Harifaroosh - intro to viruses
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
74 Terms
virus
the name comes from Latin and means poison
they contain a single nucleic acid: DNA or RNA
they are obligate intracellular parasites
replicate inside the cell; inactive outside of the
they do NOT change in size or shape or divide by binary fission
they LACK genetic information for energy metabolism, ribosomes, etc
human vs bacterial cells:
human cells
has nuclei
80S ribosomes (found in eukaryotes)
NO cell walls
human enzymes
aerobic (need oxygen)
human vs bacterial cells:
E. coli cells
NO nuclei
70S ribosomes (found in prokaryotes)
cell walls
bacterial enzymes
aerobic, anaerobic, and microaerophilic
human cells vs herpes viruses
human cell:
has membranes
80S ribosomes
requires human enzymes
requires humans for replication
herpes viruses:
carries an envelope
NOT ALL viruses have envelopes
uses 80S ribosomes
requires some human enzymes
requires humans for replication
why viral infections are hard to treat
viruses are eukaryotic
not really, but they use host cell enzymes
viruses are obligate intracellular parasites
viruses are biologically highly diverse and rapidly mutate
makes developing vaccinations difficult
infections are typically advanced before they are clinically detected
vaccinations are NOT useful after infection occurs
variations in viruses
size
shape
structure
genomic content
