Bootcamp.com - Cell Division
1/108
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
109 Terms
_____ is nuclear division followed by cytokinesis
cell division
what is another word for nuclear division?
karyokinesis
_____ is the division of the cytoplasm that happens at the end of cell division
cytokinesis
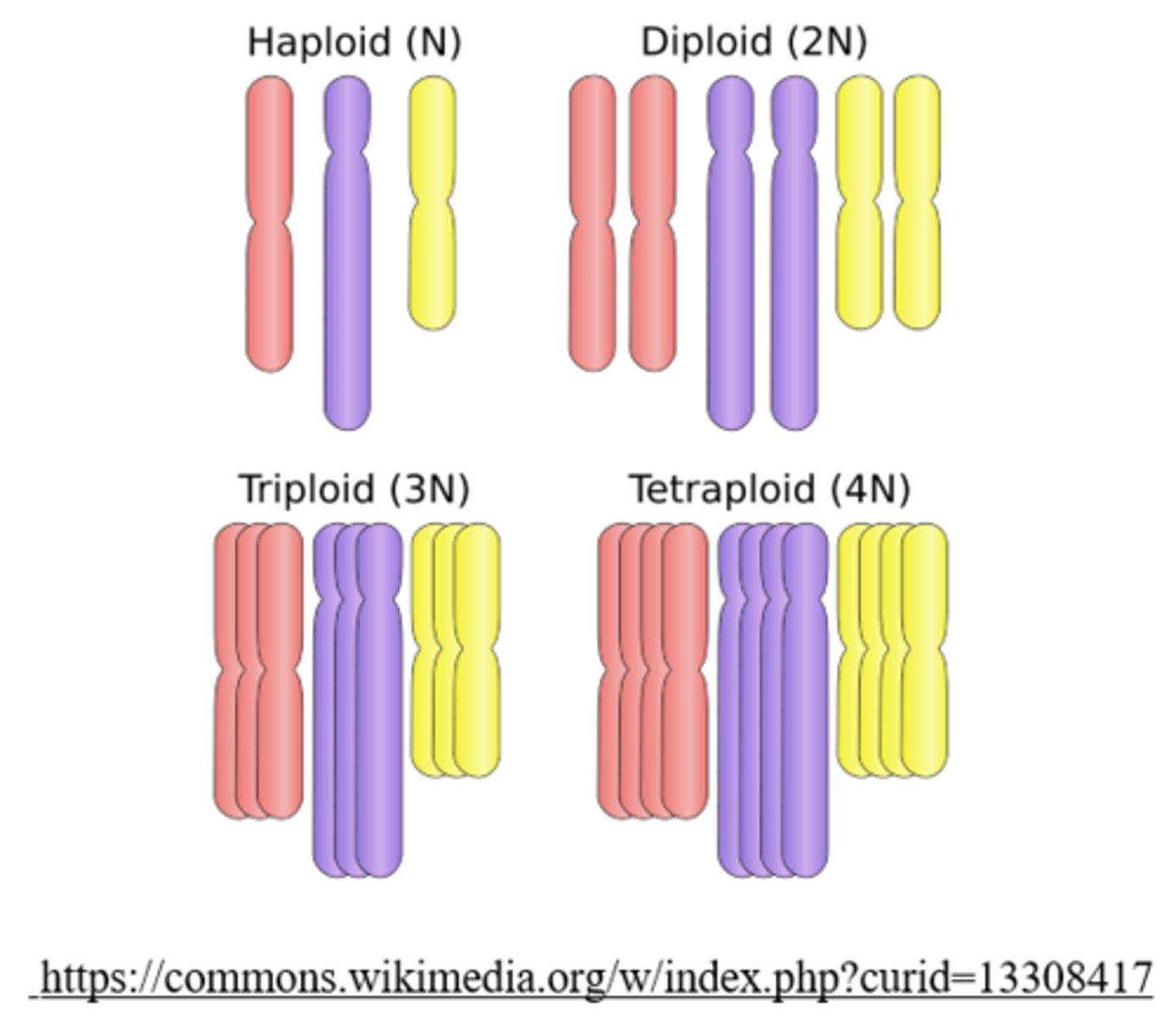
what is ploidy?
the number of chromosome sets found in a cell
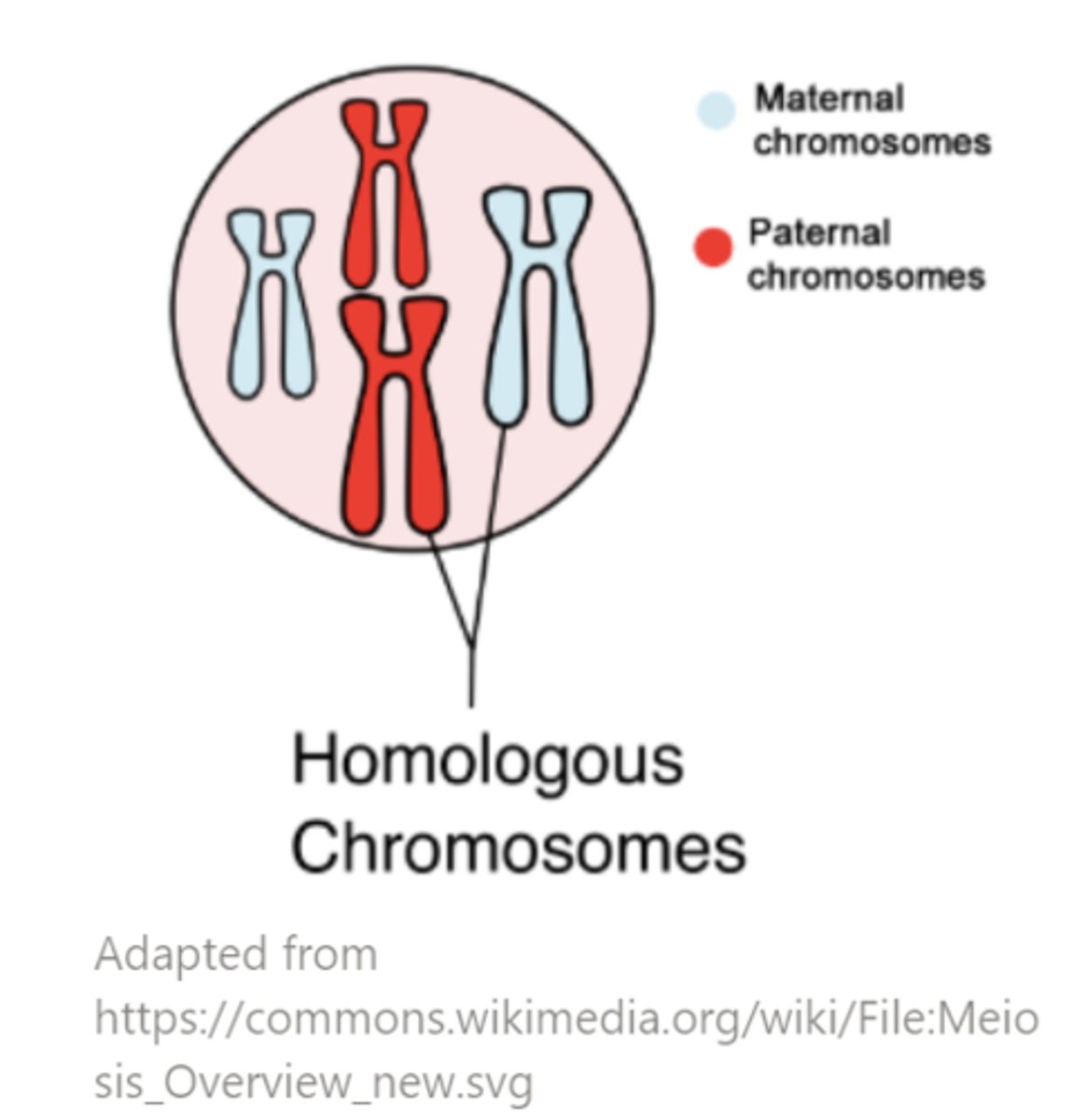
______ are any chromosomes that are non-sex chromosomes, while ______ are X and Y chromosomes that determine sex and other characteristics
autosomes; sex chromosomes
in _____ cells, there are two copies of every chromosome, forming a pair called _____ chromosomes
diploid; homologous
