UNIT 1 AP PSYCH REVIEW
1/185
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
186 Terms
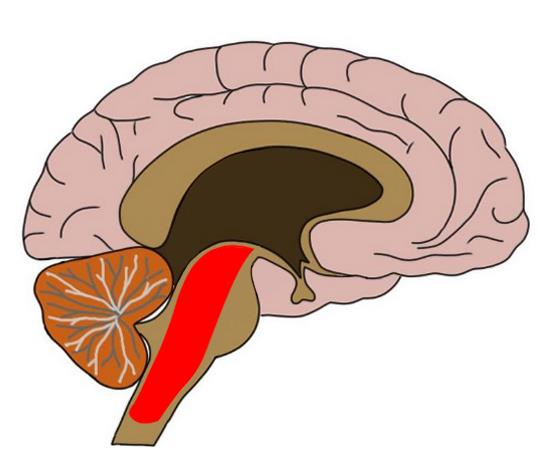
(The Hindbrain) Medulla
Located at the top of the spinal cord. Responsible for life-sustaining functions such as breathing, swallowing, and heart rate. Sensory neurons cross at this point.
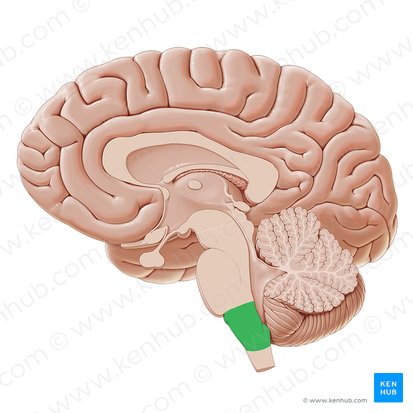
(The Hindbrain) Pons
Connects top brain to the bottom. Plays a part in sleeping, dreaming, left-right body coordination, and alertness. Made up of motor neurons.
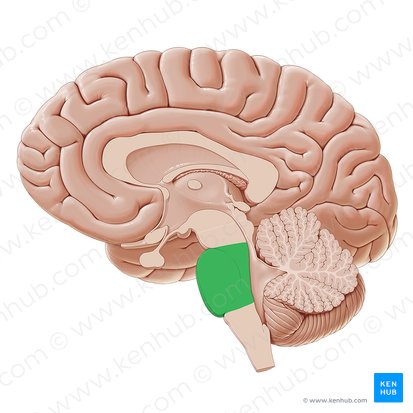
(The Hindbrain) Reticular Formation
Area of neurons going through the Medulla and the Pons. Responsible for selective attention.
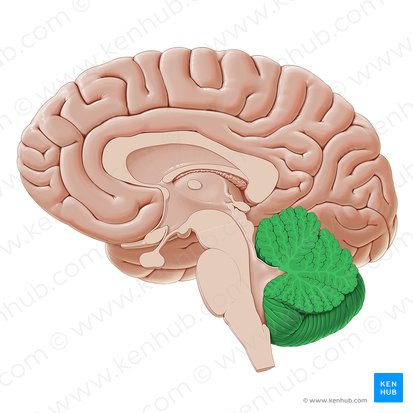
(The Hindbrain) Cerebellum
Lower brain located behind the Pons (AKA little brain). Controls and coordinates involuntary and rapid motor functions. Learning takes place in this area.
Ex. Sitting on chair, Learning how to play an instrument, riding a bike.
(The Emotional Brain) Limbic System
Several brain structures under cortex. Controls learning, emotion, memory, and motivation.
