SL Biology Paper 1A &B Previous mistakes
1/226
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
227 Terms
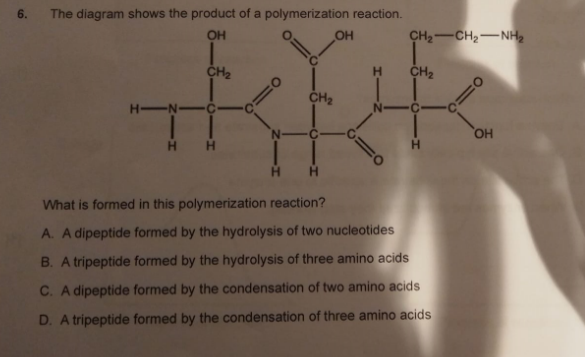
D - a tripeptide formed by the condensation of two amino acids
What are linked by hydrogen bonds?
A. hydrogen and oxygen within a water molecule
B. phosphate and sugar within a DNA molecule
C. base and sugar between DNA nucleotides
D. hydrogen and oxygen in different water molecules
D. hydrogen and oxygen in different water molecules
Which statement applies to enzymes?
A. enzyme function depends on collisions between substrate and active sites
B. one active site on the substrate is specific to one enzyme
C. the active site on the substrate is specific to one enzyme
D. when the enzymes are immobilised they stop working
D. when the enzymes are immobilised they stop working
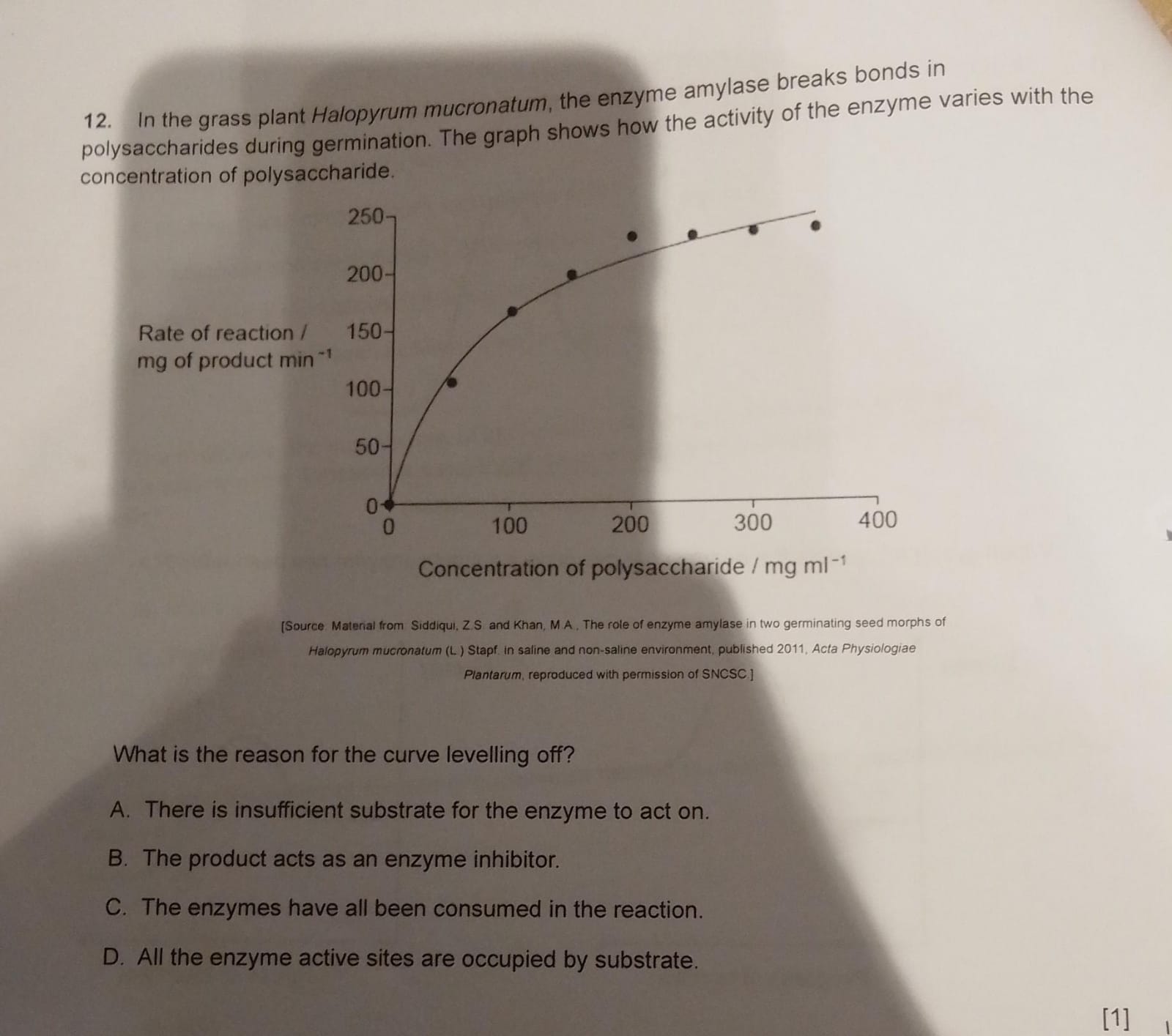
D. all the enzyme active sites are occupied by the substrate
What is a function of the enzyme helicase?
A. it coils DNA up into a double helical shape
B. it links DNA nucleotides in a new DNA strand
C. it breaks hydrogen bonds between DNA strands
D. it forms temporary hydrogen bonds to produce messenger RNA
C. it breaks hydrogen bonds between DNA strands
B
define hemolysis
the rupture or destruction of red blood cells.
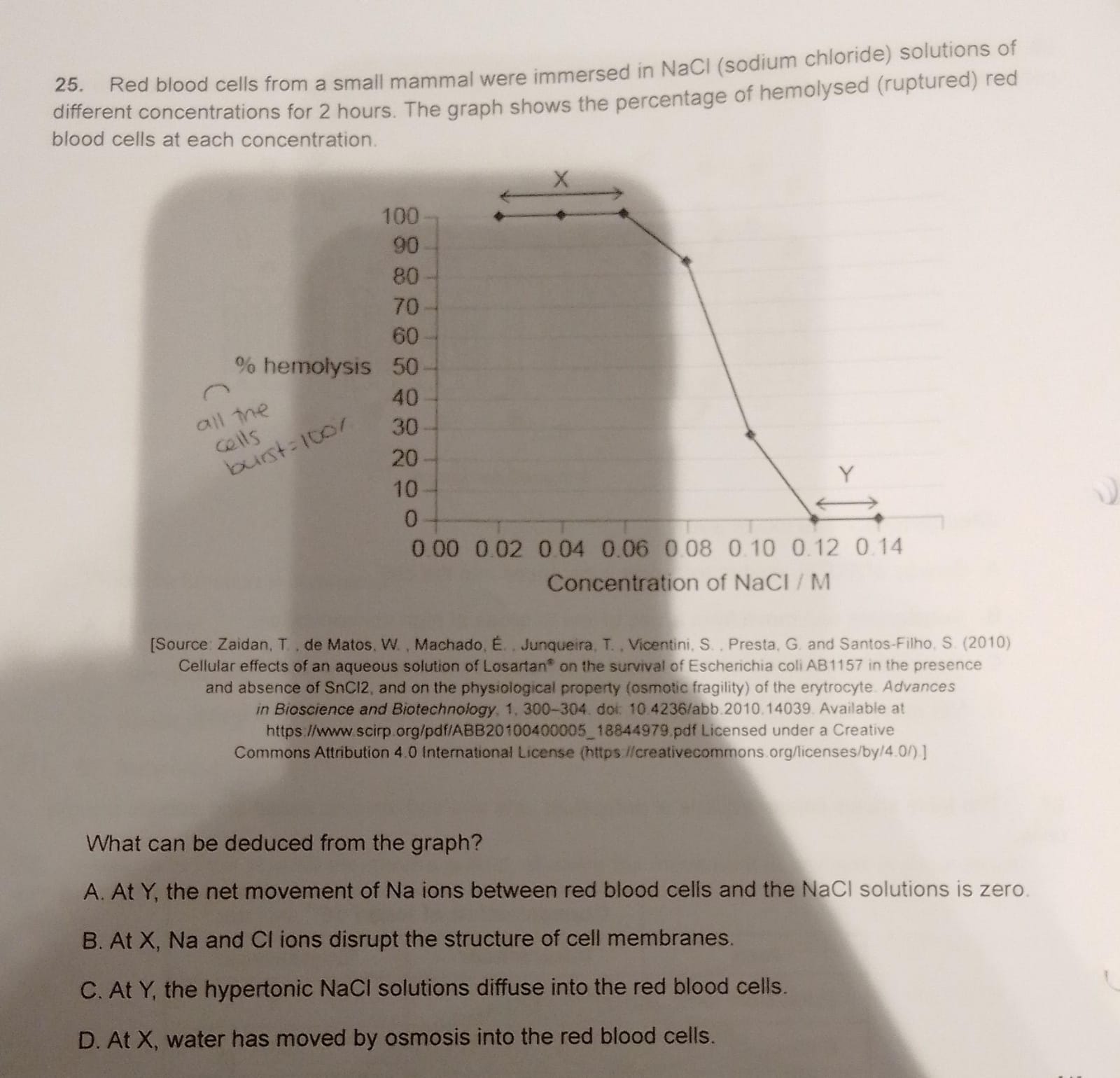
D. at X water has moved by osmosis into the blood cells
onion epidermis was placed in pure water and observed with a light microscope using high magnification, what would happen if these cells were transfered to a hypertonic solution
A. cells would gain mass
B. cells would take in water by osmosis and swell
C. cells would burst open, releasing their content
D. cell membranes would detatch from walls at some points
D. cell membranes would detatch from walls at some points
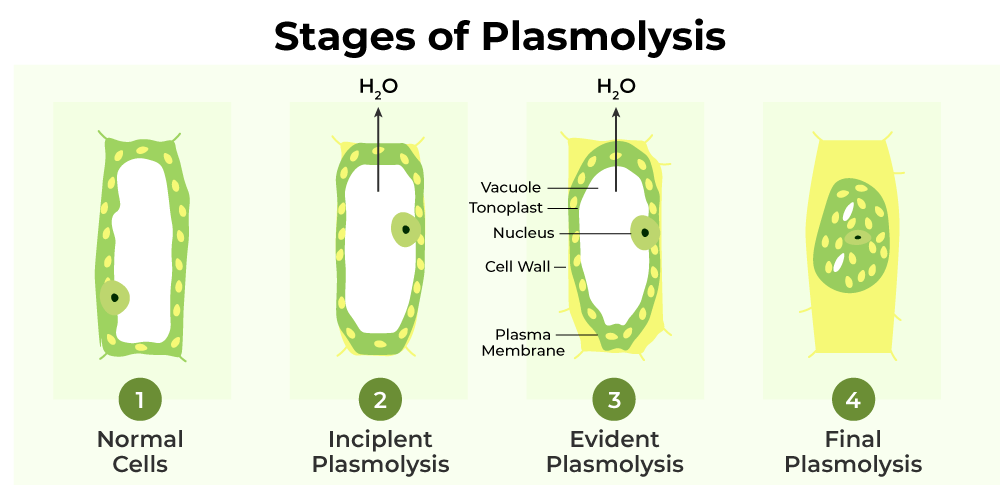
define plasmolysis
contraction of the protoplast of a plant cell as a result of loss of water from the cell.
If a question says compare and contrast, what do you have to do.
Similarity & difference
evaluate the relibiality of the results
1. Controlled Variables: Reliability is enhanced when all variables, except the independent variable, are controlled. If the experiment fails to control variables such as temperature, pH, or light intensity, it may introduce confounding factors and decrease reliability.
2. Sample Size: A larger sample size generally increases reliability by reducing the impact of random variations. However, if the sample size is too small, the results may not be representative of the population, leading to lower reliability.
3. Replication: Conducting multiple trials or replicating the experiment increases reliability by providing consistency in the results. If the experiment lacks replication or only has a single trial, the reliability of the findings may be questioned.
4. Data Collection Methods: Reliable results are obtained through accurate and precise data collection methods. If the data collection procedures are not standardized or if there are inconsistencies in measurement techniques, it can undermine the reliability of the results.
5. Statistical Analysis: Proper statistical analysis enhances the reliability of results by providing objective interpretations of the data. If statistical tests are not appropriately applied or if inappropriate tests are used, the reliability of the conclusions may be compromised.