humans have _____ chromosomes, _____ homologous pairs, and a total of _____ chromatids (depending on the stage of division)
46, 23, 92
a _____ is one of two identical parts of a duplicated chromosome
chromatid
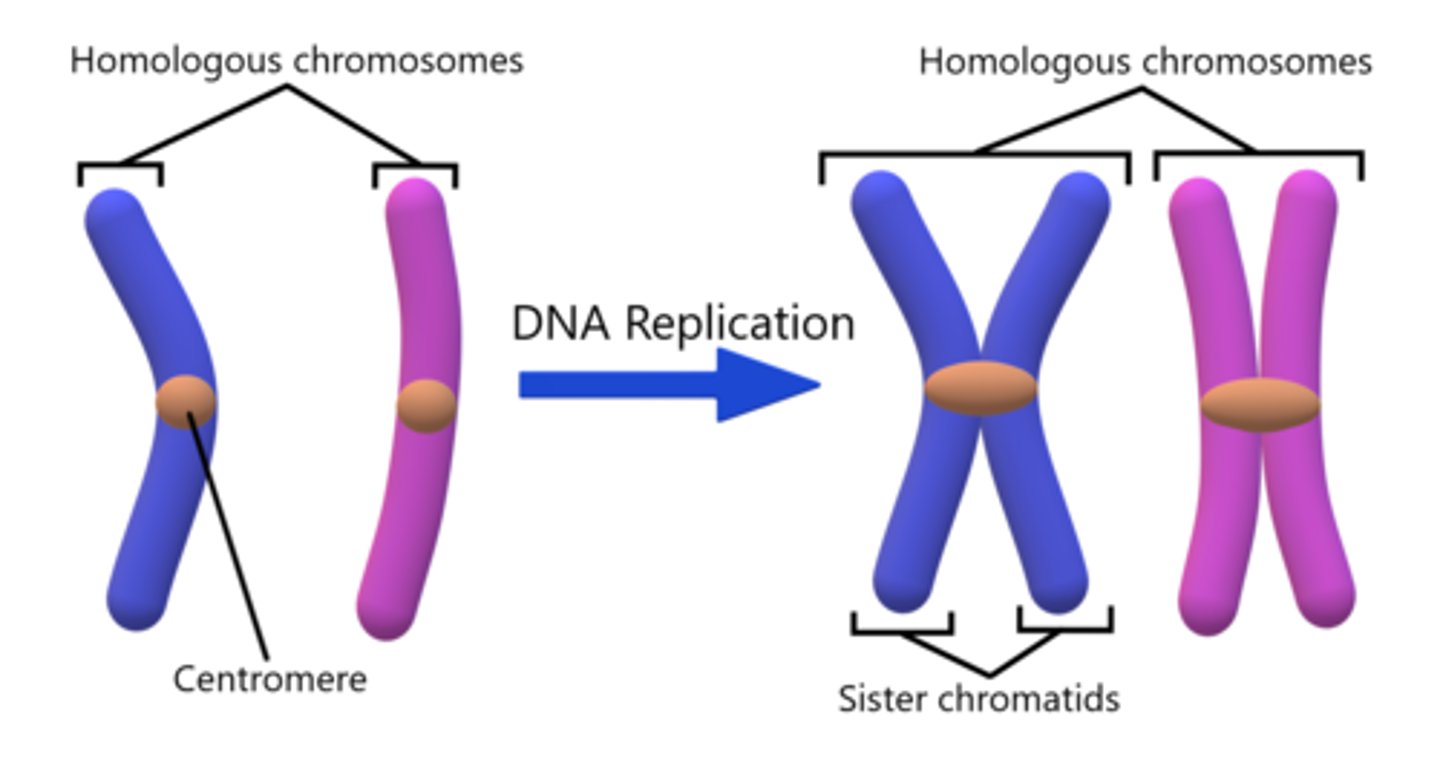
_____ is the general packaging of DNA around histone proteins
chromatin
microtubule organizing centers (MTOCs) are called _____ in animal cells
centrosomes
(MTOCs are just called MTOCs in plants/fungi)
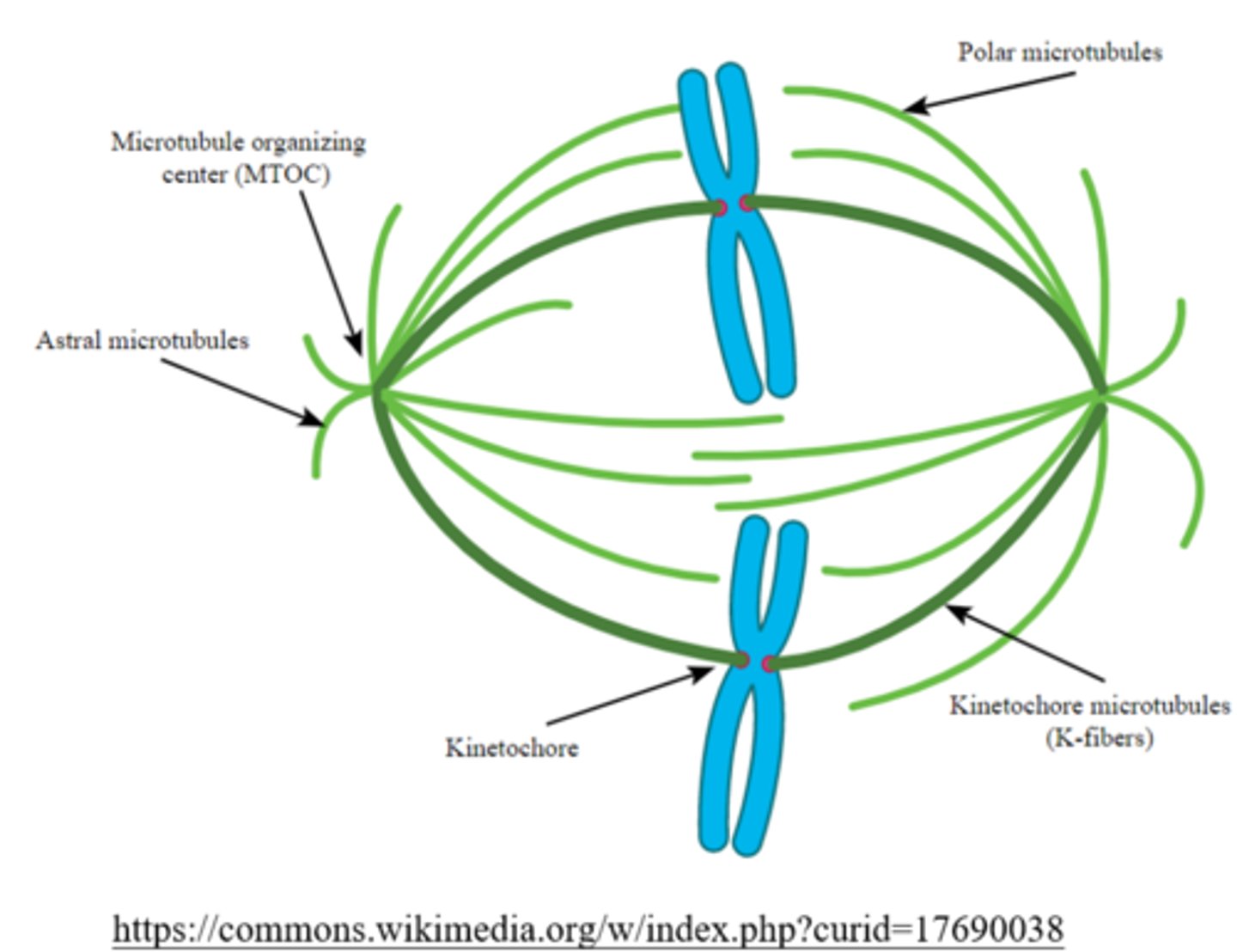
MTOCs are found outside the _____ during interphase
nucleus
centrosomes (animal cell MTOCs) contain a pair of _____
centrioles

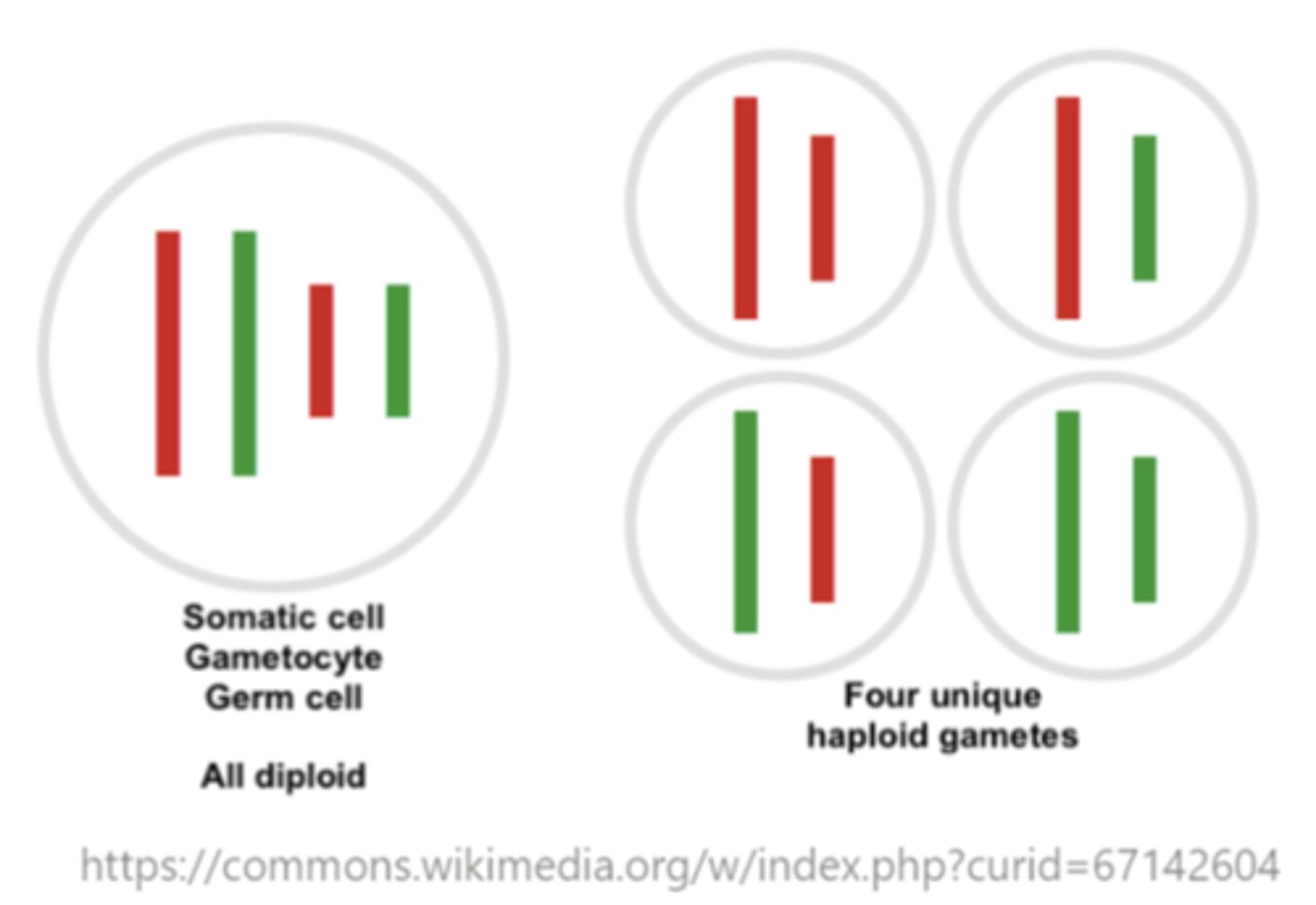
what are gametes?
haploid cells used during sexual reproduction. The fusion of two gametes of opposite sexes will conceive a zygote that is diploid