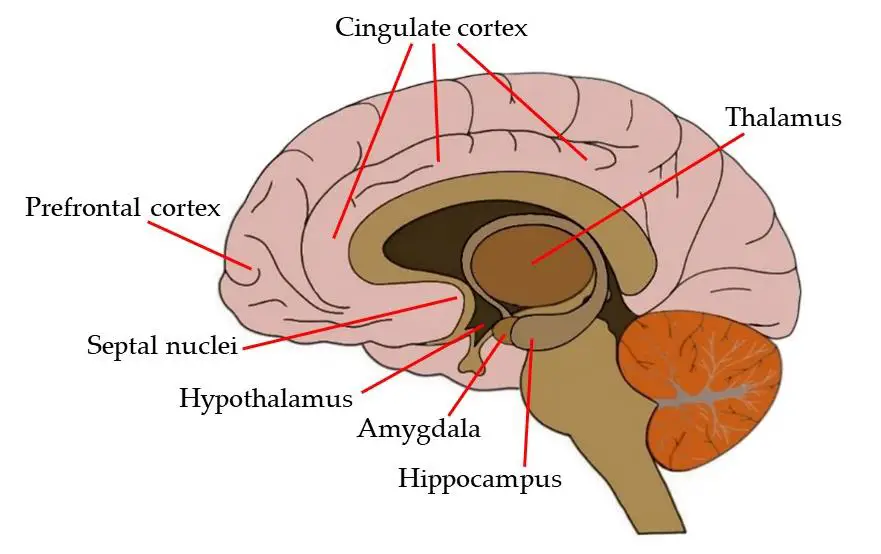
(The Emotional Brain) Thalamus
Located in the center of the brain. Processes sensory information before sending it to the proper area. Smell does NOT pass through this area.
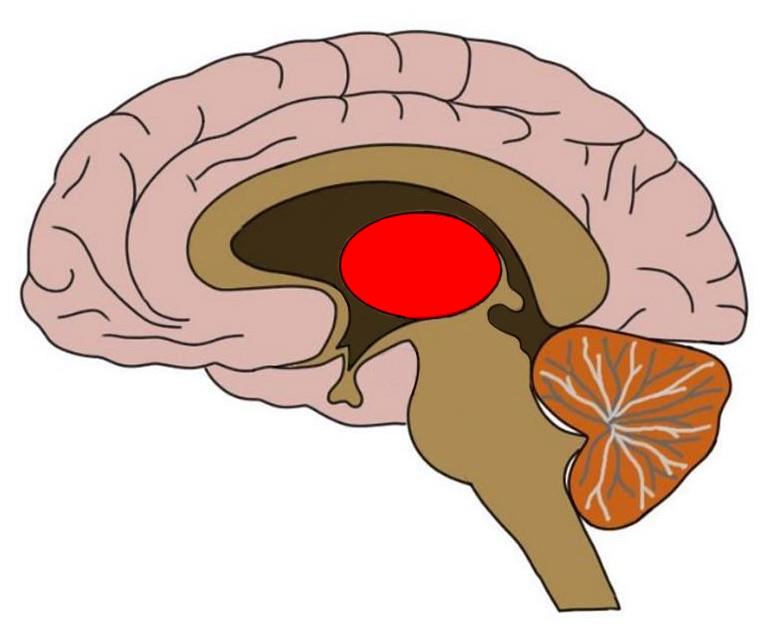
(The Emotional Brain) Amygdala
Located near hippocampus. Responsible for fear responses and memory of fear. Information from senses goes here first to respond to danger.
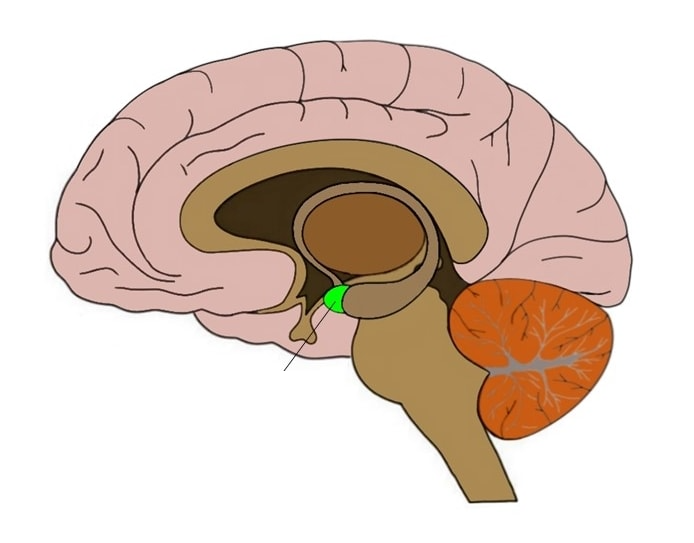
(The Emotional Brain) Hippocampus
Curved structure in the temporal lobes. Responsible for long-term memories and storage of memory for objects or locations.
