APSC 451 Exam 2
1/325
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
326 Terms
What is the largest tissue mass in the body of a horse
muscles
Muscles make up how much of the body weight
50%
True or false muscles provide movement internally and externally
True
How do muscles perform work
by contracting to allow for motion and vital functions
true or false not every muscle has a nerve bringing commands to the brain
False each muscle consists of one or more nerves bringing
commands to and from the brain
What are the 3 types of muscles the body consist of
Smooth (involuntary)
cardiac (involuntary)
skeletal
Describe smooth muscles (alternate name, where they’re found, function)
– Involuntary
– Also called visceral muscle
– Found in the digestive, respiratory, urinary and
reproductive systems
– Capable of prolonged periods of activity without
fatigue
True or false cardiac muscles are fund only in the heart
true
the rate of contraction for the cardiac muscles are controlled by what
autonomic nervous system
do the cardiac muscles require conscious control
no
Skeletal muscles are usually found where
usually attached to the bony levers of the skeleton
true or false, skeletal muscles may attach its fleshy fibers to bone
true
But usually, main part terminates in cordlike
structure called a tendon that transmits the pull of
the muscle while it contracts
true
Skeletal muscles are generally arranged in what
Generally arranged in opposing sets (one set bends
the limb or body, while the other straightens it)
are both sets of skeletal muscles operating at the same time
typically
true or false voluntary muscles can only contract for a short time before becoming fatigued
true
muscles work by ____ & _____
Contracting (shortening of muscle fibers)
– Relaxing (lengthening muscle fibers
what are flexor muscles
a muscle group that flexes causing joints to bend
that are extensor muscles
Other muscle group extends (extensor muscles)
causing joint to straighten
The contractile portion of voluntary muscles consist of what
elongated muscle cells, side by side and lengthwise of the muscle
elongated muscle cells, side by side and lengthwise
of the muscle
Muscle contraction occurs in response to…
nerve stimulaton
muscle contraction requires energy from what
Adenosine Triphosphate
true or false, all forms of energy must be converted to ATP
before contraction can occur, it is the only form of energy acceptable to muscle
true
What are the 3 basic fuel systems providing material to produce ATP for muscle contractions
Phosphagen system, Glycogen/Lactate system, Citric acid or Krebs cycle
describe the phosphagen system
• Rapidly available source of energy, stored in muscle cells
• Supports anaerobic work for approximately 30 seconds
• Does not require oxygen
• Any event done at maximum effort in less than 30 seconds is
supported entirely by this system
Describe the Glycogen or lactate system
• Can produce energy for up to 5 minutes from glycogen
stored in the muscle
• It takes over ATP production just when the Phosphagen
system is depleted
• Stored glycogen is mobilized and converted to ATP
through glycolysis
• This process does not require oxygen
Describe the citric acid or krebs cycle and the effects of VO2
Requires oxygen and produces the largest amount of ATP
• Takes over where the glycogen system ends and can last
for hours, as long as oxygen is available
• Amount of oxygen that can be delivered to the tissue and
used, is called the VO2 max
• The higher the VO2 max, the more endurance a horse has
• Fuel for this system can either be pyruvic acid (from
glycolysis) or fatty acids (from adipose tissue or the diet)
• End products are CO2 and H2O
true or false muscles are not very adaptable
false they are very adaptable
A horse muscles adapt in relation to..