usually there is/are _____ MTOC(s) per cell; however, cells replicate their MTOCs during _____
1; S phase
there is/are _____ MTOC(s) before cell division (after the S phase of interphase)
2
_____ occurs in somatic cells and _____ occurs in gametes (egg, sperm, pollen)
mitosis; meiosis
mitosis occurs in _____ cells and meiosis occurs in _____ (egg, sperm, pollen)
somatic; germ cells (to create gametes)
what is fertilization?
the fusion of two haploid gamete nuclei to make one diploid zygote
what is syngamy?
fertilization - i.e., the fusion of two haploid gamete nuclei to make one diploid zygote
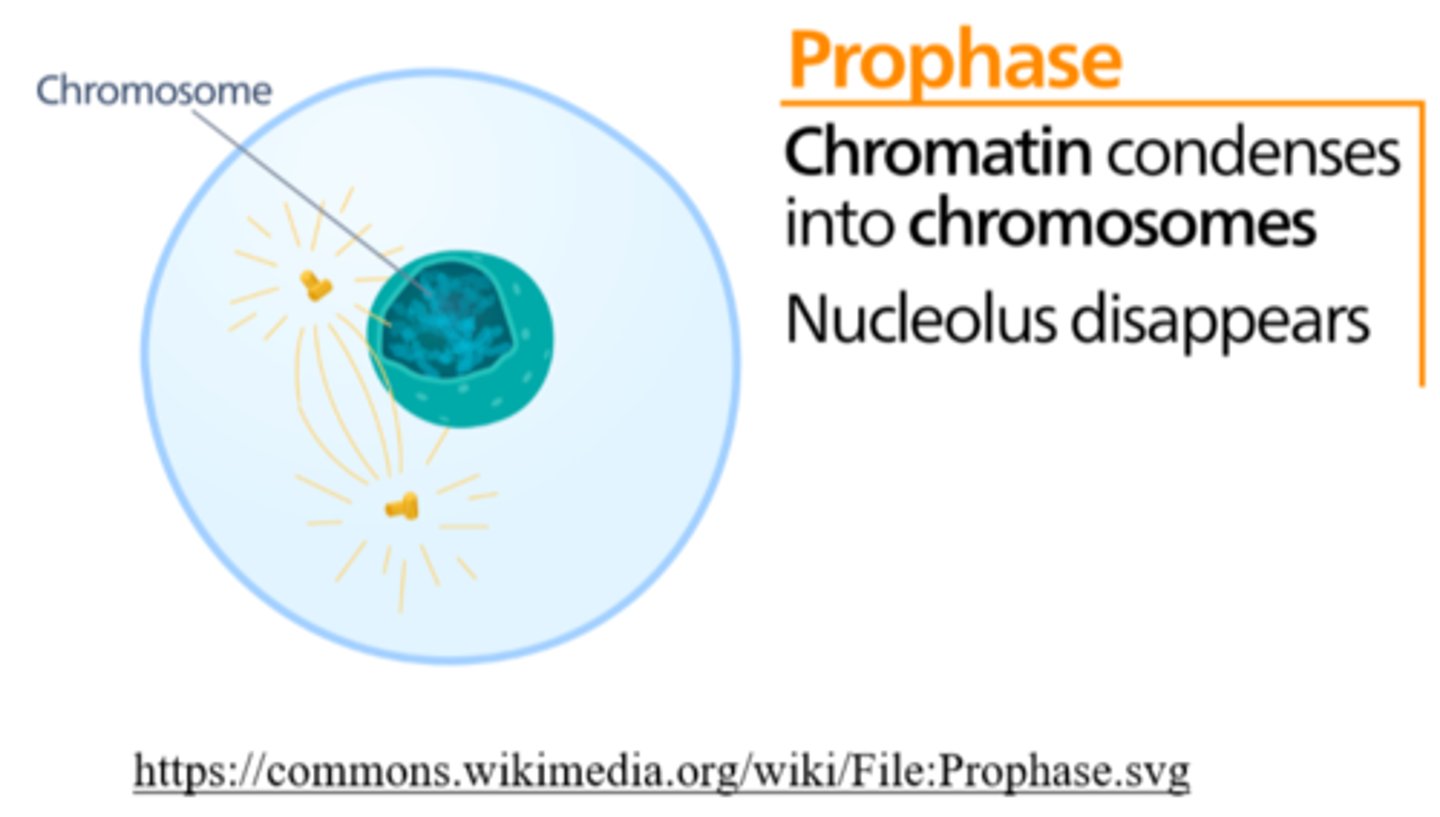
_____ is the phase of cell division, in which the nucleus disassembles and the nucleolus disappears
prophase
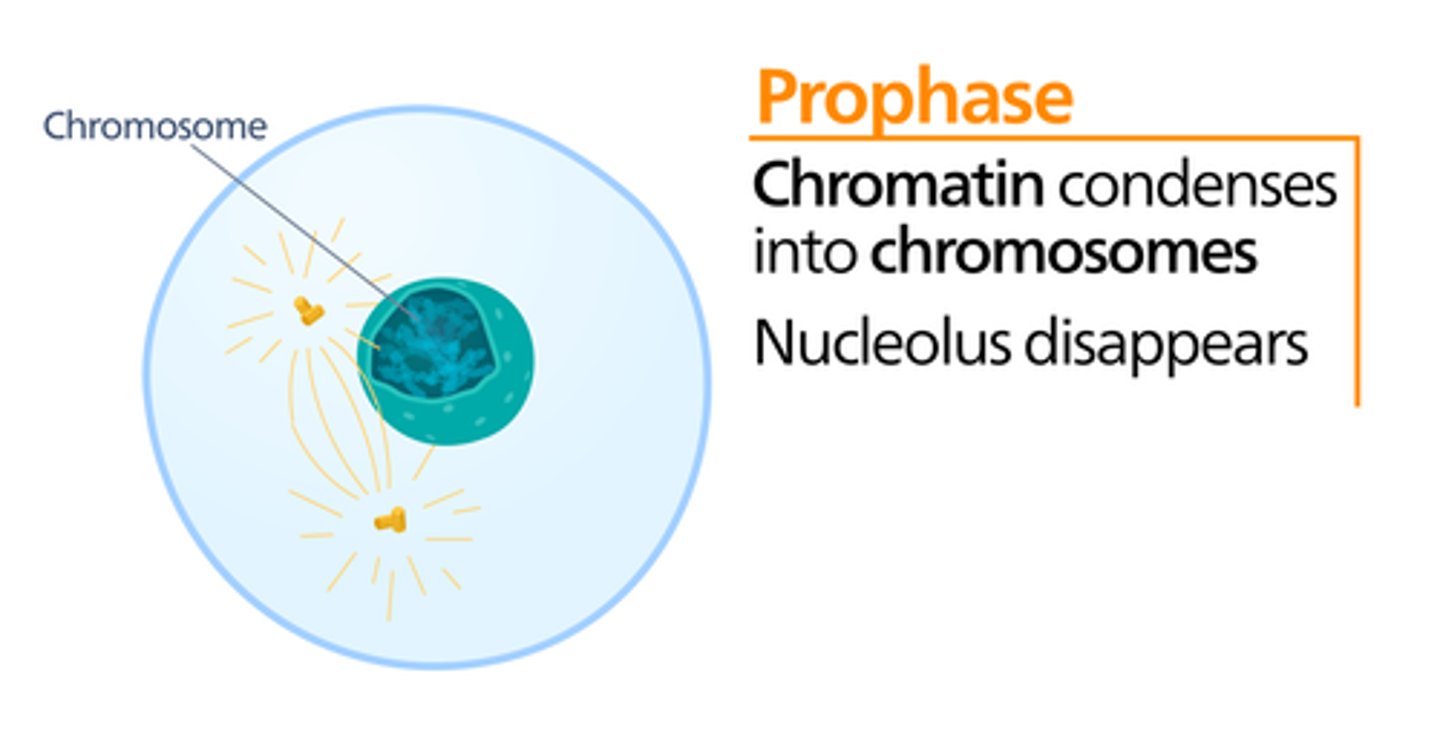