positive sense
genome used is similar to mRNA
negative sense
complimentary to positive sense so it has to be translated to positive sense by RNA replicase
virus structure
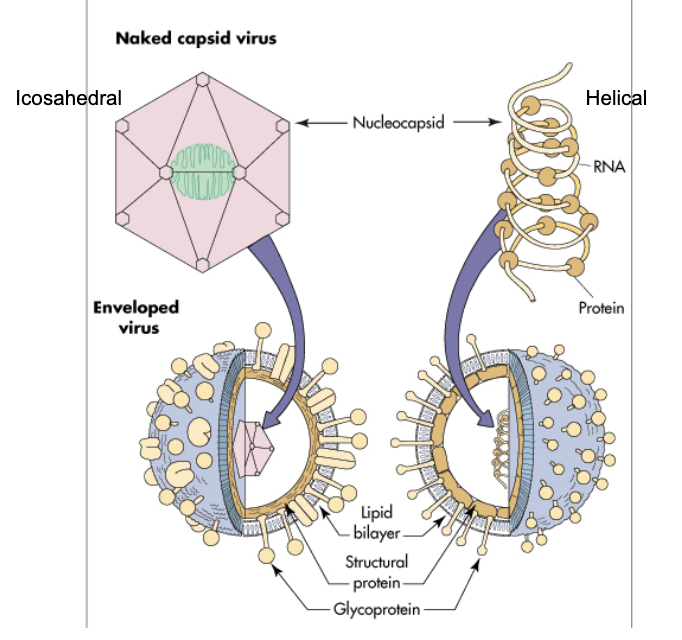
virus stability
stability of the viron affects mode of transmission
naked capsids are generally more stable outside the human body
naked capsid virus structure
nucleocapsid:
DNA or RNA
+ structural proteins
± enzymes and nucleic acid binding proteins
nucleocapsid = naked capsid virus
enveloped virus
nucelocapsid
DNA or RNA
+ structural proteins
± enzymes and nucleic acid binding proteins
+ glycoproteins and membranes
viral classification (old)
based on disease
this practice was abandoned (mostly) because many diverse viruses cause similar diseases
viral classifications (old)
hierarchical and based on structure:
nucleic acid: DNA or RNA
symmetry of structure: cuboidal, helical, or asymmetric
presence of envelope
RNA viruses:
singled stranded positive sense
enveloped
icosahedral
flaviviridae
togaviridae
retroviridae
retroviruses use DNA as intermediate
very high mutation rates due to no error checking by reverse transcriptase
RNA viruses:
singled stranded positive sense
enveloped
helical
coronaviridae
RNA viruses:
singled stranded positive sense
nonenveloped
icosahedral
picornaviridae
caliciviridae
RNA viruses:
singled stranded negative sense
enveloped
helical
orthomyxoviridae
