Salmonella
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
Describe salmonella
-Facultative anaerobe
-Gram-negative rod
-Member of the enterobactericae
-Genus consists of 2 species, Salmonella bongori (reptiles) and Salmonella enterica (all species)
-S.enterica has around 2500 subspecies

Why is salmonella an important pathogen to understand?
-Contributes as a major foodborne zoonosis
-Is a major cause of enteritis in humans and animals
-Is a major pathogen causing systemic disease in animals and humans (typhoid fever)
What is the veterinary significance of salmonella?
-Carried in the intestines of food-producing animals leading to food contamination
-Vertical transmission possible to eggs and milk
-Major disease (systemic or gastroenteritis) of production animals
-Diarrhoeal disease of companion animals (dogs and horses)
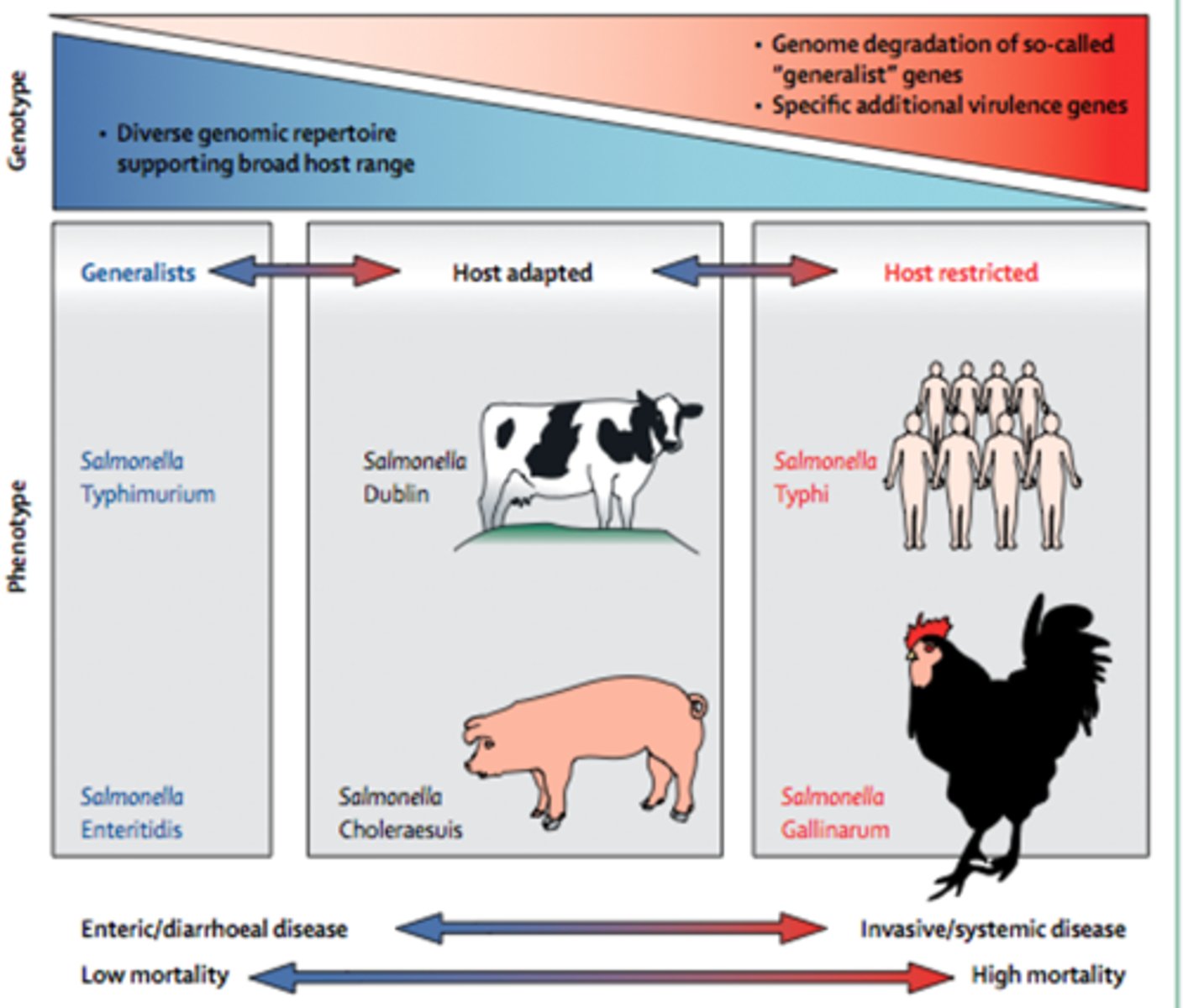