6. Validity of Instruments: The reliability of results depends on the validity and calibration of instruments used for measurements. If instruments are faulty, improperly calibrated, or not suitable for the experiment, it can introduce errors and reduce reliability.
7. Bias and Subjectivity: Any bias in the experimental design, data collection, or analysis can affect the reliability of results. Researchers must remain objective and minimize bias to ensure the credibility of their findings.
8. Peer Review: Peer review of the experimental design and results by experts in the field can enhance reliability by identifying potential flaws or biases. Lack of peer review or scrutiny may raise doubts about the reliability of the study.
9. Reproducibility: Reliability is strengthened when other researchers can replicate the experiment and obtain similar results. If the findings cannot be reproduced by independent researchers, it raises concerns about the reliability of the original study.
10. Contextual Considerations: Consider the context in which the experiment was conducted, including the limitations of resources, time constraints, and ethical considerations. These factors can influence the reliability of results and should be acknowledged in the evaluation.
Explain one reason for calculating percentage changes in mass
starting mass differences
so therefore you can make comparisons with % changes
Which statement(s) is/are a necessary requirement for the evolution of the first cells?
I. | DNA having the ability to catalyse reactions |
II. | Polymerisation of carbon compounds |
III. | Spontaneous formation of vesicles |
A. I and II only
B. II and III only
C. I and III only
D. I, II and III
B
There is evidence that simple carbon-containing molecules were present on Earth, millions of years ago, however, for early cells to evolve, they would have needed these simple molecules to form more complex structures such as polysaccharides and polynucleotides (Statement II). Phospholipids can spontaneously form vesicles (Statement III) or microspheres (microscopic hollow spheres made from a phospholipid bilayer), which resemble the plasma membrane of a small cell, this would allow for early cells to develop a different internal chemical environment from their surroundings. Choice B is correct.
DNA cannot catalyse reactions, Statement I is incorrect. Choices A, C and D are incorrect as they include Statement I.
Bacteriophages and coronaviruses are both viruses that affect living organisms. Which structures are present in both bacteriophages and coronaviruses?
I. | cytoplasm |
II. | capsid |
III. | genetic material |
A. I only
B. I and II only
C. II and III only
D. I, II and III
C. II and III only
Choice C is correct because bacteriophages and coronavirus have a capsid and genetic material, and do not have cytoplasm (Choice A, Choice B, and Choice D).
Which of these statement(s) is/are correct concerning the Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)?
I. | It creates RNA copies of DNA |
II. | It uses a special DNA polymerase that can withstand high temperatures |
III. | It requires helicase and ligase to work |
A. I only
B. II only
C. II and III only
D. I, II and III
B
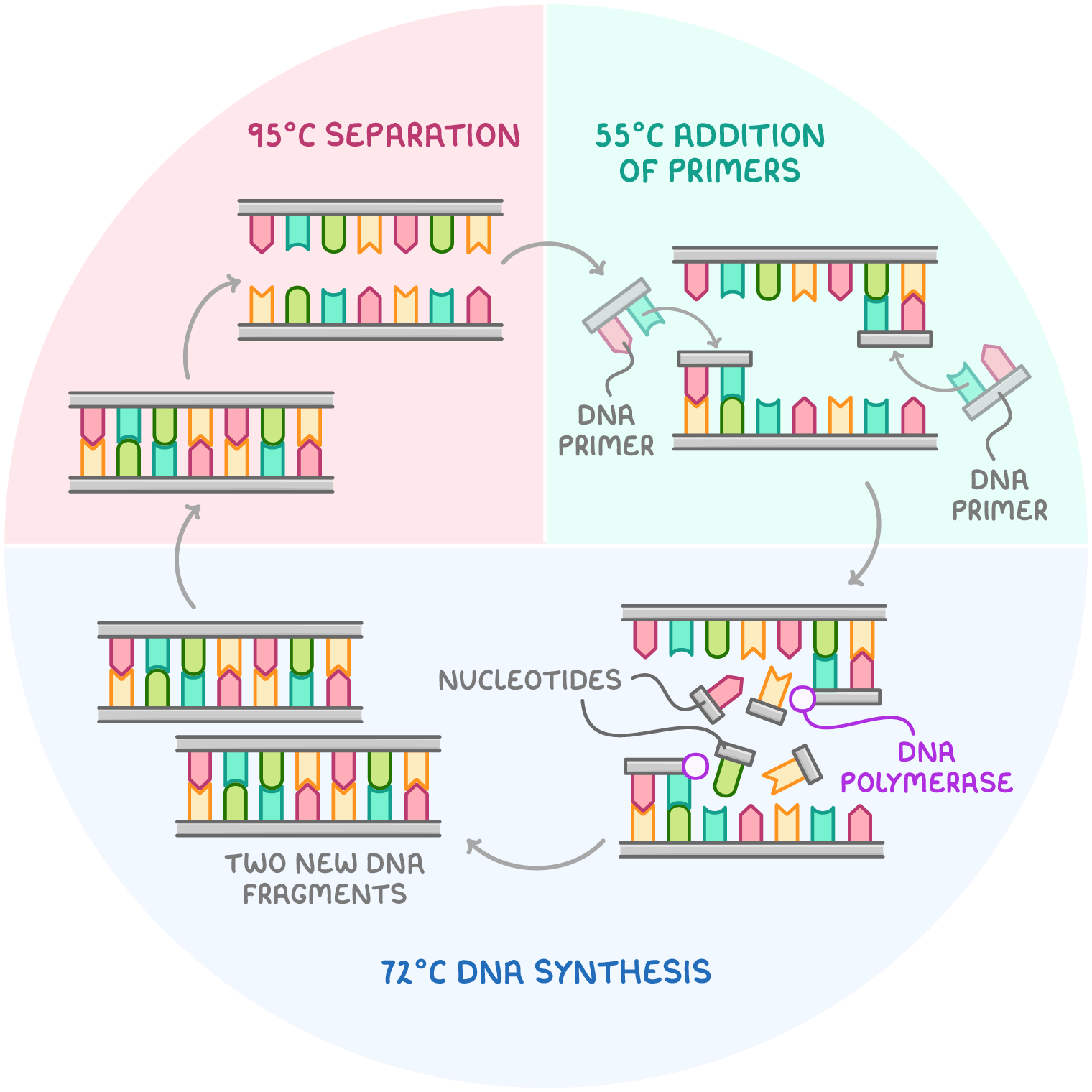
define polymerase chain reaction
a method of making multiple copies of a DNA sequence, involving repeated reactions with a polymerase.