influenza belongs to the orthomyxoviridae family
paramyxoviridae
rhabdoviridae
filoviridae
bunyaviridae
arenaviridae
RNA viruses:
double stranded (directly encode viral proteins)
nonenveloped
icosahedral
reoviridae
DNA viruses:
double stranded
(must enter cell nucleus and use host cell polymerase. highly dependent on host cell cycle)
enveloped
double stranded = must enter cell nucleus and use host cell polymerase. highly dependent on host cell cycle
herpesviridae
hepadnaviridae
DNA viruses:
double stranded
non-enveloped
circular
double stranded = must enter cell nucleus and use host cell polymerase. highly dependent on host cell cycle
papillomaviridae
polyomaviridae (formerly grouped together as the papovaviridae)
DNA viruses:
double stranded
non-enveloped
linear
double stranded = must enter cell nucleus and use host cell polymerase. highly dependent on host cell cycle
adenoviridae
DNA viruses:
single stranded non-enveloped
single stranded non-enveloped = mostly circular genomes, so can make many copies quickly
parvoviridae
DNA viruses:
complex enveloped
poxviridae
how many genes can viral genomes contain?
5 to > 200 genes
generic viral life cycle
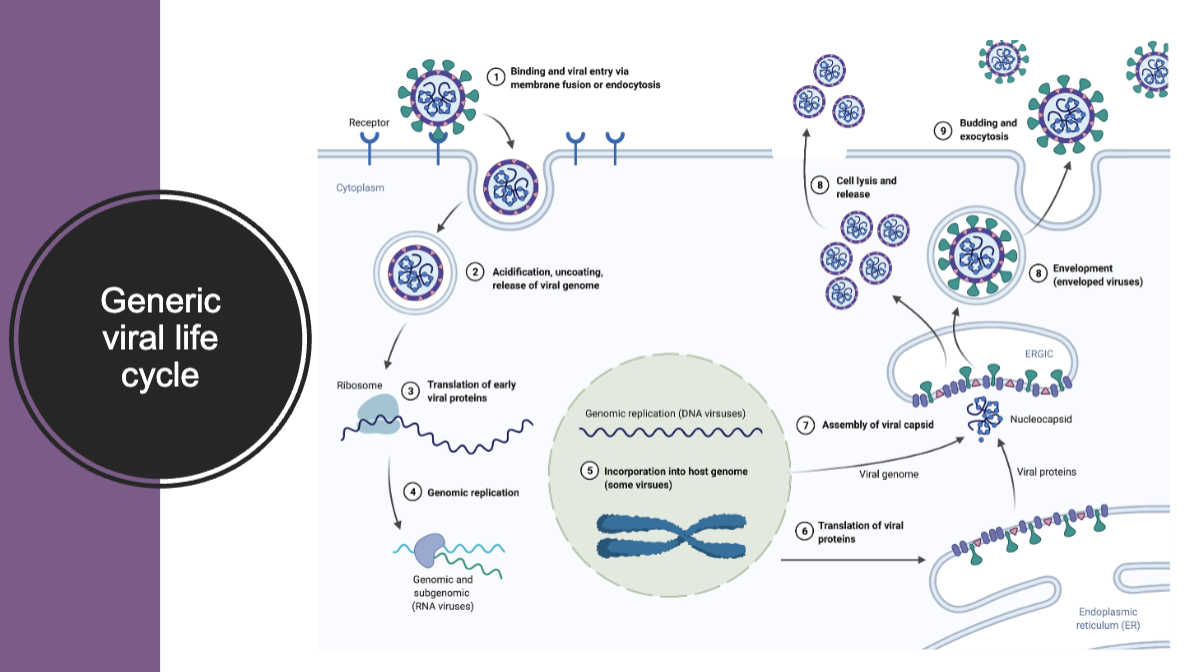
viruses: initiation of infection
virus attach to a receptor on the cell surface
penetrate into the cell following receptor engagement
the nucleic acid of the virus must be release from the virus
