Unit 1: Earth Systems and Resources APES
1/120
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
121 Terms
When did the Earth form?
4.6 Billion Years Ago
How did the Earth form?
Huge clouds of gas debris collided with heavier elements produced by supernovae at extremely high tempratures
What formed as the earth cooled?
A solid crust
Four systems in the structure of the Earth
Lithosphere, hydrosphere, biosphere, atmosphere
The lithosphere
A brittle, rigid, and strong layer made up of the uppermost part of the mantle and the crust.
Divergent Boundaries
Two plates move away from each other. Magma from crust rises and cools. Can cause underwater mountains or valleys.
Convergent Boundaries (O+C)
Older oceanic plate subduct under less dense one, volcanic islands and earthquakes can happen.
Convergent Boundaries (O+O)
Denser oceanic plate subduct under less dense one, deep ocean trenches and earthquakes form
Convergent Boundaries (C+C)
Plates collide, crust crumples and folds. Can form large mountain ranges
Transform Boundaries
Plates slide past each other. Can form fault lines, shallow earthquakes, linear valleys.
Why do tectonic plates move?
The convection currents due to the temperature differences and plastic like nature of the mantle.
The Core (Inner)
Innermost portion of the earth. Primary composed of nickel and iron (solid). Very high density.
The Core (Outer)
Innermost portion of the earth. Primary composed of molten nickel and iron (liquid). Very high density.
The Mantle
Makes up majority of mass of Earth. Composed of magnesium, aluminum, and silicon-oxide compounds. Solid except for plastic like upper region.
The Crust
Outermost layer of earth.
Theory of Plate Tectonics
Lithosphere is made up of 7 major plates and several smaller ones.
Volcanoes
Typically occur at convergent plate boundaries. Due to the extreme heat of earth, large amounts of magma move up and can produce active volcanoes.
Effects of volcanic activity on the environment
Volcanic activity can destroy habitats and pollute air and water, but it also creates fertile soil, new land, and geothermal energy, supporting long-term environmental recovery.
Earthquakes
Caused by transform boundaries.
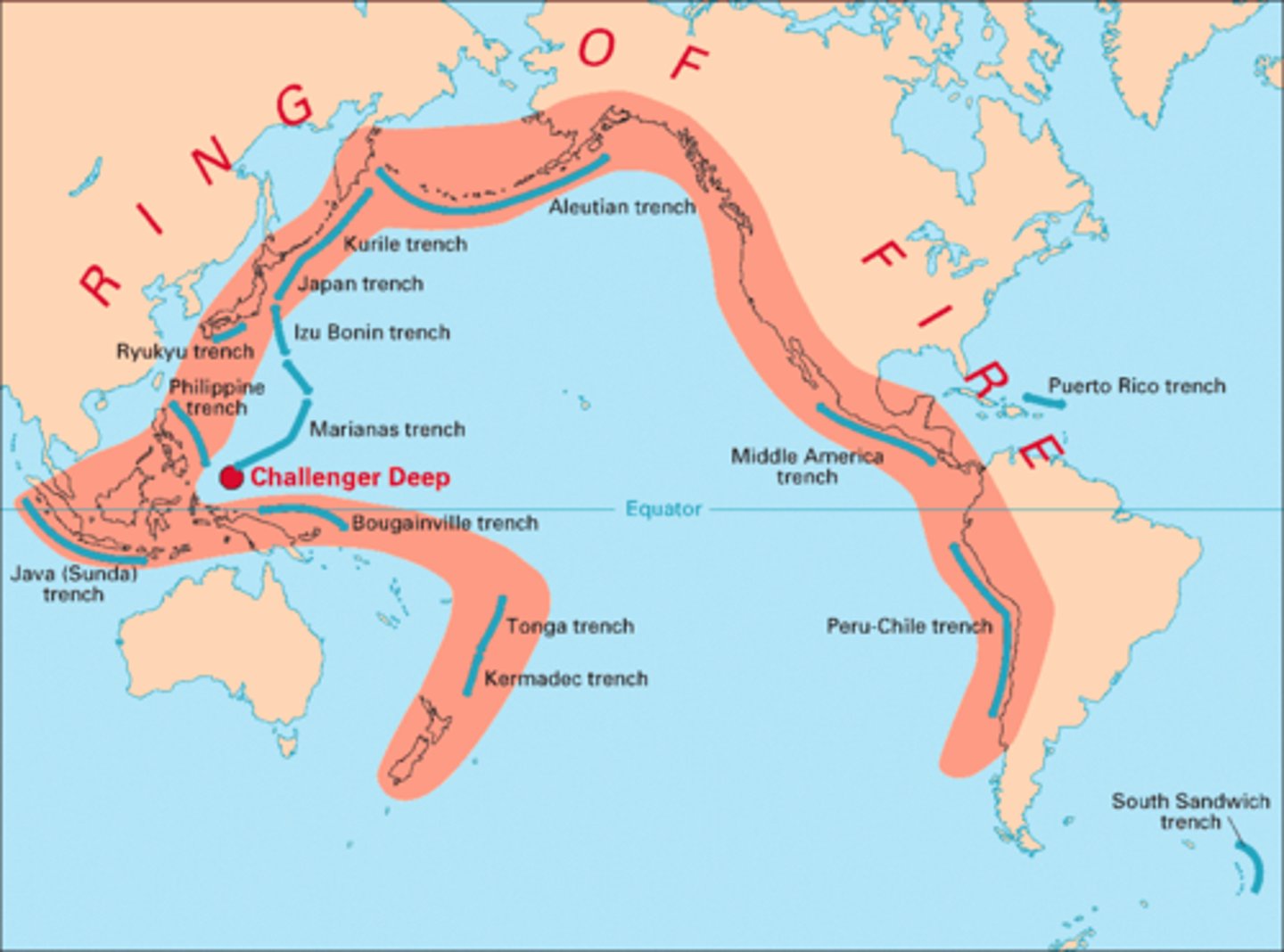
Ring of Fire
Area where majority of earthquakes occur in the pacific ocean.
Fracking
Injects high-pressure mixture of water, sand, and chemicals to crack the rock and release trapped gas or oil. Can induce earthquakes