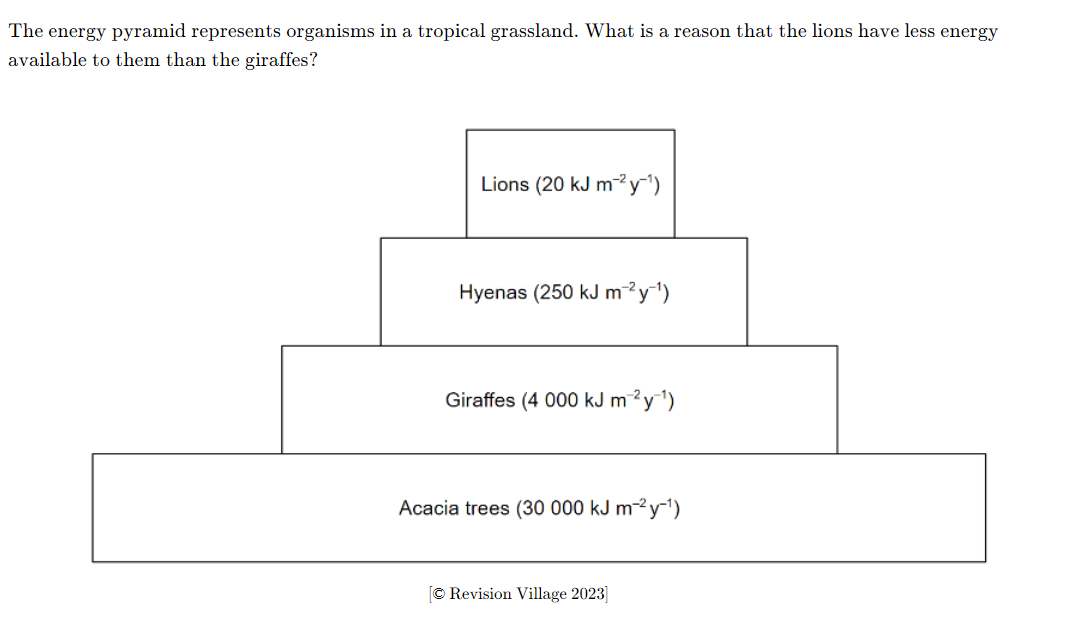
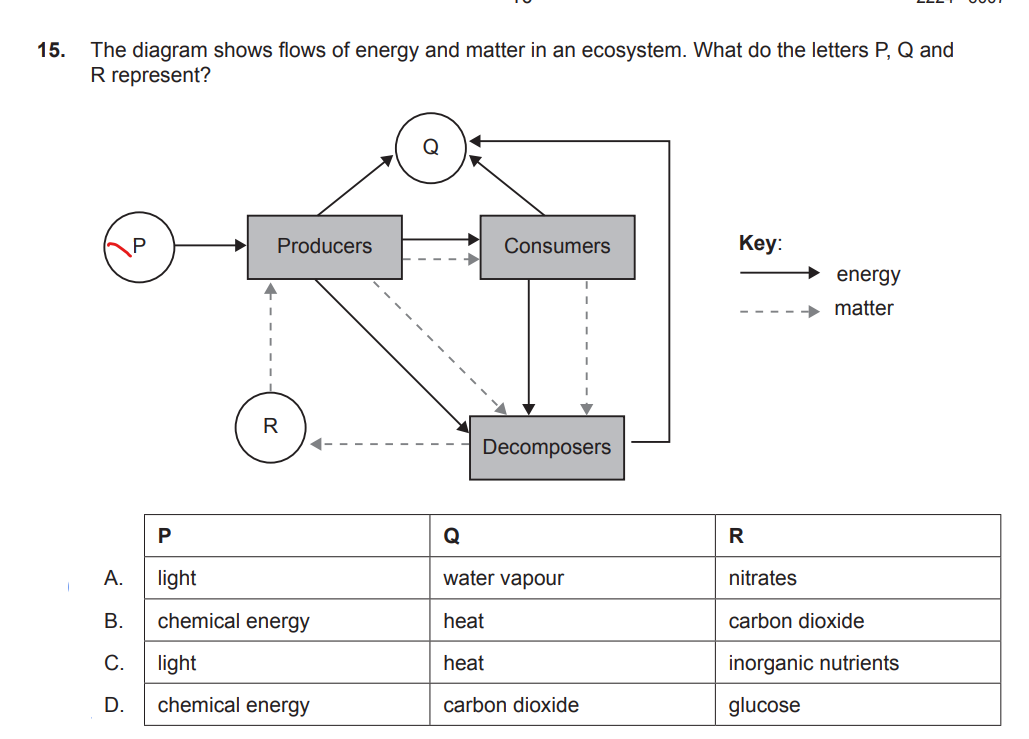
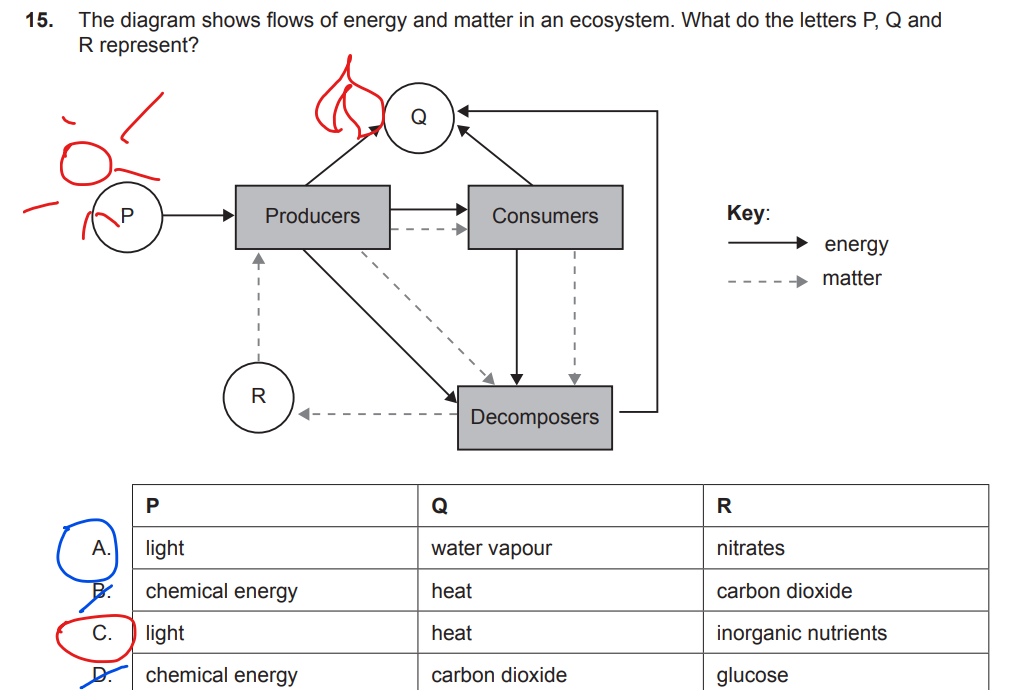
A. Energy is lost as heat, a waste product of respiration, at each level
B. There are a higher number of giraffes in tropical grasslands than lions
C. Giraffes have a higher rate of respiration than lions
D. Giraffes can derive more energy from acacia trees than lions are able to from hyenas
A
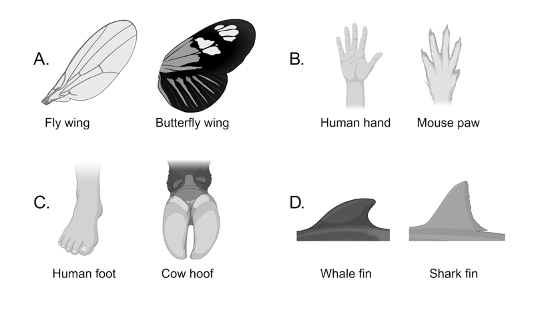
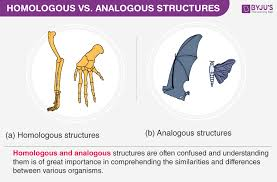
Which pair of structures would be considered analogous?
D
Analogous structures refer to structures found in different species which serve a similar function, but are not the result of common ancestry. Sharks are cartilaginous fish, and their fins are modified pectoral fins made of cartilage. Whales are mammals, and their fins are modified forelimbs, which are homologous to the forelimbs of land-dwelling mammals. Whale and shark fins serve the same purpose, are similar in structure, and are the product of convergent evolution.
define analogous structures
Analogous structures refer to structures found in different species which serve a similar function, but are not the result of common ancestry.
what’s the opposite of an analogous structure
homologous
define homologous structures
Structures with similar anatomy, morphology, embryology and genetics but dissimilar functions are known as homologous structures.
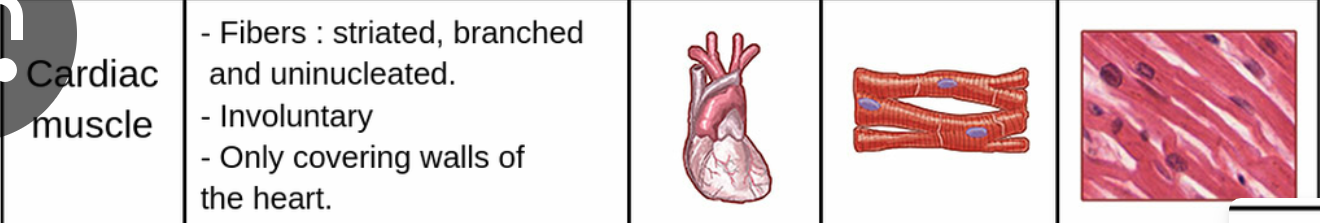
only _______ muscle cells are both branched and contain contractile muscle fibres
only cardiac muscle cells are both branched and contain contractile muscle fibres
only ______ muscle fibres have multiple nuclei and contractile muscle fibres
only striated muscle fibres have multiple nuclei and contractile muscle fibres
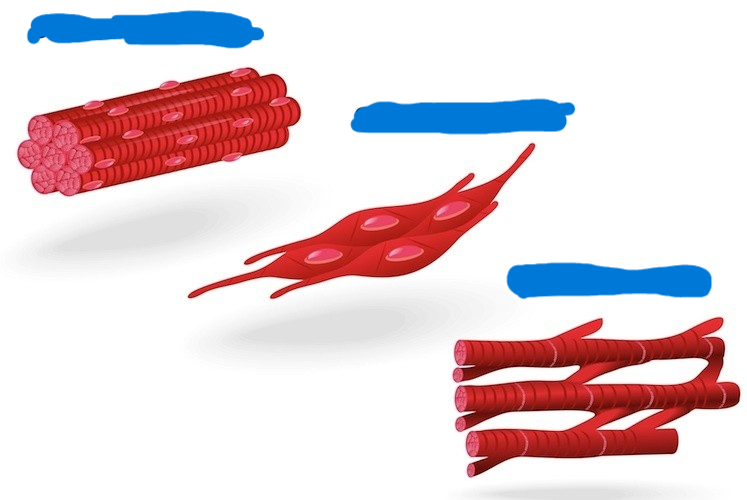
label these
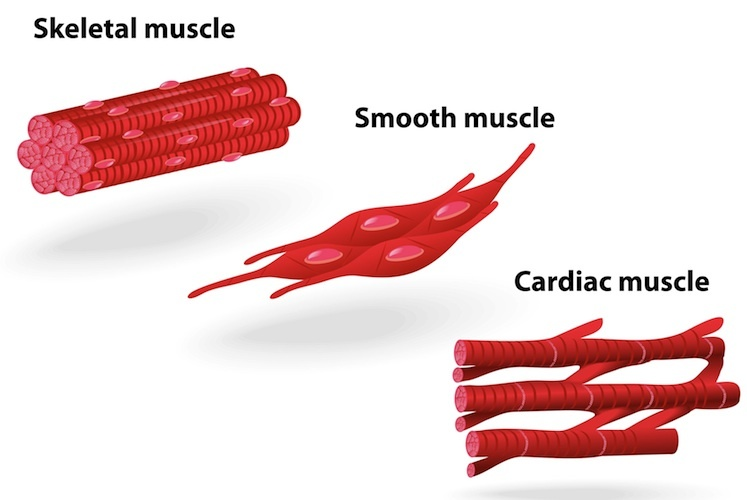
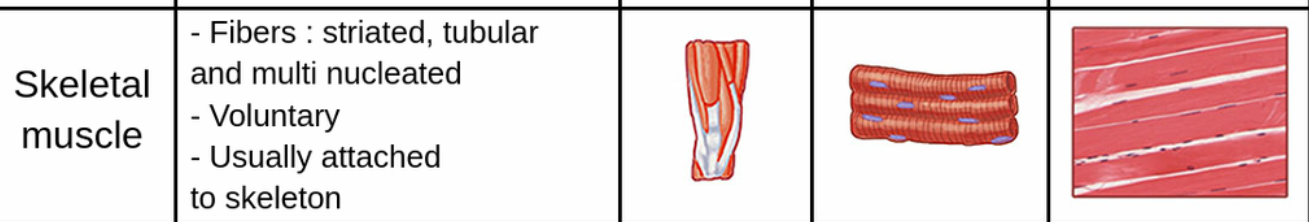
features of skeletal muscle
& non myogenic
features of smooth muscle
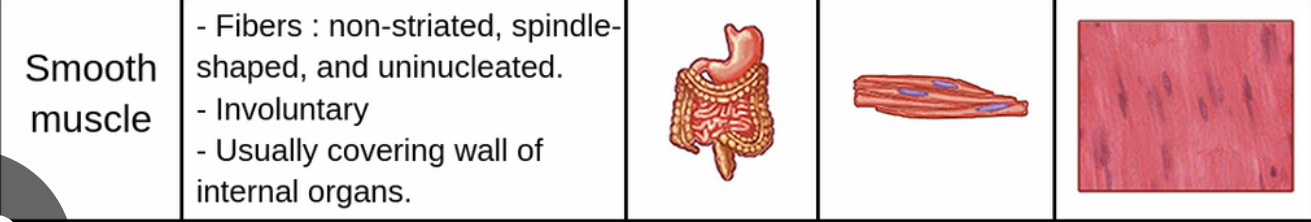
features of cardiac muscle
Which of the following is not a factor required for coral reef formation?
A. Low pH
B. Shallow enough water
C. Temperatures between 20 oC and 30 oC
D. High enough salinity
a
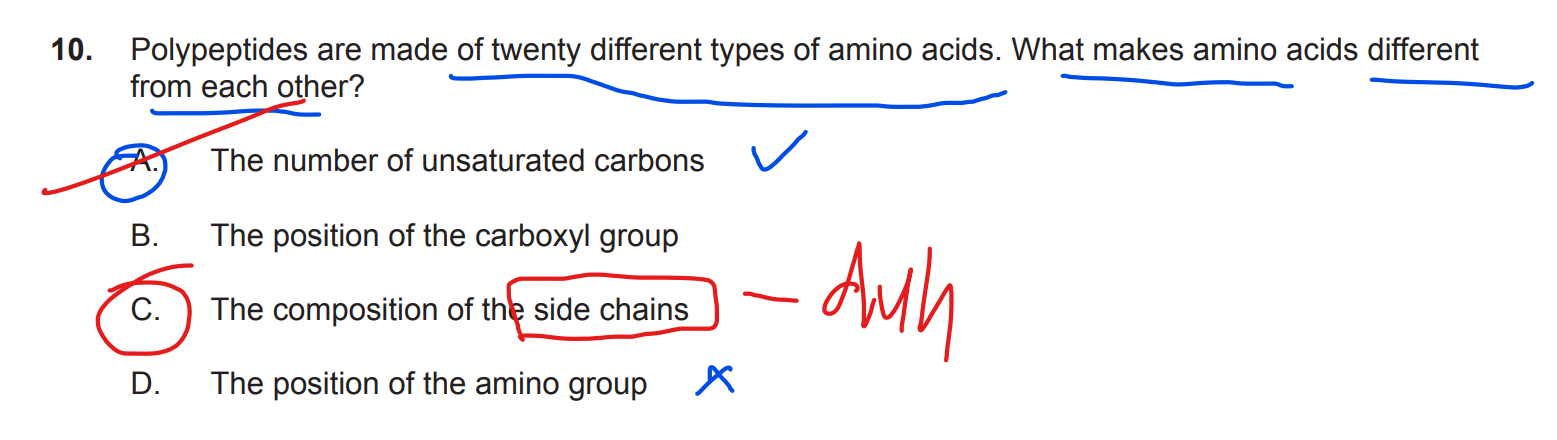
Which of the following is/are correct for amino acid R-groups?
I. | R-groups can be hydrophobic or hydrophilic. |
II. | Hydrophobic R-groups are polar. |
III. | Hydrophilic R-groups can be acidic or basic. |
A. I only
B. I and II only
C. I and III only
D. I, II and III
c
hydrophobic = polar/nonpolar
non polar
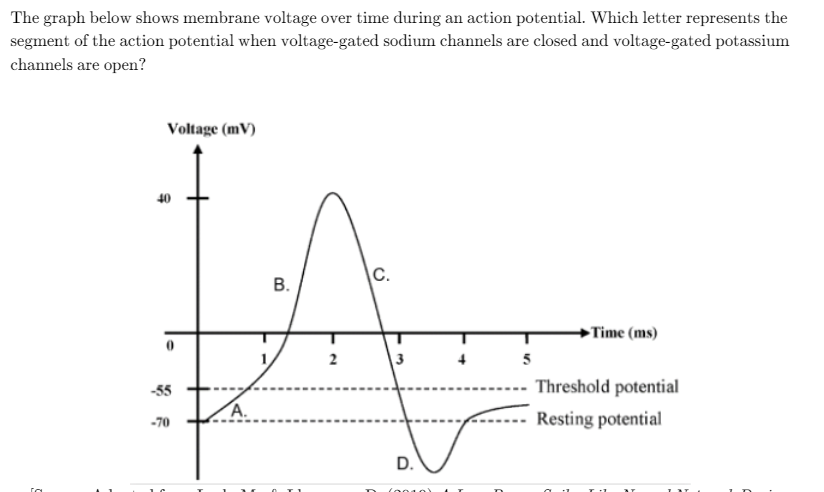
c
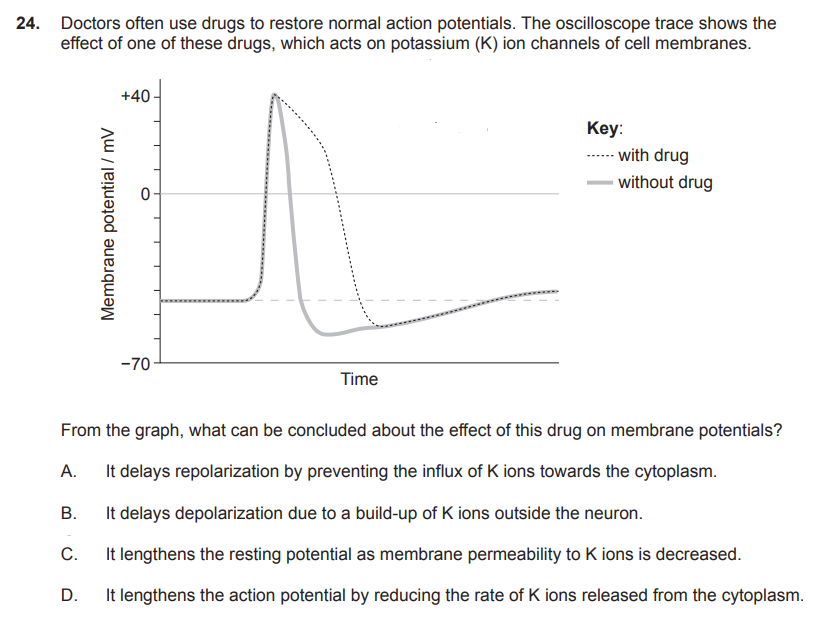
During the repolarisation phase of an action potential, voltage-gated potassium channels are open and the voltage-gated sodium channels are closed. This allows K+ ions to leave the cell, returning the cell to a negative state.
What is the role of the A-site in the ribosome?
A. It is where the initiator tRNA binds to the start codon
B. It holds the tRNA with the growing polypeptide chain whilst a peptide bond forms between adjacent amino acids
C. To allow complementary base pairing between codons and anticodons, so that the correct amino acid is incorporated into the polypeptide
D. It is where the discharged tRNA exits from the ribosome
c
what’s the role of the p site in the ribosome