to replicate, a virus must express genes that encode proteins which:
alter cellular metabolism in order to:
provide the precursors for the synthesis of virion components
preclude host response to infection
alter the physiologic state of the cell to facilitate assembly
enable virus egress from the infected cell
take over the cell’s synthetic machinery to replicate the viral genome and produce viral proteins
package the newly synthesized genomes in virions
viral macromolecular synthesis: DNA viruses
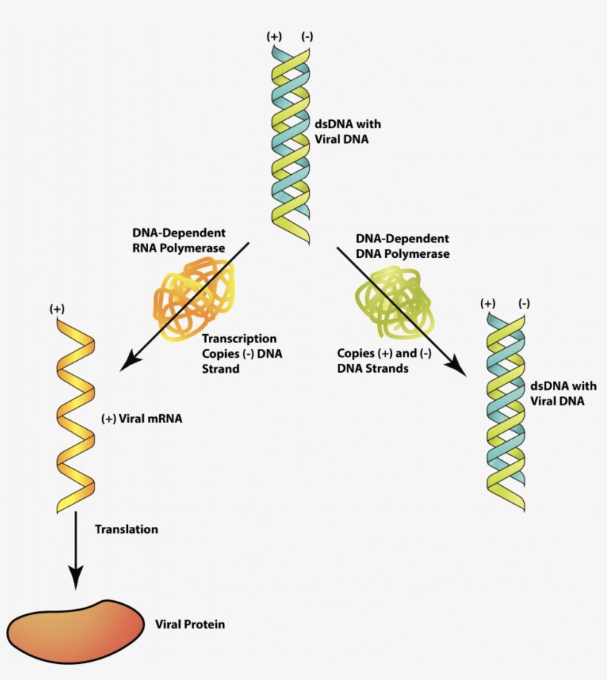
viral macromolecular synthesis: RNA viruses
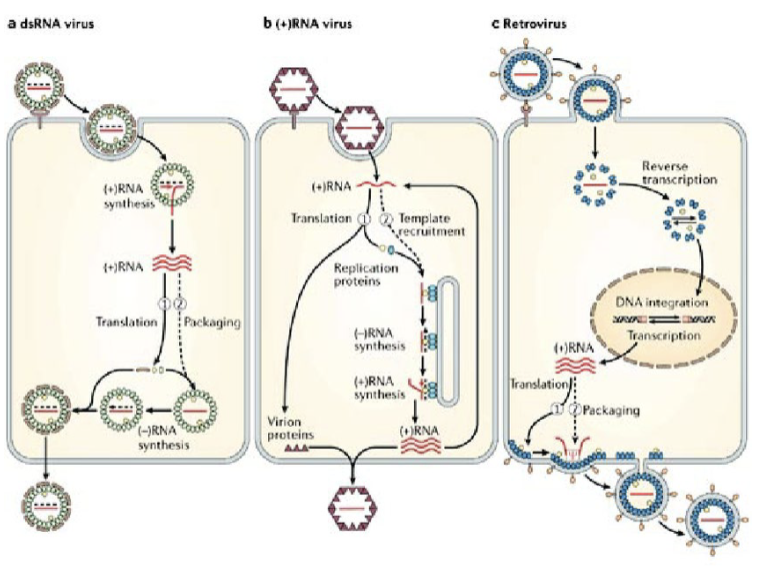
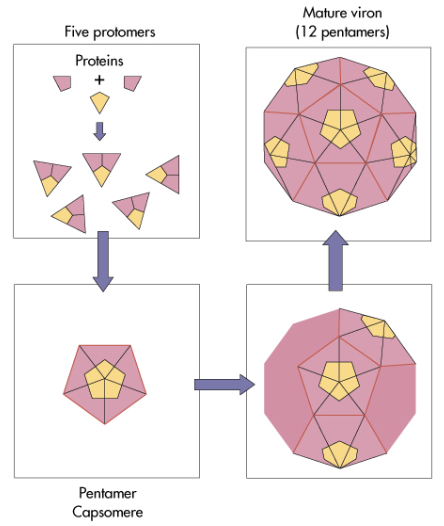
viral capsid assembly
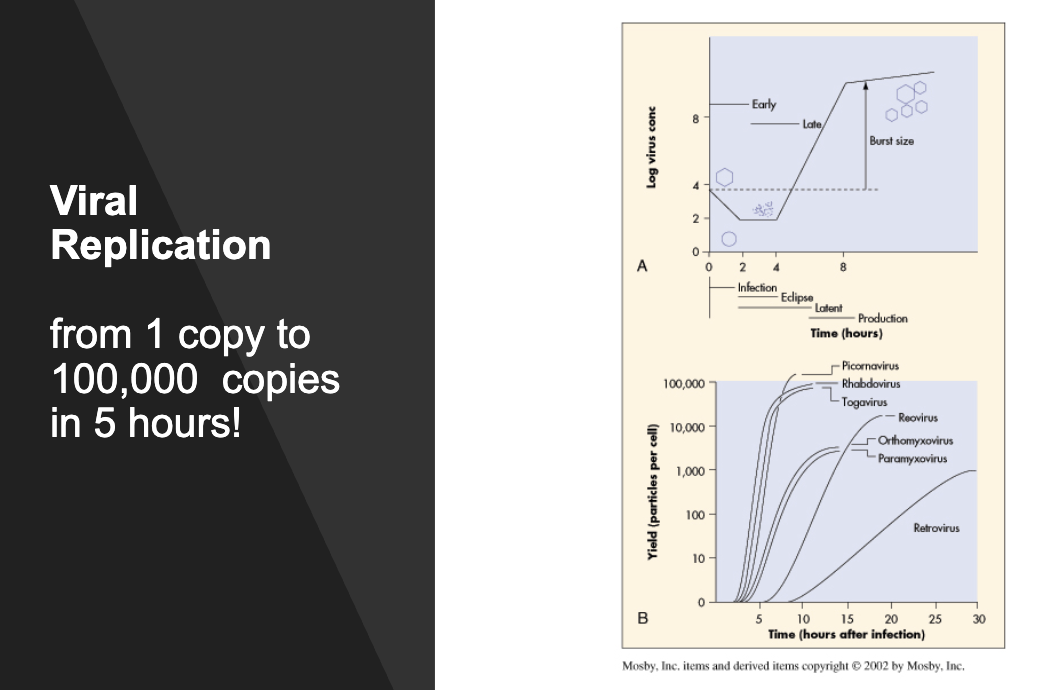
viral replication
viral egress
the process can involve one or more of the following:
lysing the cell
fusing cells (syncytia)
acquiring an envelope with viral glycoproteins
budding out of the infected cell
antigenic drift
generation of point mutations
many viral polymerases (esp RNA polymerases) have poor fidelity and lack proofreading
rapid viral life cycle and large burst size create accelerated evolution
antigenic shift
exchange of large segments of genetic material
why are the processes of antigenic drift and antigenic shift major obstacles in therapeutics?
drug resistance
resistance to immune response
ineffective vaccination
why is a new flu shot made each year?
