unit 3 aos 2 - learning and memory
1/82
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
83 Terms
learning def
relatively permanent behaviour change from experience
can be intentional or unintentional
can be passive or active
behaviourist approaches to learning
learning from associations between envo stimuli and behavioural responses
classical conditioning
operant conditioning
stimulus def
event or something that detected through senses
response def
behaviour responding to stimulus
classical conditioning def
involuntary passive learning involving repeated association of two or more diff stimuli
how to know learning has occurred via classical conditioning
when the CS consistently produces response it didn’t previously cause
classical conditioning 3 phase model
BEFORE CONDITIONING:
NS (state) produces no response
UCS (state) produces UCR (state behaviour @ ucs)
DURING CONDITIONING:
the NS (state) is presented multiple times immediately before UCS (state) to produce UCR (state)
AFTER CONDITIONING:
the NS (state) becomes the CS and on its own can produce CR (state behaviour @ CS)
aversion therapy and classical conditioning
used to condition people to stop unwanted behaviour
e.g. using foul smelling substance painted on nail to stop nail biting
operant conditioning def
active learning where likelihood of a voluntary behaviour occurring is influenced by its consequences
operant conditioning 3 phase model
ANTECEDENT:
envo cue to trigger behaviour
object or event
BEHAVIOUR:
voluntary response to antecedent
CONSEQUENCE:
occurs after behaviour response
can be reinforcement (increases likelihood of behaviour repeated in future) or punishment (decreases likelihood of behaviour repeated in future)
— positive reinforcement: add desirable stimulus
— negative reinforcement: take away undesirable stimulus
— positive punishment: add undesirable stimulus
— negative punishment: take away desirable stimulus
operant conditioning factors affecting reinforcement and punishment
order of presentation: consequence needs to occur after behaviour so learner makes association
timing: consequence needs to occur close as possible after behaviour
appropriateness of consequence: it has to actually impact/be relevant to learner
classical conditioning vs operant conditioning
CC is learning via association of two unrelated stimuli, OC is learning via association of behaviour and consequence
CC 3 phases is before, during, after conditioning, OC 3 phases is antecedent, behaviour, consequence
CC learner is passive, OC learner is active
CC response is involuntary, OC response is voluntary
observational learning
when learner uses observation of a model’s actions + the consequences to guide their own future actions
the 5 steps of observational learning
ARRMR
attention
retention
reproduction
motivation
reinforcement
observational learning step 1
ATTENTION
learner actively watches model’s actions and the consequences
more similarities between model and learner = more successful model = more chance learner imitate behaviour
learner more likely actively watch if model: is attractive, has high status, likeable or similar to learner age or gender
observational learning step 2
RETENTION
learner retain mental representation of model’s behaviour over time for future use
observational learning step 3
REPRODUCTION
learner must have physical and mental capabilities to perform behaviour
observational learning step 4
MOTIVATION
learner desires to perform behaviour
if behaviour has known reward = higher desire to perform behaviour
observational learning step 5
REINFORCEMENT
behaviour consequence influences learner’s likelihood of repeating it in future
