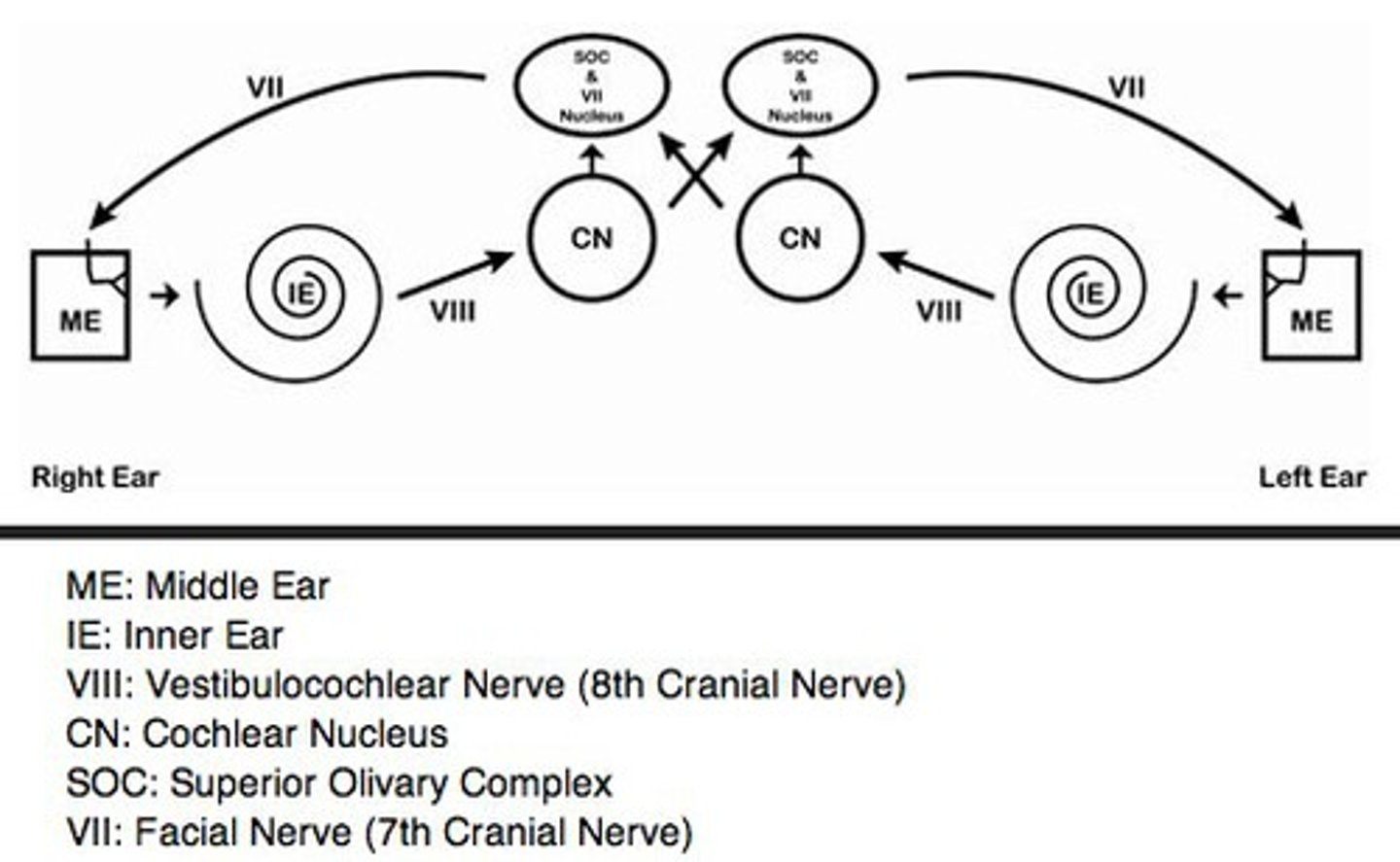
What are the parts of the acoustic reflex pathway?
superior olivary complex (SOC)
ventral cochlear nucleus (VCN)
inner ear (IE)
facial nerve (FN)
stapedius
What is the descending path of the acoustic reflex pathway?
