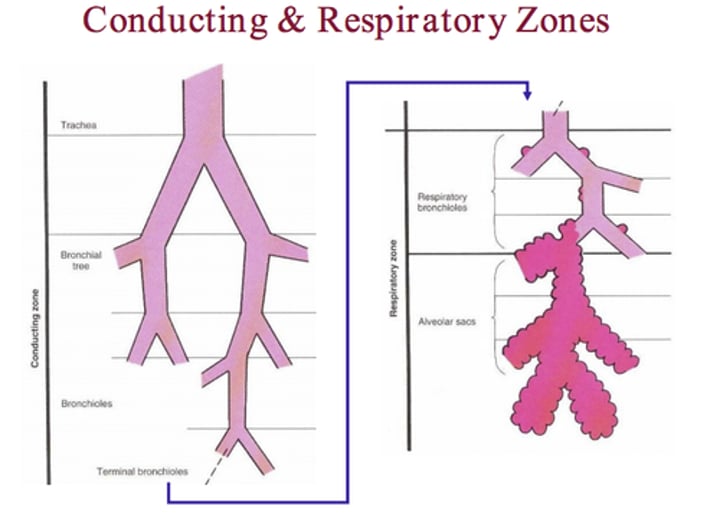
Conducting Zone VS Respiratory Zone
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
(The) conducting zone
What do we call the area where respiratory passages do not take part in gas exchange?
Terminal bronchioles
The conducting zone begins with the oral/nasal cavity. What does it end in?
Dead space
What is the air called that is inhaled that does not take part in gas exchange because it remains in the conducting airways or reaches alveoli that are not perfused?
Gas exchange
What happens in the respiratory zone?
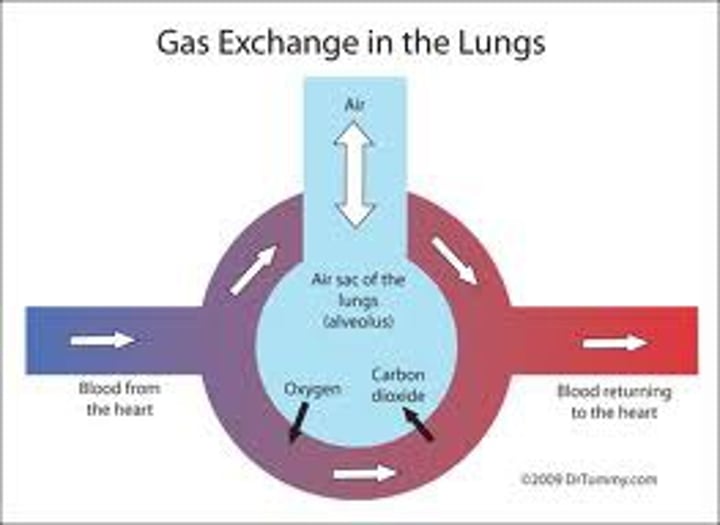
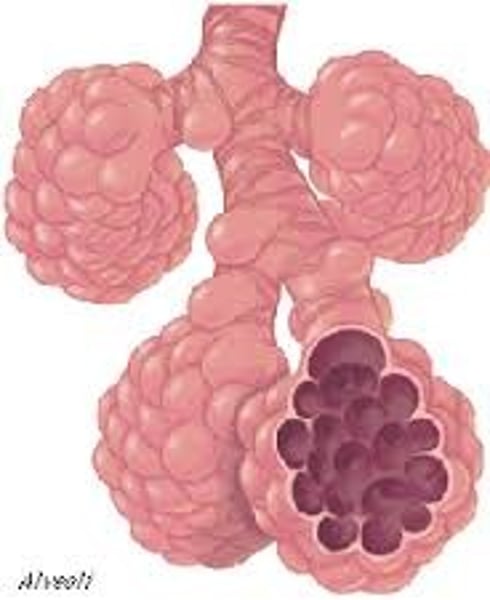
Alveoli
The respiratory zone starts at the respiratory/terminal bronchioles. What does it end in?
480 million
Roughly how many alveoli are there?
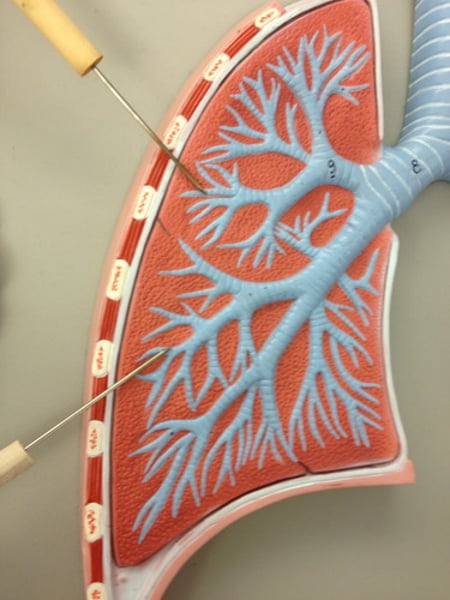
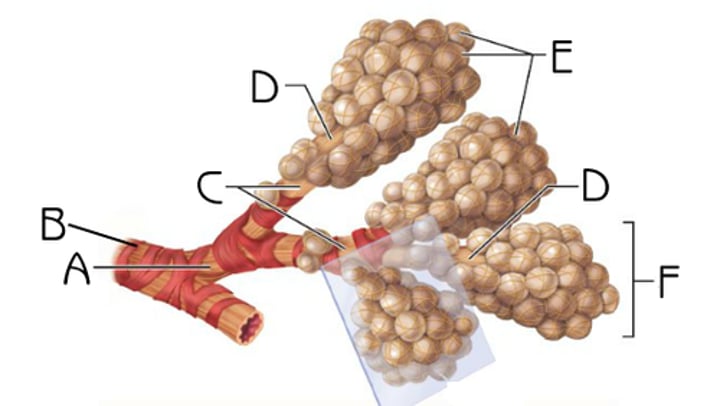
Nose, nasal cavity, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, bronchioles and terminal bronchioles
Name the structures that make up the conducting zone.
Respiratory bronchioles, alveolar ducts and alveoli, all of which are microscopic structures.
Name the structures that make up the respiratory zone, the actual site of gas exchange.
To provide conduits (passageways)for air to reach the gas exchange sites, to cleanse, humidify and warm incoming air.
Name 3 functions of the conducting zone.
To provide a patent (open) airway, to act as a switching mechanism to route air and food into the proper channels, and voice production (as it houses the vocal folds/ vocal cords)
What are the functions of the Larynx?
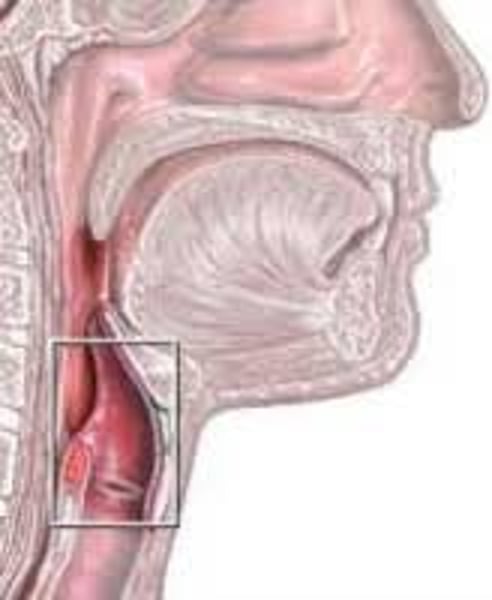
Structure that connects the pharynx to the trachea; made up of cartilage and dense connective tissue.
Describe the Larynx.