if behaviour reinforced = more likelihood learner repeating behaviour in future
can be external (learn by direct consequences), vicarious (learn from other’s consequences of that behaviour), self (learn from reaching goals we set ourselves)
exam trap for observational learning model
when doing ARRMR, after attention and retention the behaviour is being performed not learned
vicarious learning
classical and operant conditioning can occur vicariously by observational learning — vicarious conditioning
learner watches model’s behaviour + consequences → either reinforcement or punishment → then they behave same way, modified way or avoid behaving that way in future
bandura’s bobo doll experiment is on this
ATSI knowledge systems…
oldest + longest continuing form of learning in aus
are unique and complex that diff to western concepts of learning
is diverse across diff language + cultural grps
has connection + understanding between learner and teacher
is multimodal (learning thru many forms)
learner in ATSI knowledge systems
situated within a system of relationships and on Country
Country in ATSI knowledge systems
lands, waters, skies which First Nations peoples are connected thru ancestral ties
kinship connections in ATSI knowledge systems
relationships people have with others, and the knowledge + entities within Country they are responsible for
the 8 ways of knowing — multimodal learning
story sharing (learning via narrative)
symbol & images (learning via images and metaphors e.g. using art or objects to understand/represent concepts)
learning maps
non verbal
community links
deconstruct/reconstruct
non-linear
land links
observational learning + ATSI ways of knowing
older inds model behaviours to younger inds in community so they can mimic
model behaviours in natural contexts
behaviour replicated generationally
memory def
active info-processing system that receives, stores, retrieves info
memory process
sensory input → encoding (conv sensory input into usable code that can be stored in memory) → storage (holds encoded info for time period) → retrieval (locates stored info and returns to consciousness when needed)
atkinson and shiffrin's multi-store model of memory
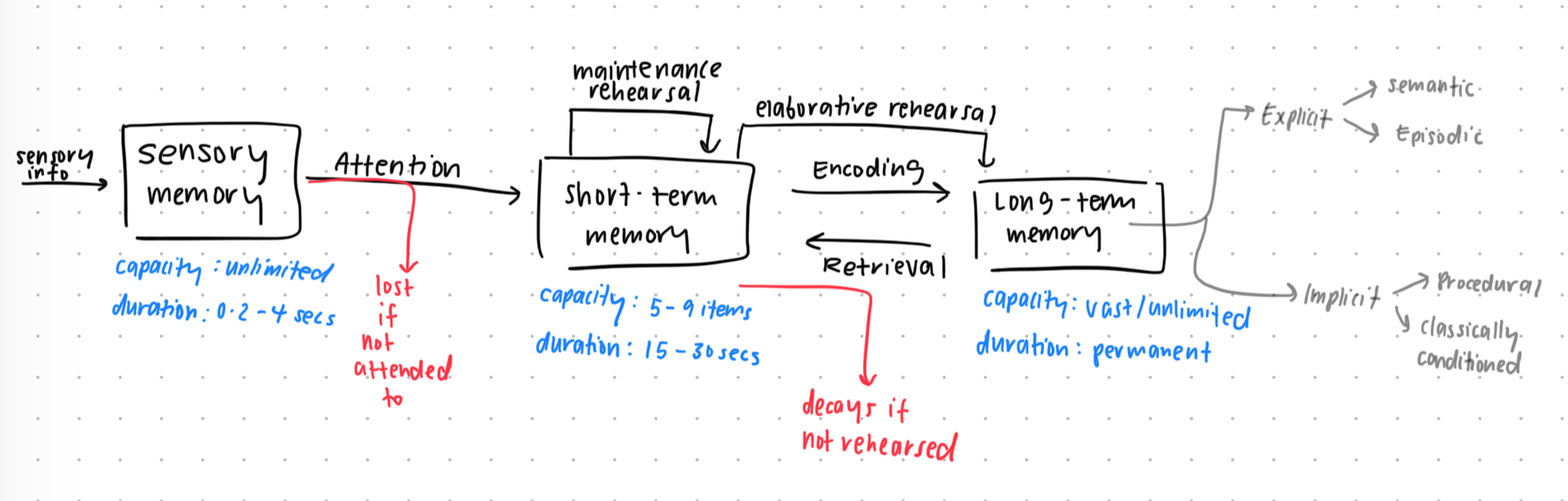
sensory memory def
stores info in its exact sensory form
(f): prevents us being overwhelmed as filters out sensory info not relevant
quick forgetting allows us to see world smoothly
if given attention to then moved to short term memory but if not then forgotten
capacity = unlimited
duration = 0.2 to 4 seconds
short term memory def
stores info ind is consciously aware of at any moment
capacity = 5-9 info pieces held at one time
duration = 15-30 seconds
varies between ppl
when full — new pieces only added by pushing others out
aka working memory (combines new info from sensory memory with stored info from LTM for mental activities)
short term memory — chunking and maintenance rehearsal
chunking → increases STM capacity by storing groups of items instead of singular items
maintenance rehearsal → increases STM duration via rote repetition of info → if interrupted then info lost quickly
long term memory
relatively permanent memory storing large amounts diff info
info is inactive and needs to be retrieved to STM for use
diff info types stored in diff types LTM
storage capacity = vast, maybe unlimited
storage duration = maybe permanent
elaborative rehearsal def
encoding via linking new info meaningfully to other new info or old info already stored LTM
more effective than maintenance rehearsal → more active process, and linking info creates cues to help locate and retrieve info later
use of mnemonics as an example of this?