descending path from brainstem to stapedial muscle via VIIth (facial) nerve
What is the ascending path of the acoustic relfex pathway?
ascending path from cochlea to brainstem via VIIIth nerve
What happens when the muscle contracts?
stiffens up the whole ossicular chain (and sometimes the eardrum)
-reduces low frequency sounds
How does the acoustic reflex affect the transmission of sound from the ear canal to the cochlea?
reduces the low frequency sounds (low frequency sounds are attenuated)
What does the acoustic reflex pathway do?
reduce the amount of low frequency vibrations that the oval window is being beaten by the stapes
Measuring the Acoustic Reflex Response
as the stimulus increases, sound energy decreases flow into the middle ear
What is the y-axis of the acoustic reflex response?
admittance or the flow of sound energy into the middle ear
What is the x-axis of the acoustic reflex response?
time
Middle Ear Protection and Distortion Reduction
the acoustic reflex threshold is determined in order to measure the function of the acoustic reflex pathways
-it is also used in part to determine the site of lesion for auditory disorders
Which sounds are reduced more?
low-frequency sounds are attenuated (or reduced) more so than high-frequency sounds
If a sound is played at a high enough level...
it will reduce a low frequency sound and let high frequency sounds pass
What is the maximum benefit loss for low frequencies?
20-30 dB
Is the middle ear protection/distortion control function a form of hearin protection?
-fatigability of the stapedius reflex in industrial noise
-effect of stapedius reflex on the auditory system of rabbits following exposure to industrial noise
-reduced stapedius reflex during exercise
Fatigability of the Stapedius Reflex in Industrial Noise
11 normal hearing emloyees at a shipbuilding yard for 7 hours, noise level 89-103 dBA
-one ear exposed the other ear protected
-stapedius reflex was measured before and after noise exposure
Does the stapedius still function in response to the highest level sounds?
yes, in the shipbuilding yard at the end of the 7 hour work period
-stapedius reflex did not fatigue (give out)
-involves the stapedius muscle and nerves to the brain
Effect of stapedius reflex on the auditory system of rabbits following exposure to industrial noise
-Rabbits, one ear with and one ear without functioning middle ear muscles (MEMs) were exposed to industrial noise
-Following the exposure, the ear without functioning MEMs had more extensive damage than the ear with functional MEMs
Effect of the Stepdius on the Auditory System
-right ear: functioning middle ear muscles
-left ear: non-functioning middle ear muscles (greater hearing loss)
-non-functioning middle ear muscles = low frequency loss
"Hearing loss"...
estimated from auditory brainstem response thresholds following industrial exposure
Brain Stem Audiometry
electrodes on bunny's head, plays sound to see when the nerves fire, measures if the sound was transmitted at the level of the brain stem (reached the bunny's brain stem)
Reduced Stapedius Reflex (SR) During Exercise
-10 normal hearing males, aged 27-34
-SR measured before, during and after "submaximal" exercise (10 minutes on an ergometer cycle, 50% work capacity)
-Exercise depresses the stapedial reflex and increases the risk of a temporary threshold shift (temporary hearing loss)
Where are high frequency sounds received?
at the base of the cochlea
Where are low frequency sounds received?
at the apex of the cochlea
The cochlea turns around the...
modiolus
Where do the cochlear nerves connect?
the inner and outer hair cells
Where do the cochlear nerves go?
through the habenula perforata, and into the modiolus
What makes up the VIIIth nerve?
nerve fibers (when they come out of the modiolus, they are the VIIIth nerve)
What makes up the VIIIth nerve?
bipolar neurons
The VIIIth nerve is made up of bipolar neurons. Where does it start and end?
