Electric charges
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
Amber
A hard, translucent, fossilized resin from extinct trees
Thales of Miletus
The Ancient Greek philosopher to:
1) Record that when amber was vigorously rubbed with a piece of fur, a force was created that caused the fur and the amber to be attracted to each other
2) Rubbed amber would not only attract the fur, and fur attract the amber, but they both now could affect the other non-metallic objects even if they are not in contact with those objects.
William Gilbert
The English physicist who studied attractive forces using various substances:
1) Worked with amber
2) Experimented with rock crystal and various precious and semi-precious gemstones
3) Experimented with several metals, to find out, metals never exhibited such forces, whereas the minerals did.
4) Also saw how an amber rod would repel another amber rod.
directions, electric forces, charge
The difference between the two types of electric charge is in the __________ of the ______________ that each type of ______ causes.
repel, attract
Like charges _____ and unlike charges _______.
coulomb (C)
SI unit of electric charge
Charles-Augustin de Coulomb
French physicist after whom the SI unit of the Electric charge was named.
physical contact, long-range
The most peculiar aspect of the electric force is that it does not require ________________ between the two objects in order to accelerate. Making it a __________ force.
Benjamin Franklin
The American physicist and statesman to found out that he could concentrate the charge in a Leyden jar
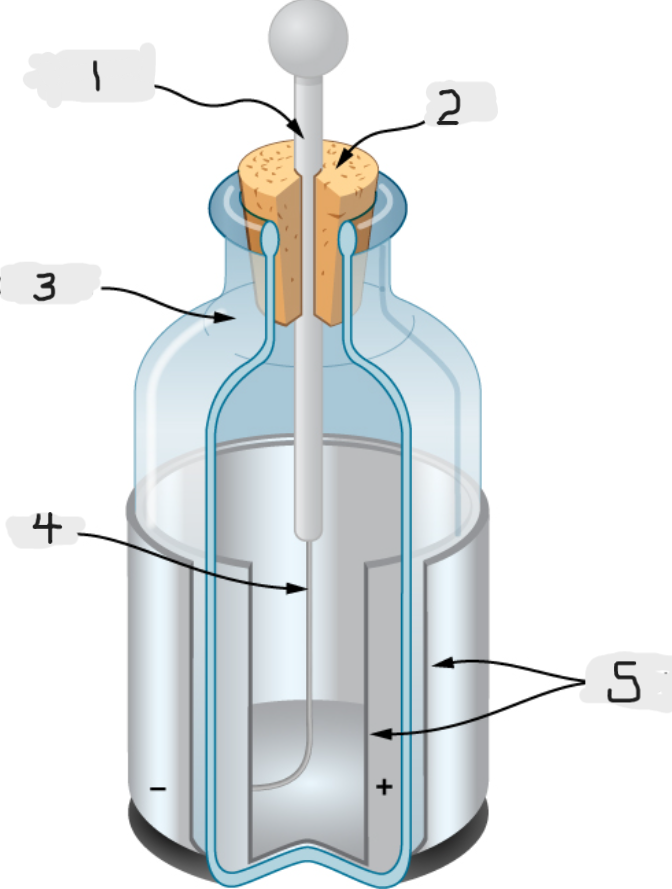
Leyden Jar
Essentially a glass jar with two sheets of metal foil, one inside and one outside, with the glass between them.
This created a large electric force between the two foils sheets
We would basically call this an early version of capacitor.