_____ is the phase of cell division in which chromatin condenses into chromosomes
prophase
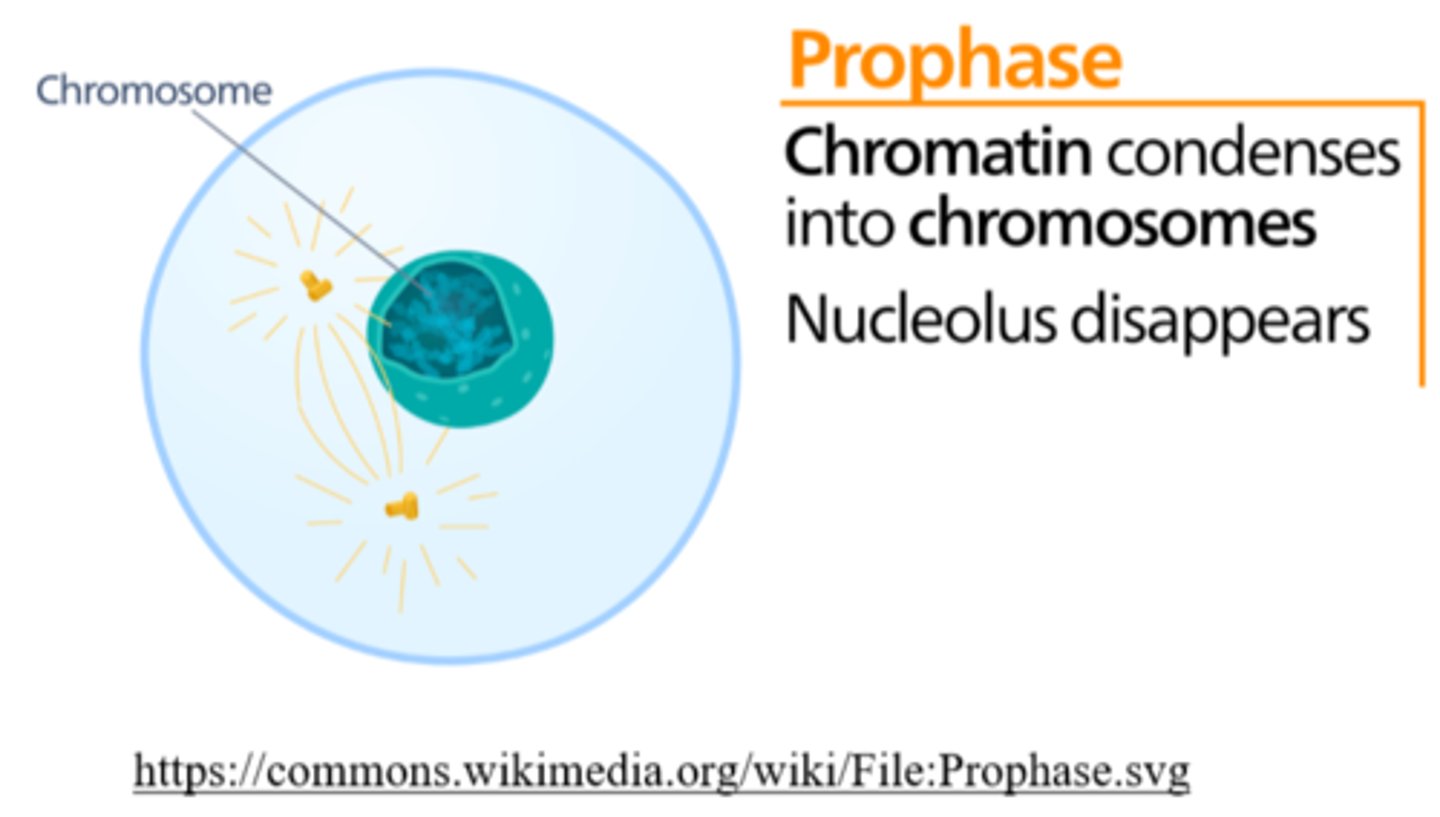
_____ is the phase of cell division, in which the nuclear envelope breaks down
prophase
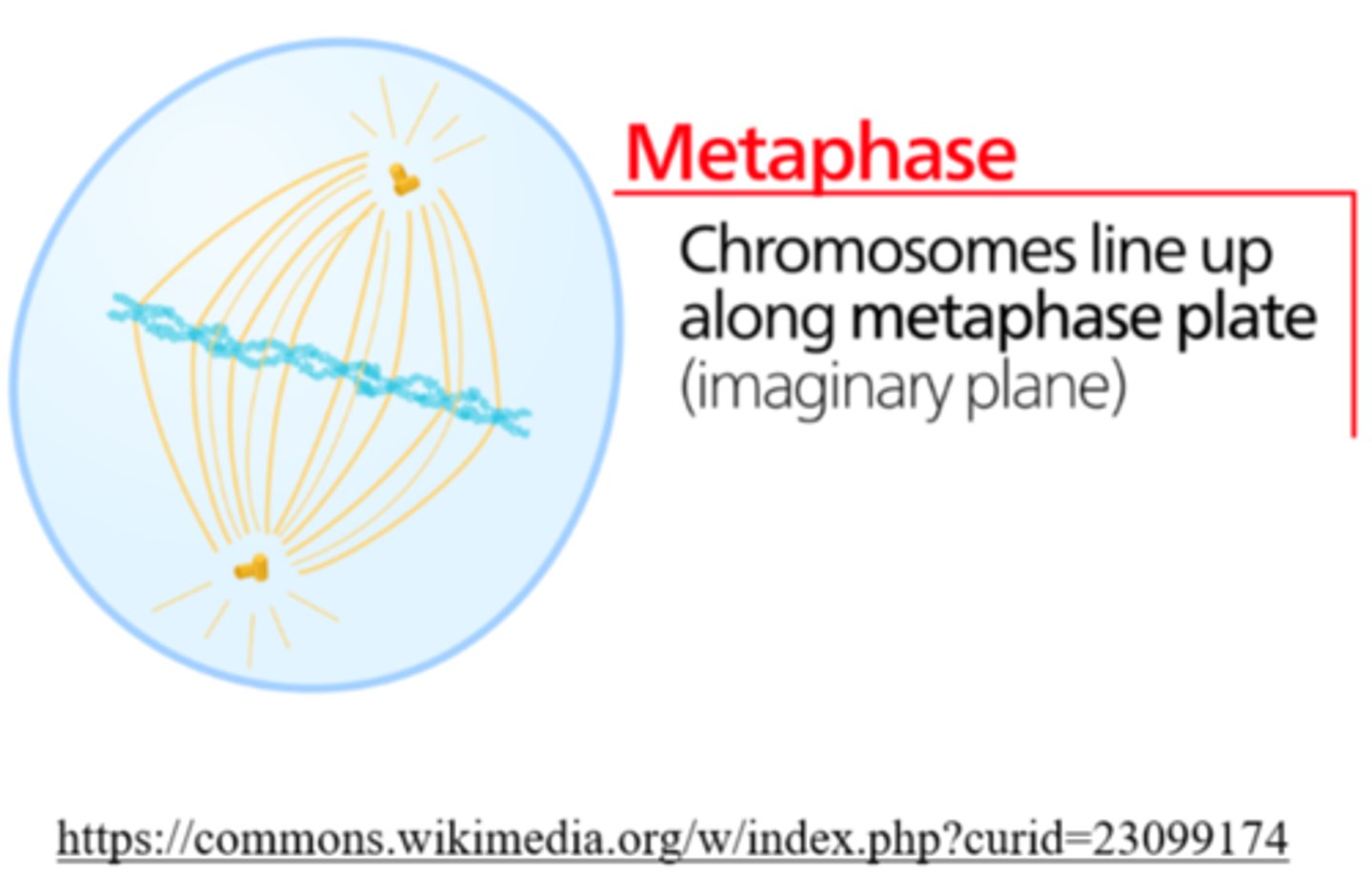
_____ is the phase of cell division in which chromosomes line up in a single file in the center
metaphase
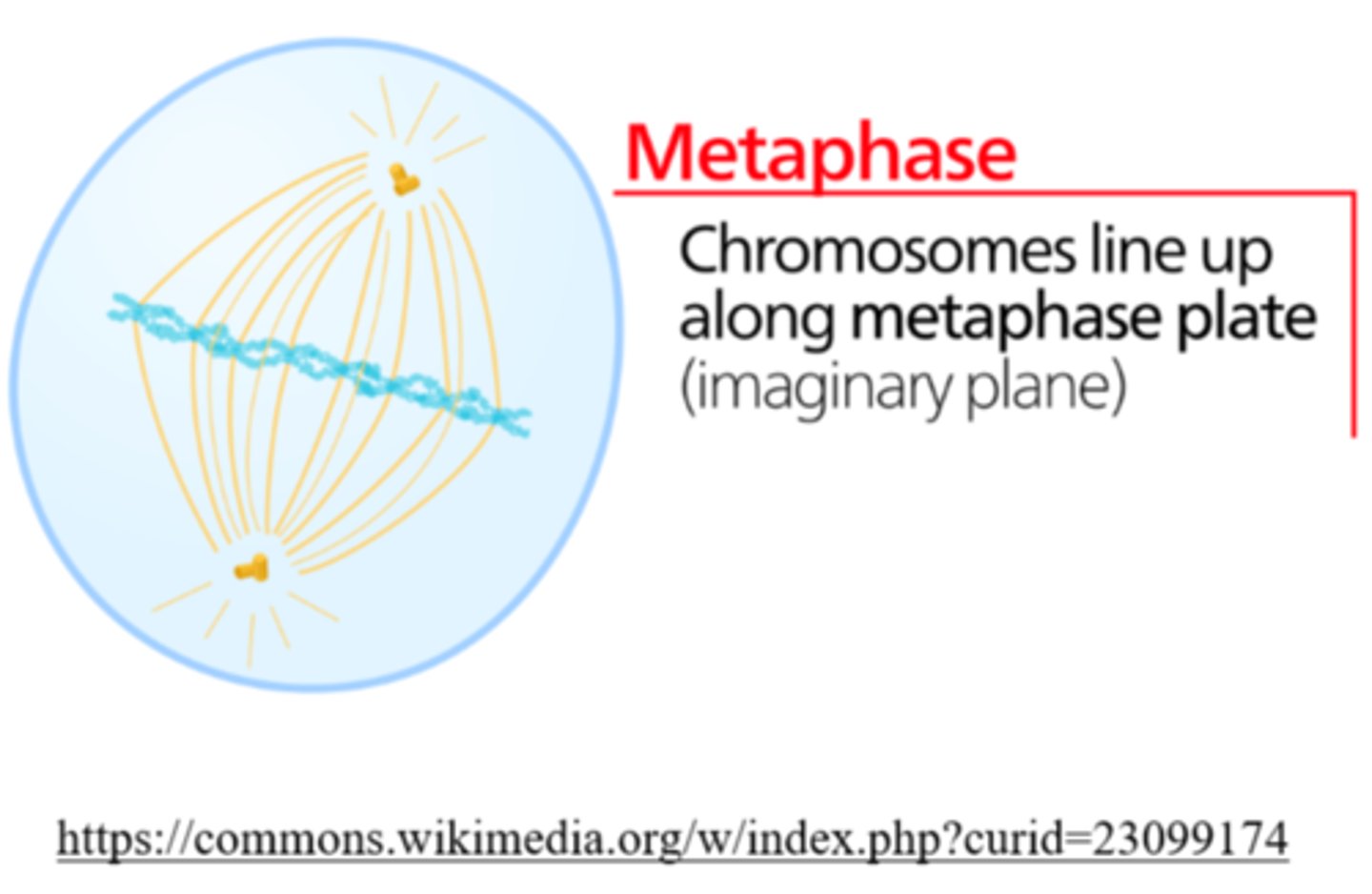
_____ is the phase of cell division in which each chromatid is complete with a centromere and attached kinetochore
metaphase
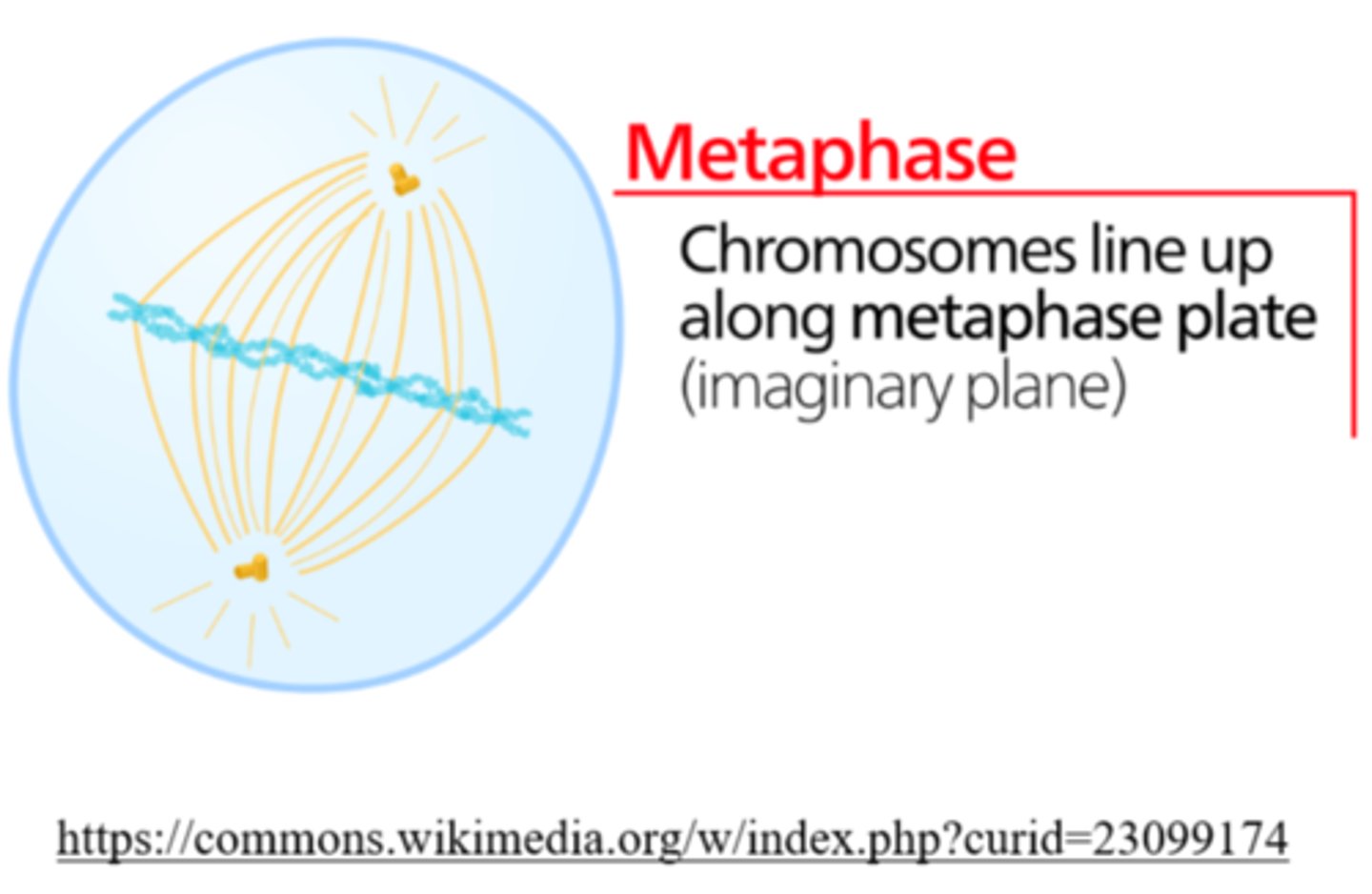
_____ is the phase of cell division in which replicated centrosomes are at opposite ends of the cell
metaphase
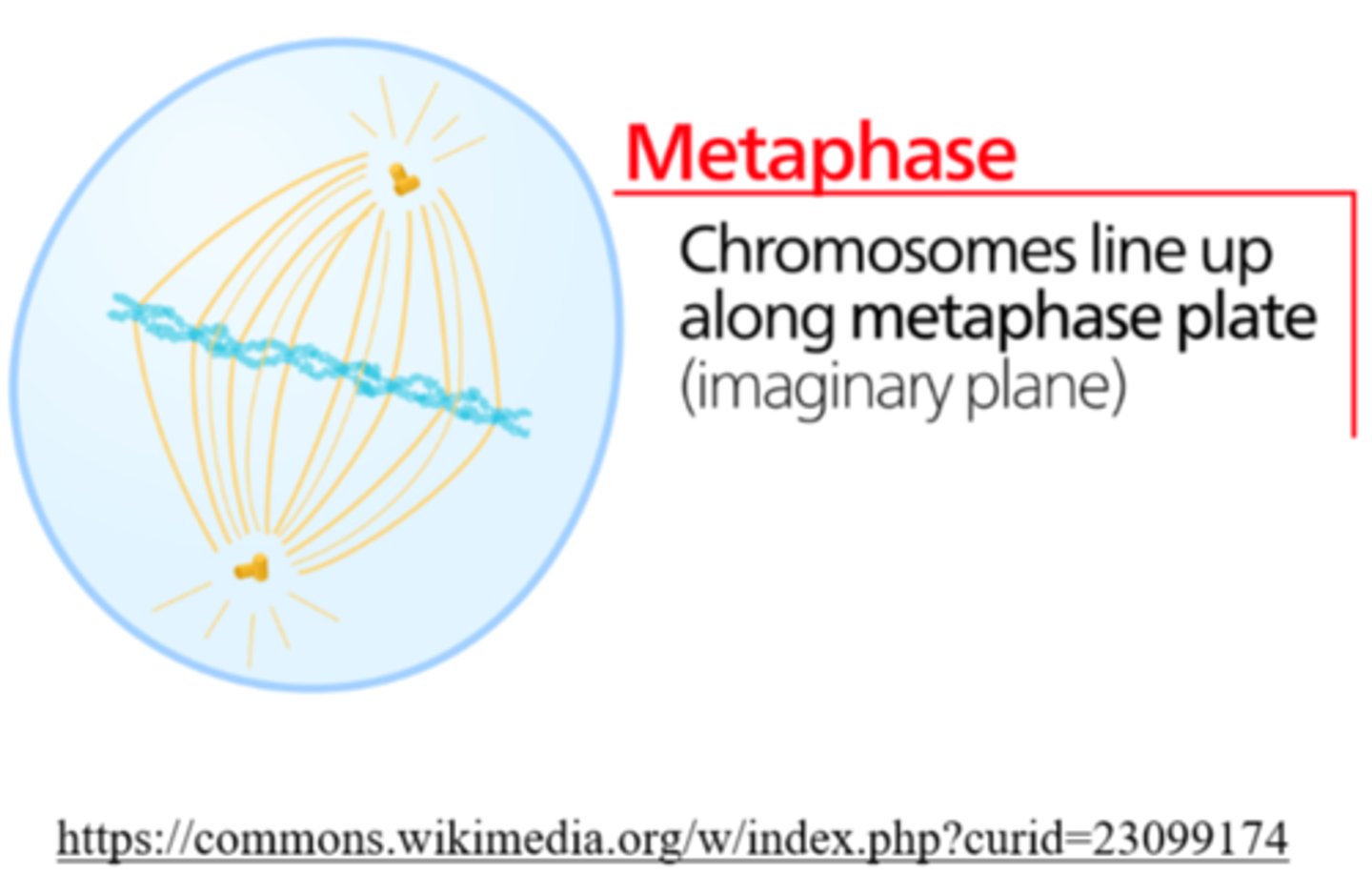
_____ is the phase of cell division in which karyotyping is performed
metaphase
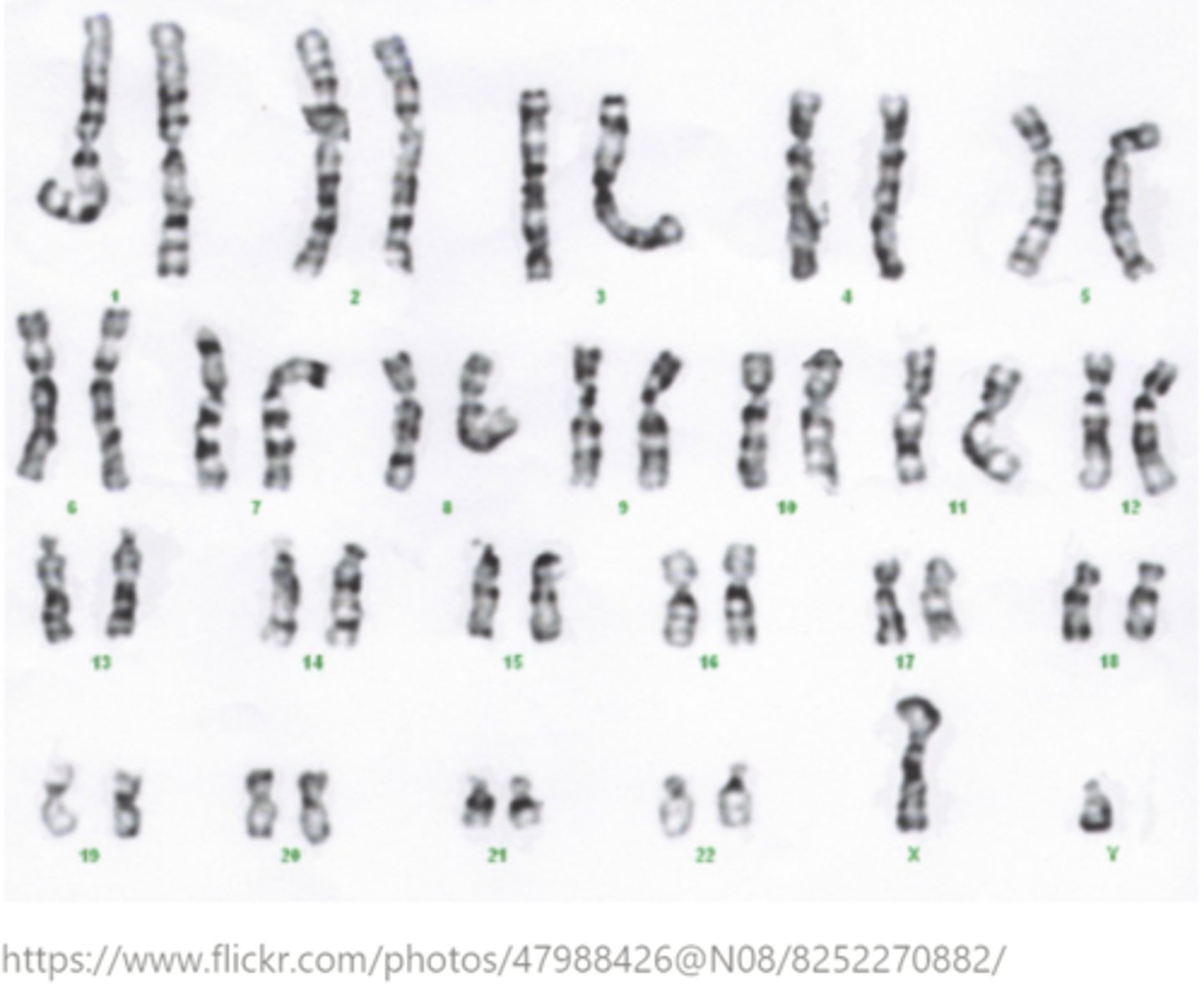