Base of hair cells, through the habenula perforata, into the modiolus (cell body is within/connects to cell body), becomes the VIIIth nerve, connects to cochlea nucleus
What happens to the nerve fibers?
the nerve fibers come out of base of hair cells, all go through habenula perforata, meet the cell bodies in the modiolus, forms the VIIIthe nerve, VIIIth nerve is connected to cochlea nucleus
What part of the cochlea is closest to the modiolus?
the medial aspect of the cochlea
Where is the tectorial membrane located?
on top of the stereocilia
What covers the tops of the hair cells?
reticular lamina (thin layer of connective tissue)
What is the modiolus closest to, inner or outer hair cells?
inner hair cells
Inner Hair Cell
-peak or flask shaped
-approx. 3,500
-single row
stereocilia not attached to the tectorial membrane
-stereocilia in cresent shape
-centralized nucleus
-organelles distributed throughout the cell body
More on the Inner Hair Cell
-95% of the afferent neurons
-many afferent neurons (inner radial fibers) connect to each IHC
-afferent neurons synapse with cell body, efferent neurons synapse with the afferent neurons
-no motility
Outer Hair Cell
-cylindrical shape
-approx. 12,000
-3 rows
-stereocilia attached under the tectorial membrane
-stereocilia in W or V shape
-nucleus found in base
-organelles found along the outer walls
More on the Outer Hair Cell
-5% of afferent neurons
-each afferent neuron (outer spiral fibers) connects to many OHCs
-efferent and afferent neurons synapse directly with cell body
-OHCs "stretch and shrink" this is called OHC motility
What is an afferent nerve fiber?
goes towards the brain
Afferent neurons synapse with...
inner hair cells
Efferent neurons synapse with...
afferent neurons
What synapses directly with the outer hair cells?
efferent and afferent neurons
What does each afferent neuron (outer spiral fibers) connect to?
many outer hair cells
Type II Fibers
associated with outer hair cells
-slow twitch
Type I
associated with inner hair cells
-fast twitch
Many Type I fibers synapse...
with one inner hair cell directly opposite their habenular opening
What makes the outer hair cells contract?
efferent nerve stimulation
