OAT Gen Chem
1/127
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
128 Terms
Strong acids
HBr, HI, HCl, HClO3, HClO4, H2SO4, HNO3
Strong bases
group 1 metal hydroxides, Ba(OH)2, Sr(OH)2, Ca(OH)2
Soluble salts
group 1 metal cations, NO3-, NH4+, C2H3O2-, ClO4- (NNCCL- nickel)
Insoluble salts
Hg2+, OH-, Pb2+, PO43-, S2-, Ag+, CO32- (HOPPSAC)
Solubles trump insolubles T/F
T
Diatomic gases (x2)
H2, N2, F2, O2, I2, Cl2, Br2 (have no fear of ice cold beer)
Ionization energy
energy to remove e-
Ionization energy exceptions
group 2>13, group 15>16
Transition metal color exception
row 4 is colorless
e- affinity
energy released when e- added
e- affinity exceptions
group 2 low, group 14>15, noble gases=0
increases up, right
electronegativity, ionization energy, e- affinity (higher is more neg), nonmetallic character
increases down, left
metallic character, atomic radius
atomic radius higher in anions or cations?
anions
increases down, right
acidity
increases up, left
basicity
Boyle
P1V1=P2V2
Charles
V1/T1=V2/T2
Avogadro
V1/n1=V2/n2
Gay-Lussac
P1/T1=P2/T2
Combined
P1V1/T1=P2V2/T2
Ideal
PV=nRT (R= 0.0821 atm, 8.314 KPa)