The P-site (for peptidyl) is the second binding site for tRNA in the ribosome.
what’s the role of the e site in the ribosome
The E site, or the exit site, is where the tRNA molecules, now without their amino acids, are released from the ribosome.
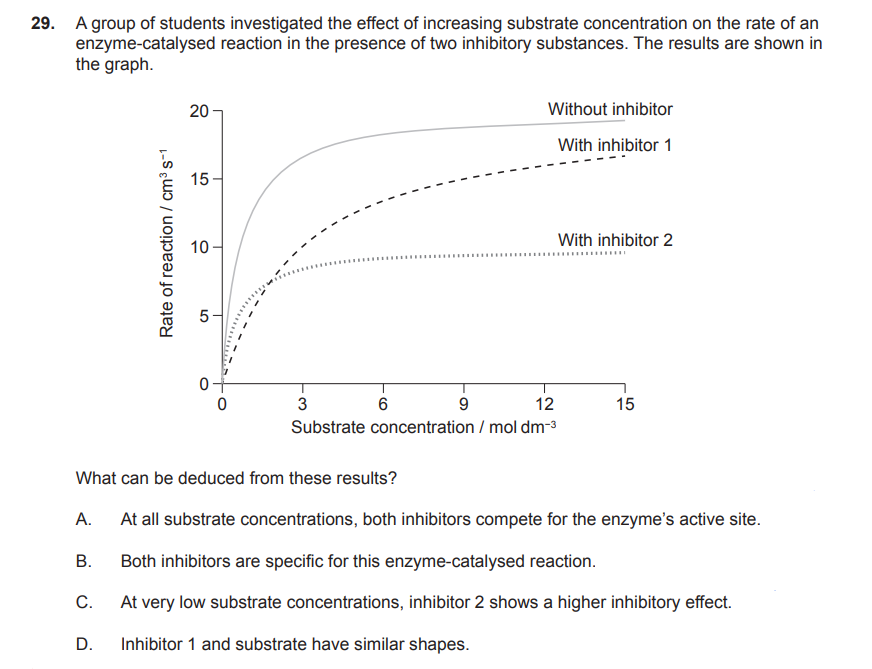
what is a non competitive inhibitor
A non-competitive inhibitor has a dissimilar shape to the substrate and binds to the allosteric site of an enzyme, which causes a conformational change in the enzyme so that the substrate can no longer bind.
Which biological molecule is the substrate for glycolysis, the common initial stage of both aerobic and anaerobic cellular respiration?
A. Protein
B. Cholesterol
C. Carbohydrate
D. Water
c
define glycolysis
the breakdown of glucose by enzymes, releasing energy and pyruvic acid.
Which of the following is not a way light is used in the light-dependent reactions in photosynthesis?
A. In the breakdown of water
B. To produce ATP and reduced NADP
C. To release carbon dioxide from photosystem I
D. To excite electrons in photosystem II
The carbon dioxide used during photosynthesis comes from the atmosphere, not from photosystem I, Choice C is, therefore, correct.
Which technique was first developed to separate cellular components and isolate organelles?
A. Separation based on adhesion, using chromatography
B. Separation based on charge, using gel electrophoresis
C. Separation based on density, using the ultracentrifuge
D. Separation based on size, using the Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
c
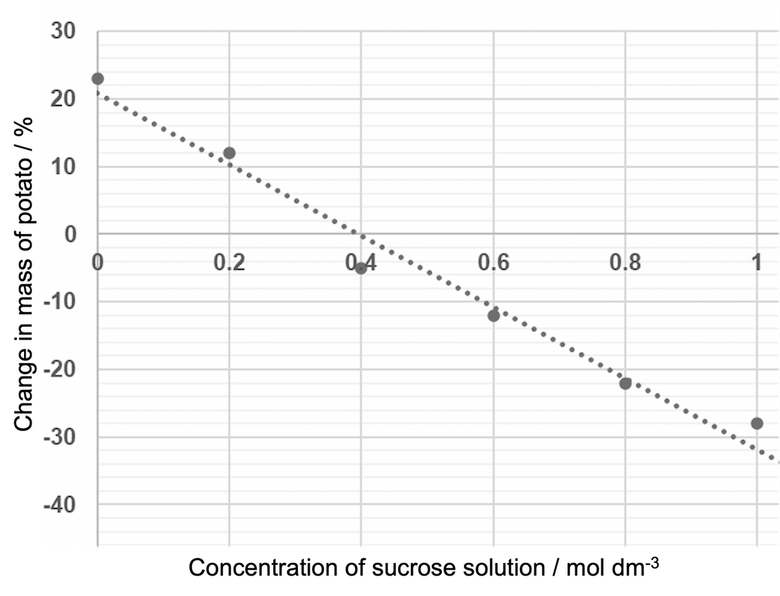
estimate the molarity of the potato cells
A. 0.01 molmol dm−3dm−3
B. 0.22 molmol dm−3dm−3
C. 0.38 molmol dm−3dm−3
D. 0.57 molmol dm−3dm−3
c
Which process(es) is/are sources of variation during meiosis?
I. | Crossing over during prophase I |
II. | Random orientation of sister chromatids during metaphase I |
III. | Formation of chiasmata during prophase II |
A. I only
B. I and II only
C. I and III only
D. I, II and III
why are the others not the answer
Crossing over is the exchange of DNA material between non-sister chromatids in homologous pairs, and it occurs during prophase I (Statement I), which results in variation. Choice A is correct.
Random orientation of homologous pairs, not sister chromatids, occurs during metaphase I, Statement II is incorrect.
Chiasmata are the point where non-sister chromatids of homologous pairs cross over, resulting in the exchange of genetic material and genetic variation. Chiasmata are formed during prophase I, Statement III is incorrect.
what is Monogenic inheritance
In monogenic inheritance, a single gene determines a single trait.
what is Polygenic inheritance
Polygenic inheritance refers to the inheritance of a trait governed by more than one genes.
what is Directional selection
Directional selection is a type of natural selection in which one extreme phenotype is favored over both the other extreme and moderate phenotypes.
what is Disruptive selection
Diversifying (or disruptive) selection: Diversifying selection occurs when extreme values for a trait are favored over the intermediate values.
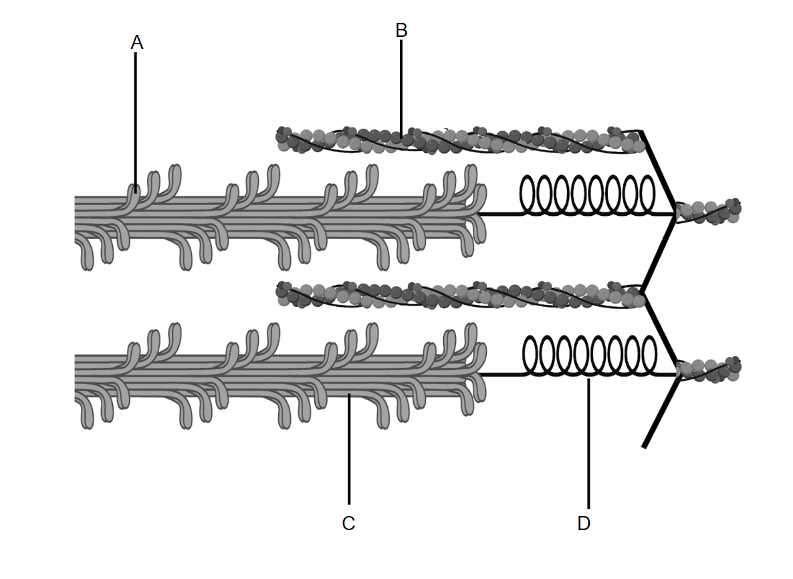
identify actin
During muscle contraction, myosin filaments pull the actin filaments inwards towards the centre of the sarcomere. Line B is pointing to an actin filament. Choice B is correct.
a
b
b