Earth's Tilt
23.5 degrees
Equator
Receives the most direct sunlight
Poles
Only receive sunlight when they are pointed towards the sun. (Specific times of the year)
Arctic zone
Lowest light, covered in ice or snow most of the year.
Temperate zone
Located between arctic and tropic zones, experience the most distinct changes, large variation
Tropic zone
Located at equator, high light intensity, mostly covered in oceans, resulting in frequent rainfall.
Why do seasons occur at different times?
Due to the tilt and unequal heating, the hemispheres experience seasons at different points in the Earth's orbit.
Main components of Earth's system
Matter and Energy
The Big Bang
Occurred 15 billion years ago and created all the matter (atoms made of protons, neutrons, and electrons)
Earth is in a closed system
Matter cannot be created nor destroyed, rather it changes forms
Sources of Energy
Radioactive decay at the core of Earth and the Sun.
5 Layers of Atmosphere
Troposphere, stratosphere, mesosphere, thermosphere, exosphere
Composition of atmosphere
78.1% Nitrogen, 20.9% oxygen, 0.9% argon, 0.1% carbon dioxide, methane, water vapor, helium, ozone.
Role of nitrogen in living organisms
Essential for making up proteins
Role of oxygen in living organisms
Essential for human respiration
Troposphere
Area of atmosphere that we exist in. Can be 7 to 18 km thick.. Temp. decreases as distance from earth increases. Gasses make up 75% of the atmosphere --> High density and pressure.
Turbulent air in troposphere
Responsible for weather we experience
Tropopause
Highest level of troposphere. Coldest.
Stratosphere
Above troposphere. Contains about 24% of gasses in total atmosphere. Typically where airplanes exist. Temp increases as altitude increases because it directly absorbs solar radiation and ozone layer.
Mesosphere
Low concentration of gas. Low pressure. Largest range of temp. that decrease as altitude increases. Meteors burn up here.
Thermosphere
Temp. increases with an increase in altitude. Few gases and low pressure.
Exosphere
Highest layer of atmosphere. Only hydrogen and helium gas here. Extremely low pressure. Temp decreases as altitude increases.
Northern lights in thermosphere
Energy from sun causes gas atoms to form ions and plasma
Temp. Inversion layers
Stratosphere, thermosphere, possibly troposphere due to pollution.
Weather
The temperature, amount of rainfall, and humidity at a certain place and time.