Influenza A mutates its coat proteins (viral genetic mutation), avoiding host immunity
CDC collaborates with organizations in UK, Australia, Japan, and China via the WHO
year-round surveillance of circulating influenza
experts meet in February each year to determine composition of vaccine for the northern hemisphere (they meet again in Sept. for the southern hemisphere flu season)
each country then makes its own vaccine
cause of major pandemics
viral genetic exchange
exchange of genetic material allows jumping from species to species
large changes subvert any immunity in the host
viral pathogenesis
the process by which a virus causes disease
virulence
capacity of a virus to cause disease
viral disease
sum of the effects of:
the virus replication and direct damage to cells (cytopathogenesis)
the immune response on the host (immunopathogenesis)
cytopathogenesis
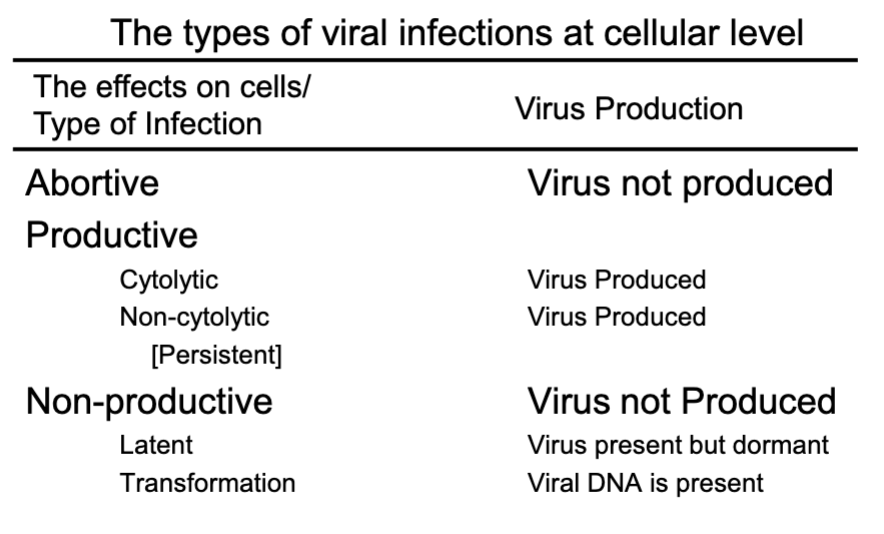
abortive infections
viruses do NOT complete the replication cycle
mutations
interfering particles
action of interferons
productive infections:
cytolytic infections
viruses replicate & produce progeny
cell death & cytopathic effects (CPE)
productive infections:
non-cytolytic infections
viruses replicate & produce progeny
viruses released by cell budding & little or NO CPE
cytopathic effects (CPE)
CPE can take several forms:
cell lysis
cell rounding
syncytium formation
inclusion bodies formation
non-productive infection:
latent infections
viruses infect cells that either restrict expression of viral genes or lack the machinery for transcribing viral genes
viral genome either integrates into cell DNA or is a circular episome, or both
persistent, non-productive infection
limited expression of viral genes
infected cell retains its normal properties
examples include Herpes Simplex Virus
non-productive infection:
transformation
causes cancer!
virus stimulates uncontrolled cell growth
alters the expression of cell cycle checkpoint genes