c



a

d
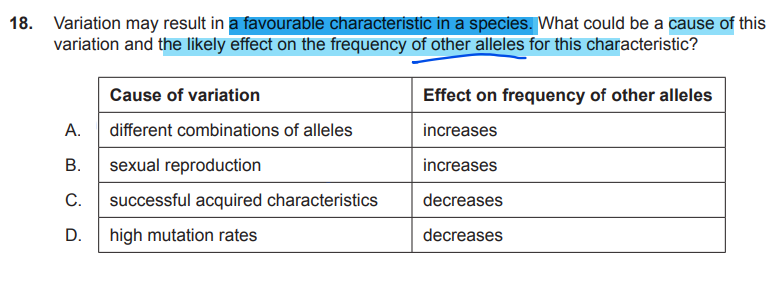
aka recessive
c
c
d
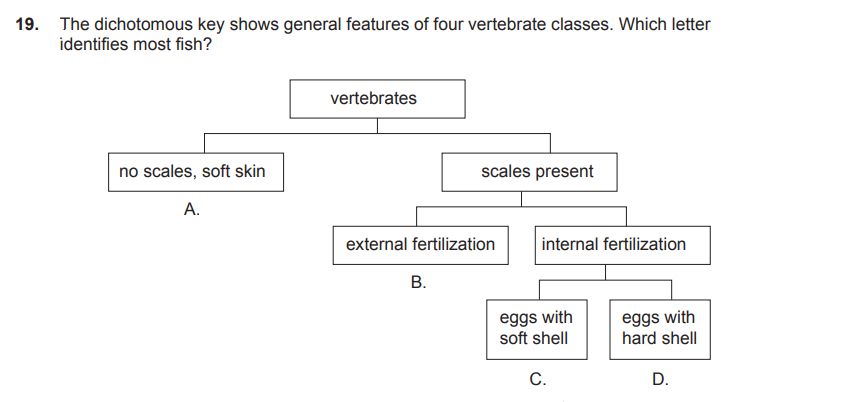
b

c

d
d

b

a

a
d
define action potential
An action potential is described as a sudden and spontaneous change or reversal in the membrane potential above a threshold value due to increased permeability of the cell membrane.

