DPT 642: The Knee
1/108
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
109 Terms
position and stability
hip and ankle weakness can affect the knees...?
femur, tibia, patella and fibula
4 bones of the knee
tibiofemoral, patellofemoral, proximal tibiofibular
3 joints of the knee
femur, tibia
the knee consists of the convex _____ and concave _______
intercondylar notch
pathway for the cruciate ligaments
intercondylar groove
the patella glides on & articulates with this
sagittal
asymmetry of medial and lateral grooves affect motions in this plane
transfer weight across knee to ankle
what;s the primary function of the tibia?
tibial tuberosity
point where the patellar ligament attaches
medial
on the tibia, the ____ condyle is concave
lateral
on the tibia, the ____ condyle is convex
lateral meniscus
this structure helps the lateral tibial condyle to become concave
quadriceps tendon
the patella is embedded in this
apex
the patellar tendon comes off of which part of the patella?
apex
inferior portion of the patella
base
superior portion of the patella
flexion and extension
movement of the knee permitted in the sagittal plane
internal and external rotation
movement of the knee permitted in the frontal plane
130-150 degrees
normal ROM for knee flexion
5-10 degrees hyperextension
normal ROM for knee extension
tibial tuberosity
rotation is based off the position of this
90 degrees
maximal amount of rotation occurs when the knee is flexed to about...?
external rotation
tibial tuberosity travels laterally
internal rotation
tibial tuberosity travels medially
external rotation
in closed chain internal rotation, what does the femur do?
internal rotation
in closed chain external rotation, what does the femur do?
anteriorly
which way does the tibia roll/slide in open chain knee extension?
posteriorly
which way does the tibia roll/slide in open chain knee flexion?
screw home mechanism
tibia externally rotates during last 30 degrees of knee extension
shape of medial femoral condyle, passive tension of ACL, and slight lateral pull of the quads
what are the causes of the screw home mechanism
internal synovial layer
of the joint capsule, this Provides nourishment and lubrication & Allows freedom of motion
external fibrous layer
of the joint capsule, this Offers joint protection & Provides stability through a large ROM
menisci
web-shaped fibrocartilaginous discs that sit on the condyles of the tibia
Provides joint congruency and stability
Disperse weight bearing forces by providing cushioning
Provides nutrition and lubrication to the articular cartilage
Facilitates joint gliding
what are some of the functions of the menisci?
peripheral
which part of the menisci has a good blood supply?
menisectomy
this procedure is done when there a tear to the outside border of the meniscus
meniscus repair
this procedure is done when there a tear to the inside of the meniscus
lateral meniscus
more circular in shape
medial meniscus
more oval in shape
MCL and capsule
where does the medial meniscus attach to?
valgus motion
due to the attachment, the medial meniscus and MCL are commonly injured together when they encounter this
forceful, axial rotation of the femoral condyles over a partially flexed and weight bearing knee
what causes a medial meniscus tear?
cruciate ligaments
Prevent motion in all directions, best for prevent shear forces
proprioception
the cruciate ligaments contribute this of the knee, which is the knees understanding of where it is and what it is doing in space
Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL)
prevents anterior displacement of tibia
extension
the ACL is most taut in what position?
posterolateral and anteromedial
2 bundles of the ACL
posterolateral
this bundle of the ACL is taut in extension
anteromedial
this bundle of the ACL is taut in flexion
strong activation of the quadriceps muscle over a slightly flexed or fully extended knee, a marked valgus collapse of the knee, and excessive external rotation of the knee
What are the 3 common components of an ACL injuries
valgus
if a person injures their ACL via landing a jump, what position did their knee go in in order to cause the injury?
valgus knee or genu valgum
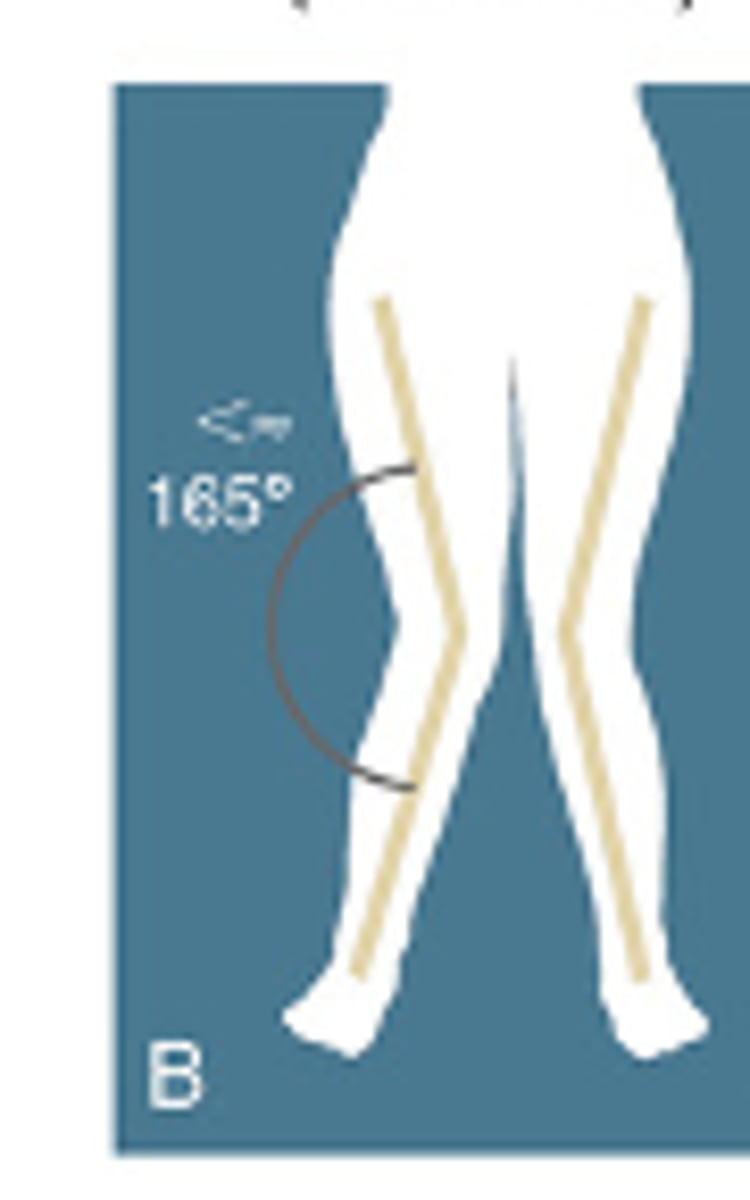
varus knee or genu varum
flexion
the PCL is most taut in what position
Posterior Cruciate Ligament (PCL)
prevents posterior displacement of tibia
