Plant hormones and growth in plants
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/33
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
1
New cards
What are tropisms?
Directional growth responses that plants carry out in reaction to specific stimuli
- Light
- Gravity
- Light
- Gravity
2
New cards
What are some abiotic stressed plants have?
- Lack of water
- Herbivory
- Competition
- Light pH and temperature changes
- Herbivory
- Competition
- Light pH and temperature changes
3
New cards
Important plant hormones
- Auxins
-Gibberellins
- Abscisic acid (ABA)
- Ethene
-Gibberellins
- Abscisic acid (ABA)
- Ethene
4
New cards
Auxin's roles in plants
- Controls cell elongation
- Growth stimulants
- Prevents abscission
- Maintains apical dominance
- Tropisms
- Stimulates ethene release
- Fruits ripening
- Growth stimulants
- Prevents abscission
- Maintains apical dominance
- Tropisms
- Stimulates ethene release
- Fruits ripening
5
New cards
Gibberellin's roles in plants
- Stem elongation
- Triggers food store mobilisation at germination
- Stimulates pollen tube growth in fertilisation
- Triggers food store mobilisation at germination
- Stimulates pollen tube growth in fertilisation
6
New cards
Ethene's roles in plants
- Ripens fruits
- Promotes abscission in deciduous trees
- Promotes abscission in deciduous trees
7
New cards
ABA's roles in roles
- Maintains dormancy of seeds and buds
- Stimulates cold protective responses
(antifreeze production, stomatal closing)
- Interferes with the action of
Gibberellin
- Stimulates cold protective responses
(antifreeze production, stomatal closing)
- Interferes with the action of
Gibberellin
8
New cards
What is abscission?
Dropping of leaves, flowers, or fruit
9
New cards
What do plants produce chemicals for?
- Signal to other species to protect against insects
- Defences against herbivores
- Defences against herbivores
10
New cards
What do plant hormones control?
Growth of plants
- Germination of the seed
- Growth of a tree
- Germination of the seed
- Growth of a tree
11
New cards
What is germination?
The process by which a plant grows from a seed
12
New cards
Outline the process of germination
- Seed absorbs water
- Embryo activated and produces gibberellins
- Gs stimulate enzyme making (breaks down food stores in seed)
- Embryo plant uses stores to make ATP
- The plant can grow and break out the seed coat
- Embryo activated and produces gibberellins
- Gs stimulate enzyme making (breaks down food stores in seed)
- Embryo plant uses stores to make ATP
- The plant can grow and break out the seed coat
13
New cards
Where are the food stores in dicot seeds?
Cotyledon
14
New cards
Where are the food stores in monocot seeds?
Endosperm
15
New cards
What are the digestive enzymes needs for germination?
Amylase and protease
16
New cards
How are amylase and protease made for germination?
Gibberellins switch in genes that code for them
17
New cards
The effect of gibberellins on the synthesis of amylase in isolated tissue from barley seeds
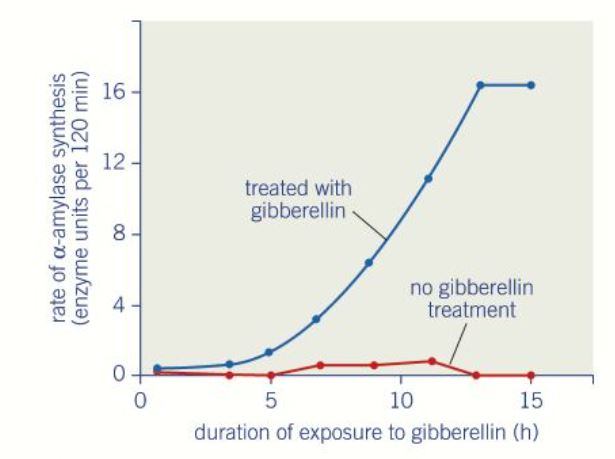
18
New cards
What affects whether a seed will germinate?
Gibberellins
Abscisic acid (Gs antagonist)
Abscisic acid (Gs antagonist)
19
New cards
What are some experimental evidence of the roll of gibberellins in germination?