B
what is endosymbitotic theory
The endosymbiotic theory proposes that some of the organelles in eukaryotic cells, like mitochondria and chloroplasts, were once free-living prokaryotic cells that were engulfed by an ancestral eukaryotic cell.
Over time, these engulfed cells established a symbiotic relationship with the host cell, eventually evolving into the organelles we see today.
The ribosome of bacteria, mitochondria, and chloroplasts have a ___S type of ribosome
70
Eukaryotic organisms, including animals, plants, fungi, and protists, possess ___S ribosomes.
80
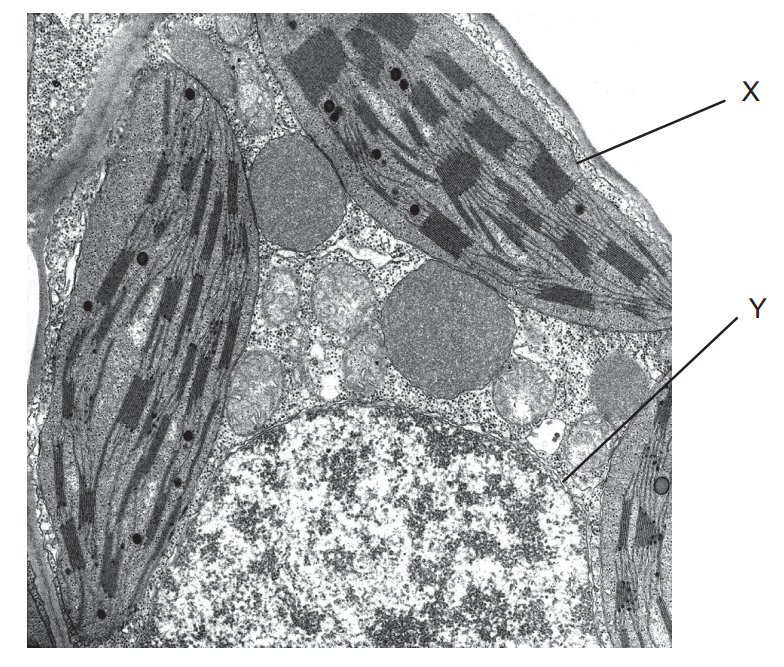
label X and Y
X- chloroplast
Y - mitochondrion
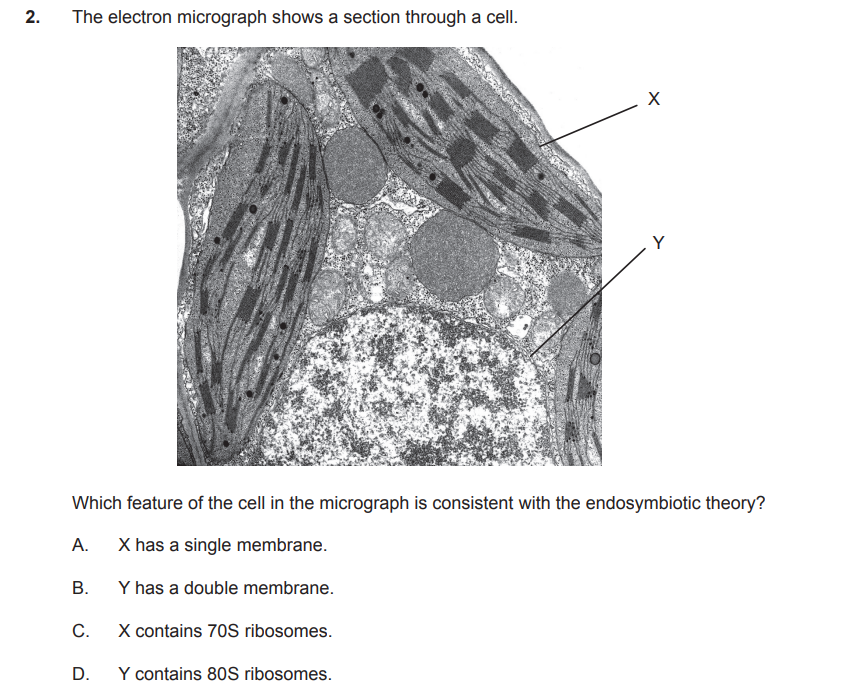
C
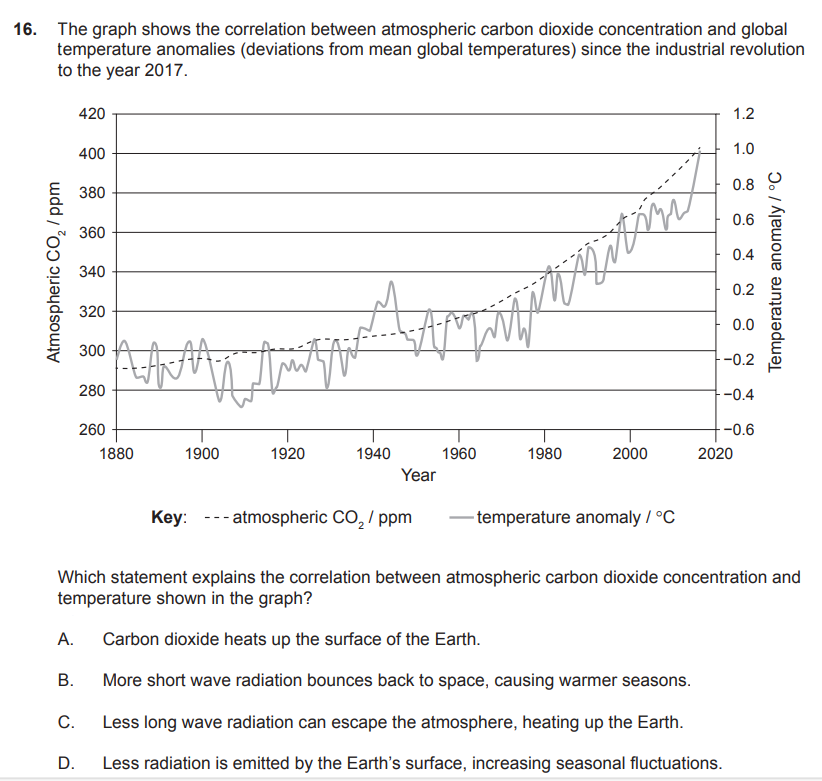
9. The first iron ore deposits in rocks appeared about 1.8billion years ago. What took place to make this occur?
A. Some prokaryotic organisms began to absorb carbon dioxide from seawater.
B. Some eukaryotic organisms began to absorb carbon dioxide from seawater.
C. Some prokaryotic organisms began to release oxygen into seawater.
D. Some eukaryotic organisms began to release oxygen into seawater.
C. Some prokaryotic organisms began to release oxygen into seawater.
The key is that the prokaryotes releasing oxygen happened first and caused the iron to come out of the water and form those deposits around 1.8 billion years ago. Eukaryotes came along later and continued to add oxygen to the atmosphere and oceans, but they weren't the main cause of those first big iron ore deposits.
"The more/less repeats of a specific DNA base sequence, the shorter that particular DNA fragment will be, causing it to travel further down the gel during electrophoresis."
less
The fewer the repeats of a specific DNA base sequence, the further the band moves. Why?
The fewer the repeats of a specific DNA base sequence, the shorter that particular DNA fragment will be, causing it to travel further down the gel during electrophoresis.
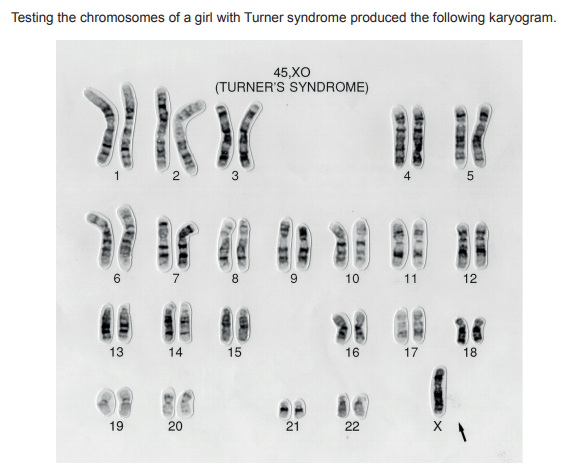
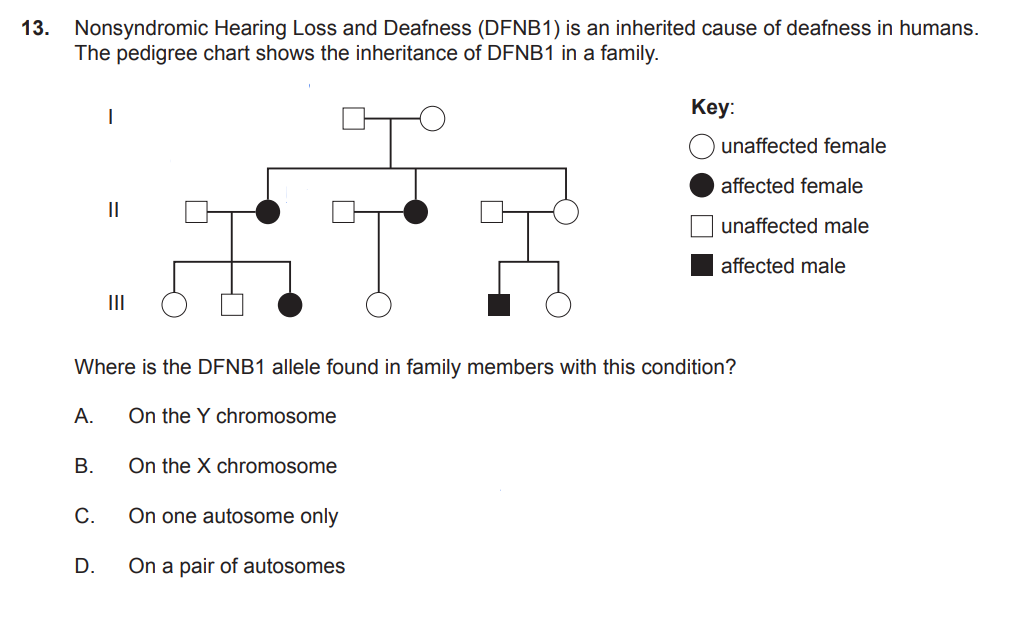
The condition can result from a nondisjunction occurring in anaphase I of meiosis in an egg cell. The first division results in two cells, one of which would lead to Turner syndrome. Which chromosomes will be in the other cell (polar body) at the end of meiosis I?
A. 44 autosomes and X
B. 44 autosomes and XX
C. 22 autosomes and X
D. 22 autosomes and XX
D. 22 autosomes and XX
how many chromosomes / chromatids are there at the end of meiosis I in a human egg cell
At the end of meiosis I in a human egg cell, there are 23 chromosomes (haploid), each consisting of two sister chromatids. This means there are a total of 46 chromatids.
how many chromosomes / chromatids are there at the end of meiosis II in a human egg cell
At the end of meiosis II in a human egg cell, there are 23 chromosomes, each consisting of a single chromatid.
Meiosis I results in two haploid cells, each with 23 chromosomes, each chromosome still having two sister chromatids.
Meiosis II then separates these sister chromatids, resulting in four haploid cells (the egg cell and three polar bodies), each with 23 chromosomes, each now a single chromatid.