virus infects then leaves behind viral genes in the host genome
no viral replication
examples: Epstein-Barr, Human Papilloma viruses
pathogenesis at the host level
transmission of the viruses & its entry into the host
replication of the virus & damage to cells
viral shedding
virus remains localized or spreads to other organs
the immune response: host defense immunopathogenesis
horizontal transmission
skin contact
blood
respiratory route
fecal - oral route
genital contact
animal-human
vertical transmission
maternal-child
common routes of human infection by viruses
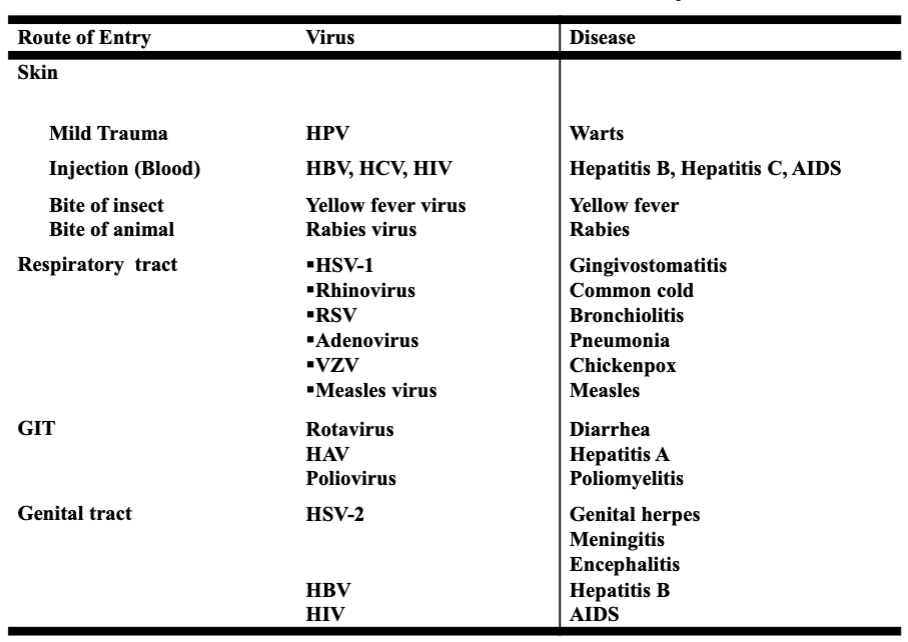
local infections
example — rhinovirus
site of pathology — portal of entry
duration — relatively short
viremia — absent
duration of immunity — variable (may be short)
systemic infections
example — measles
site of pathology — distant site
duration — relatively long
viremia — present
duration of immunity — usually, life long
macrophages
antigen presenting cell
phagocytosis
cytokine production
cytokines
interferons (IFN)
𝜶, β-IFN — inhibit the viral and the host cell mRNA translation
ɣ-IFN — stimulates phagocytosis and killing by macrophage & NK cells
interleukins (IL)
stimulate Ab production
activate T cells & cell-mediated immunity
suppress the immune response
immune response to virus
natural killer (NK) cells lyse viral infected cells
the stages of a typical viral infection
the incubation period
no symptoms
prodromal period
minimal symptoms
the specific-illness period
the signs & symptoms of viral diseases are the result of:
cell killing by inhibition of cellular macromolecular synthesis
immunologic attack (immunopathogenesis)
cytotoxic T cells (e.g., hepatitis virus infections)
the recovery period
stages of viral infection and illness
asymptomatic infection
acute infection
persistent infection
late complication of acute infection
latent infection
chronic infection
factors influencing viral disease
primary tissue infected
many viral infections are restricted to specific cell types
