Classification of Living Organisms
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
Classification
Grouping organisms by similar structures and functions.
Domains
Three major categories: Bacteria, Archaea, Eukarya.
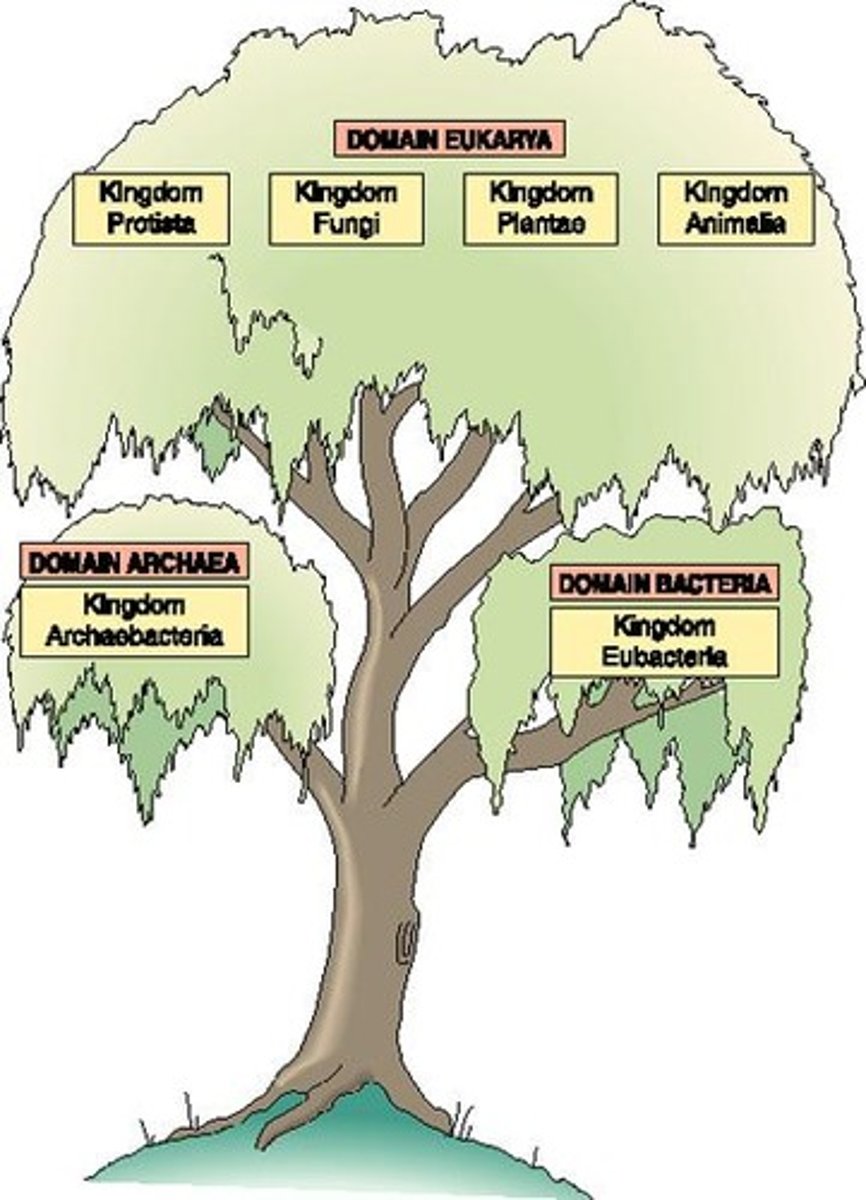
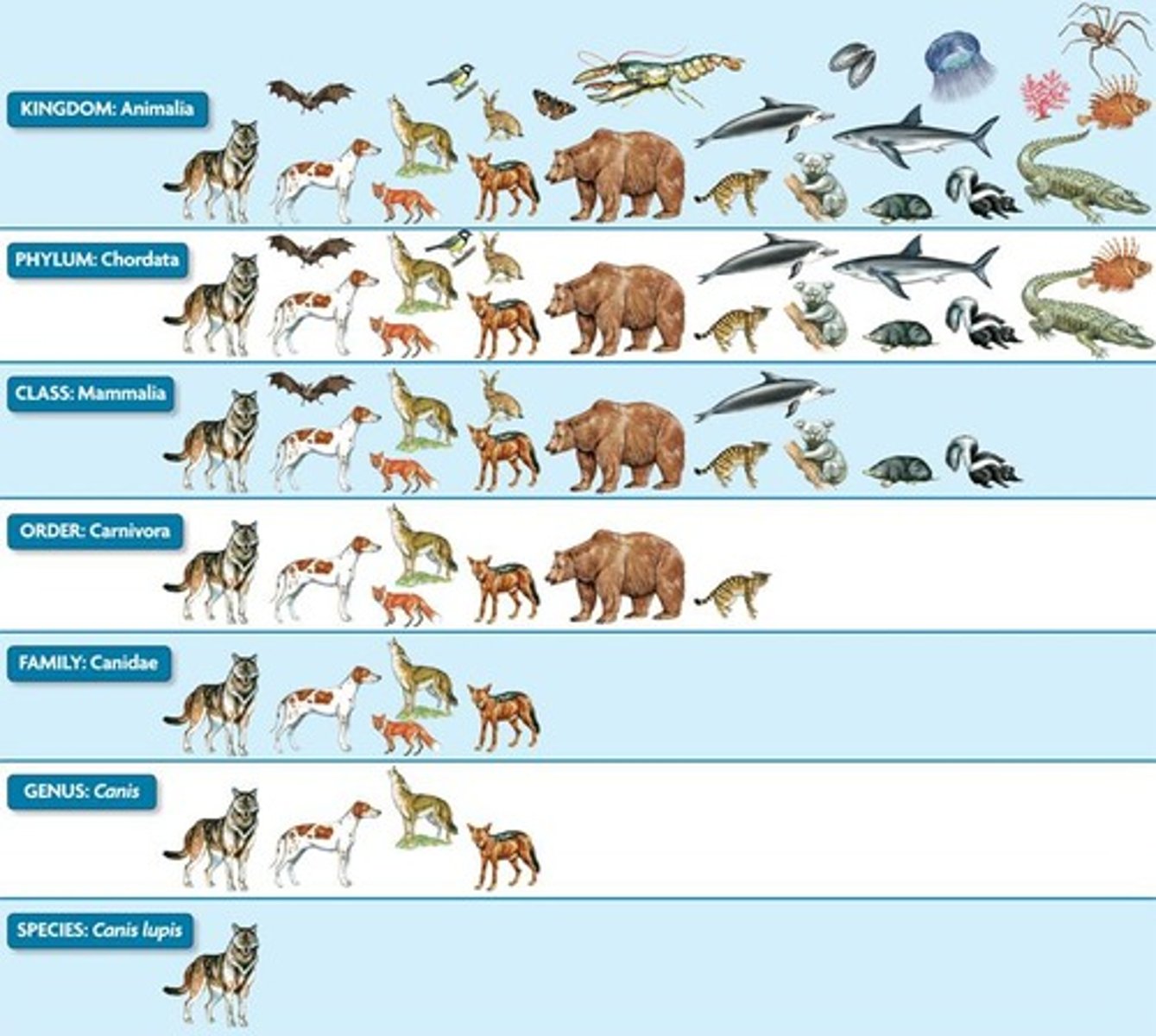
Kingdom
Most inclusive group in Linnaean hierarchy.
Phylum
Second level in the taxonomic hierarchy.
Class
Third level in the taxonomic hierarchy.
Order
Fourth level in the taxonomic hierarchy.
Family
Fifth level in the taxonomic hierarchy.
Genus
Sixth level in the taxonomic hierarchy.