Describe salmonella as a generalist pathogen
-Can infect almost any host (broad host range)
-Has a diverse genotype which gives it a diverse metabolic pathway capable of tolerating a wide range of environments
-Associated with low mortality and do not kill the host
-Instead causes milder symptoms such as diarrhoea
-E.g. S.tymphimurium, S.enteritidis
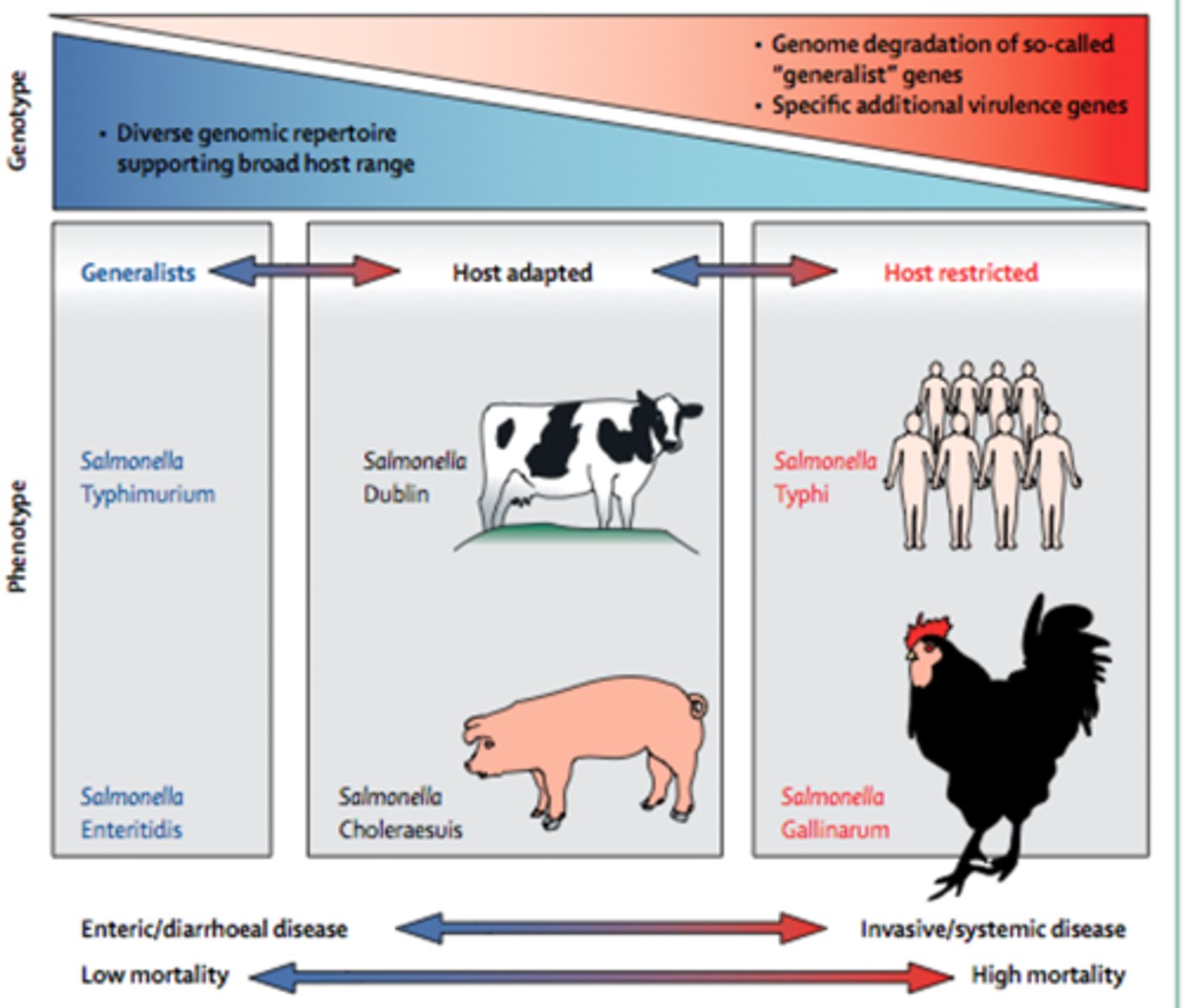
Describe salmonella as a host-restricted pathogen
-Only infects very specific hosts (narrow host range)
-Has a very conserved and specific genotype that only allows for adaptation to specific host environments
-Typically causes more invasive, systemic disease that has a high mortality
-Have increased levels of virulence factors which allow them to cause more severe disease
-E.g. S.typhi, S.gallinarum
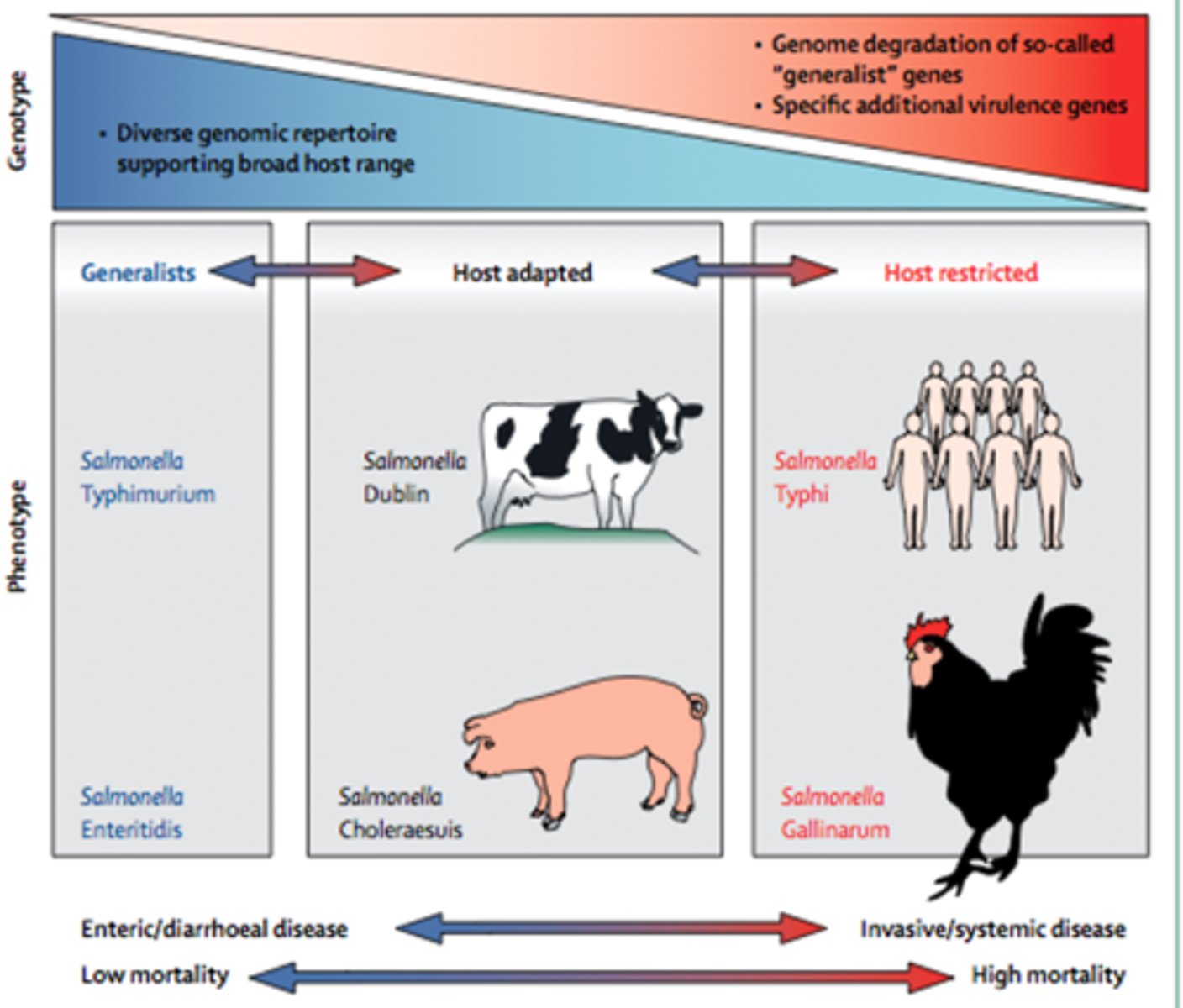
Describe salmonella as a host-adapted pathogen
