Soil Formation
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
Geotechnical Engineering
The application of the principle of geomaterials (soil and rocks)
Geotechnical Engineering Application
Foundations, Slopes, Pipelines, Roadways, Retaining walls, Dams, Landfills, Tunnels, underground constructions, geothermal energy, geological carbon storage
What do Geotechnical Engineers Do?
Cycle
Construction Site → Soil Samples → Geo-Laboratory → Soil properties → Design Office (design and analysis) → Design details
Soils starts from ______ parent material or ______
rock, magma
Percent of Oxygen by weight
47% of earth’s crust
Percent of Silicon by weight
28% of earth’s crust
Percent of Aluminum by weight
8% of earth’s crust
Percent of Iron by weight
5% of earth’s crust
Percent of Calcium by weight
4% of earth’s crust
Percent of Sodium by weight
3% of earth’s crust
Percent of Potassium by weight
3% of earth’s crust
Percent of Magnesium by weight
2% of earth’s crust
Percent of Hydrogen by weight
0.15% of earth’s crust
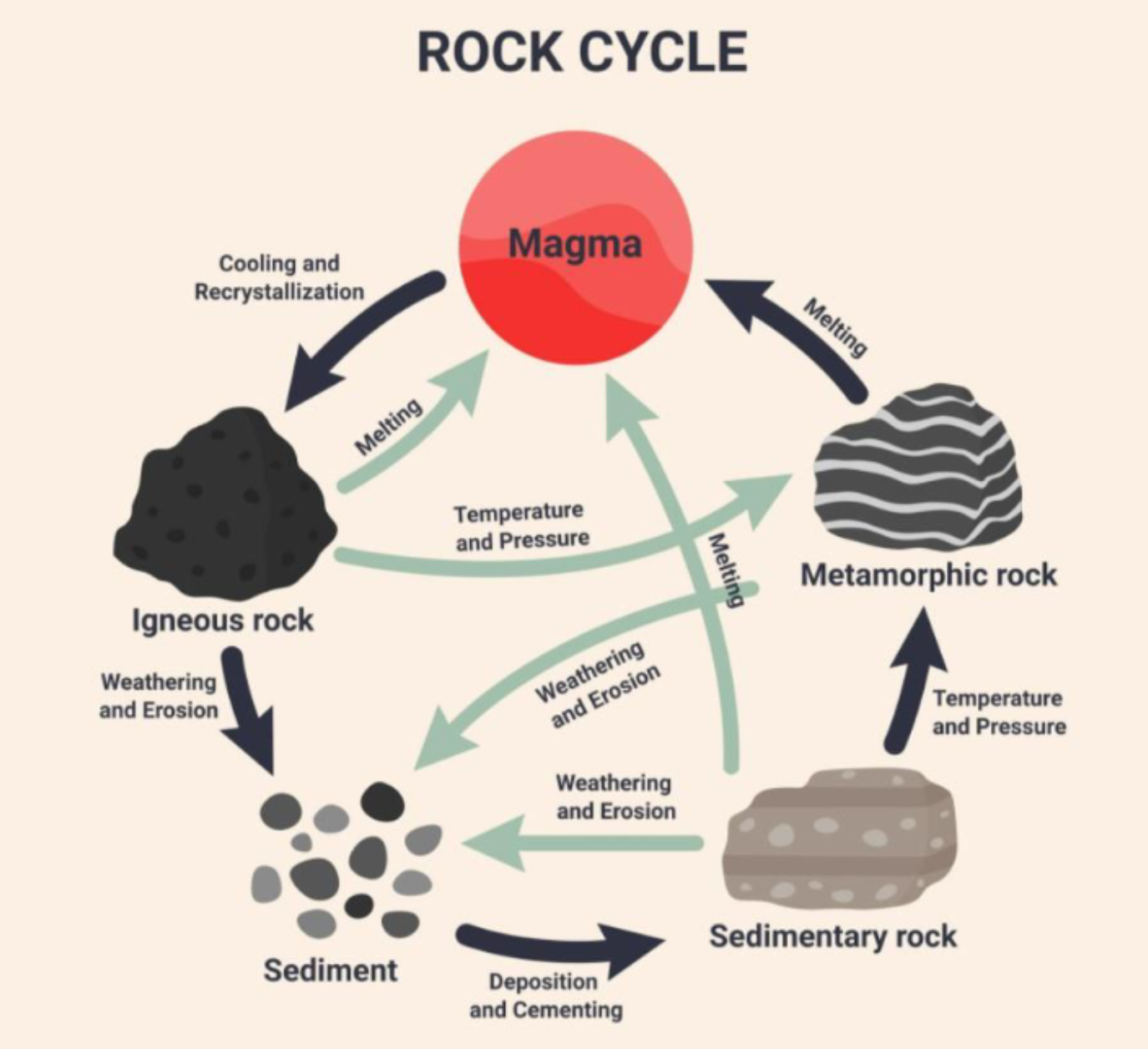
Igneous Rocks
Formed from magma (molten rock materials) emitted from volcanoes that has cooled and solidified.
