Chapter 7 medical terminology circulatory system
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
circulatory system consists of the cardio+vascul+ar system (heart and blood vessels)
lymphatic system (structures involved in the conveyance of the fluid lymph)
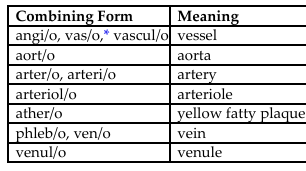
cardi/o = heart vascul/o = vessel
home/o = sameness -stasis = controlling
It leaves the heart by the arteries, which branch many times and become arterioles. arteries carry oxygenated blood away from heart to body
Blood leaving the capillaries returns to the heart through the venules, which flow into the veins
veins carry deoxygenated blood to the heart
largest vein is vena cavae
right atrium and right ventricular pump deoygenated blood
left atrium and left ventricle pump oxygenated blood
what are the artioventricular valves?
what are the semilunar valves?
atrioventricular valves: triscuspid and bicuspid/mitral valve
semilunar valves: aortic and pulmonary valve
pulmon/o = lung aort/o = aorta
peri+card+ium, a sac made up of a double membrane, encloses the heart.
The innermost layer of the pericardium is the visceral pericardium, or epicardium
peri- = around cardi/o = heart -ium = membrane
endo- = inside my/o = muscle
Coronary means encircling, in the manner of a crown, and refers to the way in which coronary arteries encircle the heart
Cardiomyopathy is a general diagnostic term that designates primary disease of the heart muscle itself
An example of a cardiomyopathy is myocarditis, inflammation of the heart muscle.
Endocarditis is often caused by infective microorganisms that invade the endocardium
Inflammation of the pericardium is pericarditis,
cardi/o = heart my/o = muscle -pathy = disease -itis = inflammation
an electrocardiogram and other measurements are taken while the patient walks on a treadmill at varying speeds and inclines.
electrical currents of the heart muscle are recorded by an electrocardiograph
electr/o = electrical cardi/o = heart -gram = a record
Echocardiography (echo) is the term generally associated with the use of ultrasonography in diagnosing heart disease
The echocardiogram is a record of the heart obtained by directing ultrasonic waves through the chest wall
echo- = sound -graphy = process of recording
Cardiac catheterization is the passage of a long, flexible tube into the heart chambers through a vein in an arm or leg or the neck
An instrument called a catheter is used.
endo- = inside scop/o = to view -ic = pertaining to
angina pectoris Severe chest pain and constriction about the heart caused by an insufficient supply of blood to the heart itself
arrhythmia (a-, without) Irregularity or loss of rhythm of the heartbeat.
dysrhythmia is more technically correct
cardiomegaly (cardi/o, heart + -megaly, enlargement) Enlarged size of the heart
congenital heart defects Abnormalities present in the heart at birth (congenital means existing at birth)
congestive heart failure (CHF) Condition characterized by weakness, breathlessness, and edema in lower portions of the body; the work demanded of the heart is greater than its ability to perform; also called congestive heart disease or heart failure
coronary artery disease (CAD) Abnormal condition that affects the heart's arteries and produces various pathologic effects
coronary heart disease (CHD) Heart damage resulting from insufficient oxygen caused by pathologic changes in the coronary arteries
fibrillation Severe cardiac arrhythmia in which contractions are too rapid and uncoordinated for effective blood circulation.
heart murmur Soft blowing or rasping sound that may be heard when listening to the heart with a stethoscope;
hyperlipidemia (hyper-, excessive + -emia, blood) Excessive lipids (fats) in the blood.
hypertension (hyper-, excessive or above normal) Elevated blood pressure above the normal values of 120/80 mm Hg
hypotension (hypo-, below normal) Low blood pressure
infarction Necrosis of a localized area of tissue caused by lack of blood supply to that area. Necrosis means death of tissue. It can result from occlusion (obstruction) or stenosis (narrowing)
Myocardial infarction (MI) is the death of an area of the heart muscle that occurs as a result of oxygen deprivation
myocardial ischemia Deficiency of blood supply to the myocardium.
septal defect Defect in the wall separating the left and right sides of the heart.
shock Serious condition in which blood flow to the heart is reduced to such an extent that body tissues do not receive enough blood.
Vasodilation is an increase in the diameter of a blood vessel.
Vasoconstriction has the opposite meaning of vasodilation. The dilation and constriction of blood vessels influence blood pressure and distribution of blood to various parts of the body.
