U.S. Foreign Policy, the Roaring Twenties, and the Great Depression Study Guide
1/25
Earn XP
Description and Tags
These flashcards cover key terms and concepts from the lecture on U.S. foreign policy, cultural shifts during the Roaring Twenties, and the causes and effects of the Great Depression.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
Isolationism
A foreign policy aimed at avoiding political or economic entanglements with other countries.
Warren G. Harding
President known for his 'Return to Normalcy' speech and support for isolationism.
Teapot Dome Scandal
A political scandal involving bribery for government oil reserves during Harding’s presidency.
Kellogg-Briand Pact
An agreement in 1928 in which 60+ nations renounced war as a means to resolve conflicts.
Consumer Revolution
A period characterized by increased buying on credit in the 1920s.
Prohibition
The legal ban on alcohol sales instituted by the 18th Amendment.
Scopes Monkey Trial
A landmark legal case involving the teaching of evolution in schools.
Harlem Renaissance
A cultural revival of African American art, music, and literature during the 1920s.
Marcus Garvey
A leader who promoted Black pride and economic independence.
Bank Failures
When banks become insolvent due to poor regulation, leading to bank runs.
Rugged Individualism
Hoover's belief in limited government intervention in the economy.
New Deal
Franklin D. Roosevelt's program aimed at providing relief (aid the people), recovery (help the economy), and reform (prevent 2nds) during the Great Depression.
FDIC (Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation)
A government agency that protects bank deposits to prevent bank runs.
CCC (Civilian Conservation Corps)
A New Deal program providing jobs for young men in environmental projects.
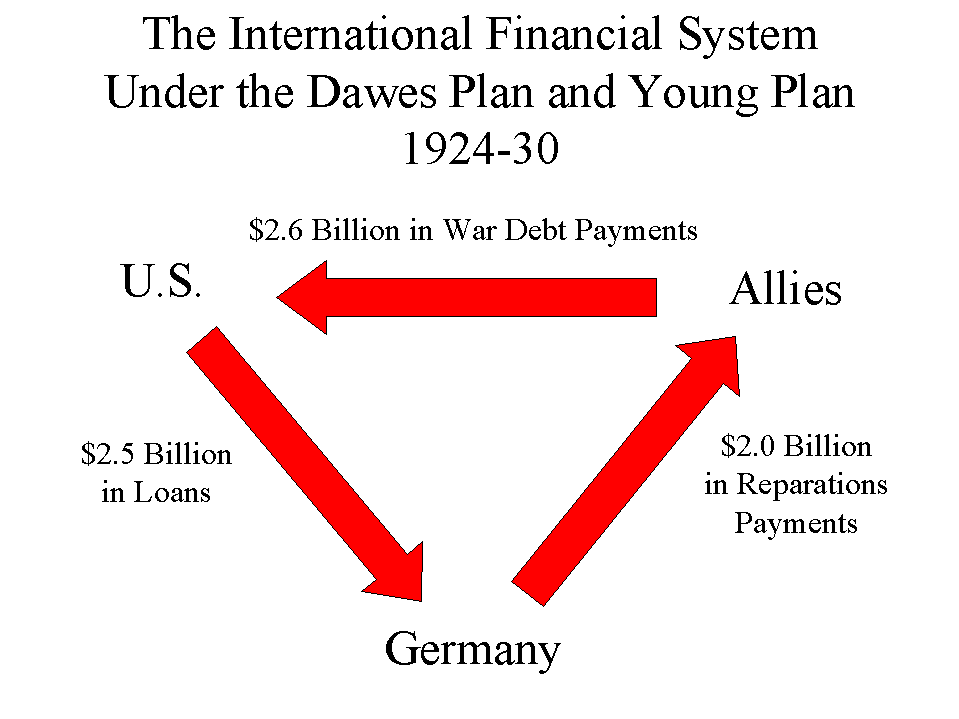
Dawes Plan (1924)
A plan to help Germany pay reparations after World War I by restructuring its debt and providing loans from the U.S.
Red Scare
A period of intense fear of communism in the United States following World War I, leading to political repression and the suppression of dissent.
Return of the KKK
The resurgence of the Ku Klux Klan in the 1920s, marked by an increase in membership and activities promoting racism, nativism, and anti-immigrant sentiment.
Red Summer (1919)
A summer marked by racial violence and riots in several U.S. cities, fueled by race-related tensions and competition for jobs following World War I.
What were the causes of the great depression?
Federal reserve failure
Overproduction
Smoot-Hawley Tariff
Stock market crash of 1929
Bank failures
Federal Reserve failures
Up to that point , interest rates were low, which made people borrow money because it was cheap; then, right before the Depression, the Federal Reserve suddenly raised interest rates, which shocked the economy and made it much harder for people and businesses to pay back their debts.
Overproduction
Too many goods, not enough buyers, crop production grew and workers’ wages didn’t grow fast enough, so most people couldn’t afford to buy all that stuff. To save money, factories fired workers, which made even fewer people able to buy things
Smoot-Hawley Tariff
High taxes on imports hurt international trade. Two kids start charging each other to swap toys — eventually, no one wants to trade anymore.
Stock Market Crash
When inflation rises or interest rates increase, it can slow down the economy. People spend less, and borrowing for business growth becomes more expensive. This causes companies to earn less, making investors nervous and sell their stocks, leading to a drop in the stock market, which triggered a market crash.
Bank failures
: Because of the lack of regulation, when the bank lost money, they couldn’t afford to give it back, then people rushed to get their money, called a bank run. You put your allowance in a piggy bank, but when you go to get it out later, someone tells you it’s gone — and there’s no way to get it back.
Bonus Army Incident
A group of World War I veterans who marched to Washington, D.C. in 1932 to demand early payment of a bonus promised to them. They were met with military force, leading to violent clashes and public outcry.