Neurodevelopmental Disorders
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
What are the defining characteristics of neurodevelopmental disorders?
1. Typical onset before puberty
2. Clinical course steady in the long term, rather than remitting/relapsing
3. Early onset neurocognitive deficits
4. More commonly diagnosed in males
5. High heritability, aetiology multifactorial
6. High level of overlap
What neurodevelopmental disorders are there, according to the DSM-V?
AD(H)D
Autism
Intellectual Disability
Communication Disorders
Specific Learning Disorders
Motor Disorders (e.g. tic disorders)
What are the “inattention” symptoms found in ADHD?
✦ Inattention to details / makes careless mistakes ✦ Difficulty sustaining attention
✦ Seems not to listen
✦ Fails to finish tasks
✦ Difficulties organizing
✦ Avoids task that require mental effort
✦ Loses things
✦ Easily distracted
✦ Forgetful
What are the “hyperactivity” symptoms found in ADHD?
✦ Blurts out answer before question is finished
✦ Difficulty awaiting turn
✦ Interrupts or intrudes on others
✦ Fidgets
✦ Unable to stay seated
✦ Inappropriate running/climbing (restlessness)
✦ Difficulty in engaging in leisure activities quietly ✦ “On the go”
✦ Talks excessively
What conditions must be met in order for someone to be diagnosed with ADHD?
➡ 6 or more symptoms (5 or more when >16y) ➡ present at least 6 months ✦ Present before age 12 ✦ Present in two or more settings ✦ Interfere with quality of life
How may ADHD be noticed in childhood?
Difficulties at school
Impulsivity
Repetitive failure
ODD
Multiple injuries
How may ADHD be noticed in adolescence?
Underachievement, no high school graduation Carelessness, substance abuse, unwanted pregnancy
Hopelessness, frustration, depression, anxiety
Criminal involvement
Risk taking, accidental injuries
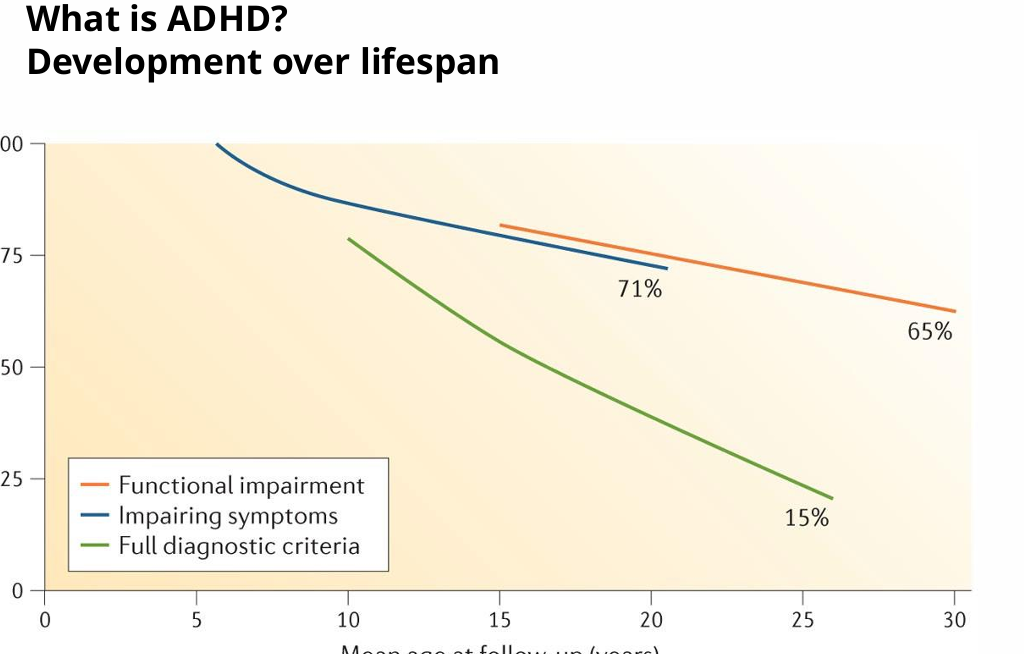
How do the symptoms of ADHD develop over the lifespan?
What is the aetiology of ADHD?
In utero:
Genetic predisposition
Fetal exposures and epigenetic changes
After birth:
Psychosocial influences, chaotic family environments, mismatch with school/work environments
What is the clinical progression of ADHD?
In preschool years: Hyperactivity and rapid speech, motor coordination and language problems
During school years: Co-morbidity, peer rejection, school failure, peer rejection and neurocognitive dysfunction
In adulthood: Inattention persists, hyperactive-impulsive symptoms wane
Substance abuse, low self-esteem and social disability
What is the pathophysiology of ADHD?
What 4 things are impaired in ASD?
Facial / Emotion perception
Theory of mind
Systemizing / Empathizing (Systemizing: Drive to analyse a variable in a system. Empathizing: Drive to understand human emotions and respond appropriately)
Central coherence