Features of the Cochlea
-mechanical (vibratory motion)
-hydraulic (wave motion)
-chemo-electrical (nerve energy)
Membranous Labyrinth
filled with endolymph
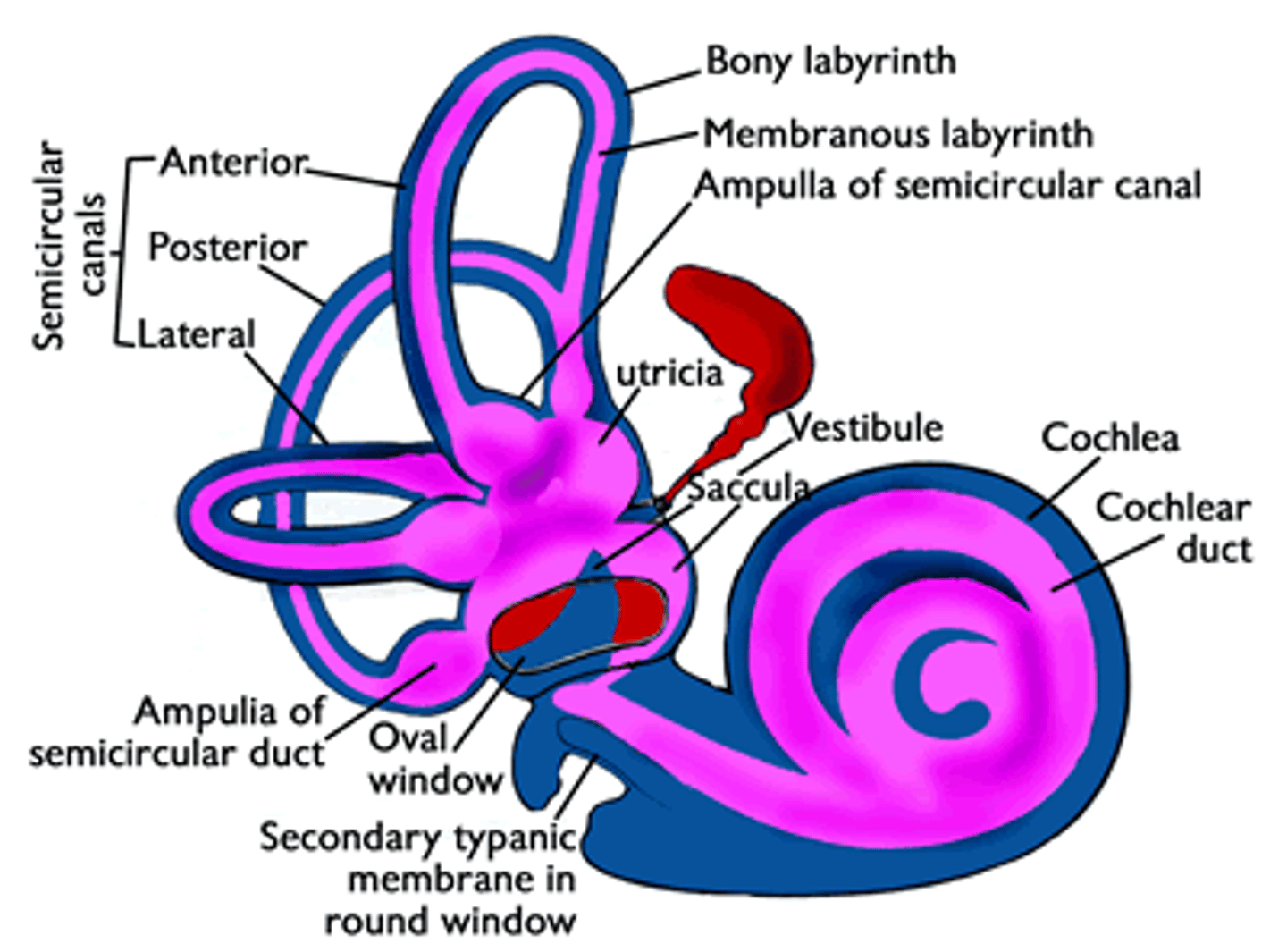
What are the three major anatomical components of the inner ear?
semi-circular canals
vestibule (saccule and utricle)
cochlea
Semi-Circular Canals
sense movement of the head, both speed and direction
-three fluid-filled tubes
How many semi-circular canals are there?
three
Vestibule
utricle and saccule are used to detect the orientation of the head
Cochlea
closed, labyrinthine (maze-like) capsule, filled with fluid
-most anterior structure
-two 5/8th turns, large bundle of nerve cells enters the center (auditory branch of the VIIIth nerve)
Modiolus of the Cochlea
bony center of cochlea
-the bony canal turns around the modiolus
-"continuous left turn" (spiral staircase)
-walls are solid bone
The auditory nerve fibers from the hair cells...
enter the modiolus
Labyrinth of the Cochlea
-2 5/8th turns
-35 mm length base to apex
-ends at the helicotrema in the apex
Where is the base of the cochlea?
near the stapes footplate
Where is the apex of the cochlea?
other end of the bony labyrinth
Story through the Cochlea
-stapes footplate removed, you see oval window
-through oval window, you would be in the Scala vestibuli
-go through Scala vestibuli, you are in the helicotrema (at apex)
Helicotrema = where the scala vestibuli and scala tympani
-past helicotrema, you are now in lower level (scala tympani)
-down spiral staircase, to round window (the base)
Osseous Spiral Lamina
bony extension of the medial wall of the bony labyrinth
-runs continuously along the medial wall
-gets skinnier as it goes from the base to the apex
The width of the osseous spiral lamina _________ between the base and the apex of the cochlea.
decreases
Why is the change in width necessary?
-basilar membrane is narrow at the base because it is responsible for detecting high frequencies
-basilar membrane is wider at apex because it is responsible for detecting low frequencies
By the time the cochlea reaches its third turn, the osseous spiral lamina has nearly ___________.
disappeared
What are the three sections of the scala?