Both cholesterol and triglycerides are lipids. High levels of these two lipids are associated with greater risk of hardening of the arteries.
Angi+omas are tumors consisting principally of blood vessels (hemangioma) or lymph vessels (lymphangioma). Such tumors are usually benign (not malignant).
angi/o = vessel -oma = tumor hem/a or hem/o = blood
Aorto+graphy is radiography of the aorta after the injection of a contrast medium to enhance the image of the aorta on an x-ray image
The record produced from this procedure is an aortogram
Arterio+graphy is radiography of arteries after injection of radiopaque material into the bloodstream.
The image produced is an arteriogram
Angio+cardio+graphy is radiography of the heart and great vessels after intravenous injection of a radiopaque solution
Angiography is a general term for radiography of vessels.
Cardiopulmonary bypass is the method used to divert blood away from the heart and lungs temporarily when surgery of the heart and major vessels is performed.
Cardiopulmonary means pertaining to the heart and lungs.
cardi/o = heart pulmon/o = lungs -ary = pertaining to
The heart has a natural pacemaker called the sinoatrial (SA) node.
Cardio+version, restoring the heart's normal rhythm using electrical shock
An automatic implanted cardioverter defibrillator (ICD) is a device that detects sustained ventricular tachycardia or fibrillation and delivers a low energy shock to the heart, restoring the normal rhythm
Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) is recommended as an emergency first-aid procedure to reestablish heart and lung action if breathing or heart action has stopped.
Antiarrhythmic drugs are used to prevent, alleviate, or correct an abnormal heart rhythm
Digoxin is a well-known drug that is prescribed in the treatment of congestive heart failure and certain arrhythmias.
The pain of angina pectoris is often relieved by rest and vasodilation of the coronary arteries with nitroglycerin, a coronary vasodilator
Nonsurgical Vascular Treatments:
thrombolytic agent administered through a catheter to dissolve the clot.
An oral anticoagulant, warfarin (Coumadin) or heparin, is prescribed in the treatment and prevention of a variety of thrombo+embol+ic disorders
thromb/o = clot -lytic = capable of destroying embol/o = embolus -ic = pertaining to
Antihypertensives are agents that are used to reduce high blood pressure
Diuretics are also used and act to reduce the blood volume through greater excretion of water by the kidneys
Antilipidemic drugs are prescribed to lower cholesterol levels in the blood,
anti- = against -emic = pertaining to blood
Balloon angioplasty uses a balloon catheter that is inflated inside an artery to flatten the plaque against the arterial wall; a stent is sometimes inserted. This procedure may be necessary in coronary artery disease (Figure 7-17). If blockage is too severe, a coronary artery bypass graft (CABG)
procedures to remove blockage include laser or a 324 specially designed catheter for cutting away plaque from the lining of an artery (atherectomy)
If a thrombus has formed, it is sometimes treated with a thrombolytic agent to dissolve the clot (intravascular thrombolysis), with the thrombolytic agent delivered through a catheter).
per- = through cutane/o = skin -ous = pertaining to
Surgical excision of a vein, or a segment of vein, is called phleb+ectomy.
A hemorrhoid+ectomy is surgical excision of a hemorrhoid.
The lymph vessels, lymph nodes, lymph, tonsils, thymus, and spleen compose the lymphatic system
. The tonsils are masses of lymphatic tissue located in depressions of the mucous membranes of the pharynx.
but these are just one type of tonsil, the palatine tonsils.
Pharyngeal tonsils are commonly called adenoids.
aden/o = gland -oid = resembling
Lymph+oma is a general term for cancer that originates in the lymphatic system
lymph+ang+itis is an acute or a chronic inflammation of lymphatic vessels and can be caused by various microorganisms
Lymphangiography is radiography of the lymphatic vessels and nodes after injection of a radiopaque substance has made them visible on x-ray film
Accumulation of lymph in tissue and the resultant swelling are called lymphedema
Lymphangiograms are useful for checking the integrity of the lymphatic system in lymphedema and for investigating the spread of malignant tumors
angi/o = vessel -itis = inflammation lymph/o = lymphatics -edema = swelling
elephantiasis, a parasitic disease generally seen in the tropics (Figure 7-22). The excessive swelling, usually of the external reproductive organs and the 329 legs, is caused by obstruction of the lymphatic vessels by parasites.
Spleno+megaly means enlarged spleen, which has many causes
-oma = swelling splen/o = spleen -megaly = enlargement
Lymph+aden+ectomy is excision of a lymph node.