Convection
As the sun heats gases in the atmosphere, denser colder air sinks and warmer less dense air rises. Creates wind.
Climate
The average weather patterns of a region over many years.
What is climate determined by?
The heating and cooling of the Earth's surface which occur due to energy exchanges of earth's atmosphere and oceans.
Temperature gradient
Causes warm air and water at the equator to travel to the poles and cool air and water at the poles to travel to the equator.
If Earth did not rotate...
The poles would be one large area of high pressure and the equator would be one large area of low pressure
Why does the movement of air not follow direct paths?
Because of earth's rotation
Coriolis Effect
Area around equator ravels faster than that of pole so air moving north is deflected east and air moving south is deflected west. Due to Earth's rotation around the axis
Convection Cells
Caused by coriolis effect. Six large ones, three in each hemisphere, that differ in the way air circulates.
Hadley Cells
Form near equator as warm air rises vertically, moves towards the poles, cools down and sinks back to the surface.
Ferrel Cells
Cold air sinks and moves toward poles and eastward before warming and rising again.
Polar Cells
Diverging of rising warm air that sinks over the poles.
Jet Streams
Where cold air meets warm air at boundaries between cells. Position, speed, and direction changes.
El Nino-Southern Oscillation, ENSO
Changing temperatures of the pacific ocean that impact weather patterns globally.
Water on Earth
97% Saltwater, 3% Freshwater
Composition of 3% Freshwater
2.2% Ice caps and glaciers, 0.8% useable freshwater
Water
Finite, renewable, moves through hydrologic cycle
Processes that add water to the atmosphere
Evaporation, transpiration, evapotranspiration, sublimation
Sustainable water use
Rate of consumption has to be less than or equal to the rate of recycling
Largest consumer of water
Agriculture (irrigation)
Water's unique properties
Polar, forms hydrogen bonds. High heat capacity, universal solvent, solid water has a lower density than liquid --> ice floats in water.
Hydrologic Cycle
Precipitation, runoff, evaporation.
Surface Water
Exists above ground on Earth (e.g. streams, rivers, ponds)
Runoff
Water that flows over land and hasn't been absorbed into the ground
Watershed
All of the land that supplies water to a river. Can have cascading effects if part is polluted.
Mississippi River Watershed
41% of US land
Aquifer
Underground layer of water
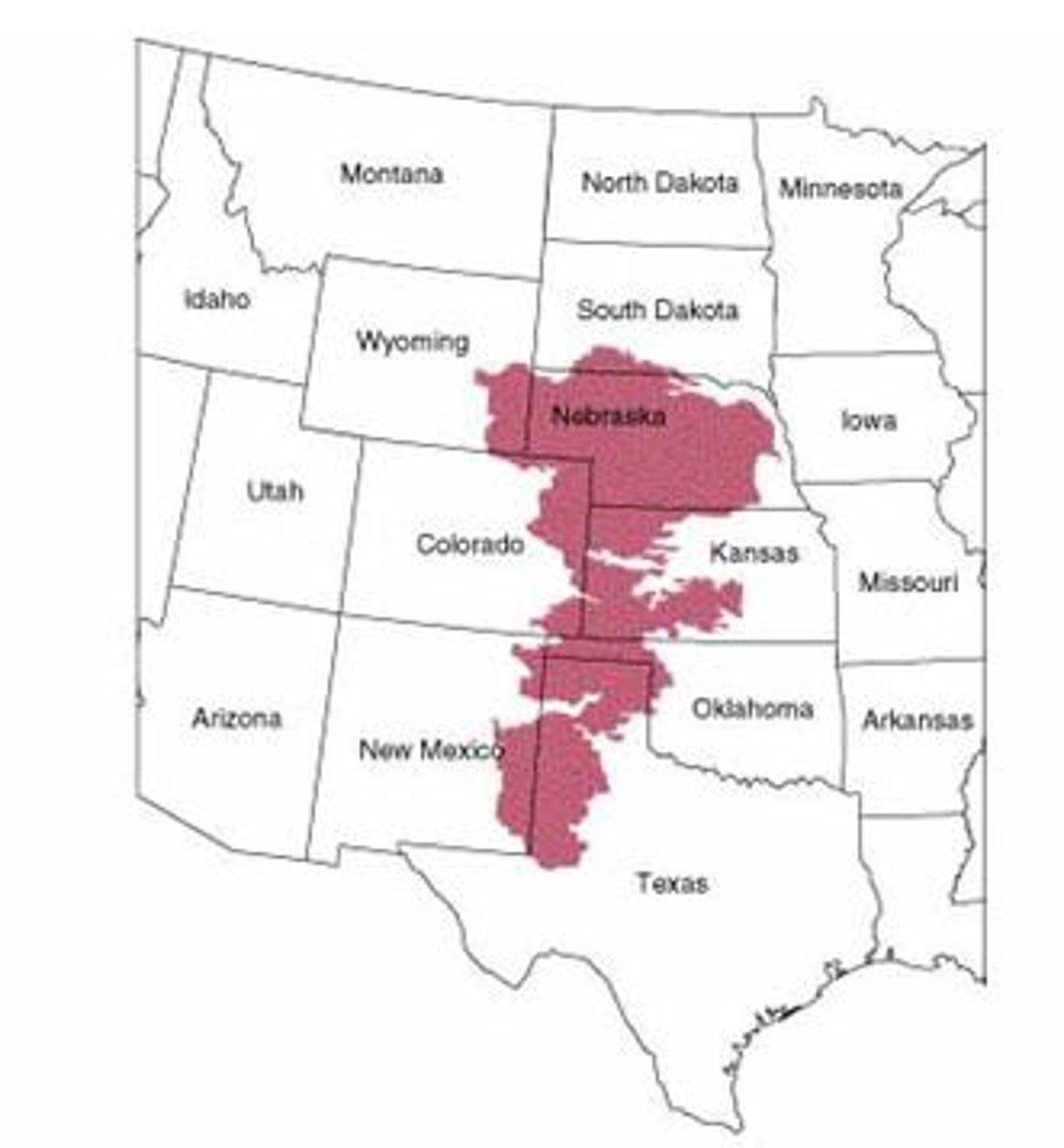
Ogallala Aquifer
Largest aquifer in North America.
Groundwater