scala vestibuli
scala tympani
scala media
Scala Vestibuli
-bounded inferiorly by Reissner's membrane
-ends at helicotrema
-contains perilymph
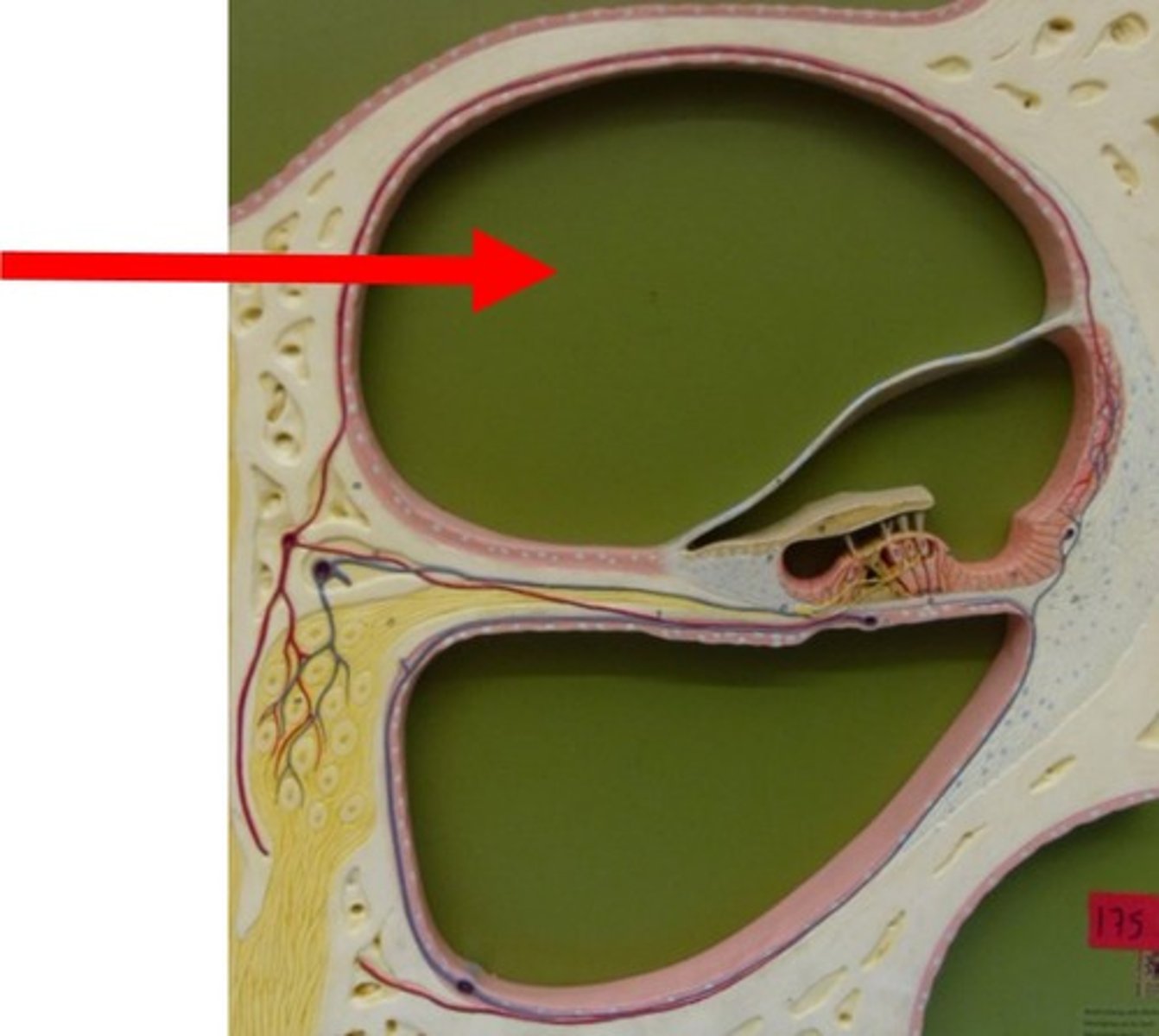
Reissner's Membrane