_____ is a visual depiction of one's chromosomes by homologous pairs, and it is usually performed during metaphase
karyotyping
_____ is the phase of cell division in which kinetochore microtubules shorten
anaphase
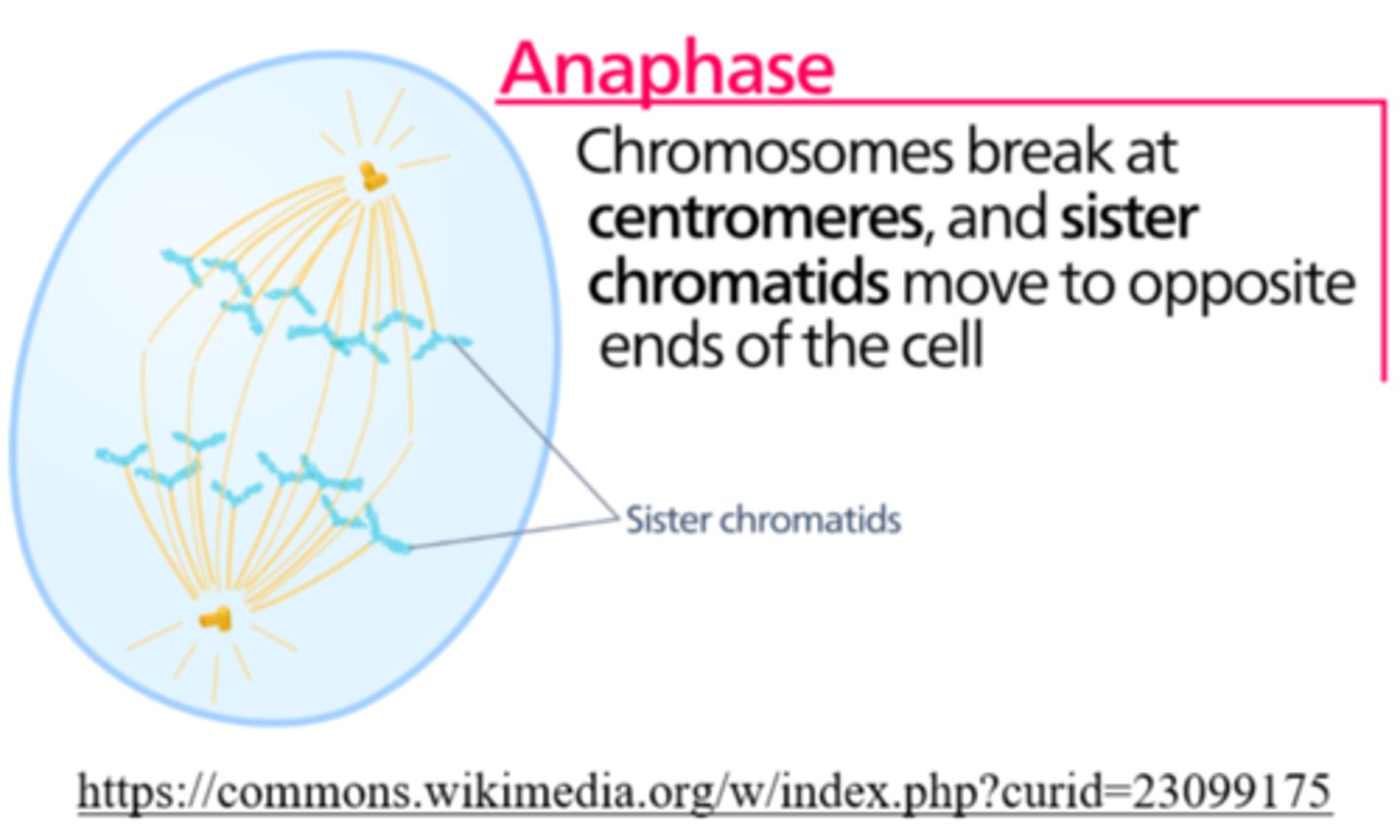
_____ is the phase of cell division in which polar microtubules lengthen
anaphase
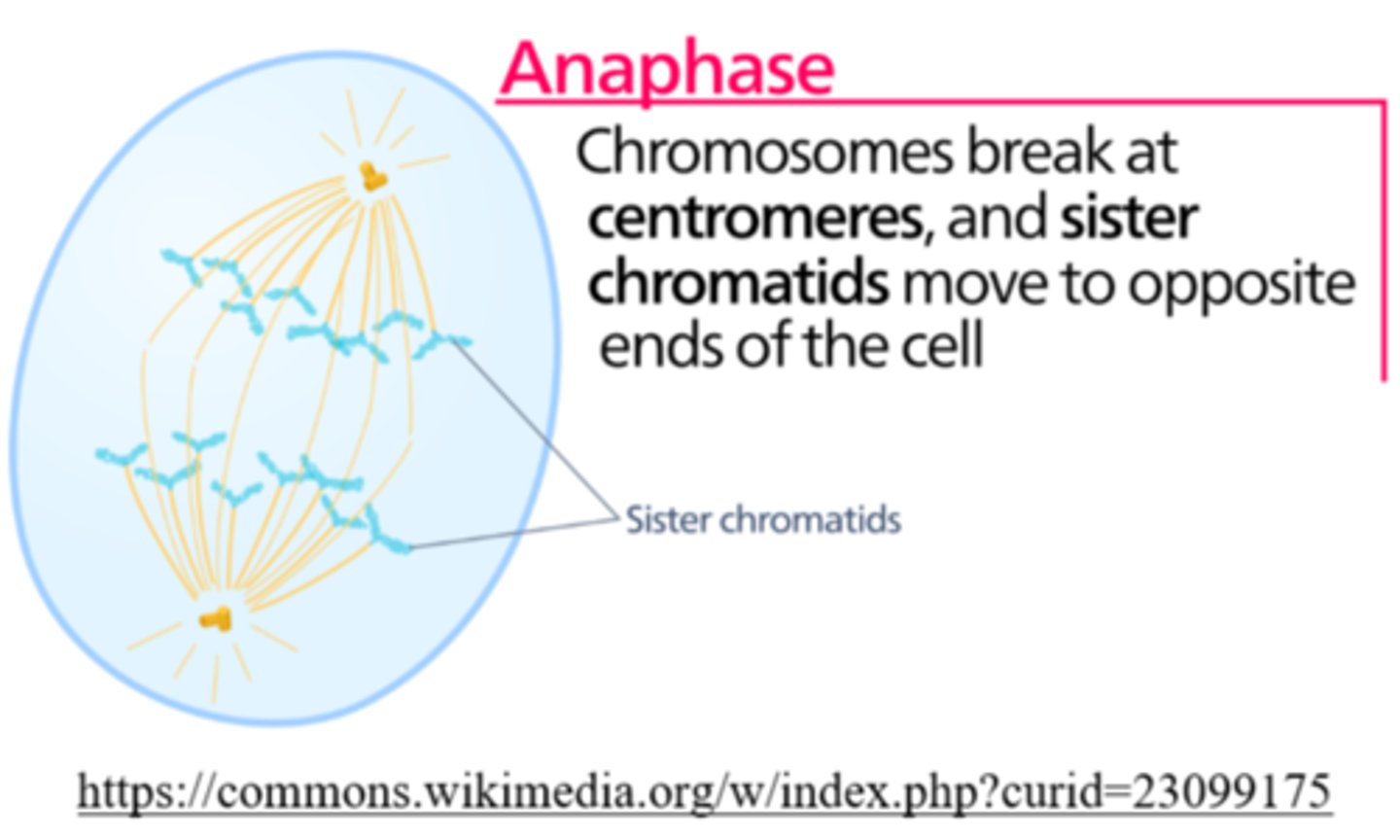
_____ is the phase of cell division in which each chromosome is pulled apart to opposite poles (disjunction)
anaphase
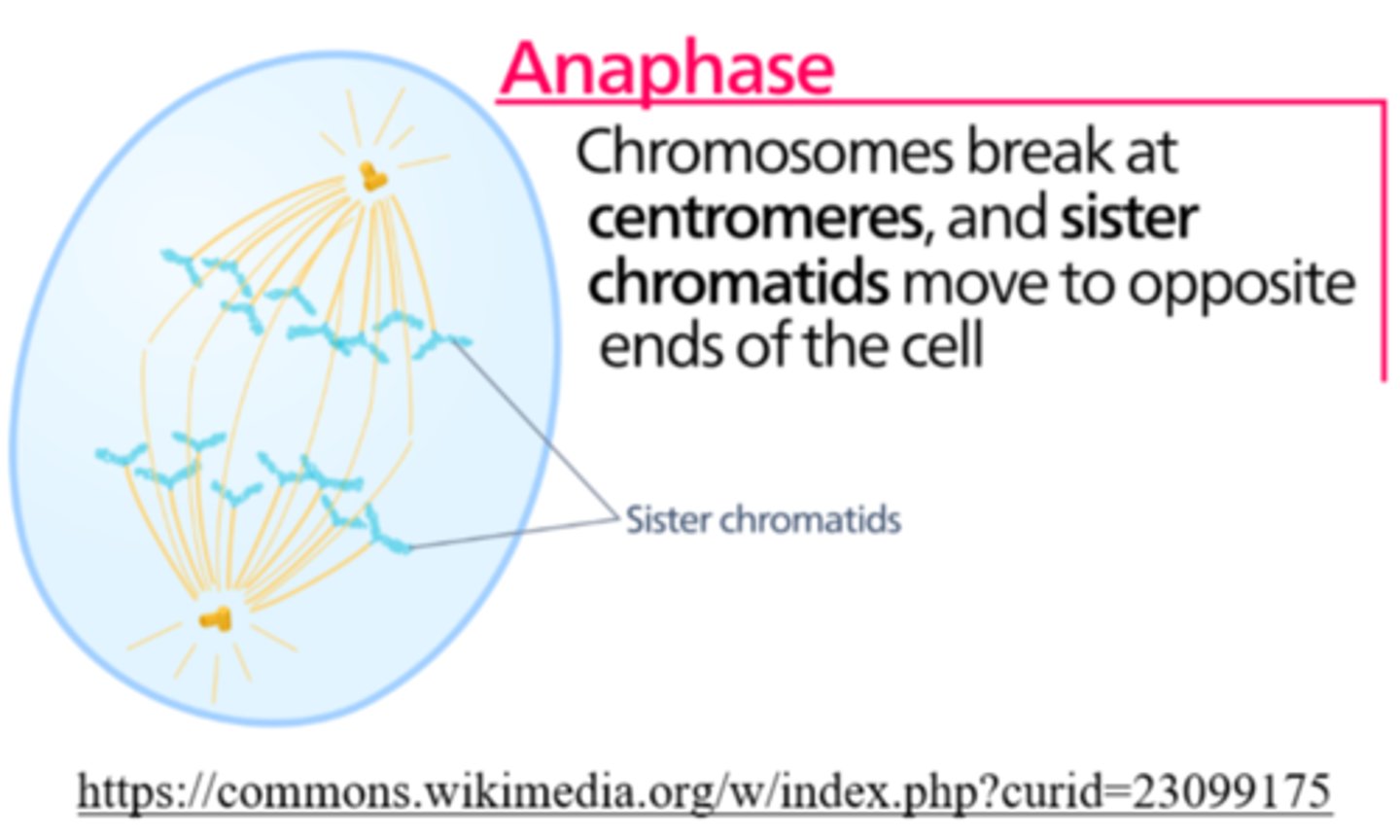
once separated at anaphase, each _____ is considered a _____
chromatid; chromosome
at the end of _____, each pole has a complete set of chromosomes
anaphase
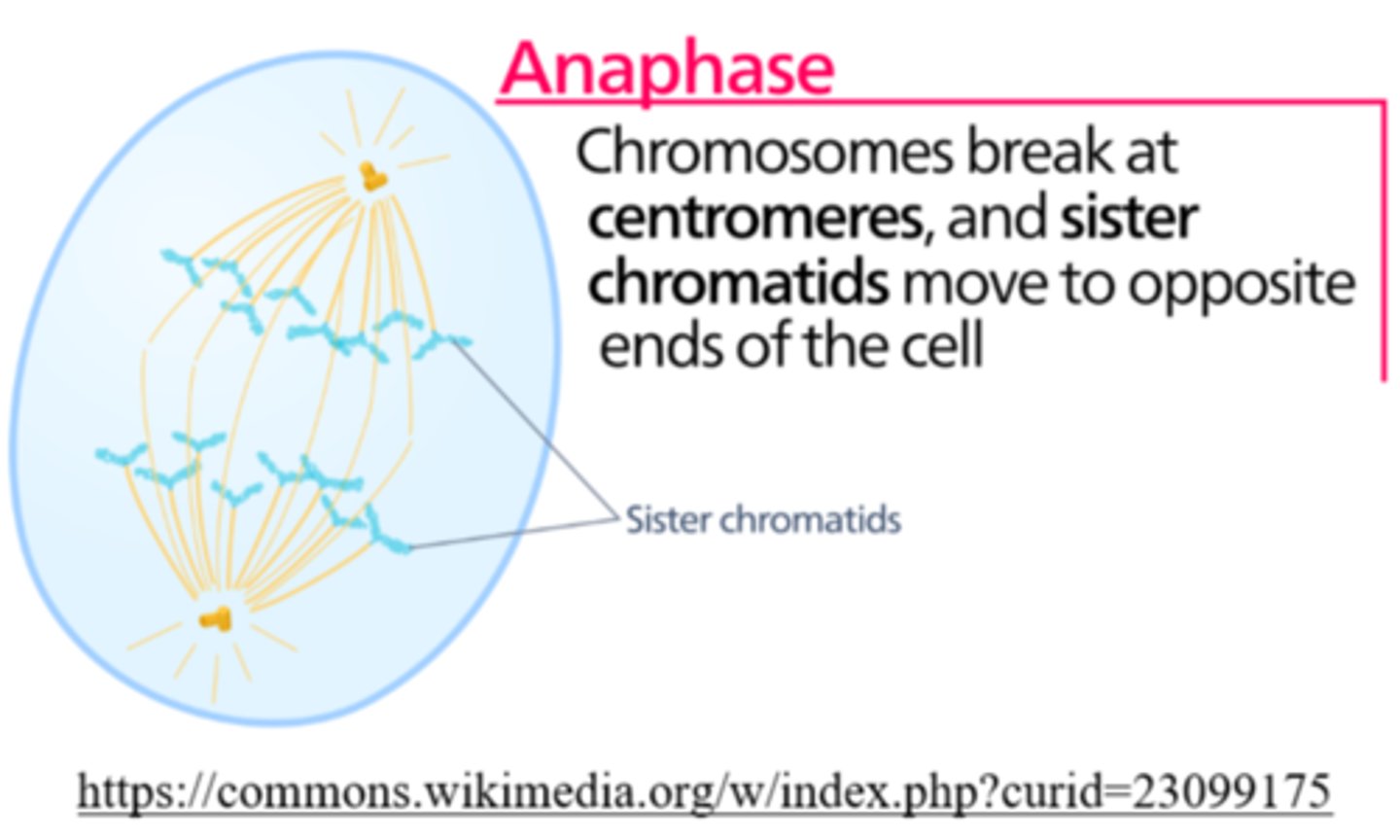
what is the shortest step of cell division?