LTM - explicit memory
memory with awareness
semantic memory = facts + knowledge about world (includes general and academic knowledge, rules, word meanings etc)
episodic memory = personally experienced events (can include details like time, place, psychological state when event occurred, like a personal mental diary of our life’s episodes)
LTM - implicit memory
memory without awareness
procedural memory = motor skills + actions (skill learned then shown through perfomance that needs little attempt to retrieve info, e.g tying shoelaces) — cerebellum, basal ganglia?
classically conditioned memory = conditioned response to conditioned stimuli (via classical conditioning) — amygdala?
explicit memory vs implicit memory
em = retrieve memory with awareness, im = retrieve memory without awareness
em subtypes = episodic + semantic, im subtypes = procedural + classically conditioned
em example = remember phone number, im example = knowing how to tie shoelaces
strengths and limitations of the memory model
— strengths: easy to understand, easy to test and gives high reliability, clear structure and division of memory process shown
— limitations: sometimes considered to be oversimplified, doesn’t account for ind diffs, can contradict recent studies that show info transfer into LTM can happen w/o rehearsal
amygdala
consolidates implicit memories that involve emotions
initiates F/F/F response and stress hormones
involved with classical conditioning emotional responses (fear anger mostly)
interacts with hippocampus = after encoding implicit part of memory it then activate hippocampus → to encode explicit event as significant (signal hc to encode explicit part of memory?)
hippocampus
consolidates
+ retrievesnew explicit memorydoesn’t store memories here
just transforms temp memory in STM to permanent memory in LTM (consolidation def)
interacts with amygdala to link emotions to explicit memories
neocortex
storage of explicit (and implicit?) memory
links tgt diff info during retrieval
top layer of cerebral cortex
amygdala, hippocampus, neocortex interactions
amygdala consolidates implicit memories that involve emotions → signals to hc to consolidate and encode explicit memories that have implicit emotions → hc does this→ sent to neocortex to store explicit memories
cerebellum
encodes and stores implicit memories involved with movement coordination
needed for motor learning + voluntary movementfocuses on coordination of motor skills + classically conditioned simple reflexes
basal ganglia
consolidates and stores implicit memories involved with habits + performance of sequenced actions fluidly
+ conditioned motor responsesplans
and coordinatesfine motor control for sequenced actions from implicit memories in fluid manner + automatically — e.g. habitsnot memories associated with emotions
cerebellum vs basal ganglia
both consolidates implicit procedural memories
both involved in fine motor skills
c = voluntary motor skills, bg = habits
c = focus on coordination motor skills (movement coordination), bg = focus on motor skills performed fluid + fast (performance of sequenced actions fluidly)
cerebellum, basal ganglia and neocortex interactions
cerebellum and basal ganglia interact → memories associated with habit formation, movement coordination, performance sequenced actions fluidly fine motor movements, reflexes sent to neocortex → neocortex stores these as implicit long-term memories
but cerebellum can store its own memories too?
surgery on hippocampus
issues consolidating new explicit memories into LTM
doesn’t affect procedural (implicit?) memories
when one removed no major effect but if two then significant issue
surgery on amygdala
issues consolidating implicit memories invovled with emotions
cannot recognise emotions in others esp fear
cannot develop conditioned fear responses
surgery on cerebellum
issues consolidation + storage of implicit memories involved with movement coordination (procedural)
surgery on neocortex
issues storage + retrieval of specific explicit memories (and some implicit?)
depends on lobe and hemisphere surgery on
surgery on basal ganglia
issues consolidating and storing/retrieving implicit memories involved with habits and performance sequenced actions fluidly
when we retrieve past events and imagine future events…
semantic and episodic memories can interact as LTM
autobiographical memory def
memory system of episodes recalled from ind’s life as mix of episodic + semantic memories
type of explicit LTM
involves reconstruction (combine stored info tgt to form coherent complete memory)
hippocampus and neocortex allow retrieval (MRI shown)
episodic vs autobiographical memory
episodic memory = series of single past events
autobiographical memory = linking multiple past events tgt to form personal history
episodic future thinking
episodic and semantic memory interact and work together to construct future possible scenarios
projecting yourself forwards in time to pre-experience event that might occur in personal future
hippocampus and neocortex lobes activated for this (MRI shown)
episodic vs semantic memory to forget
episodic more easily forgotten than semantic
because new info constantly into episodic hence hard to encode + store all (as we are constantly experiencing new events but not necessarily constantly learning new facts about world?)