-A midpoint between generalist species and host-restricted species
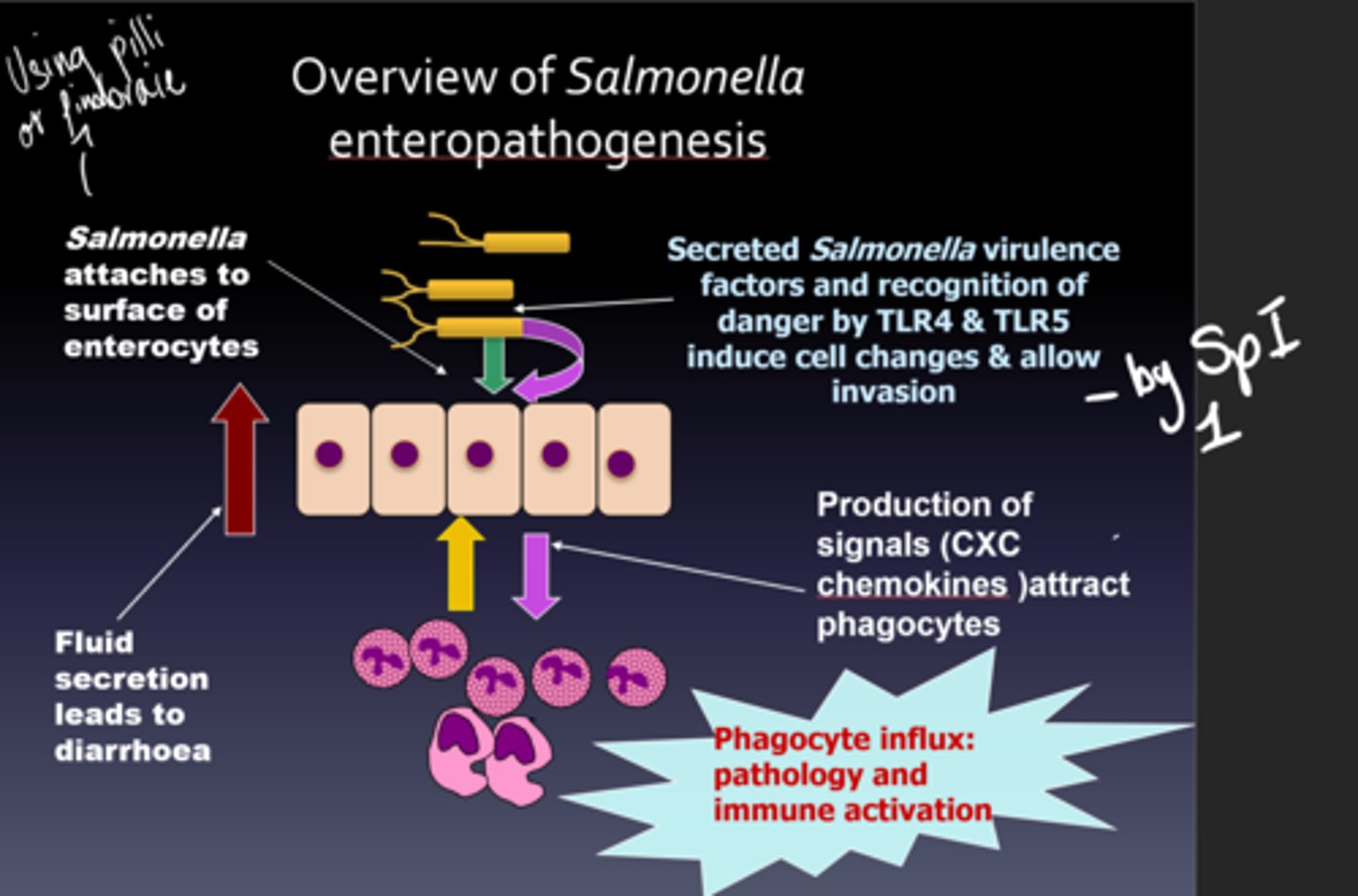
Describe how salmonella causes inflammatory and invasive gastroenteritis
-Infection leads to an influx of neutrophils
-This influx may cause damage to the gut wall allowing their invasion
-This influx also causes a large degree of inflammation
-Diarrhoea is thought to be caused by fluid efflux due to ionic imbalance
-In some species inflammation is more limited and the bacteria can persist in the intestines
What must salmonella cope with to get to the ileum of the host? How does it do this?
-Acidic pH = has proton pumps to remove H+ ions and it can change its membrane structure
-Intestinal flow = has fimbriae and pili (adhesins) that allow adhesion to the gut wall
-Low oxygen levels = facultatively anaerobic
Explain how both salmonella and the host cause gastroenteritis upon infection