anaphase
_____ is the phase of cell division when karyokinesis occurs
telophase
(karyokinesis = nuclear division - notice the formation of 2 nuclei)
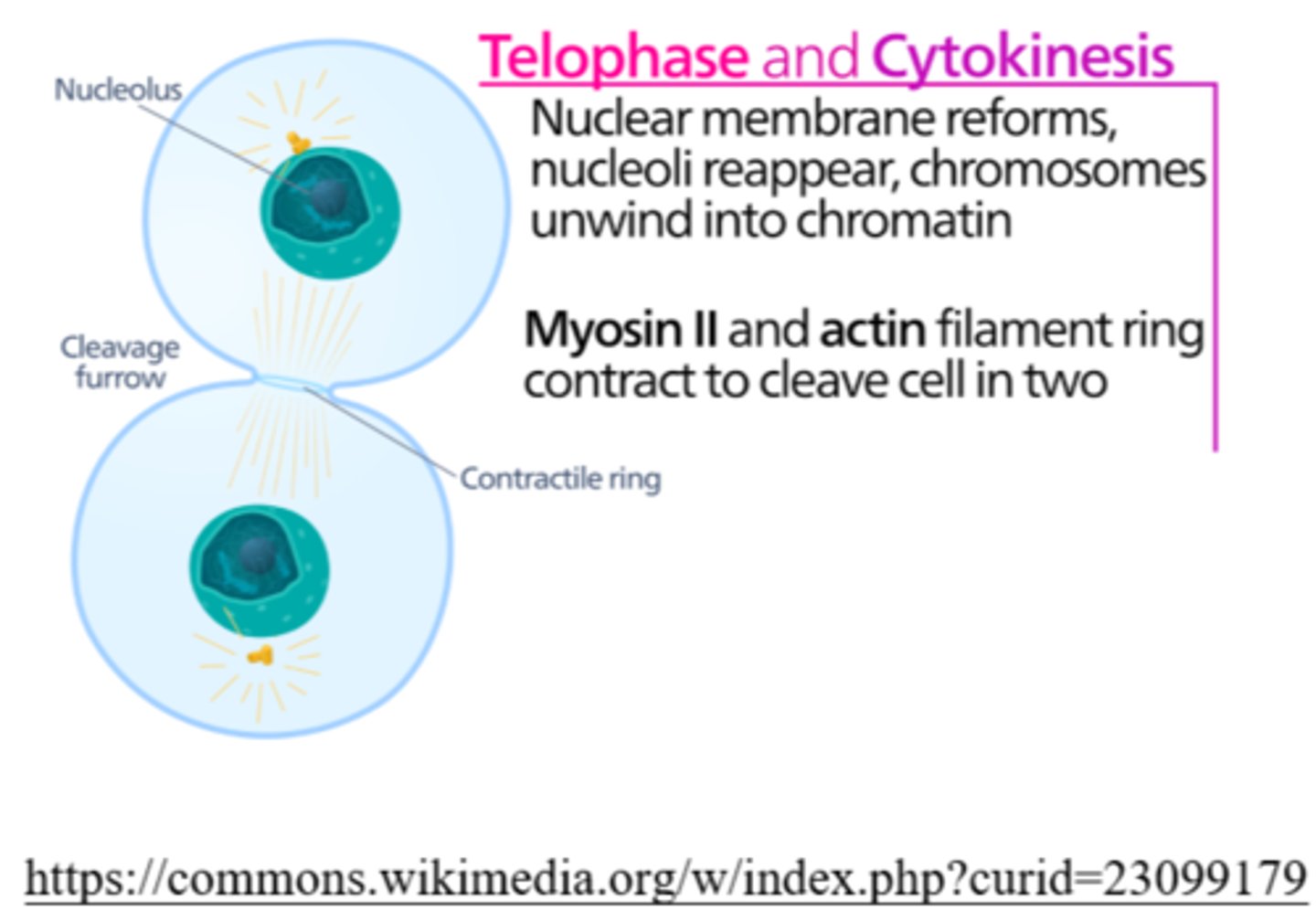
_____ is the phase of cell division in which the nuclear envelopes re-develop
telophase
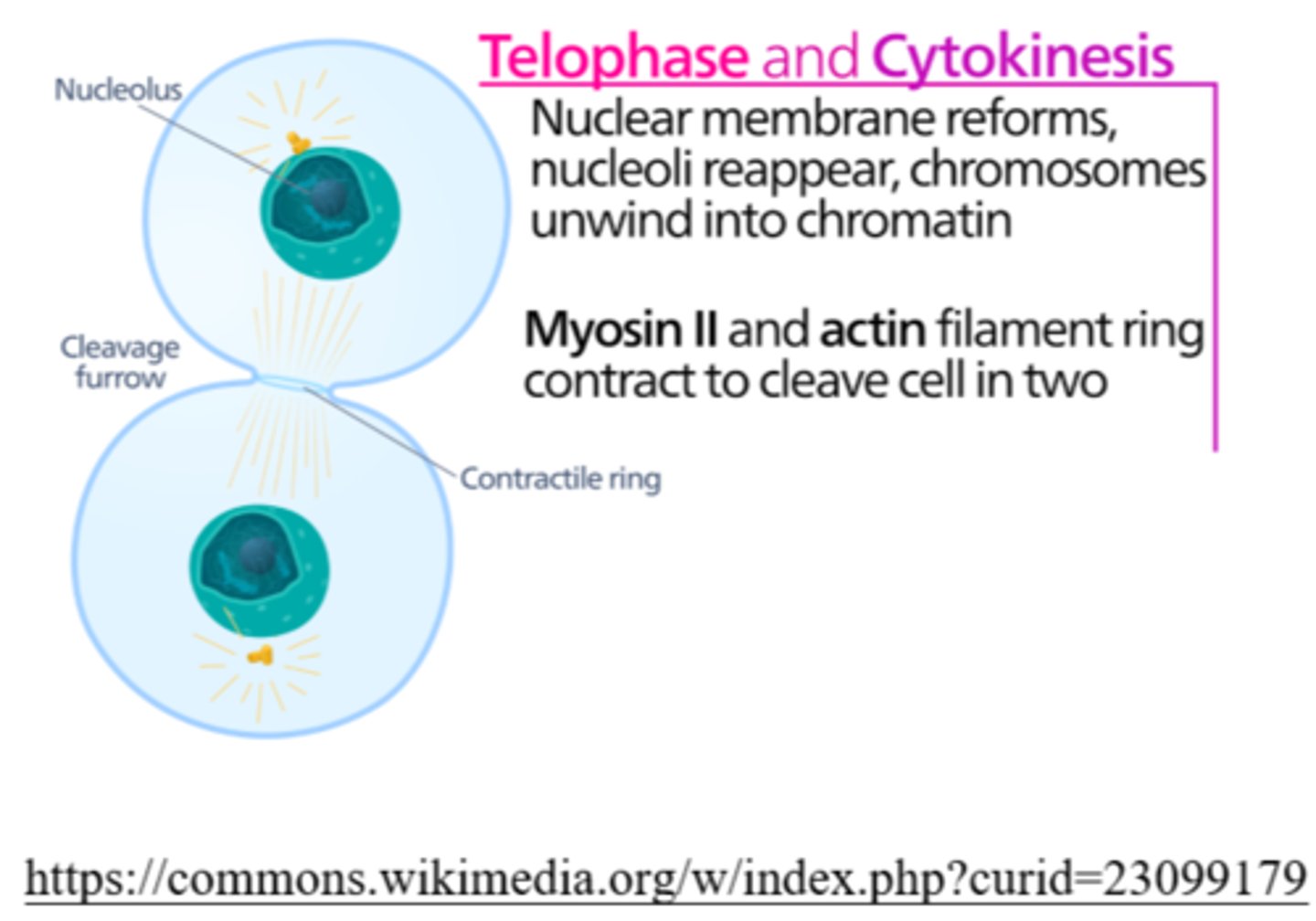
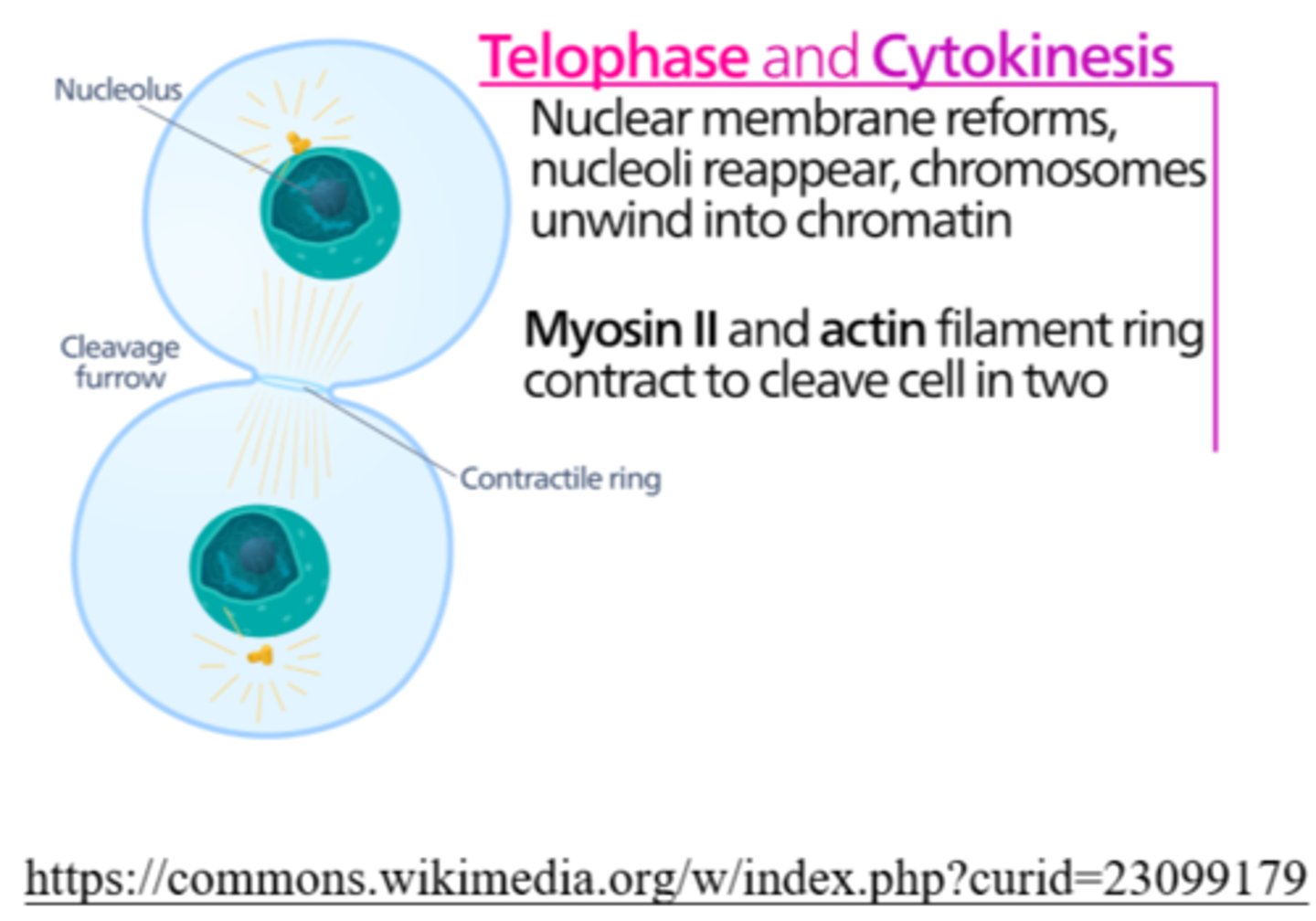
_____ is the phase of cell division in which chromosomes de-condense back into chromatin
telophase
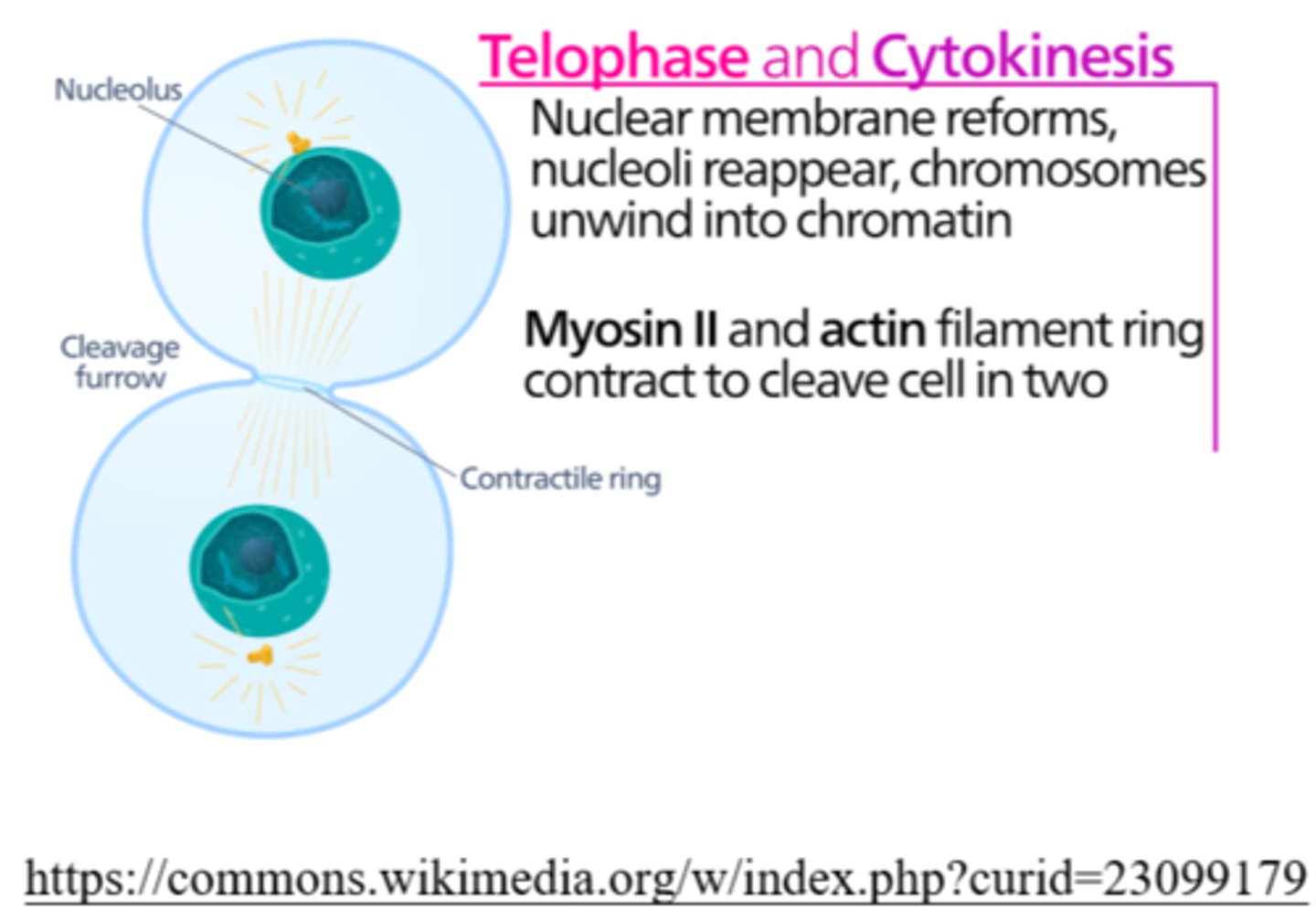
_____ is the phase of cell division in which nucleoli reappear
telophase
the presence of chromosomes means _____ is occurring
mitosis/meiosis
(cell division)
in metaphase, a chromosome consists of two closely attached _____
sister chromatids
to keep track of the total number of chromosomes during cell division, count the number of _____
centromeres
in _____, the chromosome number doubles
anaphase
at the end of anaphase, there would be a total of _____ chromosomes (separated chromatids) if a cell has 46 chromosomes at the beginning
92
