Enzymes and Metabolsim
1/26
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
Metabolism
the totality of chemical processes that occur in an organism to maintain life
web of all enzyme-catalysed reactions that occur within a cell or organism.
Metabolism
First function of Metabolic reactions
provide an energy source for cellular processes
Second function of metabolic processes
synthesize and break down molecules for growth and maintenance.
Catalyst are almost always….
enzymes
Function of enzymes
Speed up chemical reactions
Enzymes speed up chemical reaction by…
lowering activation energy
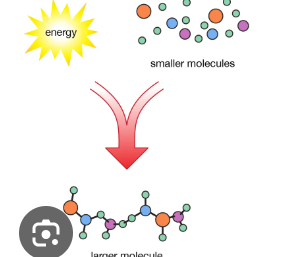
Anabolism
Monomers to polymers
What is the example of Anabolism?
(all Condensation) —> protein synthesis, photosynthesis, glycogen formation
Anabolism ____ energy
consume
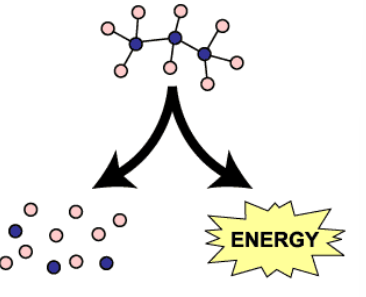
Catabolism
monomer to polynmer
Do enzymes perform catablic or anabolic reactions
both
catabolism ___ energy
release
Examples of catabolic reactions
(all Hydrolosis) —> digestion, cellular respiration, ATP hydrolysis
Enzymes are ___ proteins
globular
Fibrous proteins
structural role ( long)
Globular proteins
funtional role (round)
active site is composed of ____
amino acids
what do Binding sites do….
Bind substrate and enzyme
what do Catalytic sites do…
reduce activation energy
How are enzyme catalysis created?
Collisions between substrate and enzyme
Immobilized enzyme
enzyme anchored to a solid support
Why does lactose intolreance happen.
Not having lactase to break down lactose
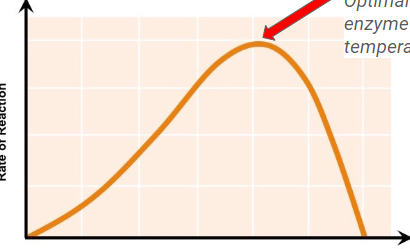
Optimal enzyme tempature
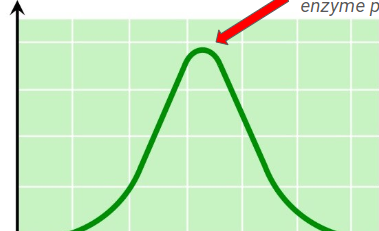
optimal enzyme ph
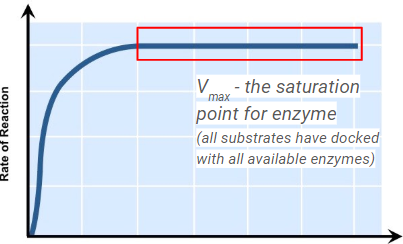
substrate concentation
Rate of reaction equation
Change in amt of reactant or product/ change in time