mode of transmission (respiratory, blood, STD, fecal/oral)
cell-specific receptor expression
presence of cell-specific replication factors
absence of antiviral proteins/RNAs
effect of infection on host cell
cytopathic effect
cellular transformation
spread of virus
secondary sites of infection
immune response to viral infection
immune destruction of infected cells
generalized inflammatory response (cytokines, etc)
“inappropriate” immune response (autoimmunity)
target tissues of HSV
brain
HSV-1 — encephalitis
HSV-2 — meningitis
mouth
skin and mucous membranes
eyes
throat (pharyngitis)
urogenital tract
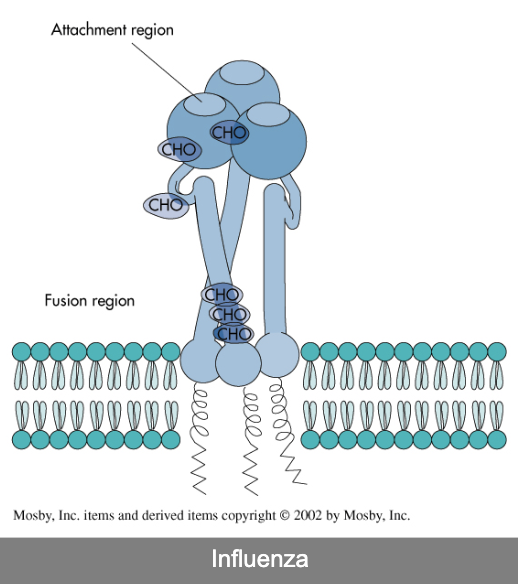
influenza A
negative-stranded RNA genome
genome divided into 8 gene segments that encode 10 proteins
spiked envelope
H-spike — hemagglutinin (subtypes H1-H18)
mediates attachment
N-spikes — neuraminidase (subtypes N1-N11)
cleaves H protein to allow fusion of viral and cellular membranes (i.e., entry into the cell)
requires cellular enzyme trypsin to facilitate infection
influenza A viral life cycle
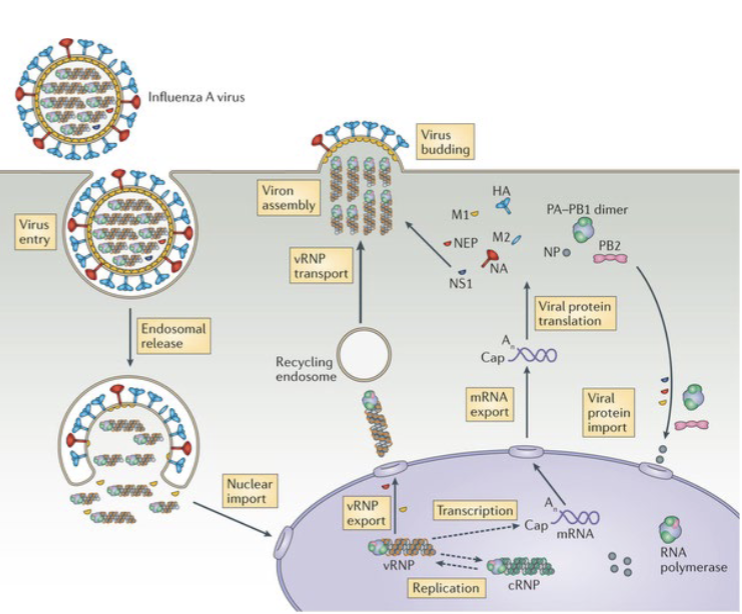
the HA and NA polypeptides
HA encodes hemagglutinin spike protein
binds to any cellular protein with a 𝜶2,6-sialic acid group
mediates penetration of viral core and RNA into target cell
it is the major target of neutralizing antibodies for vaccines and successful immune responses
NA encodes neuraminidase protein
this enzymes cleaves the HA protein upon cell binding and facilitates penetration of the viral core
together they mediate cell infection
influenza A viruses are named by their HA and NA subtypes (e.g., H5N1)
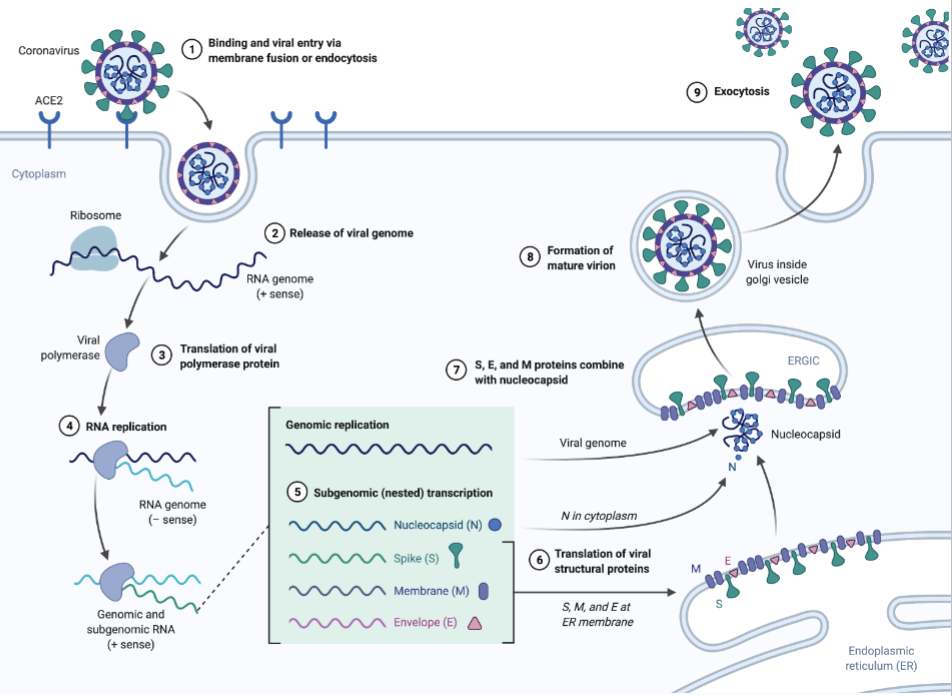
coronavirus structure
spike protein
recognizes and binds to host cell surface protein
nucleocapsid
binds the viral RNA to protect and stabilize it
membrane
outer protective layer of lipid, hold spike proteins in place
envelope
proteins that form and stabilize the outer protective layer of the virus particle