1. Seeds have been made without gibberellins
2. Gibberellin biosynthesis inhibitors
* Seeds don't germinate
20
New cards
Role of gibberellins in germination
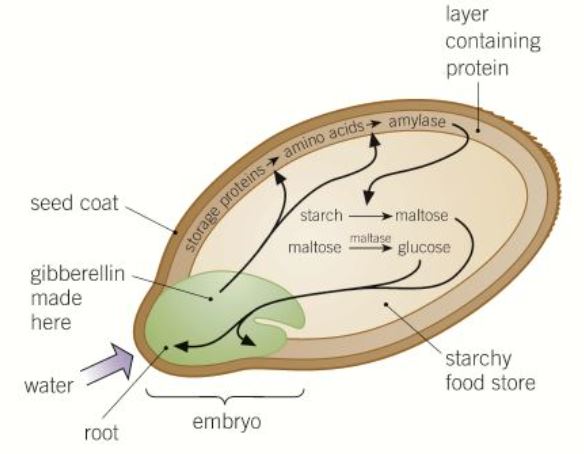
21
New cards
What do auxins do?
Cell elongation
22
New cards
Where are auxins made?
Tips of roots and shoots
Meristems
Meristems
23
New cards
What direction do auxins move in a plant?
Down the stem and up the root in transport tissue from cell to cell
24
New cards
What does the effect of auxins depend on?
- Auxin concentration
- Interactions with other hormones
- Interactions with other hormones
25
New cards
What effects do auxins have on plant growth?
- Stimulate growth of apical shoot
- High concs suppress growth of lateral shoots
- Low conc promote root growth
- High concs suppress growth of lateral shoots
- Low conc promote root growth
26
New cards
How do auxins stimulate the growth of the main apical shoot?
* Auxin binds to specific receptor sites in the plant cell membrane
* pH falls to 5 (op pH for enzymes to keep walls flexible and plastic)
* Cells mature, auxin is destroyed, pH rises, enzymes are inactive, walls are rigid no growth
* pH falls to 5 (op pH for enzymes to keep walls flexible and plastic)
* Cells mature, auxin is destroyed, pH rises, enzymes are inactive, walls are rigid no growth
27
New cards
The effect of auxin on apical shoot growth
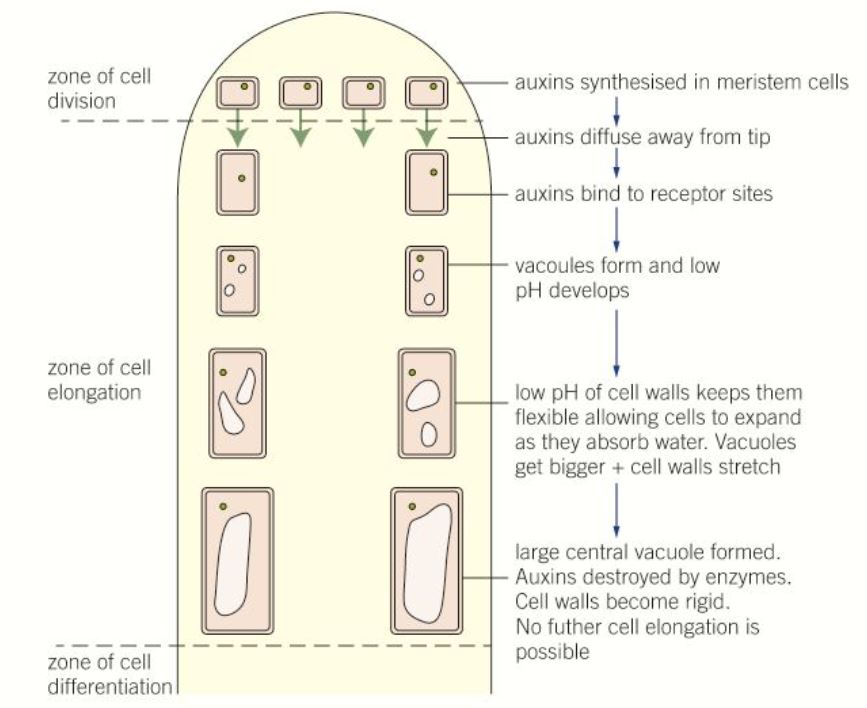
28
New cards
Graph to show the effect of an external application of auxin on pH levels in the cell walls and on shoot growth
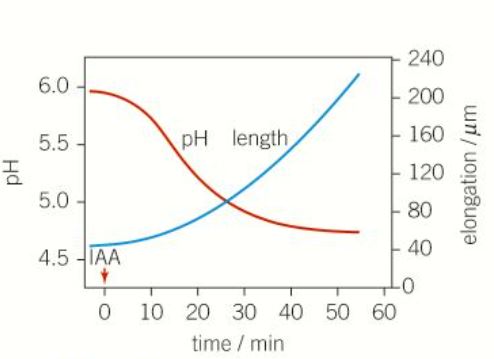
29
New cards
How do high concs of auxins suppress the growth of the lateral shoots?
