South College AVL Lab Med: Thyroid Function Tests - Lecture 9
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
thyroid gland
endocrine gland - produces triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4) that affect many aspects of your metabolism
Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH)
secreted by the anterior pituitary gland - stimulates thyroid gland to secrete T4 and T3
Initial test to assess thyroid function
used to diagnose and monitor thyroid conditions - hypo/hyperthyroidism
what are some other uses of TSH labs?
in the AM (basal levels occur around 10am, and highest around 10pm)
When is the best time to order a TSH lab?
ALWAYS REPEAT ABNORMAL TSH TO CONFIRM ABNORMAL READING! (fluctuations are transient)
Should we repeat an abnormal TSH level or just accept it as is?
discontinue any biotin supplements 48 hrs or more before lab draw
Is there anything you need to tell a patient before collecting a TSH lab?
T4 (thyroxine)
Secreted by the thyroid gland
almost all of this is bound to protein and NOT active
total T4 = bound T4 + unbound T4
What is the equation for total T4?
free T4 - metabolically active
T4 that is not bound to a protein is considered what?
hyperthyroidism, hypothyroidsm
what does a high free T4 mean? low free T4?
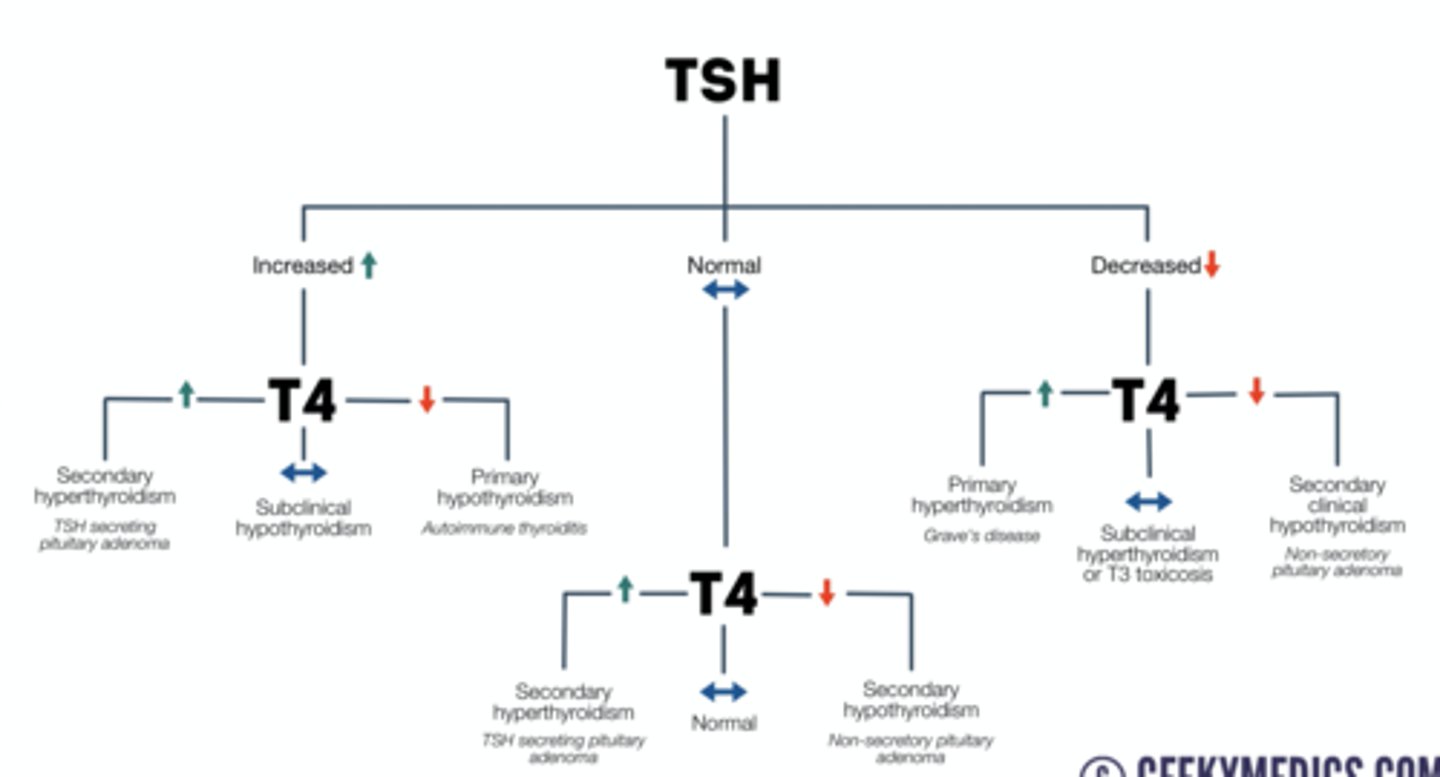
normal, primary hyperthyroidism, primary hypothyroidism, secondary hypothyroidism
TSH: normal, T4: normal - diagnosis?