the specific type of training it receives
overexertion of muscle without adequate conditioning leads to…
muscle fatigue
proper conditioning and nutrition prevents what
muscle disorders
What are some muscle disorders
• Bowed tendon
• Compartment syndrome
• Equine Exertional Rhabdomyolysis (ER, "tying
up")
• Equine polysaccharide storage myopathy (EPSM)
• Glycogen Branching Enzyme Deficiency (GBED)
• Hypocalcemia
• Hyperkalemic periodic paralysis (HYPP)
• Muscle atrophy
• White muscle disease seen in horses with a
selenium deficiency
Do animals have different types of digestive systems based on how and where they digest food
yes
what are non-ruminant systems characterized by
Non-ruminant systems characterized by enzymatic
digestion of carbohydrates, proteins and fats in the
foregut and limited fiber digestion in the hindgut
Horse referred to as non-ruminant herbivore
(high rates of enzymatic digestion in the foregut
(mouth to ileum) and high rates of microbial
digestion in the hindgut (cecum to rectum)
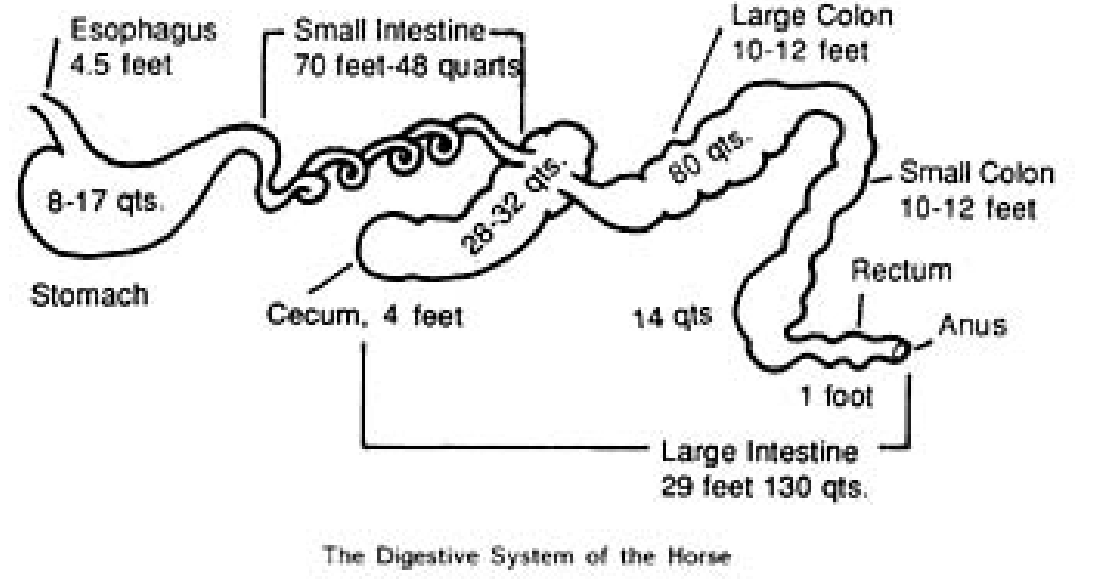
How long is the digestive tract of a horse and what is its capacity
100 ft
40-50 gallons
How much of the digestive system does the stomach, small intestine, and hind gut make up
Stomach of adult horse – less than 10%
of total tract
Small intestines – 30% of total tract
Hind gut - ~ 65% of the digestive
system
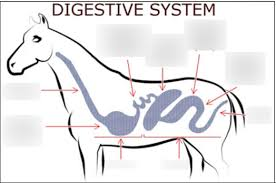
The foregut includes what
mouth, esophagus, stomach, and small intestines
What 3 sets of paired glands secrete saliva
parotid
submaxillary
sublingual
True or false, water makes up 99% of saliva with 1% composed of inorganic salts and proteins
true
do horses have enzymes in their saliva
no
saliva secretion is stimulated by what
mechanical action of food on the mucous membrane of inner cheek
t or f horse produce 7 gallons of saliva in a day
no 10
describe the pharynx
food is moved from the mouth through
the pharynx very quickly so it will not enter the
larynx or be forced into the nasal passages
once food enters the pharynx can it return
no due to a blocking action
Can horse breath through their mouth
no because of pharynx
any food or water returning from the pharynx goes through what
the nostrils
Describe the esophagus
Esophagus: about 50-60 inches in length
Extends from the pharynx down the left side
of the neck to the stomach
Solid and semi-solid food moves down the