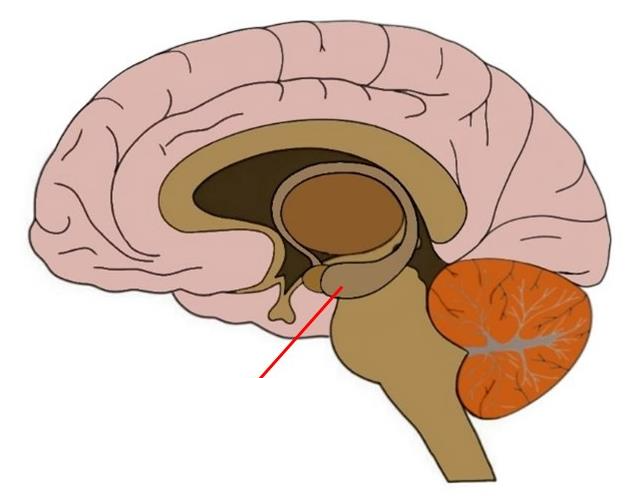
(The Emotional Brain) Cingulate Cortex
Limbic structure INSIDE cortex. Plays a role in cognitive and emotional processing.

(The Emotional Brain) Hypothalamus
Located below Thalamus. Responsible for behaviors such as sleep, hunger, thirst, sex, etc. Regulates body temperature.
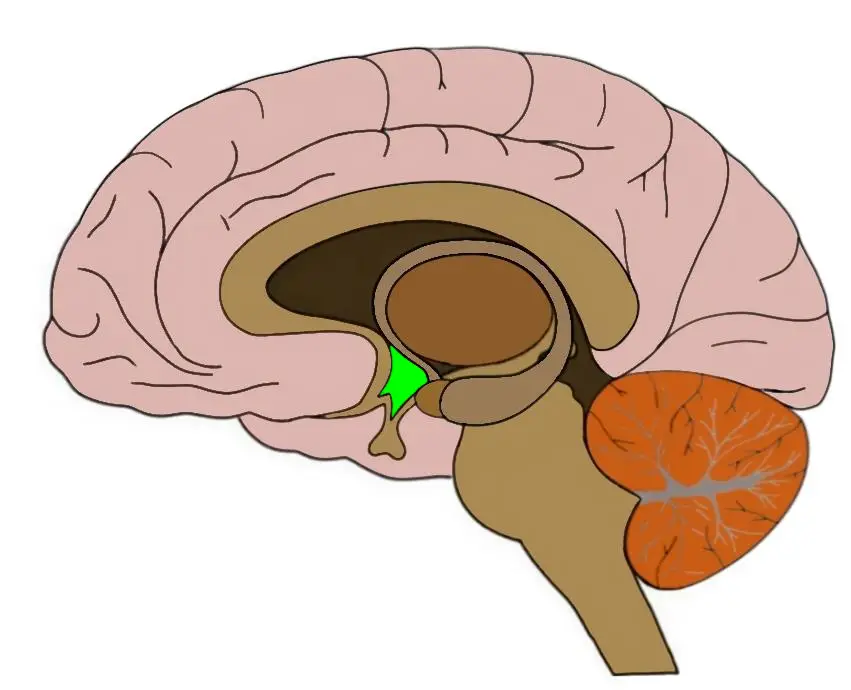
(The Cortex) Left Hemisphere
Detail, reading, calculations, written language.
(The Cortex) Right Hemisphere
Emotional thought, facial recognition, artistic & musical recognition, processes the ”whole.”
(The Cortex) Corpus Callosum
Transfers information between hemispheres such as sensory, motor, and cognitive information.
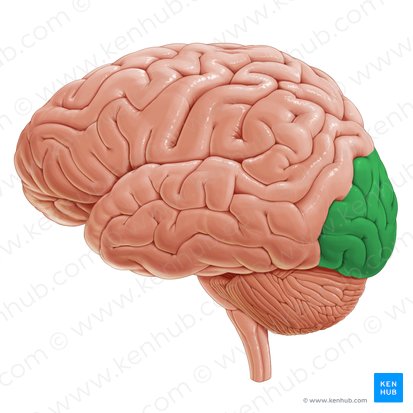
(The Cortex) Occipital Lobe
Located at the rear and bottom of each hemisphere. Processes visual information from eyes.