posteromedial and anterolateral
2 bundles of the PCL
posteromedial
PCL bundle taut in flexion
anterolateral
PCL bundle taut in increasing extension
dashboard injury
injury to PCL because proximal anterior tibia of flexed knee hits the dashboard forcing excessive posterior translation of tibia on femur
fall on fully flexed knee with ankle in full plantar flexion
describe how a PCL may be torn during contact sports?
skip
study checkpoint- i hope someone studying this understands this meme.
anyways, you're doing great, keep up the focus & the great work! 💙
answer is 'skip'
frontal plane stability
collateral ligaments play the biggest role in this
Medial Collateral Ligament (MCL)
limits valgus force and some anterior translation
Lateral Collateral Ligament (LCL)
limits varus force & excessive lateral rotation
biceps femoris
the LCL blends with this tendon
valgus force with foot planted or severe hyperextenstion of knee
Common MOI to MCL?
varus force with foot planted or severe hyperextenstion of knee
Common MOI to LCL?
hyperextension or combined hyperextension with external rotation of the knee
Common MOI to posterior capsule?
patellar tendon and patellar retinacular fibers
connective tissue that reinforces the anterior capsule
lateral collateral ligament/lcl, lateral patellar retinacular fibers, IT band
connective tissue that reinforces the lateral capsule
oblique popliteal ligament and arcuate popliteal ligament
connective tissue that reinforces the posterior capsule
arcuate popliteal ligament and lateral collateral ligament/lcl
connective tissue that reinforces the posterior-lateral capsule
medial patellar retinacular fibers, medial collateral ligament and thickened fibers posterior-medially
connective tissue that reinforces the medial capsule
quadriceps
muscular-tendinous reinforcement of the anterior capsule
biceps femoris, tendon of the popliteus and lateral head of gastrocnemius
muscular-tendinous reinforcement of the lateral capsule
popliteus, gastrocnemius, hamstrings (especially semimembranosus tendon)
muscular-tendinous reinforcement of the posterior capsule
tendon of the popliteus
muscular-tendinous reinforcement of the posterior-lateral capsule
expansions from the tendon the semimembranosus and tendons of sartorius, gracilis and semitendinosus
muscular-tendinous reinforcement of the medial capsule
20-30° of flexion
Patella moves inferiorly and sits in the shallow part of the trochlear groove
60-90° of flexion
Patella continues to move inferiorly and is in max contact with the trochlear groove
135° of flexion
Patella continues to move inferiorly and sits below the trochlear groove
the patella loses much of its mechanical engagement with intercondylar groove
why is 20-30° of flexion a common position of instability of the patellofemoral joint?
fixed patella
During femoral on tibial movement, the intercondylar groove moves relative to the...?
Medial and lateral patellar retinacular fibers or medial and lateral patellofemoral fibers
aid in patellar tracking in trochlear groove
medial patellofemoral ligament
becomes taut in extension due to its connection to oblique fibers of vastus medialis
Q-angle
angle represented by force vector of quads and long axis of patellar tendon
10-15 degrees
average Q-angle in men
15-20 degrees
average Q-angle in women
lateral pull force
Q-angles above 20 degrees increase...?
compressive forces
Force within quadriceps and knee flexion angle affect this greatly
contact force
compressive forces create a bigger __________ thanks to compressive forces
90
Flexion angles greater than _____ degrees increase contact from quad tendon & it helps to offset forces
quadriceps femoris
muscle(s) responsible for knee extension
hamstrings, sartorius, gracilis, popliteus, and gastrocnemius
muscle(s) responsible for knee flexion/rotation
quadriceps
Consists of rectus femoris, vastus lateralis/medialis/intermedius
Most internal torque is created between 45-70 degrees of flexion
bowstring force
the quads oull the patella superior and lateral, causing this force
vastus lateralis
largest component of bowstring force
internal rotation
if the muscle is more medially located, what kind of rotation will it do?
external rotation
if the muscle is more laterally located, what kind of rotation will it do?
biceps femoris
does External rotation of knee (flexed knee)