-The bacterium secretes proteins that alter host cell function and structure via type 3 secretion systems (SPI 1 and 2) that allow invasion from the gut and cause inflammation
-The host's innate immune system recognises repeated features (flagella and LPS) of the bacterium by recognition receptors (Toll-like receptors) and initiate an inflammatory response
What are T3SSs?
-Type 3 secretion systems
-They deliver effector proteins or toxins to host cells via a needle and syringe-like structures
-Salmonella contains T3SS encoded on pathogenicity islands SPI1 and SPI2
-SPI1 plays key roles in the gut
-SPI2 plays key roles in systemic infection
Describe the effects of SPI1 T3SS on host cells
-Induces cytoskeletal changes in host epithelial cells
-Cause polymerisation of actin leading to membrane ruffling thus allowing cell invasion causing inflammation
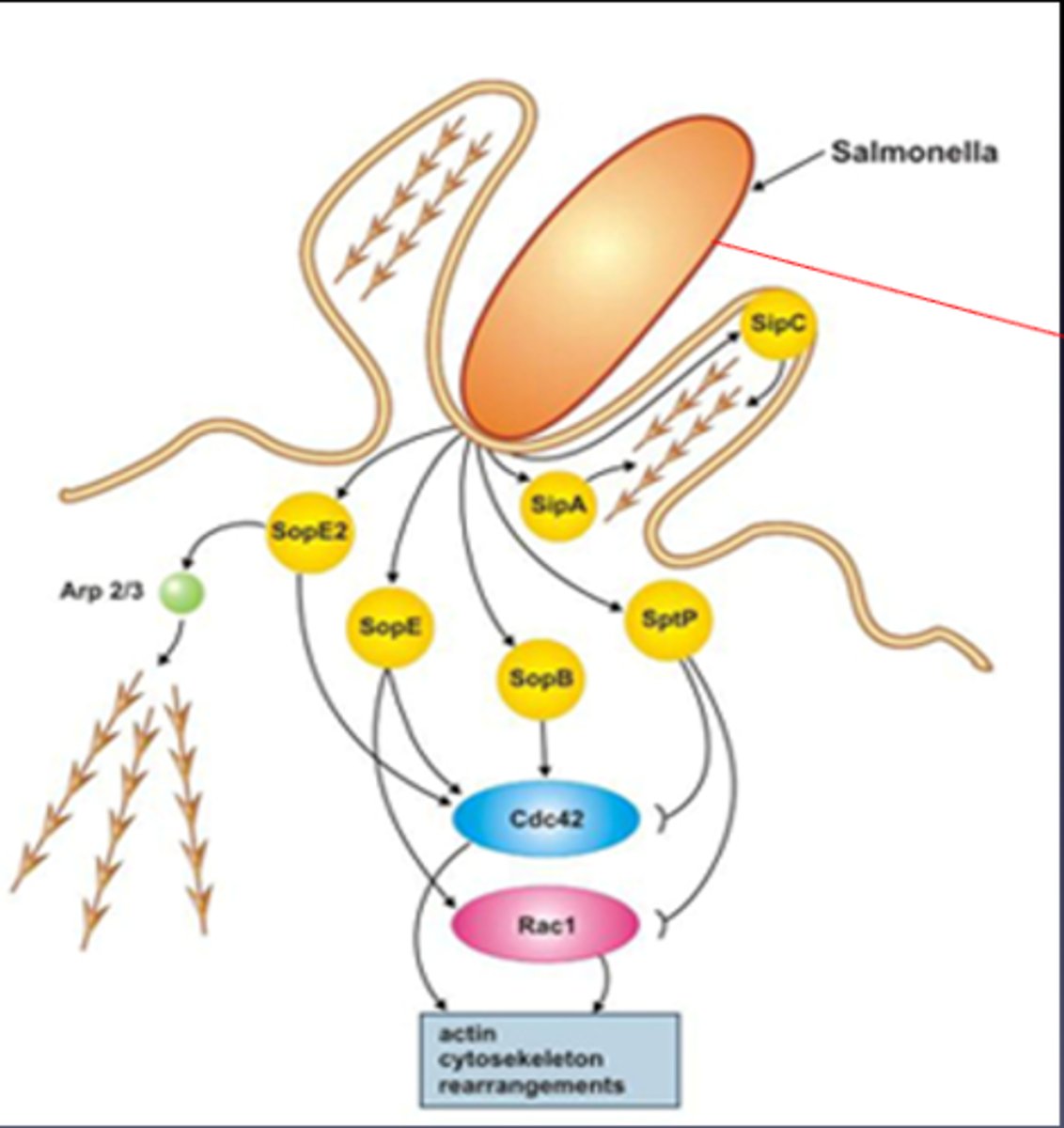