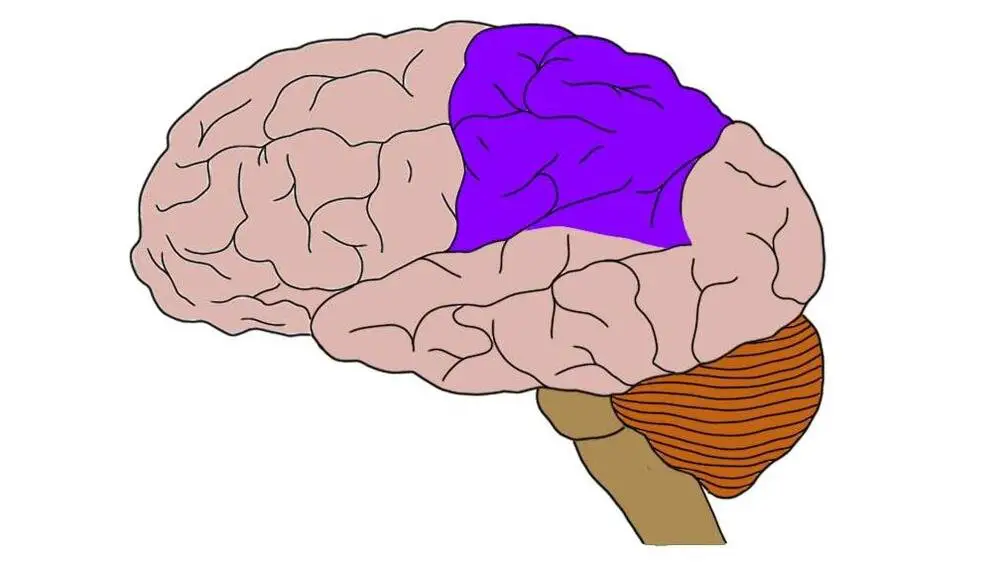
(The Cortex) Parietal Lobe
Located at the top and back of each hemisphere. Contains center for perception, spelling, and math. Processes body part movement, pain, and touch.
(The Cortex) Temporal Lobe
Located behind temples. Contains neurons responsible for hearing and speech.
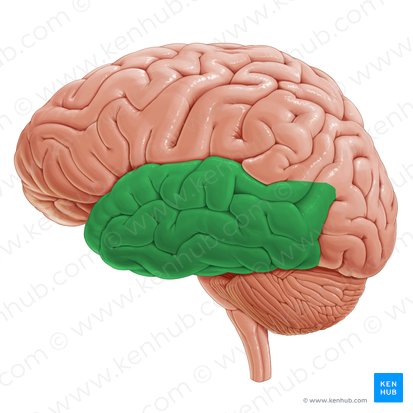
(The Cortex) Frontal Lobe
Located at the top and front of the brain. Responsible for decision making and fluent speech.
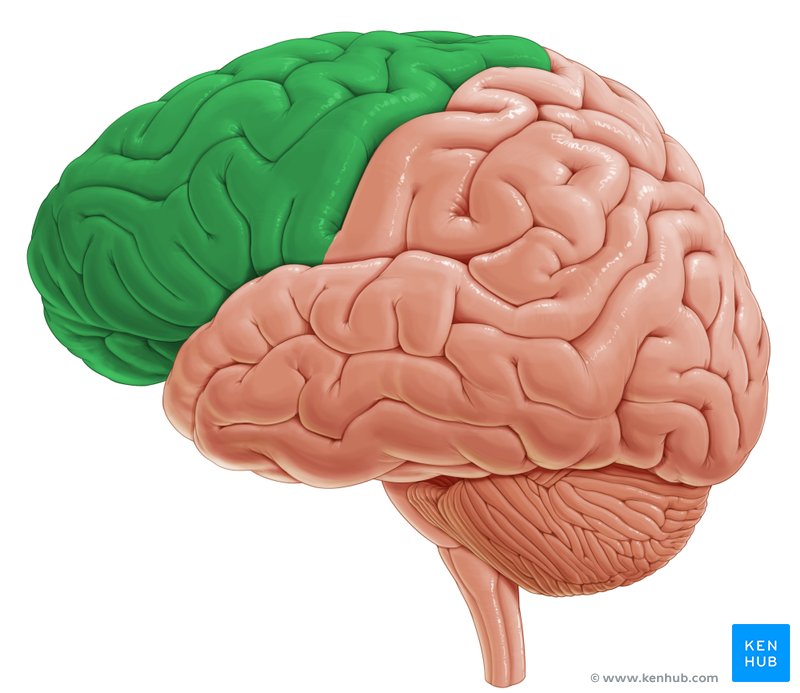
(The Cortex) Somatosensory Cortex
Area of neurons running down the front of Parietal Lobe. Responsible for processing information from the skin and internal receptors for body position, temperature, and possibly taste.