-floor of scala vestibuli
-roof of scala media
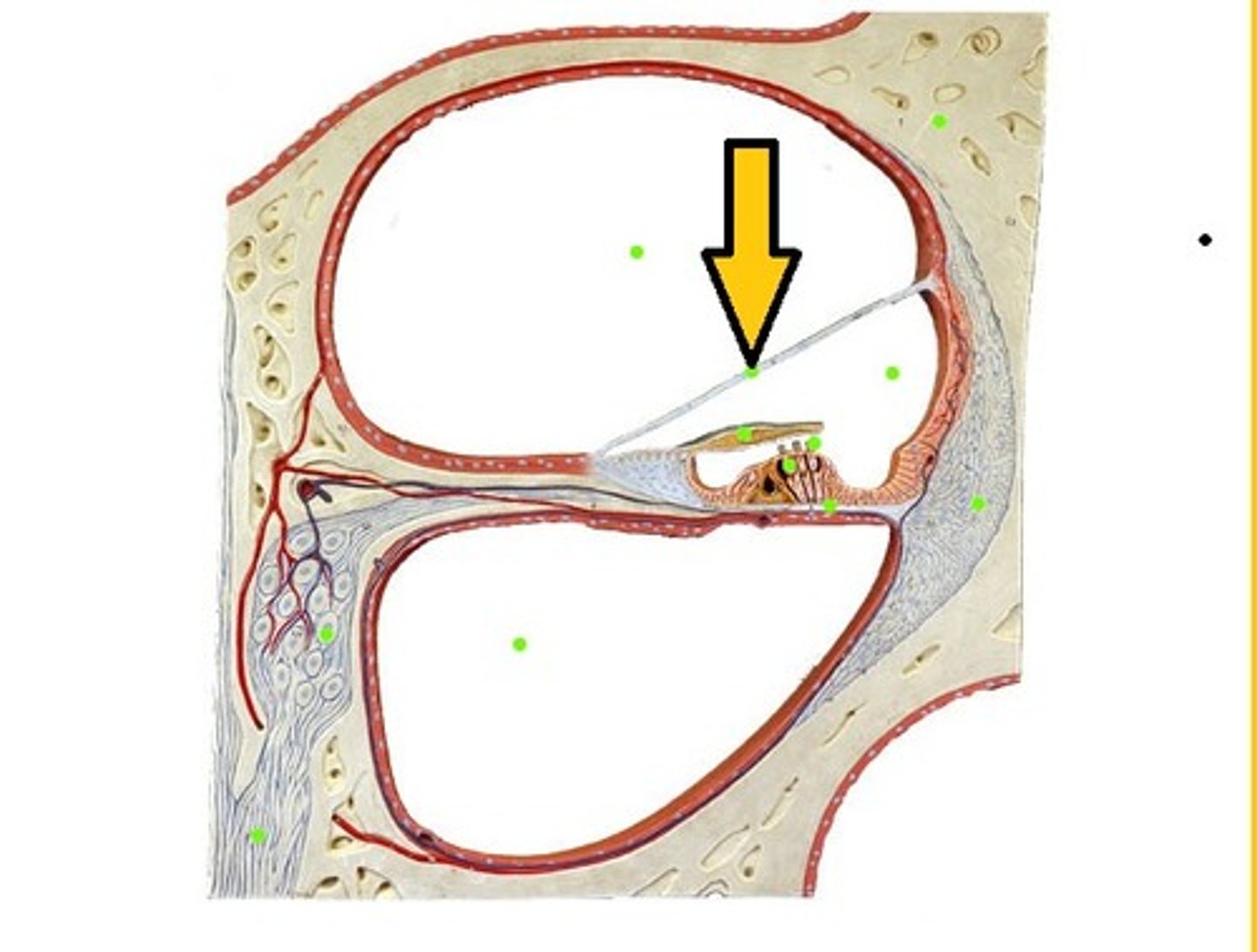
Perilymph
fluid around scala media (fills scala vestibuli and scala tympani)
The scala vestibuli is bounded inferiorly by...
