Passive and Active Transport
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
Active transport goes from_____ to _____
low; high
Which method moves against the concentration gradient
Active transport
What are the requirements of active transport
the input of energy (ATP)
always occurs across a cell membrane
requires carrier proteins to move the molecules
What is required to transport macromolecules?
endocytosis and exocytosis
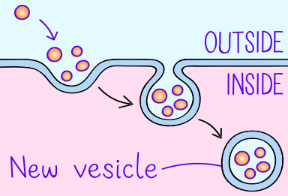
Endocytosis
moves cell inside, cell membrane takes in macromolecules by folding in on itself and forming new vesicles derived from the membrane
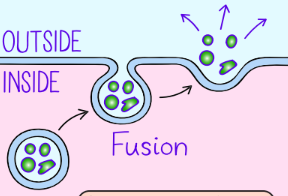
Exocytosis
Internal vesicles containing macromolecules move to the cell surface and fuse with the cell membrane. The macromolecules are released into the extracellular space
Example of active transport
A plant absorbing mineral ions into its roots in low quality soil so it is against the concentration gradient
Sodium-potassium pump is a _____ in the ______
protein; cell membrane
Whats it called when the sodium potassium pump continues to repeat?
electrochemical gradient
Whats the purpose of the sodium-potassium pump?
to maintain the resting potential of the cell membrane by helping establish an electrochemical gradient
Why is the sodium-potassium pump active transport?
Sodium ions are pumped out of the cell AGAINST their concentration gradient from low to high concentration. Potassium ions are pumped into the cell also moving AGAINST their concentration gradient.
What is diffusion?
the movement of a substance from high to low concentration
Molecules in diffusion do not move randomly
false
is the net movement of molecules in diffusion up or down?
down
When the concentration is equal there is
equilibrium
Is diffusion passive or active
passive; no energy required
Whats required of cells to function correctly?
many molecules and ions
What are the types of diffusion?
simple and facilitated
Examples of diffusion
Nutrients from digested foods diffuse into small intestines into the blood stream
What controls when can and cant enter the cell membrane?
the properties of the cell
Simple diffusion
when molecules can pass directly through the cell membrane, small
In simple diffusion molecules must be able to fit through the gaps between the ______
phospholipids
The middle of the cell membrane is ____ so only ____ can easily pass through
hydrophobic; nonpolar
Facilitated diffusion
when proteins have to help transport larger, polar molecules
What are the types of channel proteins?
Channel and carrier
Whats the interior of channel and carrier proteins?
hydrophilic
What does increasing the concentration gradient do?
It increases the rate of diffusion
Does increasing the surface area of a cell increase or decrease its rate of diffusion?
increase
Does a thinner or thicker exchange surface slow down diffusion?
Thicker
Increasing the temp, ____ the rate of diffusion
increases
Osmosis is a passive process
true
Osmosis is the diffusion of _____ from a ___ to ____ concentration
water; high; low
Semi/partially/selectively permeable membrane
only specific molecules can pass through
osmosis
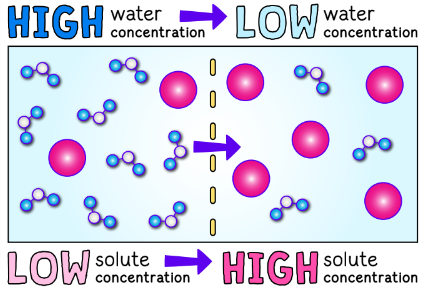
Increasing the solute concentration of a solution ____ the concentration of water
lowers
Hypotonic
the solution has a lower concentration of solute, water will move into the cell
What happens when an animal cell is hypotonic
It swells and bursts called lysis
What happens when a plant cell is hypotonic
there is pressure against the cell wall and is “turgid”, normal
Isotonic
the solution has the same concentration of solute as the cell, no net movement
What happens when an animal cell is isotonic
red blood cells didn’t lose or gain water and is normal and concaved
What happens when a plant cell is isotonic
The cell hasn’t gained or lost water, no pressure on cell wall, cell is flaccid
Hypertonic
Solution has a higher concentration of solute than the cell. Water moves out of the cell
What happens to an animal cell when it is Hypertonic
red blood cells loses water and appears shriveled and spikey
What happens to a plant cell when it is hypertonic
The cell lost water so cytoplasm pulls away from the cell wall and vacuole shrinks, cell is plasmolyzed