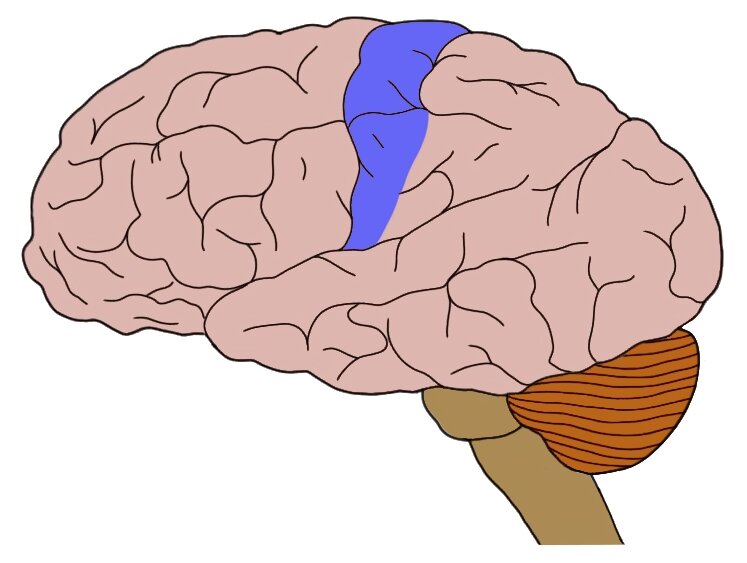
(The Cortex) Motor Cortex
Section of the Frontal Lobe located at the back. Responsible for sending motor commands to muscles of the somatic neuron system.
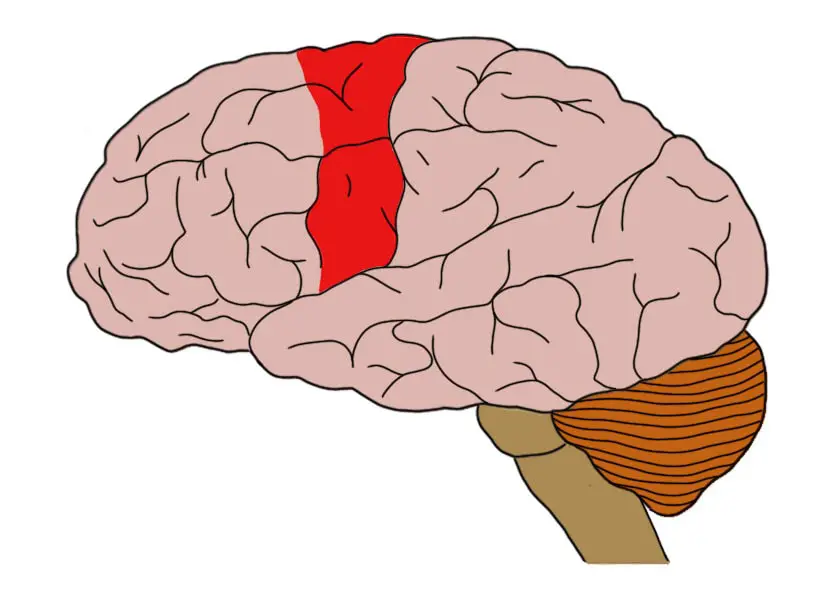
(Language Areas) Broca’s Area
The “planning” of what to say. Damage to this area causes speech delay.