Reissner's membrane
Scala Tympani
-bounded superiorly by the basilar membrane
-ends at helicotrema
-contains perilymph
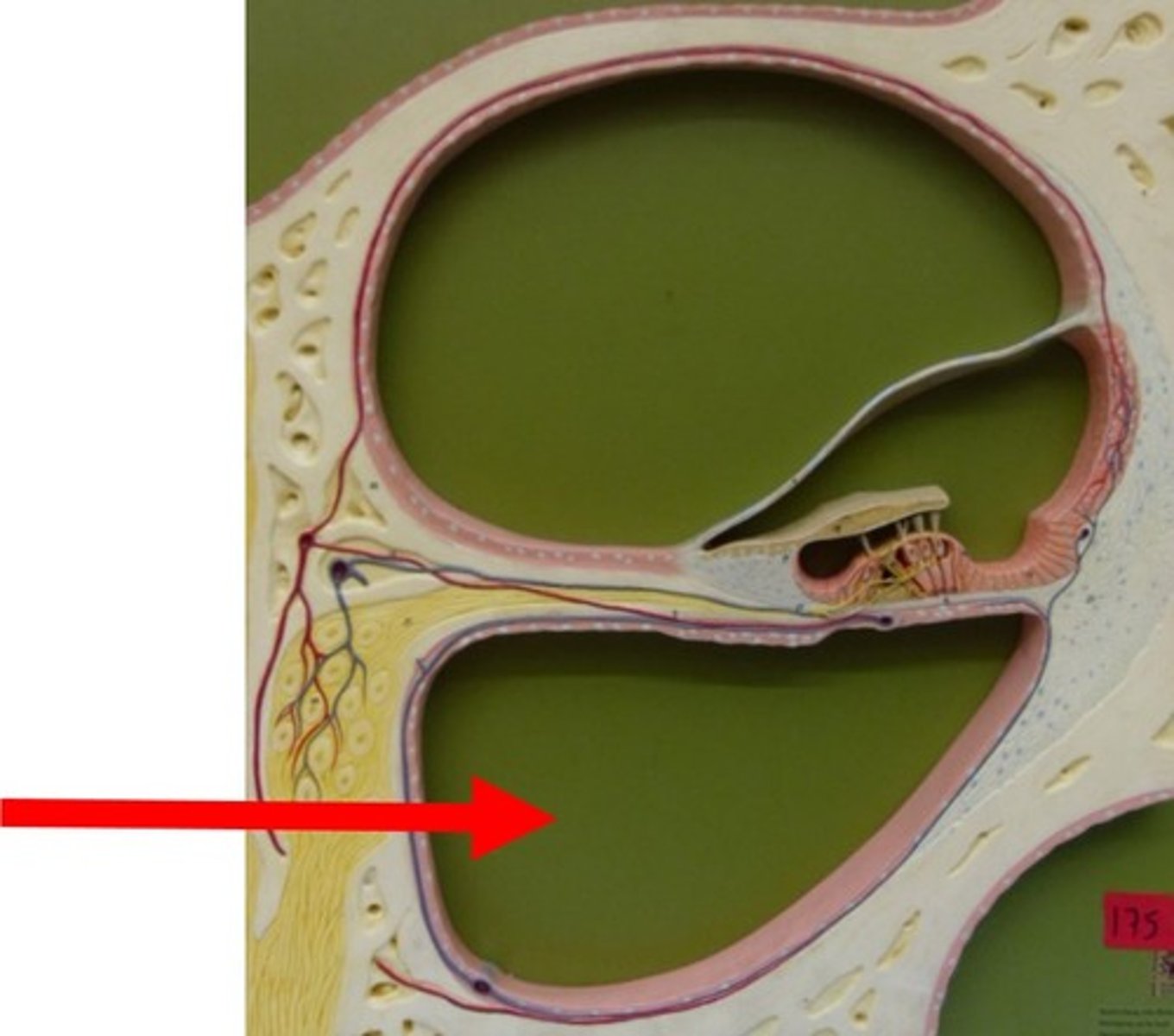
The width of the basilar membrane ___________ between base and apex of cochlea.
increases
Tonotopic
pertains to the way in which the primary auditory cortex is organized so that neurons that respond to particular frequencies are grouped together
The scala tympani is bounded superiorly by the...