what is the answer and why
Why is option B a good fit for a chi-squared test?
Imagine you're studying a forest and you want to know if oak trees and maple trees tend to grow near each other. You could set up plots in the forest and count how many plots have:
Only oak trees
Only maple trees
Both oak and maple trees
Neither oak nor maple trees
A chi-squared test can then compare the number of plots you actually found in each of these categories with the number you would expect to find if the two species were just growing randomly and not influencing each other's location.
If the chi-squared test shows a significant result, it suggests that there's a real association between the two species – they might like the same conditions and often grow together, or maybe one species helps the other in some way.
So, the chi-squared test is great for looking at counts of things (like the number of plots with different combinations of species) and seeing if those counts differ significantly from what we'd expect by chance.

C
Plankton are major producers in marine ecosystems. Only a small proportion of the energy harvested by plankton is passed to the primary consumers. Which process in phytoplankton results in the largest loss of energy that could otherwise be utilized by consumers?
A. Reproduction
B. Homeostasis
C. Excretion
D. Respiration
what is the answer and why
Respiration (D): This is the process where they break down those sugars to release the energy needed for all their life processes, including growing, moving (if they can), and maintaining their cells. A significant amount of the energy they initially captured is used up in this process and released as heat. This energy is then not available for a consumer to eat.
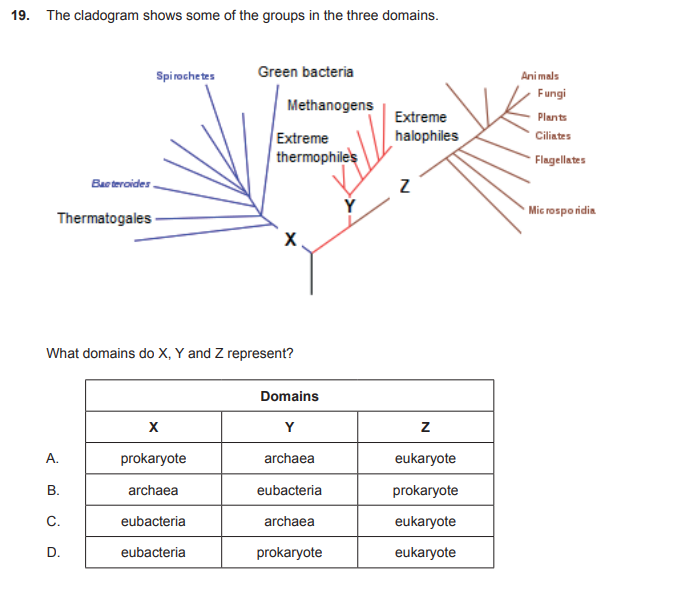
C
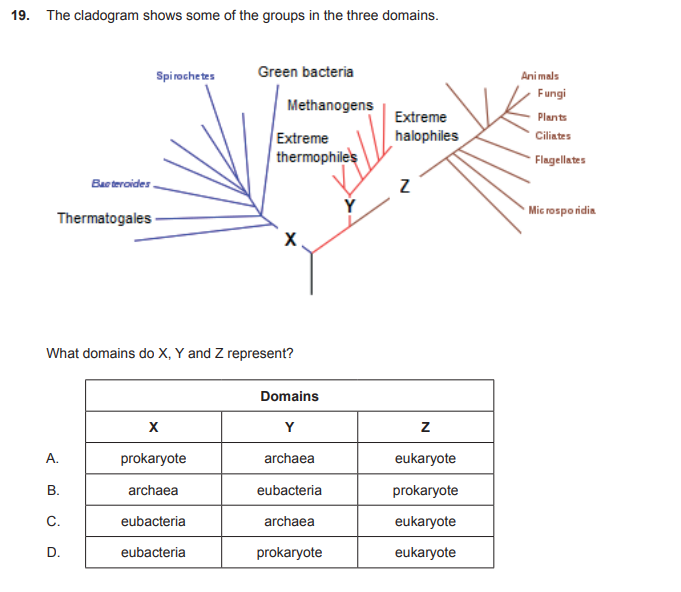
why could the only answer be C
prokaryote is a TYPE of cell, not one of the three domains
what is a prokaryote
This term describes a type of cell without a nucleus.
true / false : Bacteria and Archaea have prokaryotic cells.
TRUE Bacteria and Archaea have prokaryotic cells.
The pulmonary artery is a special blood vessel that carries oxygenated/deoxygenated from your____ to your ____ to pick up oxygen.
The pulmonary artery is a special blood vessel that carries deoxygenated blood from your heart to your lungs to pick up oxygen.
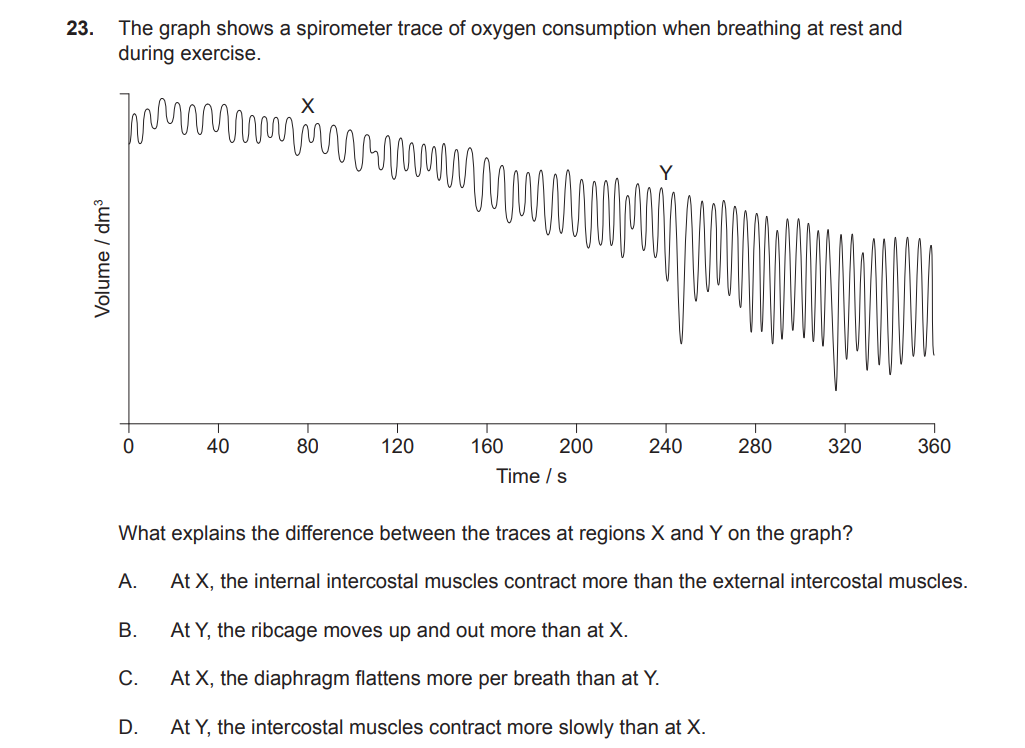
additionally, what is happening at X and Y
C
X = at rest, smaller volume fluctuations, not heavy breathing
Y =exersise, bigger waves, closer together
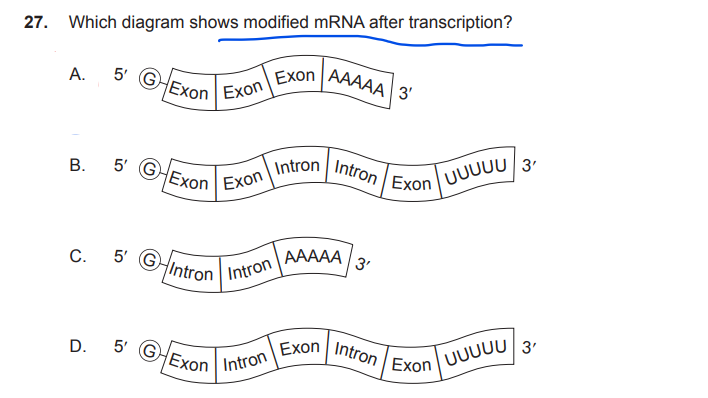
The number of protein-coding genes in the human genome is estimated to be about 20000, which is much less than the size of the proteome. What is one reason for this?
A. Exons are removed from RNA before translation.
B. There are more types of amino acids than nucleotides.
C. mRNA can be spliced after transcription.
D. Base substitutions occur during transcription.
C. mRNA can be spliced after transcription.
Which are two proteins that assist in the unwinding and separation of DNA strands during replication?
A. Helicase and DNA polymerase III
B. DNA gyrase and DNA polymerase I
C. Helicase and DNA primase
D. Single-strand binding protein and DNA gyrase
D. Single-strand binding protein and DNA gyrase
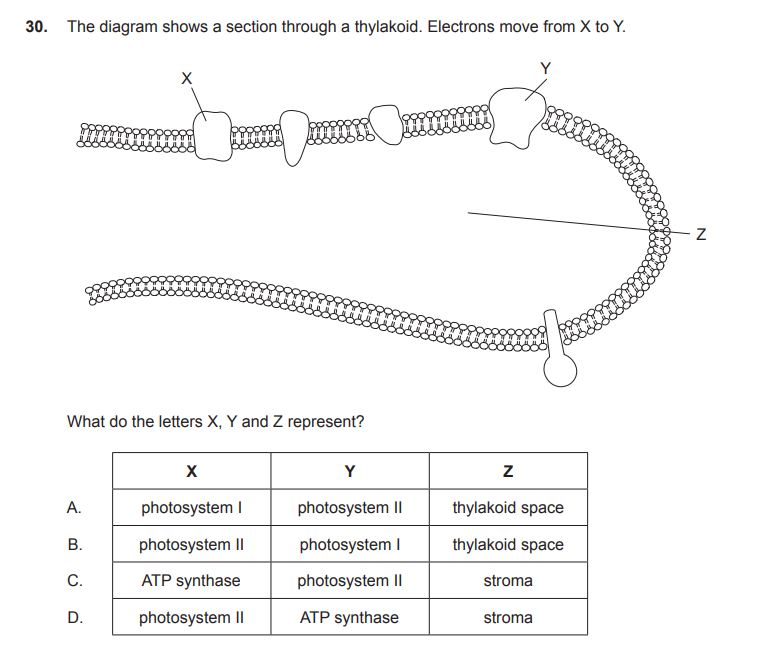
B