TSH: low, T4: high - diagnosis?
TSH: high, T4: low - diagnosis?
TSH: low, T4: low - diagnosis?
routine annual physical
monitor diagnosed thyroid disease
physical exam: bradycardia, tachycardia, or goiter
high risk: pregnancy, elderly, autoimmune disease
what are some reasons as to why we would order thyroid function tests, in general?
fatigue, constipation/diarrhea, depression/anxiety, heat intolerance/cold intolerance, hair thinning, weight loss/weight gain
what are some symptoms that would be suspicious of thyroid disease?
everything slows down/dries up
everything is on overdrive
how can we remember the symptoms associated with hypothyroidism? hyperthyroidism?
weight gain, hair loss, puffy face, fatigue/weakness, slowed heart rate, elevated cholesterol, muscle weakness, muscle aches, constipation, dry skin, cold sensitivity, etc.
what are some common symptoms of hypothyroidism?
unintentional weight loss, bulging eyes, rapid/irregular heart rate, increased sweating, increased appetite, muscle fatigue, heat sensitivity, changes in bowel patterns
what are some common symptoms of hyperthyroidism?
chronic autoimmune hypothyroidism (Hashimotos)
what is the most common cause of hypothyroidism in iodine-rich countries?
past hyperthyroidism treatment w/ radioiodine
thyroidectomy
iodine deficiency or excess
drugs - lithium, amiodarone
what are some causes of primary hypothyroidism?
TPO
what is elevated in more than 90% of patients with Hashimotos (chronic autoimmune hypothyroidism)?
goiter in absence of hypothyroidism (identify immunologically-mediated goiter)
subclinical hypothyroidism (high TSH with normal free T4)
painless thyroiditis/postpartum thyroiditis (predict the likelihood of converting to overt hypothyroidism)
Although TPO is not routinely measured in patients with hypothyroidism, what are some indications for obtaining TPO labs?
T3 (triiodothyronine)
One of two major hormones released by thyroid that affects metabolism
used to diagnose and monitor hyperthyroidism
T4 (in the liver)
Large portion of T3 is converted from what?
age
What are normal levels of T3 dependent on?
Graves disease
autoimmune disorder and the most common cause of hyperthyroidism
ophthalmopathy (bulging eyes)
large, non-nodular thyroid
moderate/severe symptoms of hyperthyroidism
what are some key symptoms/indicators that someone likely has Graves disease?
continue with labs, +/- imaging
What happens if Graves is not evident from the key criteria/symptoms?
toxic multinodular goiter/nodules
postpartum thyroiditis
subacute thyroiditis
silent thyroiditis
meds (amiodarone, high iodine Ingestion, cancer drugs)
pregnancy
What are some other causes of hyperthyroidism?
TPI (thyroid stimulating immunoglobulins) and TRAb (thyroid receptor antibodies)
antibodies directed against the thyroid to stimulate the production of T4 and T3
diagnosis of Graves disease
What do high levels of TSI and TRAb indicate?
Autoimmune thyroid diseases:
Hashimotos (both anti-TPO antibodies and anti-thyroglobulin antibodies)
Graves disease (TSI)
What do each of these tests help us with diagnosing?
Anti-TPO antibodies
Anti-thyroglobulin antibodies
TSI (TSH receptor antibodies)
non-thyroid illness (sick euthyroid syndrome - septic, ICU)
meds (biotin - false low TSH, amiodarone - disrupts thyroid hormones, glucocorticoids - suppress TSH)
pregnancy (estrogen increases thyroxine-binding globulin)
What are some confounding factors that can impact the results of thyroid disease testing?
clinical: symptoms present, labs abnormal
subclinical: no symptoms, labs abnormal
what does clinical vs subclinical mean in terms of thyroid disease?
TSH elevated, free T4 normal (common in elderly, especially women)
may progress to overt hypothyroidism
(want to monitor b/c could be associated w/ other issues)
What do subclinical hypothyroid labs typically look like?
TSH low, Free T4 and T3 normal
Risks: Afib, osteoporosis
What do subclinical hyperthyroidism labs typically look like?
TSH chart reference
TSH chart reference