Sedimentary Rocks
formed from sediments and animal and plant materials that are deposited in water or on land on the earth’s surface and then subjected to pressures and heat
Metamorphic Rocks
Formed deep within the earth’s crust from the transformation of igneous and sedimentary rocks into denser rocks
Rock Cycle
Bowen’s Reaction Series
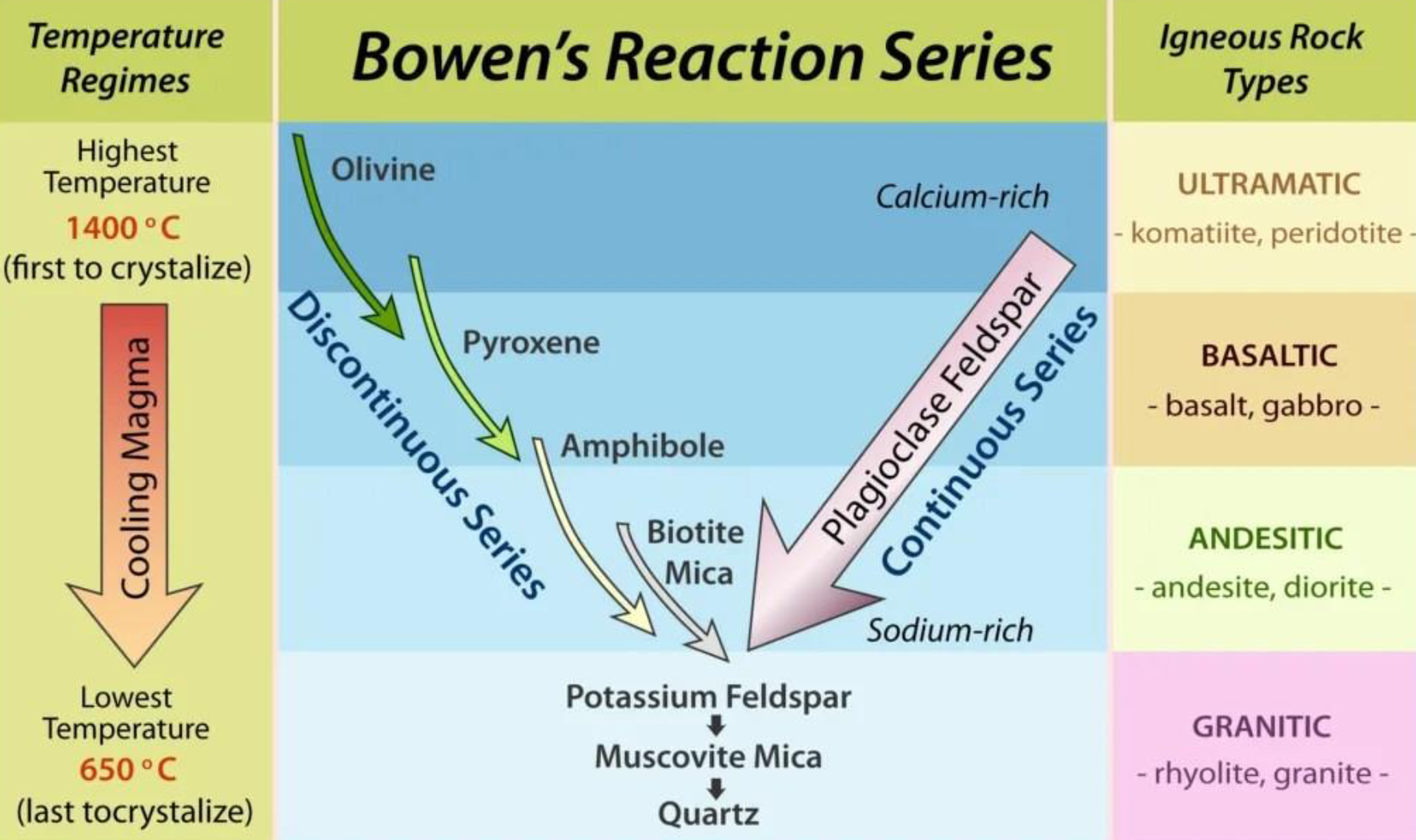
Bowen’s Reaction Series Basic Rocks (Discontinuous Series) Characteristics
Dark in color
low silica content by may contain iron, magnesium
form fine-grained soils (clay and silt) due to weathering)
As temperature decreases, the composition of the minerals changes significantly
If the melt has enough silica, mineral will change to next mineral in the lower series as temperature reduces
If silica is not enough or temperature drops too fast, lower mineral will not form
Bowen’s Reaction Series Acidic Rocks (Continuous series)
light in color
high silica content (greater than 60%), with minerals like quartz and feldspar
Typically rich in sodium and potassium, with low levels of iron and magnesium
Form coarse-grained soils (sand and gravel) due to weathering
As temperature/pressure decreases, minerals crystallize gradually, with plagioclase, feldspar changing from calcium-rich to sodium-rich
If the melt has enough silica, it will form quartz and potassium feldspar at lower temperatures
If silica is not enough or temperature drops too, fast these minerals won’t form
Physical Weathering is caused by and reactions to
Reactions
Reduce particle size
No change in chemical composition
Make the coarse fraction of soil (gravel, sand, and silt)
Caused by
Thermal Stress
Mechanical stress (Wedging, rolling, scraping and abrasion, and human activates)
Length and specific surface area of Gravel/Sand