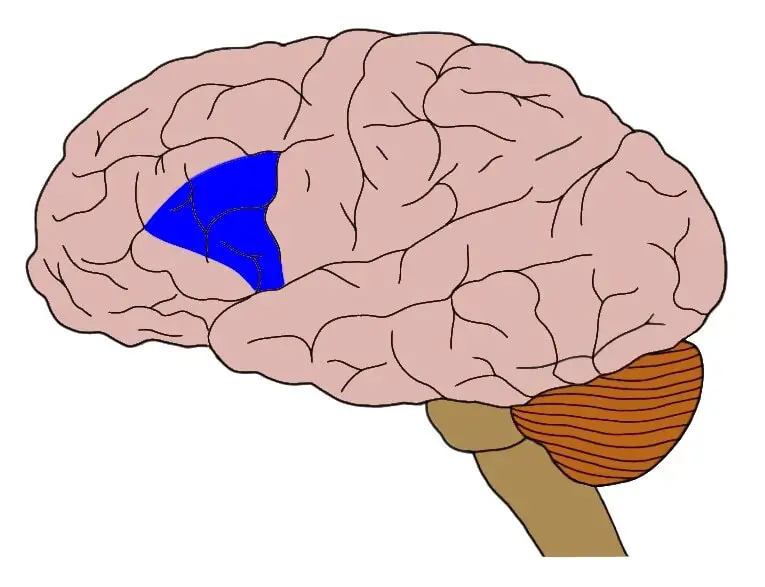
(Language Areas) Wernicke’s Area
Responsible for comprehending language and speaking comprehensively. Damage to this area causes speech that can not be understood.
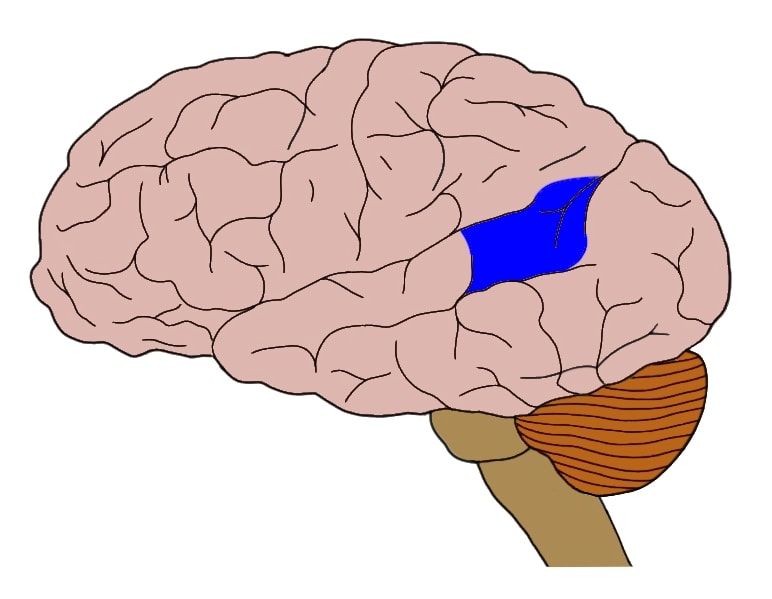
(Brain Mapping) Computed Tomography - CT
A method for taking X-ray images of the brain using a computer.
(Brain Mapping) Magnetic Resonance Imaging - MRI
A method for taking picture of the brain using radio waves and magnetic fields.
(Brain Mapping) Electroencephalogram - EEG
Records electrical activity of the brain below certain areas of the skull. Measures sleep and seizures. Shows tumors, injuries, abnormal structures.
(Brain Mapping) Positron Emission Tomography - PET
Radioactive sugar is injected into the subject to measure color-coded brain activity. Lighter colors means more activity. Measures metabolism, blood flow, oxygen use.
(Brain Mapping) Functional MRI - fMRI
A “movie” that shows change in brain activity during different periods of time. Can identify Alzheimers.
(Brain Mapping) Lesioning Studies
Case study of people with brain damage. The cases vary heavily from one another.
(Brain Mapping) Electrical Stimulation of the Brain
Weak electrical current that stimulates neurons.
(Structure of a Neuron and how it fires) Dendrites
Branch-like structures that receive message from other neurons.
(Structure of a Neuron and how it fires) Soma
Responsible for maintaining the life of the cell. The cell body of the neuron
(Structure of a Neuron and how it fires) Axon
Tube-like structure that carries message through the neurons.
