Week 6B: Physiological foundation
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
Muscles controlling movements of the limbs typically come in pairs: the (…) and the (…)
agonist, antagonist
The strength of a muscle depends on its (…)
length
Hooke’s law formula
F = k* delta L
The group of muscle fibers that are innervated by a single motor neuron is called a (…)
Motor unit
The inverted U-shape of the length tension relation of active muscles follows from the way actin-myosin bridges are formed, why?
Fully stretched the filaments hardly overlap, only few bridges can be formed, fully contracted the different filaments compete for binding sites and there are less bridges. The u shape is optimal because this is the mid-range between stretched and contracted
The somatosensory system - Perception of body posture
Proprioception
The somatosensory system - Kinesthesis
Perception of force and motion
The somatosensory system - External forces
Cutaneous touch
Proprioception is mediated by three different types of mechanoreceptors
Joint receptors (joint position)
Golgi tendon organs (muscle tension)
Muscle spindles (muscle length)
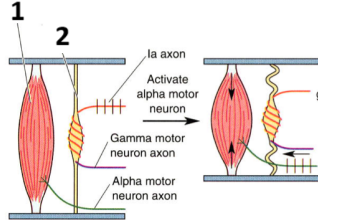
1,2
Extrafusal fiber
Intrafusal fiber
Experiment: Vibration is given to the inside of the left elbow, stimulating the muscle spindles and Golgi tendon organs. The participant has to match the left and right elbow angle. What is the result
The muscle vibrated appears longer than it actually is
What is the contralateral crossed extensor reflex
Flexion of one side leads to extension on the contralateral side
A frog with the brain removed still shows a wiping reflex, this suggests
A spatial map encoded in the spinal cord
How can reflexes be suppressed
Drugs and diseases
Cerebellum is involved in regulation of (4 items)
Muscle tone
Coordination
Timing
Learning
Hypermetria
Overshooting targets
S
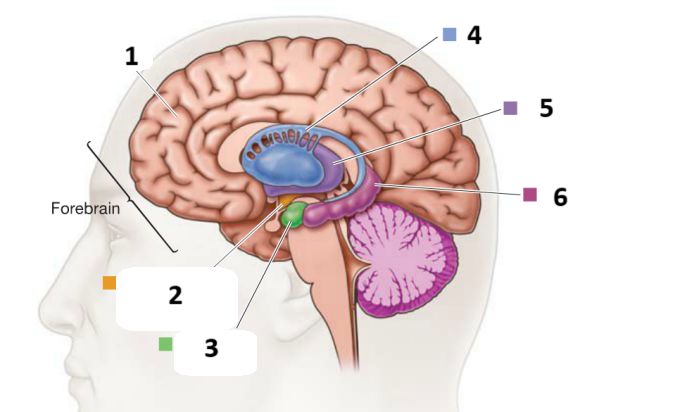
1,2,3,4,5,6
Cerebral cortex
Hypothalamus
Amygdala
Basal ganglia
Thalamus
Hippocampus
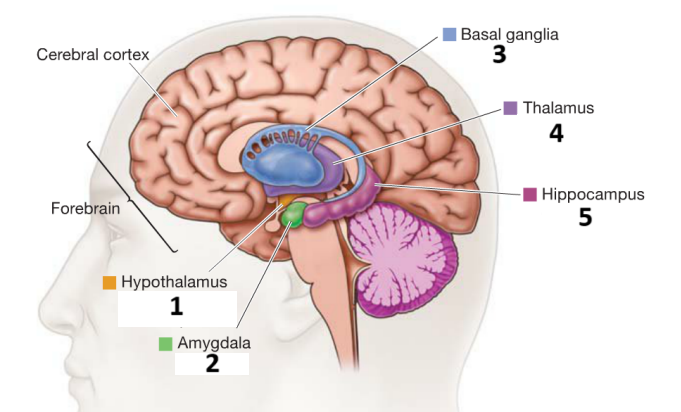
Main functions
Regulates body function
Emotion
Movement, reward
Sensory gateway
Memory
Which body parts controls the output and execution of movement plans
Basal ganglia
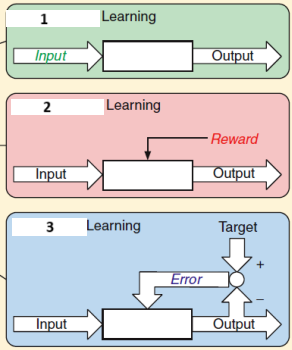
1,2,3
Unsupervised
Reinforcement
Supervised
Which part of the brain is most relevant during 1. Unsupervised learning 2. Reinforcement learning 3. Supervised learning
Cerebral cortex
Basal ganglia
Cerebellum
Symptoms of Huntington’s disease and what is causing these symptoms
Uncontrollable ballistic movements due to abnormal production of GABA neurotransmitters
Symptoms of Parkinson’s disease and what is causing these symptoms
Tremors and slow movement initiation due to dopamine deficit
What is supplementary motor area involved in
High-level planning of movement sequencing and coordination
Function premotor cortex
Orienting the body
Function parietal cortex
Processing sensory information, spatial awareness, and movement
Disorder: ideational apraxia
Problems in sequencing movements
Disorder: ideomotor apraxia
Inability to imitate
What is response chaining
Each motor act causes a (sensory) stimulus that triggers a subsequent motor act
The name of skill acquisition through refinement of perceptuomotor feedback loops and the name of it if based on motor plans
Closed-loop theory, open loop theory
Why is mirror-symmetric tapping of sequences transferring more easily from one hand to the other than symmetric patterns
Because the muscle activations are symmetric
Three stages of skill acquisition
Cognitive stage
Associative stage
Automatic stage
Novices (…) their joints to (…) DoF, experts (…) their joints in order to (…)
lock, reduce, unlock, improve skills further
Ideomotor theory
Ideas are tightly linked to motor actions and as such mental activities automatically trigger actions