esophagus by peristalsis, while liquids are
squirted down
t or f Peristalsis is a one-way action in the horse (esophagus to stomach), therefore, it is very difficult for a horse to vomit
t
how many times should a horse be fed
2-3 times daily
True or false the horses stomach is small relative to the rest of the digestive tract
true
What is the capacity of a horses stomach
8-17 qts
Gastric juices contain what
Hydrochloric acid, pepsin, and gastric lipase
what does pepsin do
helps digest protein
What does gastric lipase do
helps digest some fats into fatty acids and glycerol
Where does most fat digestion occur
in the small intestine
How long does food remain in the stomach
15 mins
What is the site for major portion of nutrient absorption
small intestine
How long is the small intestine and what is the capacity
70 feet long and 2-4 inches in diameter capacity of 48 quarts
material leaving the stomach into the small intestine is called the what
chyme
What secretions influence digestion in the small intestine
Secretions from the pancreas (pancreatic juice),
liver (bile), and intestinal glands (intestinal juice)
influences digestion in the small intestines
pancreatic juices contain what and what are the functions
Pancreatic juice contains Trypsin which
converts proteins and partly hydrolyzed
proteins into peptides and amino acids;
pancreatic lipase which hydrolyzes fats to
fatty acids and glycerol, pancreatic amylase
which breaks down starch to maltose
the liver secretes _____ which_____
Liver secretes bile which activates
pancreatic lipase and assists in the
absorption of fatty acids
What does the gallbladder in the horse do
The horse does not have a gallbladder to
store bile, so there is a direct secretion of
bile into the small intestines from the liver
What are the sugar digesting enzymes in the small and large intestines and what do they break down
Other glands throughout the small and
large intestines secretes sugar digesting
enzymes (maltase, sucrase, lactase) which
breaks down maltose, sucrose and lactose
into glucose which can be absorbed
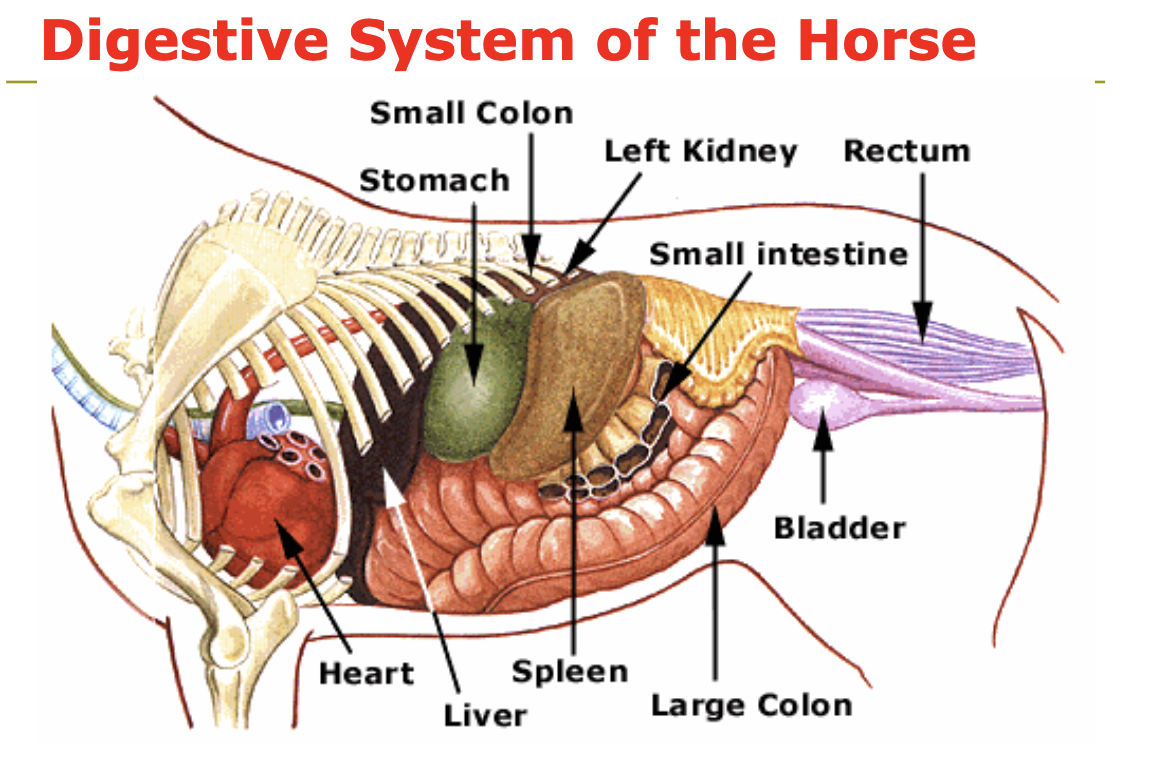
What is included in the hindgut
cecum, large colon, small colon, and rectum
true or false the hindgut contains microbes (bacteria and protozoa)
t
What do the microbes in the hindgut do
they break down fibrous feeds in to short chain volatile fatty acids
Microbial action allows the horse to..