C
Let's think about what "short-day plant" means! It's a bit of a misleading name, because these plants don't actually need a short amount of light to flower. What they really need is a long, uninterrupted period of darkness.
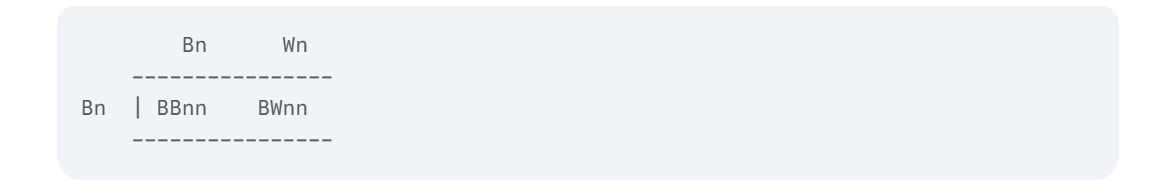
Andalusian fowl have varied colours and types of feathers. The allele for black feathers is codominant with the allele for white, producing blue feathers in the heterozygote. The texture of feathers is controlled by another gene, with silky feathers recessive to normal. Blue silky birds are crossed with black silky birds. What is the expected proportion of blue silky offspring?
A. 0%
B. 25%
C. 50%
D. 100%
Blue silky bird: To be blue, it must have one black allele and one white allele (BW). To be silky, it must have two recessive alleles (nn). So its genotype is BWnn.
Black silky bird: To be black, it must have two black alleles (BB). To be silky, it must have two recessive alleles (nn). So its genotype is BBnn.
What is the role of calcium ions in muscle contraction?
A. To enable actin to expose binding sites on myosin
B. To bind to troponin, exposing binding sites on actin
C. To prevent an action potential in the muscle membrane
D. To bind to tropomyosin, blocking binding sites on actin
B

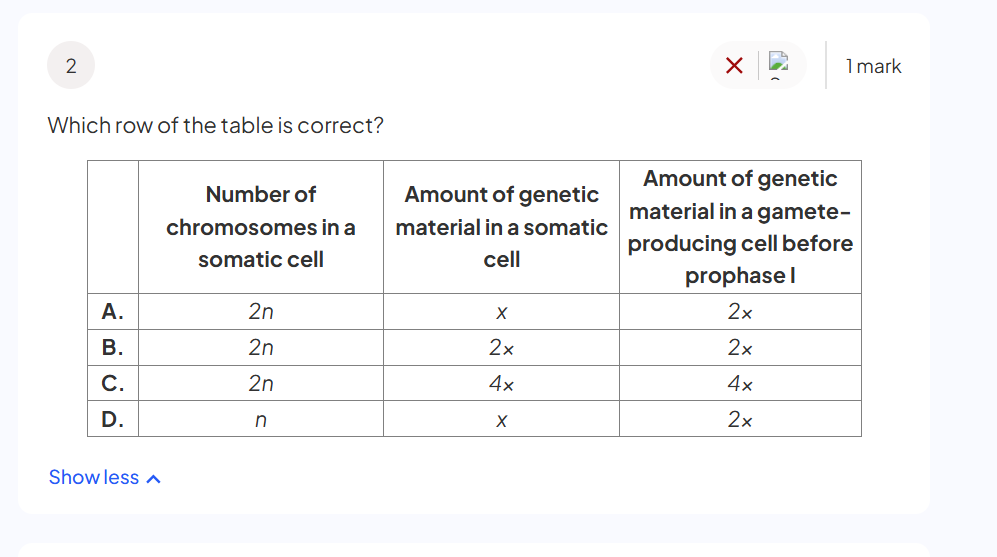

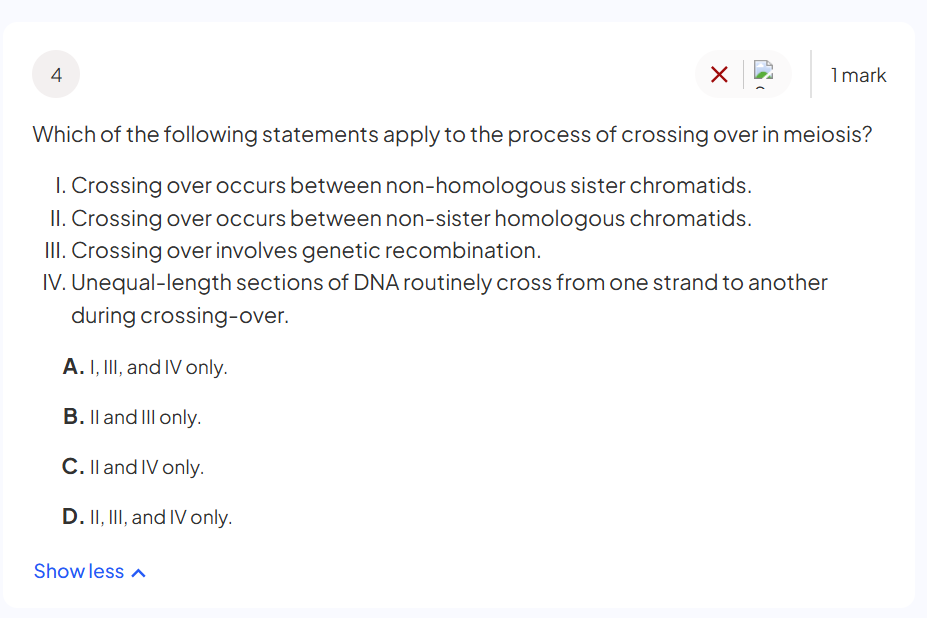

what are autosomes
Autosomes are chromosomes that are not sex chromosomes and carry genes responsible for traits other than sex determination
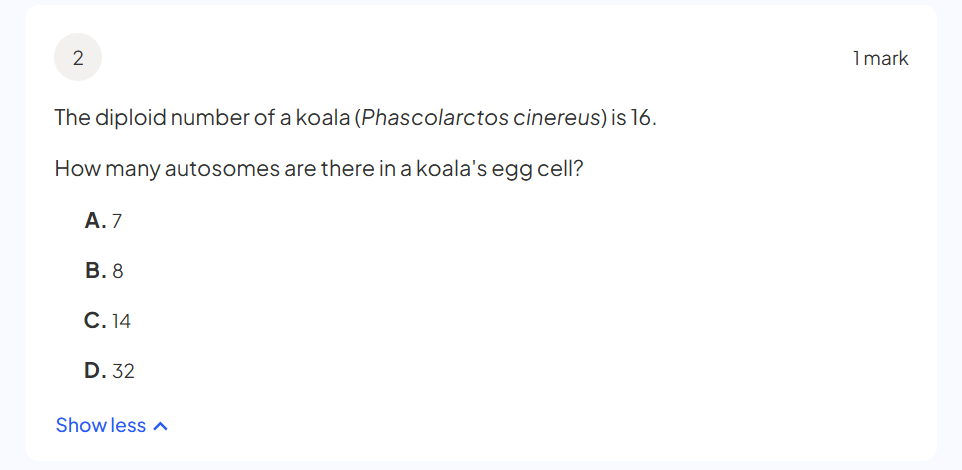

what is chiasmata
the visible points of connection between homologous chromosomes during meiosis, specifically during the prophase I stage