Length: 4.75 mm
Specific Surface Area: 1.3 1/mm
Length and specific surface area of Sand/Silt
0.075 and 80
Length and specific surface area of Silt/Clay
0.002 and 3000
Specific Surface Area Formula
Surface Area/ Weight
Surface Area Formula of a Cube
6L2 / L3 =6 / L
Surface Area Formula of a Sphere
pi ( D2 ) / 1/6 (pi) (D3) = 6/D
Chemical Weathering Reduction in Form
Chemically Breaks Down Parent Material
Changes Parent into Something Else
Usually reduces unit weight (increasing bulk)
New form is more stable in some ways than old material
Chemical Weathering form the _____ fraction of the soil.
fine (clay)
Hydration
Chemical Weathering process where water enters structure
Hydrolysis
Chemical Weathering process that breaks its chemical bond
Oxidation
iron-rich minerals
Carbonization
removal of limestone by solution
Common Clay Minerals
Silicon Tetrahedron: Si1 O4
Aluminum Octahedrons: Al1 OH6
Common Clay Types
Kaolinite, Illite, and Montmorillonite
Kaolinite Characteristics
Stable physically and electrically
Not affected much by water
Stable so it can be used for ceramic, medicines, cosmetics, food
Kaolinite Mineral Structure Thickness and Composition
0.72 nm and silicon tetrahedron (upper layer) and aluminum octahedron (lower layer) (Hydrogen bonds)
Montmorillonite Characteristics
Not stable physically or electrically
very affected by water
Crystal attract water and cations
used for clay liners, seals for wells
Montmorillonite Composition
Silicon Tetrahedron (upper layer) and Aluminum Octahedron (middles layer) and Silicon Tetrahedron (lower layer) , Potassium bonds
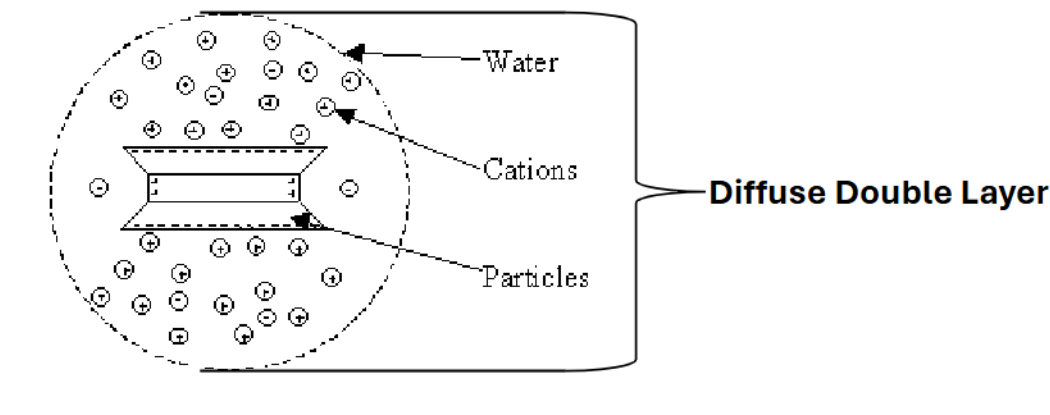
Clay absorbs ______ and ______ to form ________.
water, ionic cations (salts), micelle
What is the structure of clay deposits?