efficiently utilize forages (hay, grass, etc)
volatile fatty acids are a source of..
energy
the amount of VFA produced depends on
composition of diet
What happens to starch that reaches the hind gut
it is fermented to VFA and Lactic Acid
Why is it best to not have too much soluble carbs reach the hindgut
because it can cause digestive disorders`
What is the cecum also referred to as
blind gut
the presence of food in the stomach causes what in the cecum
the presence of food in the cecum causes the emptying of the cecum into the large colon
What happens in the large colon
bacterial action, some digestion, and impaction occurs
What happens in the small colon
water is reabsorbed and feces are formed
True or false a horse voids about 33 to 50 lbs of feces daily
true
True or false vigorous horses defecate 4-8 times per day
false 5-12
HORSES IN SERVICE
What is equine assisted psychotherapy
therapeutic activities with horse under guidance of mental health professional and an equine specialist
activities can be grooming, feeding, leading the horse and more
What is hippotherapy
Hippotherapy is a specialized form of physical, occupational, and speech therapy in which a
therapist utilizes the horse’s natural movements to provide targeted motor and sensory input.
the use of horseback riding as a therapeutic or rehabilitative treatment, especially as a means of improving coordination, balance, and strength.
What does hippotherapy do and who is it used for
Hippotherepy shortens recovery times
Improves balance and muscle control
People with:
§Autism
§Cerebral palsy
§Arthritis, sclerosis
§Head injuries
§Strokes
§Spinal cord injuries
§Behavioral disorders
§Psychiatric conditions.
define therapeutic horseback riding
Therapeutic riding focuses
on teaching riding skills to
individuals with
disabilities, serving as
exercise and recreation
rather than treatment.
• While the primary goal is
riding and working with
the horse, it still offers
physical, emotional, and
psychological benefits.
The first guide horse foundation was set
up as an experimental program by the
Burlson's farm in 1999.
• In 2002 Dan Shaw became the first
person to use a guide horse.
• 2010 the US Department of Justice
ruled that mini horses can be recognized
as service animals
list pros and cons of guide horses
Pros
○ Miniature horses have an average lifespan of 30
years compared to dogs' lifespan which is 12
years.
○ Horses have heighten senses due to them being
prey animals allowing them to react to situations
faster.
○ Due to their size it allows for better stability for
individuals with mobility issues
● Cons
○ Horses won't have as much access to indoor
spaces due to their size
○ Horses have a strong flight or fight response
causing less predictable behavior
What are mobility horses
service animals that assist people with mobility issues
what are other ways service horses can be used
law enforcement
search & rescue
learning programs
rehabilitation
list some common horses used in service
Quarter Horse – Therapeutic Riding, Emotional Support
● Morgan – Equine-Assisted Psychotherapy, Mobility Assistance,
Leadership
● Friesian – Mobility Assistance, Therapeutic Riding, Leadership
Tennessee Walking Horse – Emotional Support, Search and Rescue,
Therapeutic Riding
● Miniature Horse – Guide Work, Animal-Assisted Interventions
● Percheron & Belgian Draft – Mounted Police, Mobility Assistance
● Mustang & Arabian – Search and Rescue, Leadership
OWNING A HORSE PPT
what are some care requirements
Housing and environment
nutrition and feeding
routine veterinary care and health care
equipment and tack
What are five factors that contribute to the price of a horse
breed
age
training level
primary use
pedigree
What is the highest expense for horses
housing
What are challenges of owning horse
financial commitment
time management
socialization and training
housing/security
potential illness/injury
right horse suited for lifestyle
veterinary care
benefits of owning a horse
physical exercise
mental, emotional, and social development through companionship
financial/investment potential
RESPIRATORY SYSTEM