(Structure of a Neuron and how it fires) Glial Cells
Grey fatty cells that deliver nutrients to neurons, provide support for the neurons to grow, and produce myelin to coat axons.
(Structure of a Neuron and how it fires) Myelin
Protect, insulate, and speed up the neural impulse in neurons.
(Structure of a Neuron and how it fires) Nerves
Groups of axons in the peripheral nervous system.
(Structure of a Neuron and how it fires) Axon Terminal
Rounded areas at the end of the branches that communicate with other nerve cells.
(Structure of a Neuron and how it fires) Synaptic Vesicles
Sack-like structure found inside axon terminal containing neurotransmitters.
(Structure of a Neuron and how it fires) Synapse
Space between axon terminal and the surface of the next cell.
(Structure of a Neuron and how it fires) Receptor Sites
Holes in the dendrites shaped to fit certain neurotransmitters.
(Structure of a Neuron and how it fires) Axon Buttons
Small knobs found at the end of the axon. Release neurotransmitters that send signals to other neurons.
(Structure of a Neuron and how it fires) Diffusion
The process of moving ions form areas of high concentration to areas of low concentration.
(Structure of a Neuron and how it fires) Resting Potential
The state of the neuron when it is not firing a signal.
(Structure of a Neuron and how it fires) Action Potential
When a signal fires, causing the reversal of the ions within the axon. Allows sodium ions to enter the cell.
(Structure of a Neuron and how it fires) Refractory Period
After a neuron fires, it takes a split second break to recharge.
(Structure of a Neuron and how it fires) Ions - Sodium
Responsible for initiating electrical signals by moving into the cell.
(Structure of a Neuron and how it fires) Ions - Potassium
Responsible for amplifying electrical signals, helping them move down the cell.
(Neurotransmitters) Excitatory Synapse
Neurotransmitter that causes the cell to fire.
(Neurotransmitters) Inhibitory Synapse
Neurotransmitter that causes the cell to STOP firing.
(Neurotransmitters) Antagonist
Blocks or reduces the effects of a neurotransmitter. Blocks receptor site.
(Neurotransmitters) Agonist
mimics or enhances the effects of a neurotransmitter. Blocks the reuptake. Have the same molecular shape.
(Neurotransmitters) Acetylcholine - ACH
Responsible for controlling muscles. Located in the hippocampus. Associated with Alzheimer’s.
(Neurotransmitters) Curare
An antagonist to ACH and paralyzes the target.
(Neurotransmitters) Dopamine
Controls mood, attention, sensory perception. Located at the Basal Ganglia. Too little = Parkinson’s. Too much = Schizophrenia.
(Neurotransmitters) Serotonin
Controls sleep, mood, appetite, and anxiety. Located in the lower part of the brain. Too little = depression.
(Neurotransmitters) Glutamate
Responsible for learning & memory, nervous system development, and is connected to synaptic plasticity. Too much = head injury, stroke, and Alzheimers.
(Neurotransmitters) GABA
Controls sleep, inhibits movement, anti-anxiety. Located in the brain. Alcohol acts as an agonist.
(Neurotransmitters) Neuropeptide
(Neurotransmitters) Endorphins
Involved in pain relief.
(Neurotransmitters) Reuptake
Regulates neurotransmitter levels by “cleaning up” after neuron has fired.
(Endocrine System) Endocrine Glands
Glands that secrete hormones into bloodstream.
(Endocrine System) Hormones
The chemicals RELEASED by Endocrine Glands.
(Endocrine System) Pituitary Glands
Gland that controls all other glands. Secrets oxytocin, a stress hormone. located in brain and is known as the master gland.
(Endocrine System) Pineal Gland
Secretes melatonin. Located near the cerebellum.
(Endocrine System) Thyroid Gland
Regulates metabolism. Located near the neck. Too much = hyperthyroidism. Too little = hypothyroidism
(Endocrine System) Pancreas
Controls blood sugar levels by secreting insulin and glucagon. Too little insulin = diabetes. Too much = hypoglycemia.
(Endocrine System) Gonads
Secrete hormones that control sexual development, behavior, as well as reproduction.
(Endocrine System) Ovaries
The female gonad. Estrogen.
(Endocrine System) Testes
The male gonads. Testosterone.