Does strength of acids and bases depend on concentration?
No
Standard T, P, 1mol
T=273k, P=1 atm, 1 mol= 22.4L
Density
m/v=PM/RT
What type of collisions occur in an ideal gas?
Collisions are elastic, no energy is lost.
What is the motion of gas particles in an ideal gas?
Gas is in continuous, rapid, random motion.
What kind of forces exist between gas particles in an ideal gas?
There are no attractive or repulsive forces between gas particles.
Does an ideal gas have volume?
An ideal gas has no volume.
How do gas particles relate to each other in terms of distance in an ideal gas?
Gas particles are spread far apart from each other relative to their size.
Buffers
1. weak A +CB 1:1
2. weak B+ CA 1:1
3. strong A + weak base 1:2
4. strong B + weak acid 1:2
effusion
rate1/rate2=radical M2/M1
diluted/conc equation
M1V1=M2V2
Zeff
P-shield e-
Moles (n)
mass/molar mass
% error
(A-T)/T x 100
Bond order
(bonding-anti bonding)/2
Molarity (M)
moles solute/L solution
Absorption
(molar extinction coefficient)(conc- M)(path- cm)
vapor-pressure depression
x*p, x=mole fraction of solvent (mol solv/(mol solvent + mol solute)), p=pure vapor pressure of solvent