How does the hosts innate immune system recognise pathogens quickly?
Have recognition receptors (Toll-like receptors) that recognise repeated structures on pathogens (PAMPs).
What are PAMPs?
-Pathogen associated molecular patters
-Repeated structures on pathogens that are recognisable by host immune cells
What occurs when PAMPs are recognised by host immune cells?
-Danger signalling
-Cytokines and chemokines are released by cells that have recognised the pathogen inducing the immune response
What are the main PAMPs of salmonella?
-Flagella
-Lipopolysaccharides (LPS)
Draw a diagram that summarises salmonella enteropathogenesis
Salmonella enteropathogenesis.
Which salmonella species rarely causes inflammation and why?
-S.typhi
-By hiding from TLRs using the Vi capsule to prevent the LPS of the flagella from being recognised
How might other salmonella species avoid the immune response?
-Switching off flagellar genes when they aren't needed
-Having no flagella altogether
Which cells do salmonella bacteria colonise? How?
-Macrophages
-They use SPI2 T3SS which prevents the phagocytic vacuole from fusing with antimicrobial vesicles
Describe how salmonella may cause systemic infection
-Entry via the gut (or targeting lymphoid tissue in the gut)
-Salmonella invade underlying immune cells (macrophages and dendritic cells)
-Infected cells traffic via the lymphatic system to the spleen and liver
-Intracellular replication in cells occurs
-If this replication isn't brought under control it can lead to septicaemia and death
What is a carrier-state infection?
-Persistent systemic infection without disease
-Important for pathogen transmission as the carrier appears healthy but can transmit the infection
-E.g. typhoid Mary with S.typhi persistence in the gall bladder and spreading it to over 50 people