Freshwater underground. Needs to be space between particles for water to exist. The deeper you go, the denser materials get, making less room for water.
How does groundwater exist?
Gravity pulls water towards the center of earth and bedrock underground allows water to accumulate. Comes from rain or snowmelt, surface water, septic tanks, irrigation.
Reservoirs
A large natural or artificial lake used as a source of water supply. Important to communities with less access to lakes and rivers. Provides drinking water, generate electricity, prevent communities from dangerous floods, and provide space for recreational activities.
Porosity
Measure of space between soil particles that can hold water and oxygen.
Permeability
How easily water can get into soil --> depends on size and shape of pores.
Recharge zones
Areas where water infiltrates the ground rather than becoming runoff.
Good recharge areas
Wetlands and flat vegetated areas
Least sustainable source of freshwater
Deep ground water.
What is crucial to maintaining the sustainability of aquifers?
Recharge zones
Salinization
High salt concentrations in water; result of extracting groundwater at a high rate.
Dams
Used to collect water in reservoirs.
Negatives of dams and reservoirs
Habitat destruction, increased salinization
Turning ocean water into freshwater
Desalinization, reverse osmosis, distillation
Sector responsible for the greatest consumption of water
Agricultural
Water insecurity
1.1 billion people lack access to clean water, and 2.7 billion have trouble finding fresh water for at least one month of the year.
Water Stress Causes
High populations, low precipitation.
The rock cycle
The process in which soil forms.
3 Types of Rocks
Igneous, sedimentary, metamorphic
8 Processes that change rocks into different types
Weathering, erosion, transportation, deposition, compaction, cementation, melting, metamorphism
Igneous Rock
Formed when magma cools and crystalizes below the surface or lava cools and crystallizes on the surface.
Sedimentary Rock
Formed when sediments settle into layers and are compacted and cemented.
Lithification
Layers being compacted and cemented
Metamorphic rock
Formed when high pressure and temperature changes the chemical composition of a rock.
Healthy soil composition
45% minerals, 25% water, 25% air, 5% organic matter
Soil
Composed of minerals, decomposing plant and animal matter, and open space filled with air and water. NON RENEWABLE
Weathering of Rock
Physical changes due to wind and water, chemical changes due to reactions with other substances, changes caused by activity of living organisms
Clay
Smallest particle size, small pores, retain water better