freezing pt depression
-kfim, m=molality
bp elevation
kbim, m=molality
osmotic pressure
iMRT, R=0.0821
Pressure
F/A
1/2 life
initial(1/2)^n, n=# half lives
Single step rxn rule
halogens higher up are more reactive
ex. won't see CaF2+Br2->CaBr2+F2
Endothermic
heat absorbed, solid to gas
Exothermic
heat released, gas to solid
Deposition
gas to solid
Sublimation
solid to gas
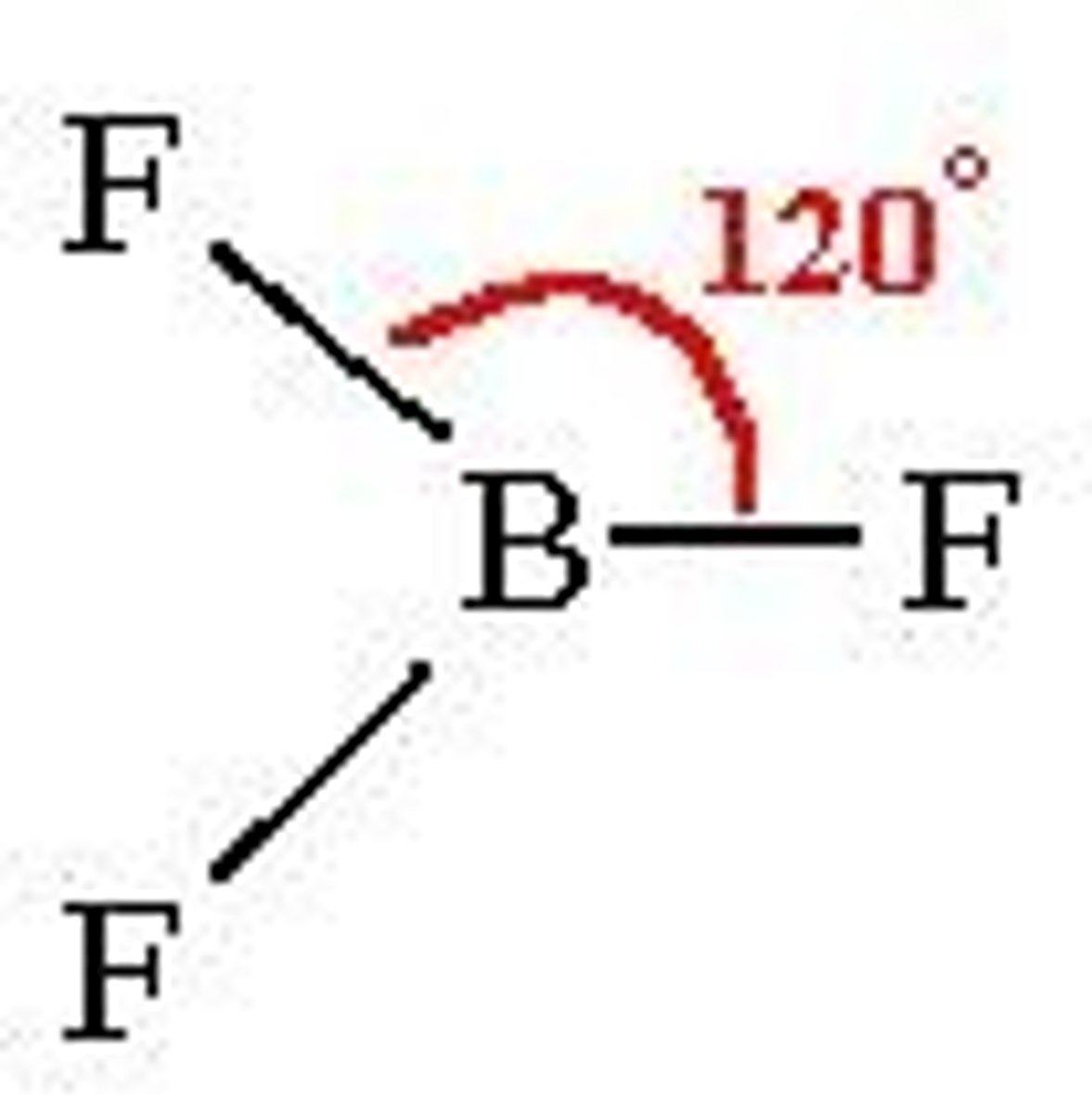
Trigonal planar
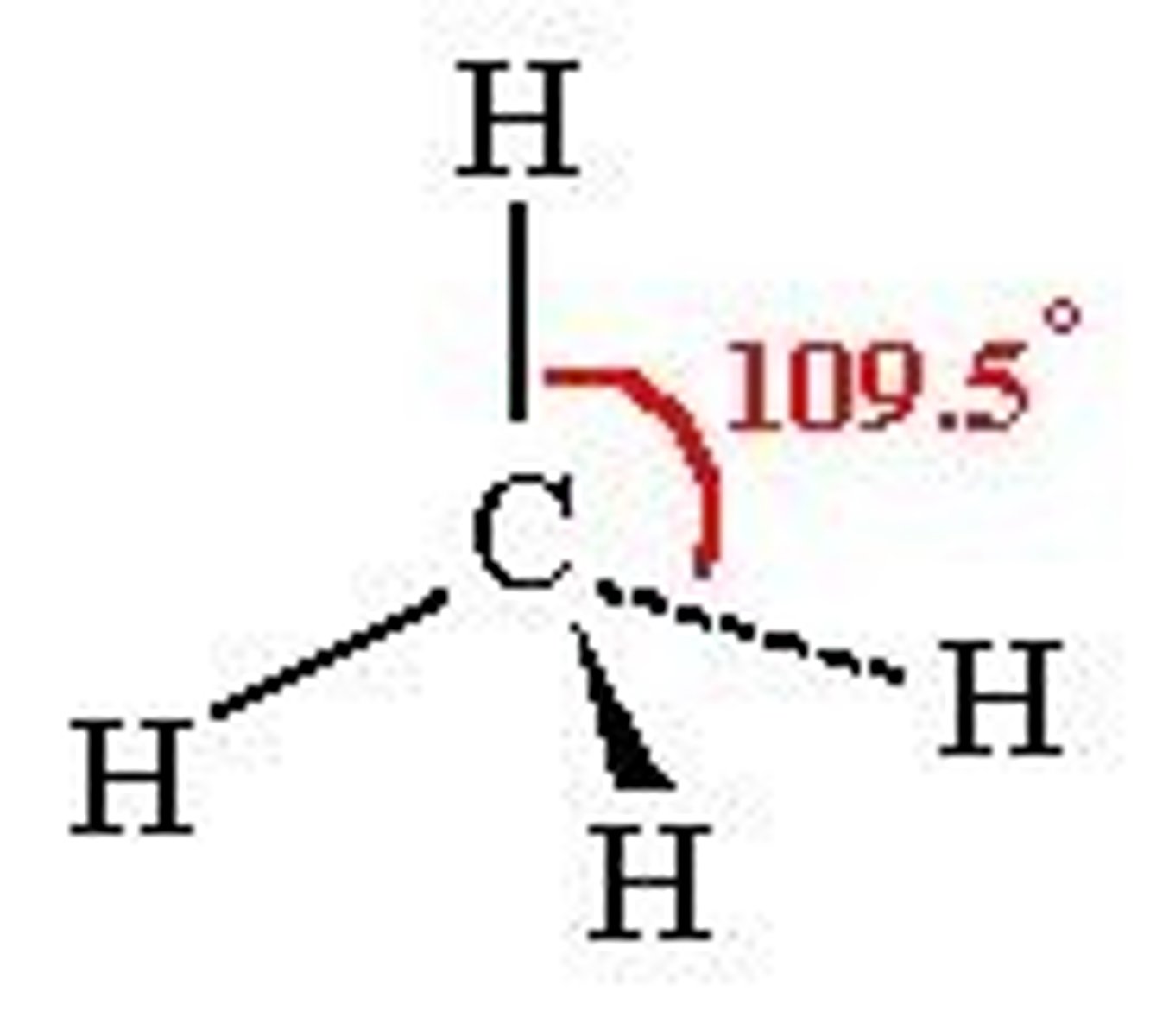
Tetrahedral
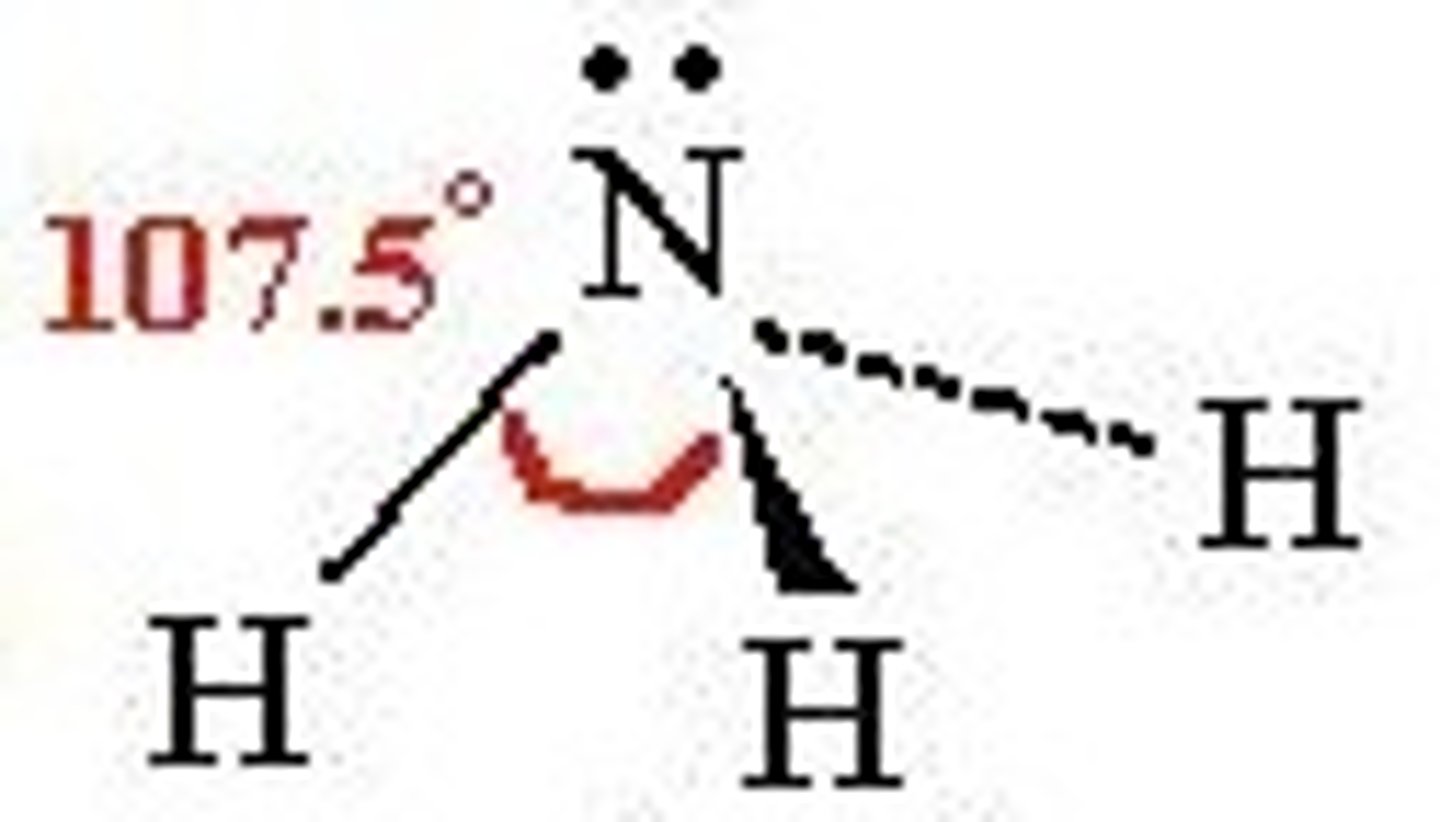