alzheimer’s disease def
type of dementia involving gradual widespread neuron degeneration
progressively causes memory decline + declining cognitive and social skills + personality changes
type of neurodegenerative disease
how to diagnose alzheimer’s disease
via CT, MRI, fMRI scans
but note only post-mortem study can view brain lesions properly
note MRI’s don’t show active brain → series of scans taken over period of time → physicians track changes in scans (decline in brain struc)
what is alzheimer’s believed to be caused by
build up of amyloid plaques and neurofibrillary tangles
amyloid plaques def
protein build ups outside neurons → affects synapses → disrupt neural transmission
neurofibrillary tangles def
protein build ups inside neuron → stops substances passing thru → neuron dies
neuronal death — alzhiemer’s disease
begins in hippocampus → move outwards to cerebral cortex→ to hindbrain
alzheimer’s disease symptoms
— as neuronal death begin in hippocampus → STM difficulties + forming new explicit LTMs (anterograde amnesia) → disease progresses → autobiographical memory decline→ semantic memory declines → recognition ability declines → episodic future thinking declines → later stages → procedural memories decline → person lose ability to perform skills (e.g. eating, swallowing, moving)
aphantasia def
disorder where ind lacks ability. to generate mental imagery
people with vs people without aphantasia
ppl without = use episodic and semantic memory to create mental imagery
ppl with = unable to visualise richly detailed episodic memories as unable to generate mental imagery → use semantic only?
people with aphantasia also…
struggle to retrieve autobiographical events + construct possible future scenarios → they just apply non-visual components hence more difficult + less vivid
mnemonic def
any technique that improves/enhances memory
mnemonic notes
active at encoding stage (of memory processing)
at same time of info encoding, retrieval cues also encoded
allows organisation + easier retrieval of info location in ltm with retrieval cues
organises as whole and connects new info to existing info → retrieval of part of it usually cause retrieval of all of it
types of mnemonics in sd
acronyms
acrostics
method of loci
written cultures def
stories and info shared & kept via reading and writing
e.g. mnemonics = acrostics, acronyms, method of loci
oral cultures def
ppl comm vital info and stories via word of mouth
e.g. mnemonics = stories, poems, sung narratives
mnemonic — acrostics
first letters of items create phrase to aid memory
useful for remembering order
link new info to familiar phrases to help encode + store info
first letter = retrieval cue to bring info to STM for use
e.g. north south east west = NESW = never eat soggy weetbix
mnemonic — acronym
first letter of items form pronounceable word to aid memory
link info to familiar words or sounds
first letter = retrieval cue to bring info to STM for use
e.g. SAME = sensory afferent motor efferent
mnemonic — method of loci
committing a familiar sequence of locations to memory → then visually link these with info that needs to be recalled
each location/landmark = retrieval cue that makes easier to retrieve info when needed
steps:
visualise familiar sequence of locations
/ routeselect memorable landmarks
create visual imagery for each item (the more bizarre / funny, more likelihood of item recall)
link each item to one landmark
imagine
walking route orbeing at location and retrieving each item by observing each landmark
similarities between acrostics, acronyms, method of loci
make info more elaborate
organise new info into cohesive whole
more useful for lists of info
useful for info that must be known but not understood
sung narratives def
story told thru singing, music, dance that contain large amounts cultural + moral teachings to others
— combo of techniques adds to mnemonic value
— more memorable as song + with song cycles
— usually related to specific landscape location
song vs sung narratives
sung narratives can just use rhythm (critical component) — music accompanies often drums or clapsticks
if song then has rhythm, music and may have tonal variation and envo sounds
Country for ATSI memory systems
landscape + cultural knowledge associated with it
songlines def
sequence of short sung narratives associated with specific locations as linked via physical or imagined path thru Country
— diff language groups diff words for songlines
— tells creation stories of ancestral journey thru landscape, seas, skies, knowledge of spiritual beliefs, laws, how to survive on Country, food and med sources
— can recall vast amounts info
— also can be sung maps of Country → connect diff clans and Nations along trade routes
— how knowledge is patterned on Country
— performances can evoke emotions → increases memory retrieval
neuroscience of songlines
hippocampus activated with spatial knowledge from info linking to landscapes → consolidates STM into LTM explicit memories via neural pathways → allows thinking of one aspect to trigger memory of other (info and location) = temporal snapshot
the more vivid or grotesque the story the more active brain neurons the more likely memory encoded and stored
songlines vs method of loci
songlines have performance of knowledge using song and movement at each location but method of loci just associates info to landmarks
songlines layer new info on top of what already known at each location but method of loci not necessarily layered
songlines basis of knowledge system from Country but method of loci not necessarily
songlines memory process
encoding = thru listening, repeating, practicing, instruction, observational learning
— strengthened via journey navigation, narrative structure, vivid imagery, emotions, rhythm and melody, dance, symbols in art
storage = within networks of kinship relationships between locations and entities in Country that song about + pathways thru Country store knowledge
retrieval = learning on then navigating thru Country enhances retrieval as more cues + brings to mind the song and story hence the knowledge