RNA viral genome
contains the genetic code of the virus
SARS-CoV-2 replication
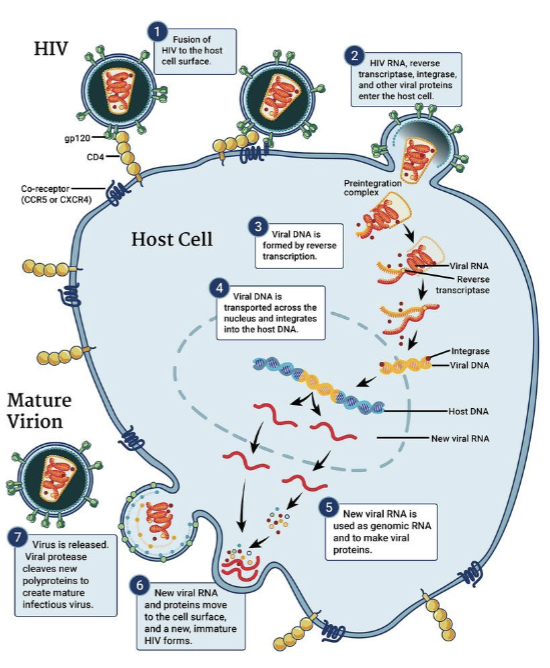
HIV
a retrovirus that infects and destroys helper T cells of the immune system
HIV is a lentivirus
genus of the Retroviridae family
produce multi-organ diseases
characterized by long incubation periods and persistent infection
HIV life cycle
ssRNA + strand (2 copies)
RNA gets reverse transcribed to DNA by HIV reverse transcriptase
DNA gets integrated into host genome by HIV DNA integrase
viral RNA and proteins made by host machinery
HIV proteases process proteins to assemble mature virons
hepatitis
these are different classes of viruses, but still are named after the disease (old classification)
hepatitis A (HAV) infectious hepatitis
hepatitis B (HBV) blood bourne
hepatitis C (HCV) non A, non B
hepatitis D (HDV) delta virus
hepatits E (HEV) similar to HAV
hepatitis A
picornaviridae family
27-29 nm icosahedral structure
ssRNA
only one serotype
oral-fecal transmission
water
infected food handlers
hepatitis B
hepadnaviridae family
42 nm icosahedral structure
enveloped, circular dsDNA, 3200 nucleotides
forms Dane particles
small pleomorphic particles 20-22 nm
excess viral capsids released into blood stream
blood-blood, sexual, perinatal transmission
hepatitis C
Flavivridae family
6 genotypes
60 nm icosahedral structure
ssRNA
blood borne
transfusions
nocosomial transmission
herpes simplex
herpesviridae family
2 genotypes, HSV-1 and HSV-2
icosahedral structure
dsDNA, 74 genes
persistent infection via latent virus neural ganglia
spread by intimate contact
HSV-1 cold sores
HSV-2 genital herpes
human papilloma virus
papillomaviridae family
over 170 genotypes
icosahedral structure, 60 nm
dsDNA, non-enveloped
most transmission via sexual intercourse
causes warts and linked to cancer of many organs (cervix, vulva, vagina, penis, anus, mouth, throat)
vaccines (Gardasil) effective against most common forms of HPV