Trigonal pyramidal
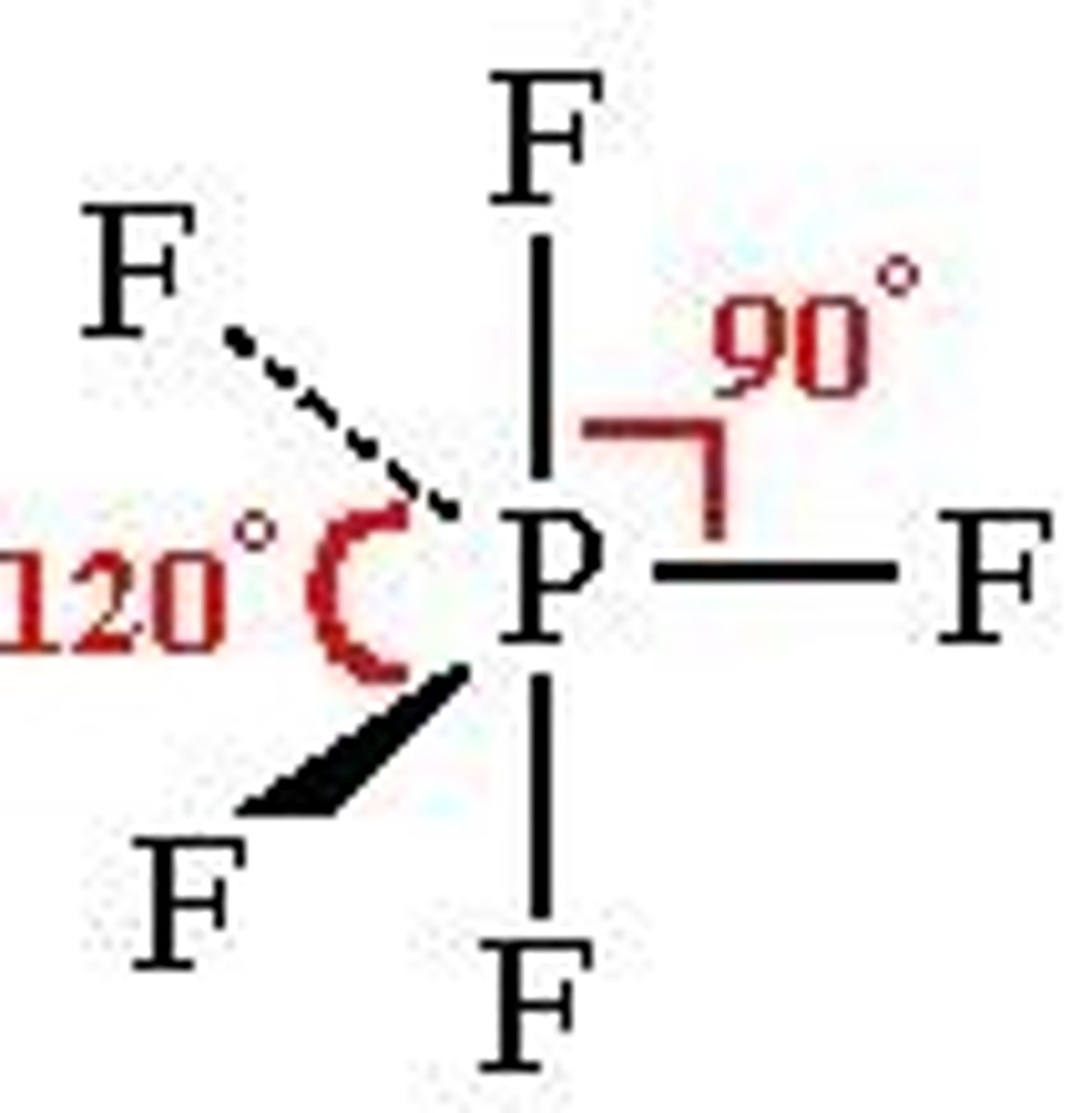
Trigonal bipyrimidal
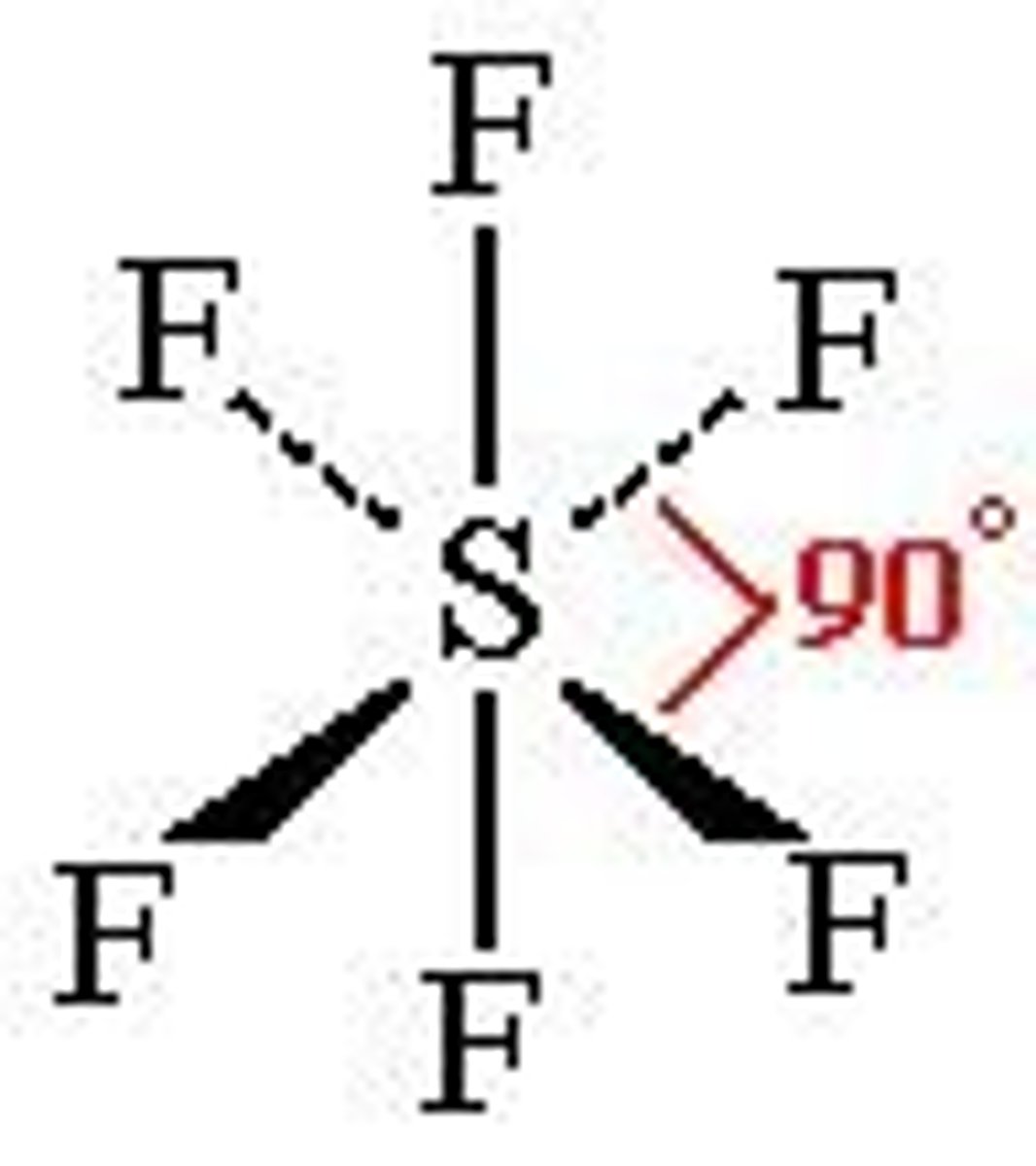
Octahedral
alpha decay
A-4, Z-2
beta+ (positron)
A, Z-1
beta- (beta)
A, Z+1
e- capture
A, Z-1
gamma decay
A, Z
Enthalpy
△H=Hprod-Hreact
=n(△Hprod)-m(△React), don't include mol in standard state (ex. O2, Cl2)
=bonds broken (react)-bonds formed (prod)
△H>0
Endothermic, break bonds
△H<0
Exothermic, form bonds
Entropy

Does increase dissolution (aq) increase/decrease entropy?
Increase
Does #product mol>#reactant mol increase/decrease entropy?