unlike meiosis, NO _____ occurs in mitosis
genetic variation
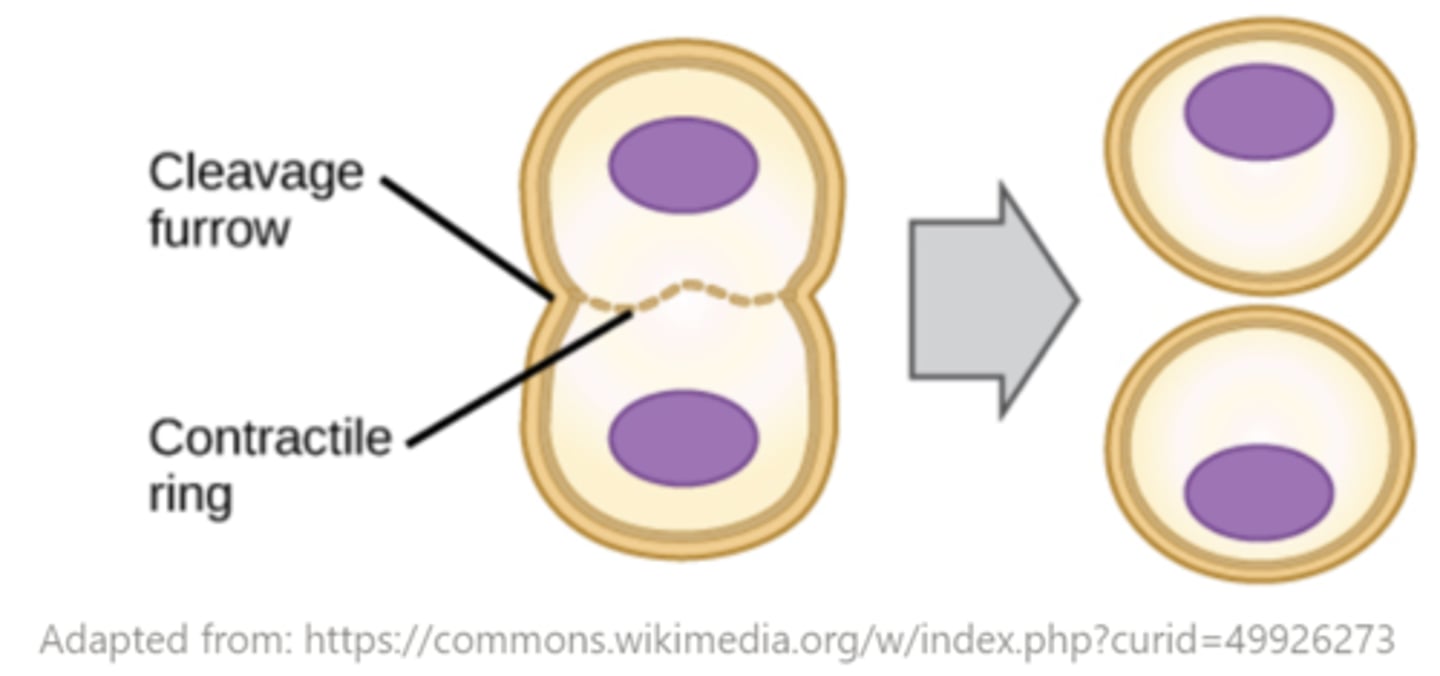
during cytokinesis, animal cells separate via creation of the _____
cleavage furrow
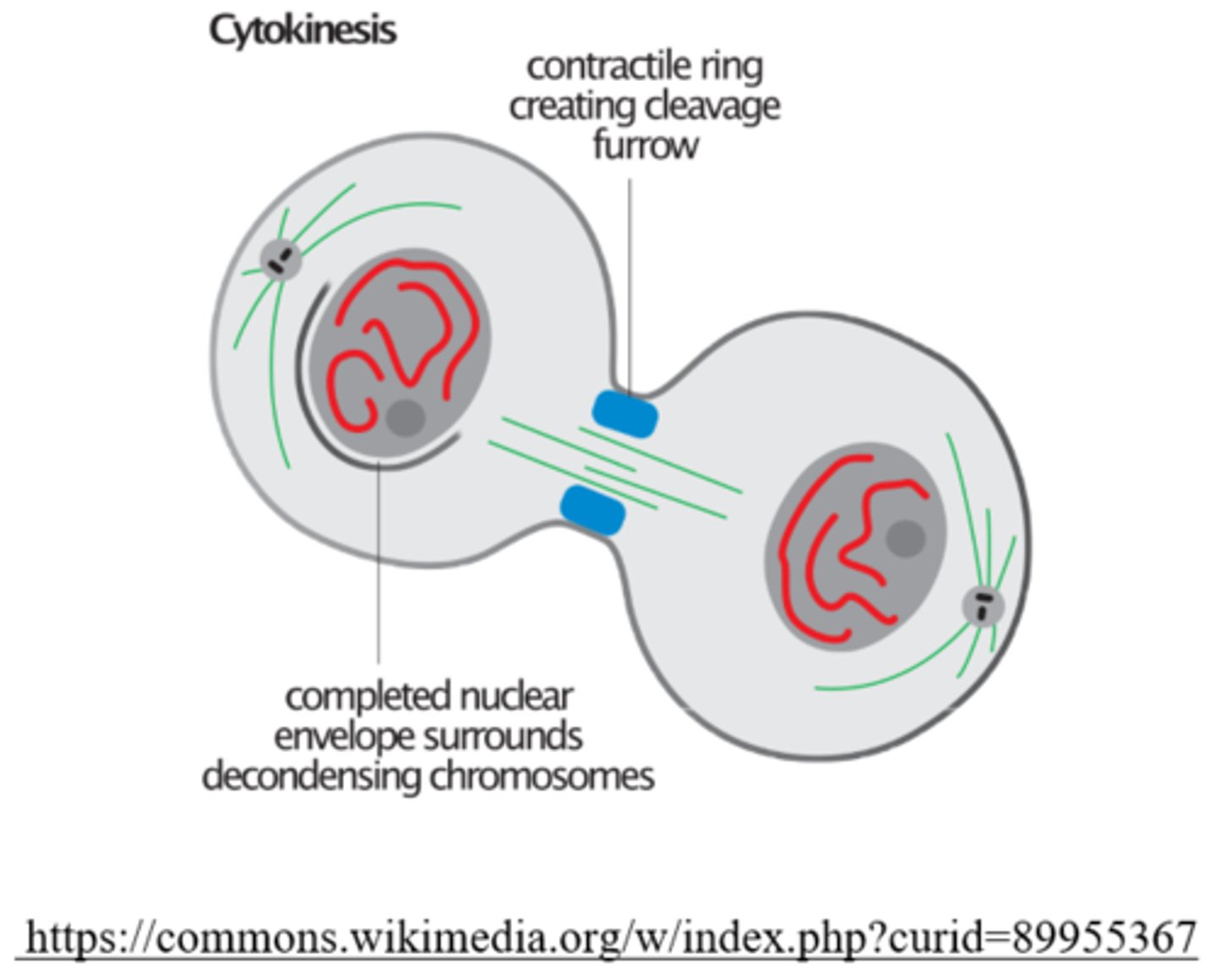
during _____ in animals, actin and myosin microfilaments shorten and the plasma membrane is pulled into the center, creating a _____
cytokinesis; contractile ring/cleavage furrow
plant cells undergo cytokinesis via formation of a _____
cell plate
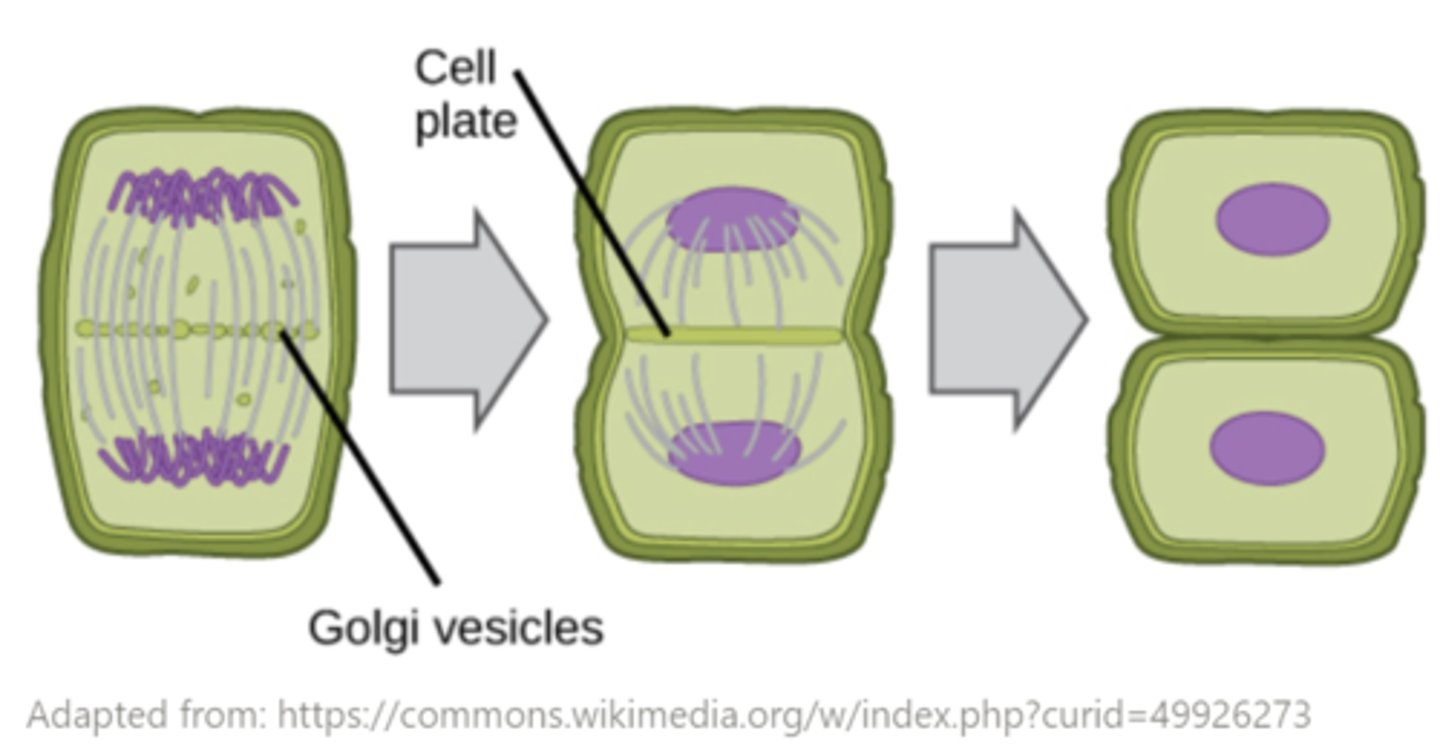
as plant cells undergo cytokinesis, vesicles from _____ migrate and fuse to form a cell plate
golgi bodies
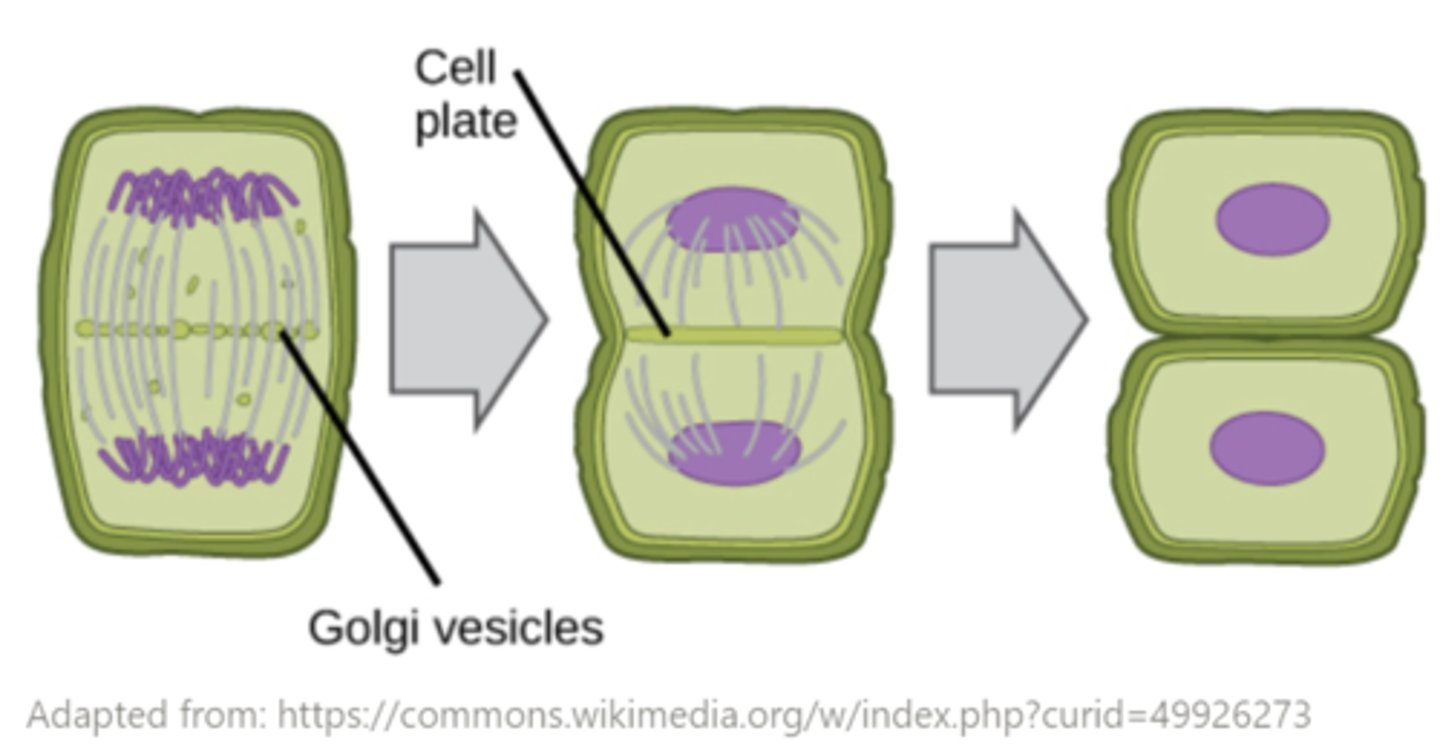
during plant cell division, the cells don't actually separate from each other because the _____ cements adjacent cells together
middle lamella
_____ begins after mitosis and cytokinesis are complete
interphase
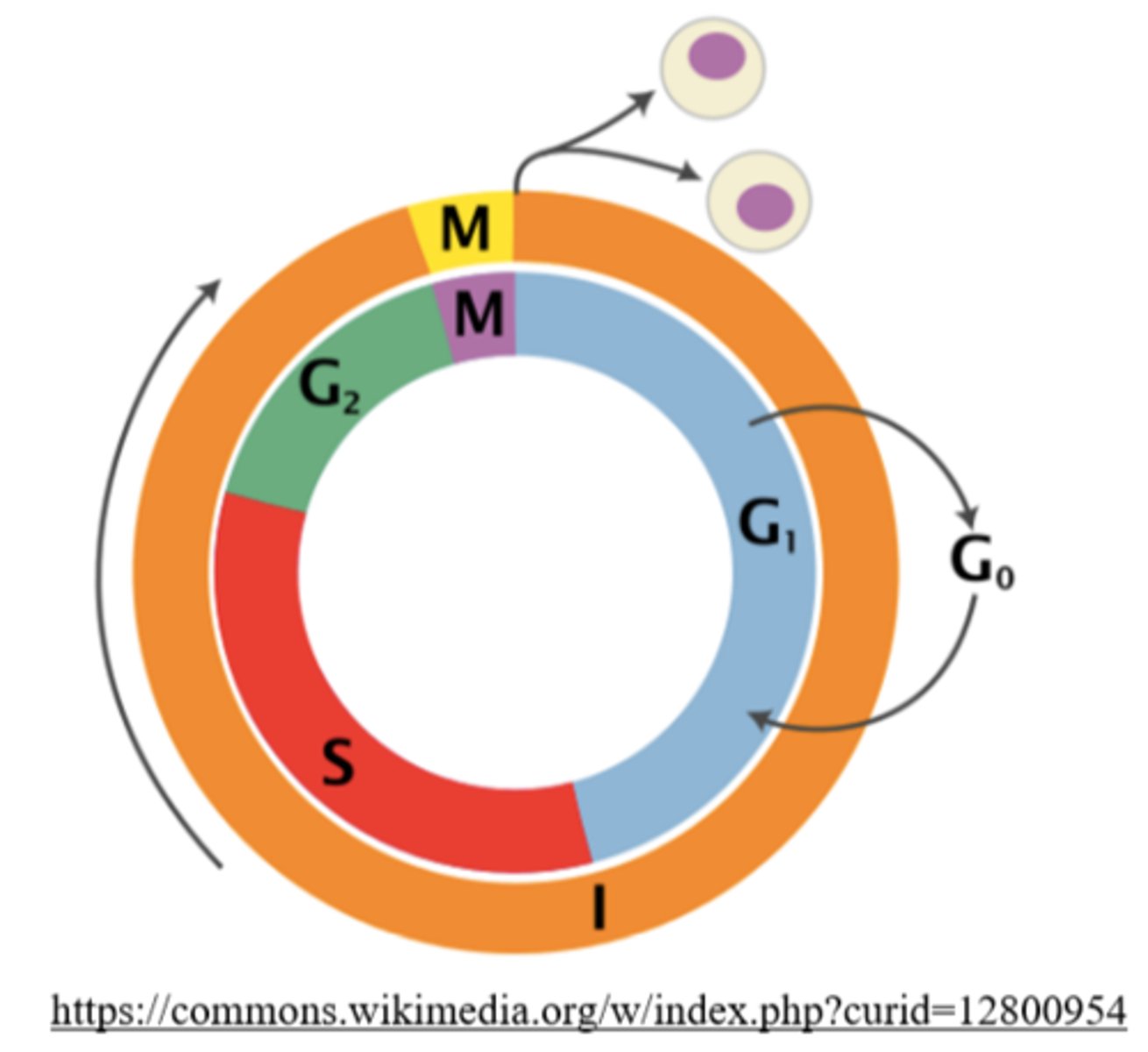
only the somatic cells that divide by _____ undergo interphase
mitosis
gametes do undergo _____ after they are made
interphase
what are the phases of interphase?