Metal rod
(1)
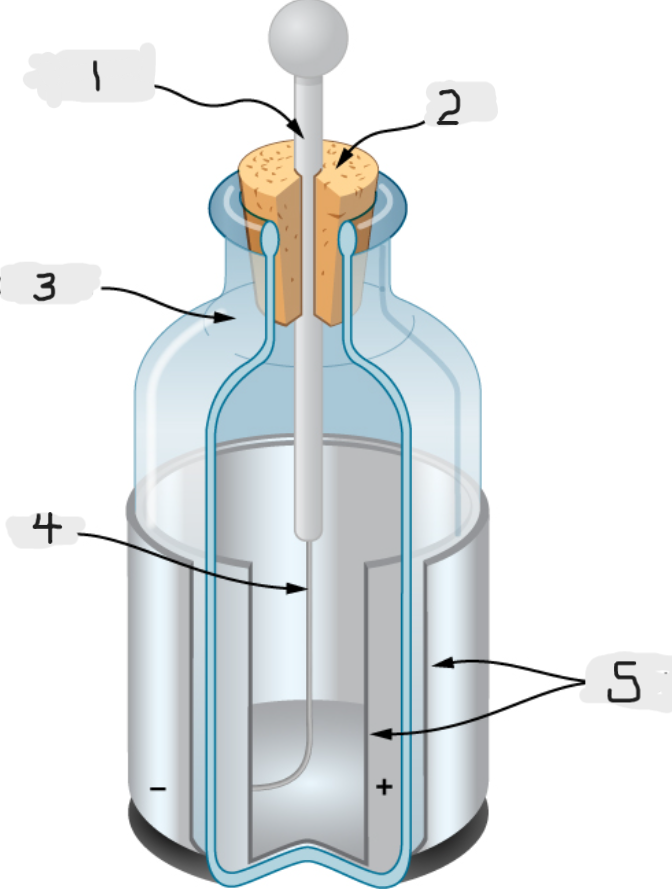
Top
(2)
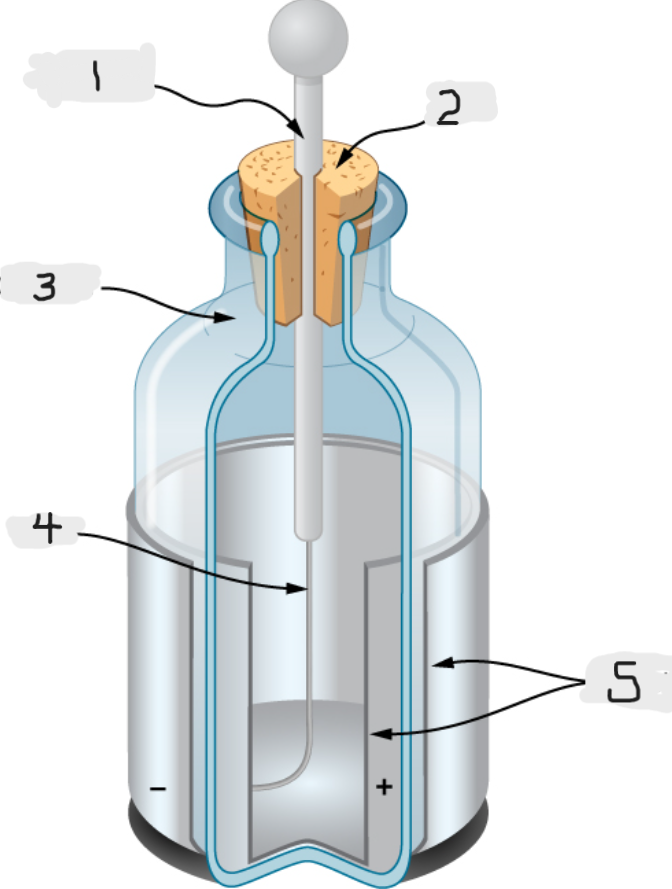
Glass jar
(3)
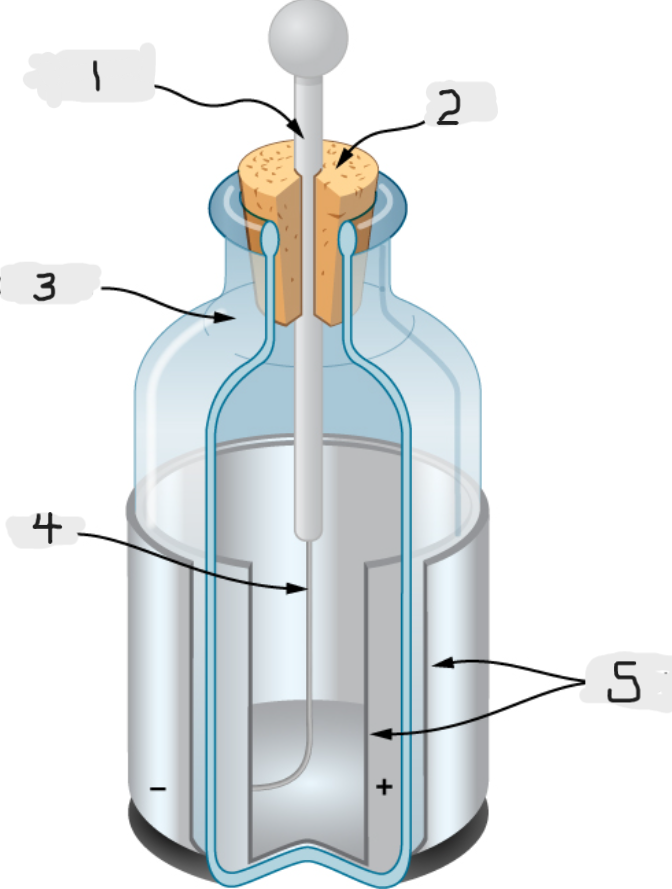
Wire
(4)
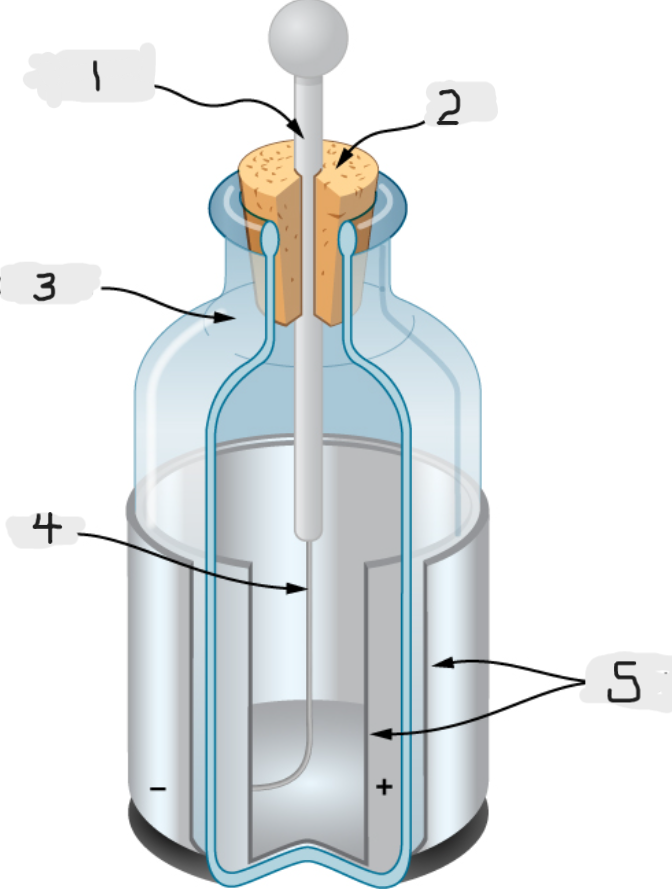
Tin foil
(5)
Negative charges
________________ are the ones that flow from one piece to the another.
Positive charges
________________ are the ones that largely remain motionless.
Electrostatic attraction
The type of force that is attractive because of the two unlike charges coming close to each other.
Electrostatic repulsion
The type of force that is repulsive because of the two like charges coming close to each other.
Yes, it is true.
Is it true that not all objects are affected by the electric force?
decreases rapidly, increasing, distance
The magnitude of the electric force _________________ with __________ separation ________ between the two objects.
decreases, one-fourth, decreases, square, distance, increases.
When the distance between two interacting object is doubled, the force between them _________ to _________ what it was in the original system. Stating that the force between two objects _________ as the ______ of the ________ between the two interacting object _________.
quantized
The electric charge is quantized
e
Symbol to represent the elementary electric charge
1.602×10^-19 C
Value of the elementary electric charge
+1.602×10^-19 C
The smallest possible positive charge
-1.602×10^-19 C
The smallest possible negative charge
conserved, created, destroyed, transferred, constant
Electric charge is _________. Charge can neither be _______ nor _________; it can only be ___________ from one place to another. The net electric charge of the universe is ________.
The law of conservation of charge
1) The total charge in the local system is changing. There will be a measurable flow of charge into or out of the system.
2) Charges can move around and their effects can cancel out, but the net charge in the local system (if closed) is conserved.
Nuclear physics
The branch of physics that studies the structure, behavior, and interactions of the atomic nucleus.