Increase
Positive work (+w)
Compressed, work done on system, △V<0
Negative work (-w)
Expansion, work done by system, △V>0
Internal energy △U
△U=q+w
Work given pressure and volume
w=-p△V, p=pressure
heat given mass and heat fusion/vap
q=m△H
Calorimetry equations
qrxn=-qcal, qcal=C△T
Reaction rate, Aa+Bb→Cc+Dd
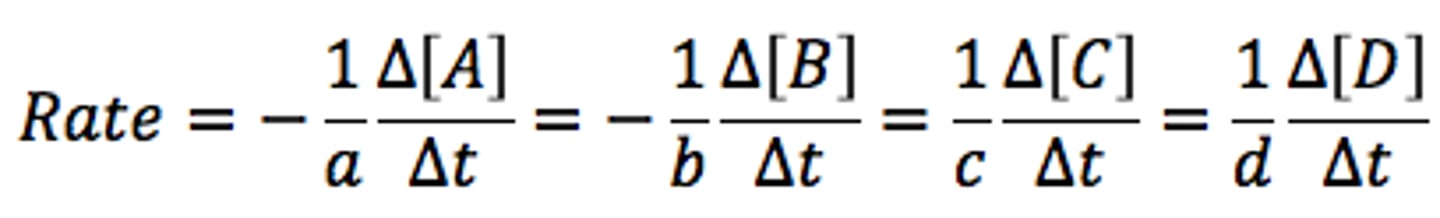
Rate and order, A+B→C+D
rate=K[A]^m[B]^n
order=m+n (if 0, then not depend on reactants)
k and rate when temp increases
both increase
k and rate when decrease in Ea (add catalyst)
both increase
k and rate when reactants increase
k same, rate increase
Free energy (△G)
△G=△H-T△S
△G>0
Endergonic, not spontaneous
△G<0
Exergonic, spontaneous
-△H, △S, -△G
Spontaneous
-△H, -△S, -/+△G
Spontaneous (low T), not spontaneous (high T)
△H, △S, -/+△G
Spontaneous (high T), not spontaneous (low T)
△H, -△S, △G
Not spontaneous
keq and result when -△G
keq>1, product fav
keq and result when △G
keq<1, reactants fav
keq and result when △G=0
keq=1, equilibrium (not spontaneous or spontaneous)
0 order
rate=k
k=m/s
conc/t graph straight w negative slope
[A]/t graph straight w negative slope
slope=-k
decrease concentration is decrease 1/2 life
![<p>rate=k</p><p>k=m/s</p><p>conc/t graph straight w negative slope</p><p>[A]/t graph straight w negative slope</p><p>slope=-k</p><p>decrease concentration is decrease 1/2 life</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/4ea9b106-3f5b-407b-bbe0-25f37d3f6872.jpg)
1st order
rate=k[A]
k=s^-1
conc/t graph curved w negative slope (exponential)
ln[A] graph curved w negative slope
slope=-k
1/2 life=0.693/k
![<p>rate=k[A]</p><p>k=s^-1</p><p>conc/t graph curved w negative slope (exponential)</p><p>ln[A] graph curved w negative slope</p><p>slope=-k</p><p>1/2 life=0.693/k</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/bf887ecd-998b-463d-9ce7-2bbe7cfba9a5.jpg)
2nd order
rate=k[A]^2
if A+B→C+D, rate=k[A][B]
k=M^-1S^-1
conc/t graph curved w negative slope (exponential)
1/[A] graph straight w positive slope
slope=k
decrease conc, increase 1/2 life
![<p>rate=k[A]^2</p><p>if A+B→C+D, rate=k[A][B]</p><p>k=M^-1S^-1</p><p>conc/t graph curved w negative slope (exponential)</p><p>1/[A] graph straight w positive slope</p><p>slope=k</p><p>decrease conc, increase 1/2 life</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/30afd50c-0913-4d16-a83e-5d18a3be5abc.jpg)
equation to work out k for order reaction
k=m^1-n, s^-1
k=Ae^(-Ea/RT), Ae=frequency factor, Ea=activation energy
pH
-log[H+]
pKa+log[A-]/[HA]
pOH
-log[OH-]
[H+]
10^-pH
[OH-]
10^-pOH
pKa
-logKa=([H+][A])/[HA]
Kw
=1 x 10^-14 at 25C
=[H+][OH-], 1x10^-7 each
=Ka(Kb)
Reducing agent
Oxidized, oxidation # increases, gains oxygen, loses H
H2, Fe, Zn, alkali metals
Oxidizing agent
Reduced, oxidation # decreases, gains H, loses oxygen
O2, O3, H2SO4, halogens
Oxidation number for oxygen
-2