Biology: Osmosis
1/23
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Created on 25/9/24.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Osmosis
The movement of water molecules across a semi-permeable membrane from a region of high water concentration to a region of lower water concentration.
Diffusion
The movement of molecules from a region of high concentration to a region of lower concentration.
Give two examples of diffusion
1.) Water entering xylem of a leaf.
2.) Gas exchange in capillaries in the lungs.
What is osmosis known as
A special type of diffusion.
Membranes can be
1.) Impermeable
2.) Semi or selectively permeable
3.) Permeable
Impermeable
Substances can’t pass through.
Semi or selectively permeable
Allows some, but not all substances to pass through.
Permeable
Substances can pass through.
Turgor/Turgor pressure
The pressure the cytoplasm and vacuole exert on the cell wall of a plant.
What does turgor do for plants
Gives more strength to plants with no wood.
Turgid cell
When the cell is enlarged and swollen with water.
Plasmolysis
The movement of the cell membrane away from the cell wall.
What does plasmolysis do for plants
Causes plants to wilt
What is tonicity
Refers to the solute concentration.
Isotonic
Same solute concentration in solution as in the cytoplasm.
Water enters and leaves at same rate.
Hypotonic
Lower solute concentration in solution than in the cytoplasm.
Water enters cell.
Hypertonic
Higher solute concentration in solution than in the cytoplasm.
Water leaves the cell.
Effect of hypotonicity on animal and plant cell
Animal cell: Cell swells and bursts
Plant cell: Makes cell turgid
Effect of hypertonicity on animal and plant cell
Animal cell: Cell shrivels and bursts
Plant cell: Cell is plamolysed
Effect of isotonicity on plant cell
Cell is flaccid (flabby).
Crenation
Cells shriveling and dying when water leaves.
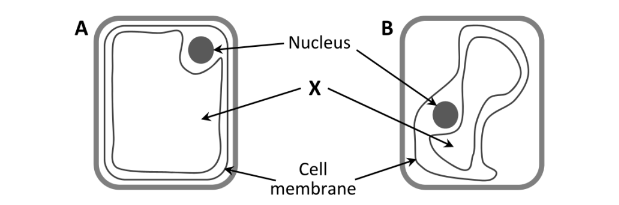
Which cell is turgid?
A
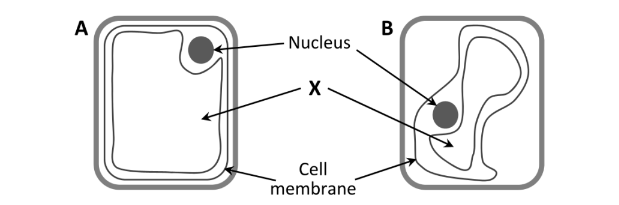
Explain in detail what has happened to cell B
The cell membrane moved away from the cell wall due to a loss of water.
Active transport
The movement of molecules (usually ions) from a region of lower concentration to a region of higher concentration (opposite of diffusion and energy is required).