(Endocrine System) Adrenal Gland
Secretes hormones called corticoids (steroids) to help deal with stress and regulates salt intake. Helps kickstart puberty. Located on top of the kidneys.
(The Nervous System) Central Nervous System
Part of the nervous system consisting of the brain and spinal cord.
(The Nervous System) Sensory Neurons - Afferent
Neuron that carries information from the senses to the central nervous system.
(The Nervous System) Motor Neurons - Efferent
Carries message from the CNS to the muscles of the body.
(The Nervous System) Interneuron
Neuron found in the center of the spinal cord that receives information from the sensory neurons and sends commands to the muscles.
(The Nervous System) Neuroplasticity
The ability to change the structure and function of the brain in response to experience or trauma.
(The Nervous System) Peripheral Nervous System
The nerves in the body itself, not the brain or spinal cord. Divides into Somatic Nervous System and Autonomic Nervous System.
(The Nervous System) Somatic Nervous System
Division of the PNS that carries sensory information from the CNS to the muscles of the body.
(The Nervous System) Sensory Pathway
Nerves from the sensory organs (Ears, eyes, mouth) to the CNS.
(The Nervous System) Motor Pathway
Nerves coming from the CNS to the voluntary muscles. Consists of motor neurons
(The Nervous System) Autonomic Nervous System
Division of PNS consisting of nerves that control all muscles, glands, and organs. Controls the automatic functions of the body
(The Nervous System) Sympathetic Nervous System
Part of the ANS that is responsible for responding to stressful events. Flight or fight response.
(The Nervous System) Parasympathetic Nervous System
Part of the ANS that calms the body and is responsible for day-to-day functions of organs and glands
Consciousness
How aware someone is about the space around them at a given moment.
Sleep
The process of rest.
Circadian Rhythm
A 24 hour cycle that tells you when to go to sleep and when to wake up.
REM Sleep
Stage of sleep where the eyes move rapidly and most people dream. Occurs more after an emotional or stressful day.
NREM Sleep
N1: Light sleep. Body jerks occur.
N2: Body temp lower, heart rate slows.
N3: Deep sleep. Growth hormone releases.
Sleep Cycle
The whole process between being awake and entering REM sleep.
Brain Waves
Wake stage: Alpha & Beta
N1: Alpha & Theta
N2: Theta
N3: Delta
REM: Alpha & Beta
Hypnagogic Sensations
Hallucinations that occur when someone is falling asleep.
Ex. Feeling like you’re falling when sleeping.
Suprachiasmatic Nucleus
Part of the Brain that is affected by light/dark, cues for night and day. Controls the Circadian Rhythm.
Theories of Why We Sleep
Sleep Protects: It keeps you still while you rest.
Sleep Restores: Cleans toxic waste that can lead to Alzheimer’s, heals body, and restores neurons.
Sleep Aids Memory: Sleep strengthens neural connections, helping us learn faster by placing memories in a permanent storage in the cortex.
Sleep Supports Growth: Pituitary gland releases growth hormones that helps muscles develop.
Sleep Conserves Energy: Sleep preserves energy.
Sleep Helps Creative Thinking: Sleep boosts creative learning and solving. Pondering about a problem before bed helps you solve it faster the next day.
Melatonin
Hormone that makes you sleepy.
Insomnia
The inability to fall asleep or get good quality sleep.
Narcolepsy
When a person randomly falls asleep.
Sleep Apnea
When a person stops breathing for half a minute while sleeping.
REM Sleep Behavior Disorder
When muscles are still active during sleep. Allows for a person to get up or act out nightmares.
Sleep Walking
Moving around or walking around in one’s sleep.
Theories of Dream
Info. Processing: Solidifies our memories
Physiological Function: Preserve neural pathways
Activation Synthesis: Neural activities evoke random visuals, which our brain turns into stories.
Cognitive Development: Reflect knowledge and understanding. Dreams simulate our lives.
Sleep Deprivation
Trembling hands, droopy eyelids, inattention, day dreaming, discomfort, memory issues, delay of puberty, and diabetes.
Sensory Receptors
Specialized forms of neurons that are stimulated by different kinds of energy rather then neurotransmitters.
Transduction
The process by which sensory receptors convert stimuli from the environment into neural signals that the brain can interpret.