Species
Seventh level; most specific classification.
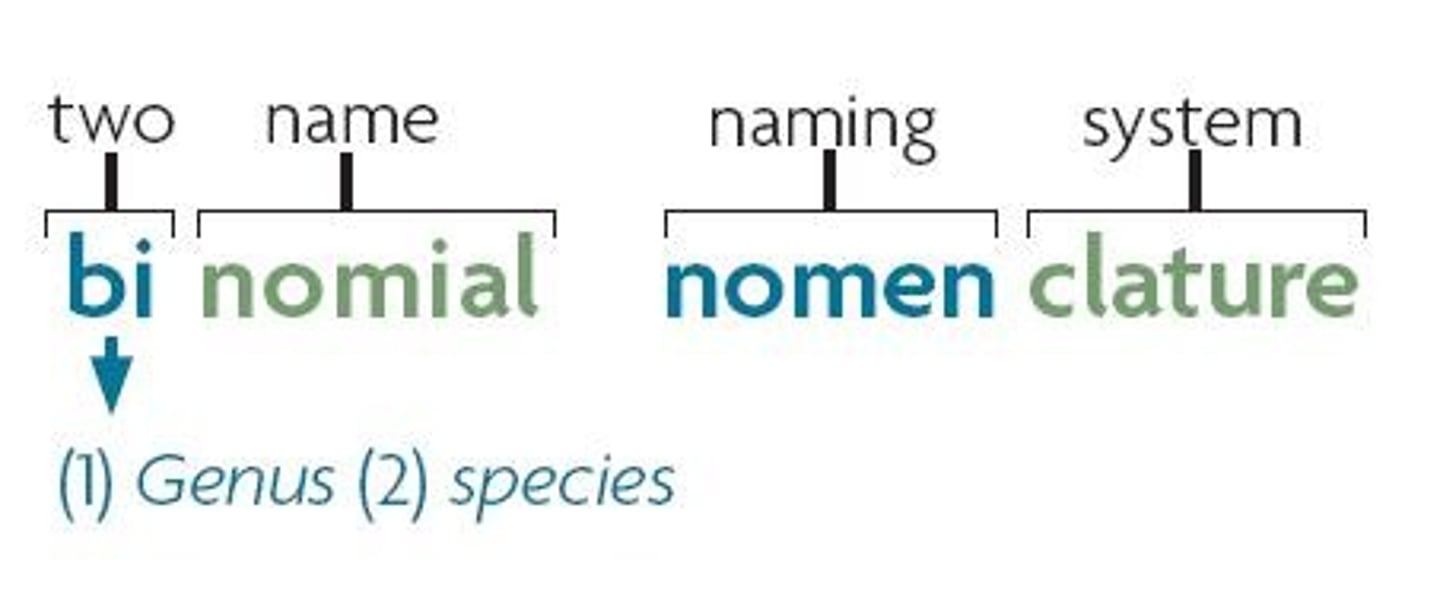
Binomial Nomenclature
Two-part naming system for organisms.
Linnaean Hierarchy
System of classification developed by Linnaeus.
Two Kingdom System
Linnaeus's initial classification: Plantae and Animalia.
Five Kingdom System
Proposed by Whittaker; includes Monera, Protista, Plantae, Fungi, Animalia.
Prokaryotes
Single-celled organisms without a nucleus.
Eukaryotes
Organisms with complex cells containing a nucleus.
True Bacteria
Group of prokaryotes classified under Domain Bacteria.
Archaea
Prokaryotes distinct from true bacteria.
Photosynthetic Protists
Eukaryotic organisms capable of photosynthesis.
Taxonomic Hierarchy
Levels of classification from general to specific.
rRNA Comparisons
Method used by Woese to classify prokaryotes.
Distinguishing Characteristics
Traits used to differentiate domains and kingdoms.
Evolutionary Relationships
Connections between organisms based on common ancestry.