basilar membrane
Scala Media
-bounded superiorly by Reissner's membrane
-bounded inferiorly by basilar membrane
-contains Organ of Corti
-contains endolymph
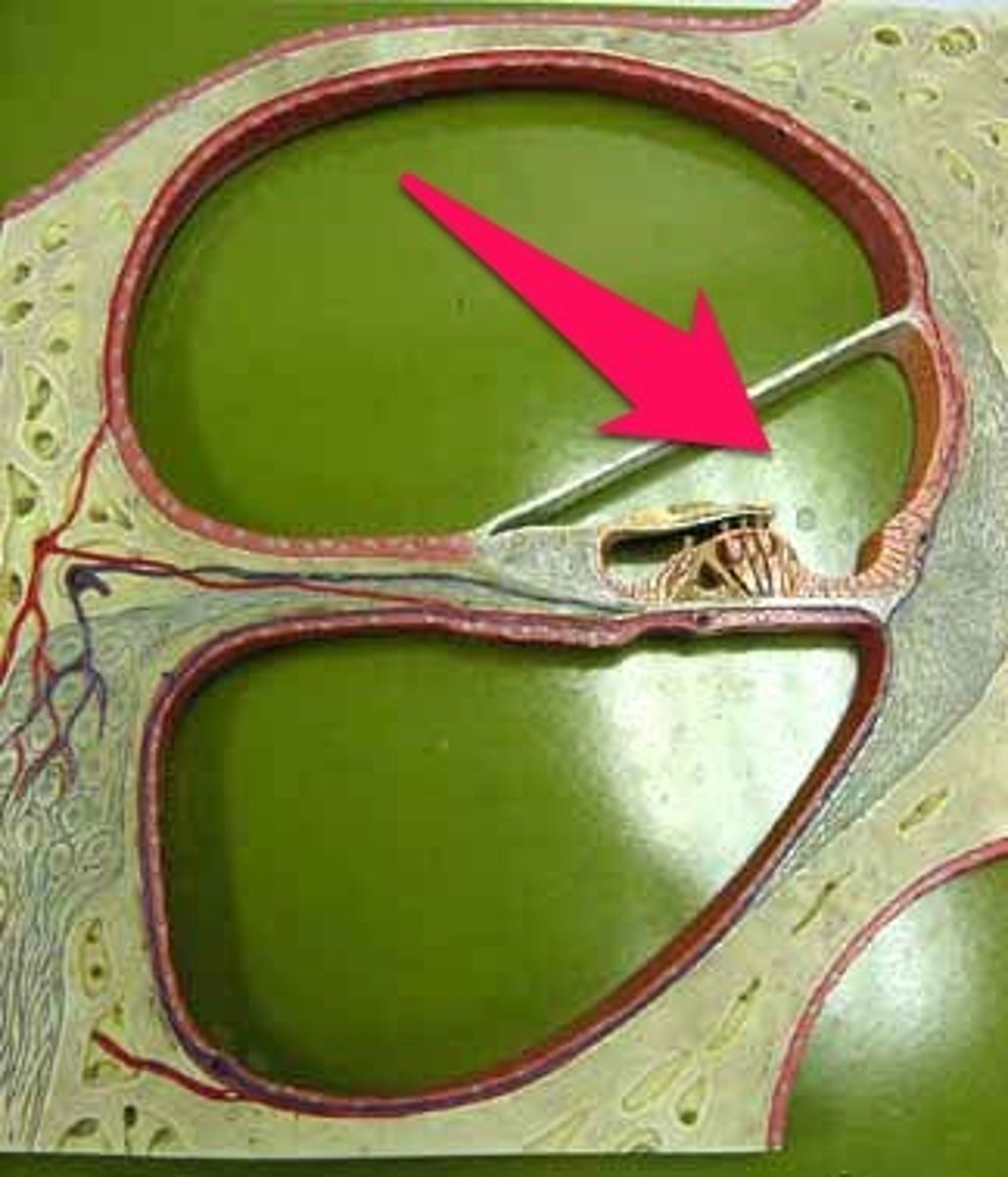
The scala media is bounded superiorly by...
Reissner's membrane
How do the scala vestibuli and scala tympani share perilymph?
at the helicotrema
What keeps the endolymph in the scala media?
reissner's membrane and basilar membrane
Gross Anatomy of Scala Media
-Reissner's Membrane
-Basilar Membrane
-Osseous Spiral Lamina
-Spiral Limbus
-Tectoral Membrane
-Organ of Corti
-Stria Vascularis