- Results in apical dominance
- Lateral shoots are inhibited at the tip
- Further down conc is low so lateral shoots are stimulated
- Lateral shoots are inhibited at the tip
- Further down conc is low so lateral shoots are stimulated
30
New cards
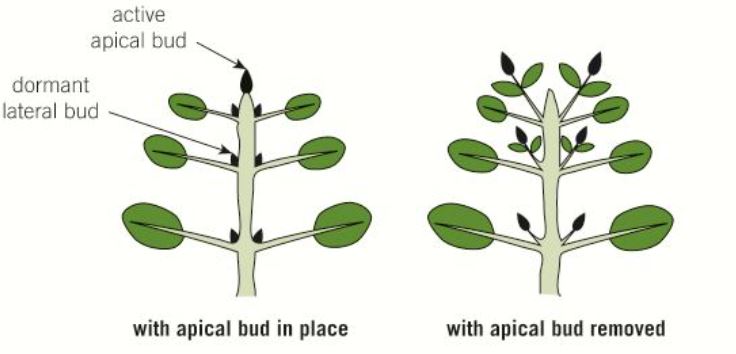
What is apical dominance?
Suppression of the growth of lateral buds by hormones produced by the apical meristem.
31
New cards
Apical dominance affects the form of a plant and can be clearly seen in conifers
32
New cards
How do low concs of auxins promote root growth?
- If apical shoot is removed the amount of auxin reaching roots is decreased
- Root growth slows
- High concs inhibit root growth
- Root growth slows
- High concs inhibit root growth
33
New cards
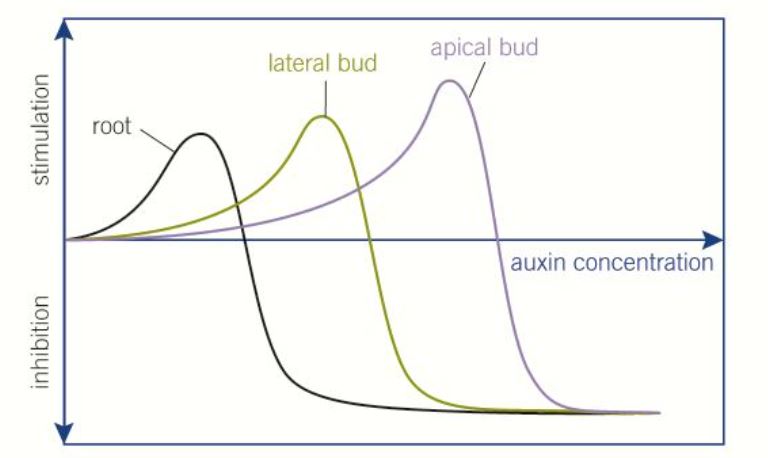
Effect of auxin on roots, lateral and apical buds
Auxin can inhibit and stimulate
- Highest conc apical bud is most stimulated
- No cell elongation
- Further down stem lateral bud is stimulated
- Cell elongation
- Lowest conc promotes root growth
- Highest conc apical bud is most stimulated
- No cell elongation
- Further down stem lateral bud is stimulated
- Cell elongation
- Lowest conc promotes root growth
34
New cards
What do gibberellins affect?
Length of internodes
- regions between leaves on a stem
- regions between leaves on a stem