G1 (possibly G0), S, and G2 phase
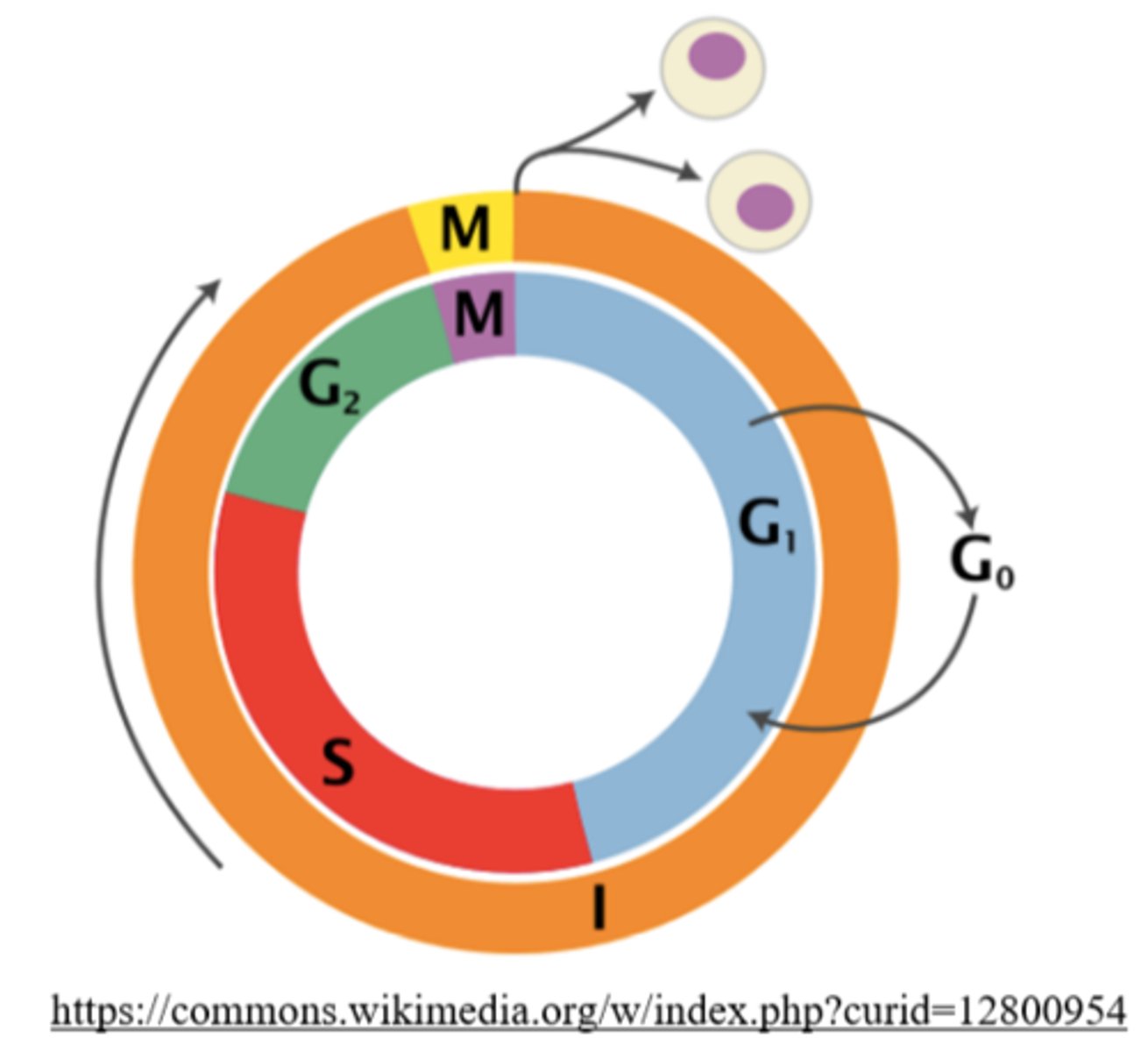
what are the three *main* phases of the cell cycle?
mitosis, cytokinesis, interphase
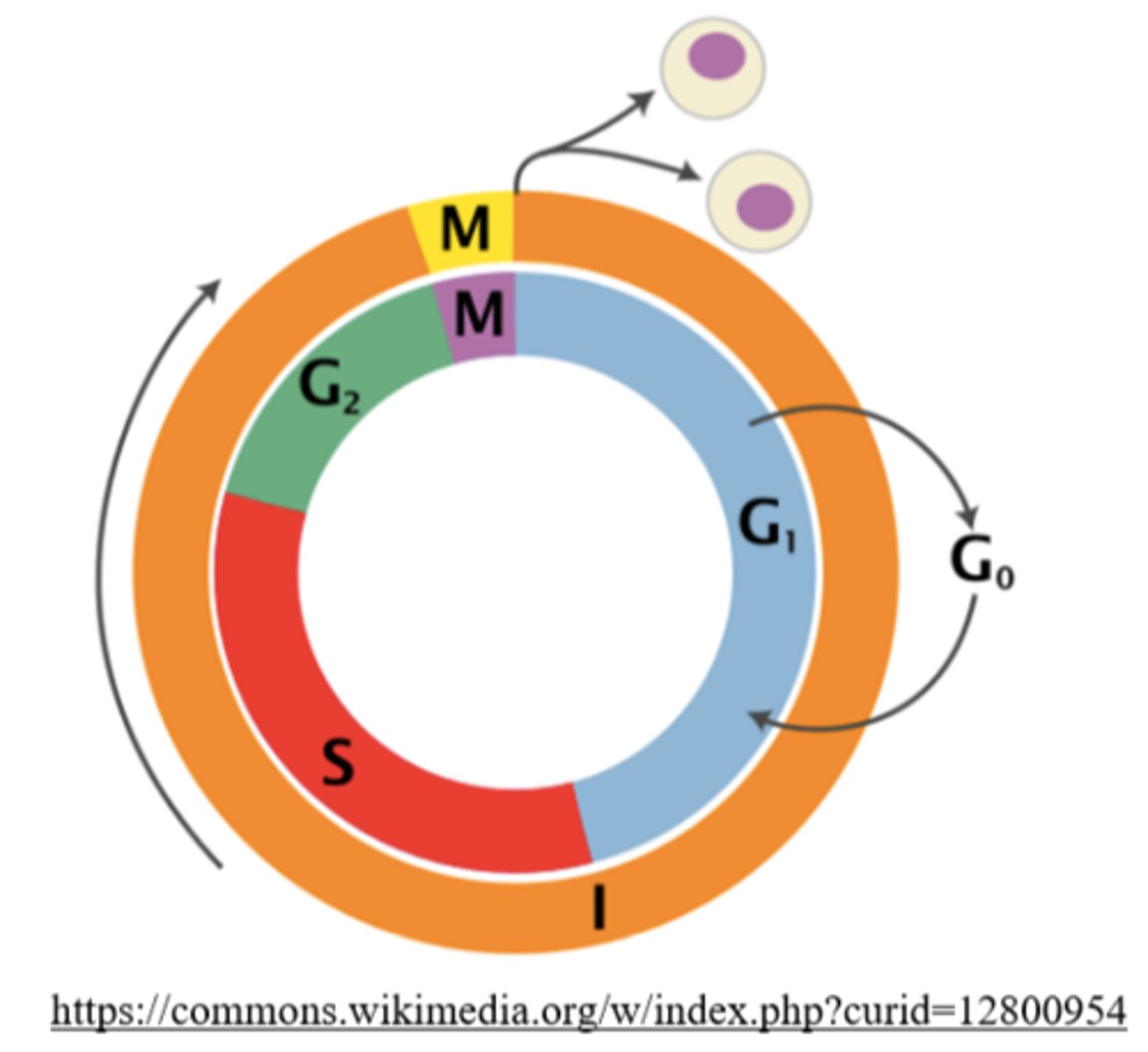
90% of the cell cycle is spent in _____
interphase
the phase of interphase in which a checkpoint ensures everything is ready for DNA synthesis
G1
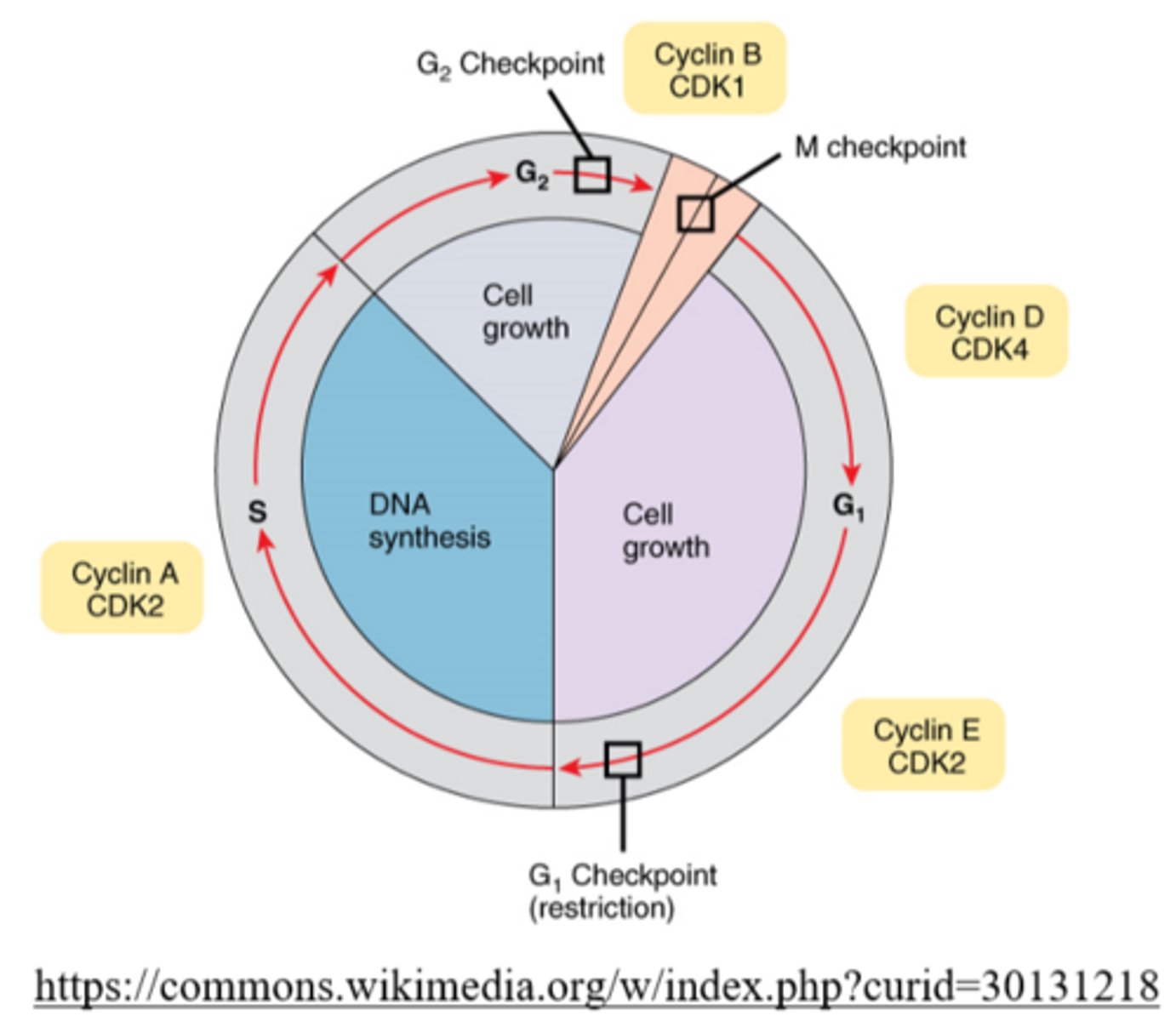
cells produce protein, ribosomes, and mitochondria in the _____ stage of interphase
G1
in what phase of the cell cycle will DNA synthesis occur?
the S phase of interphase
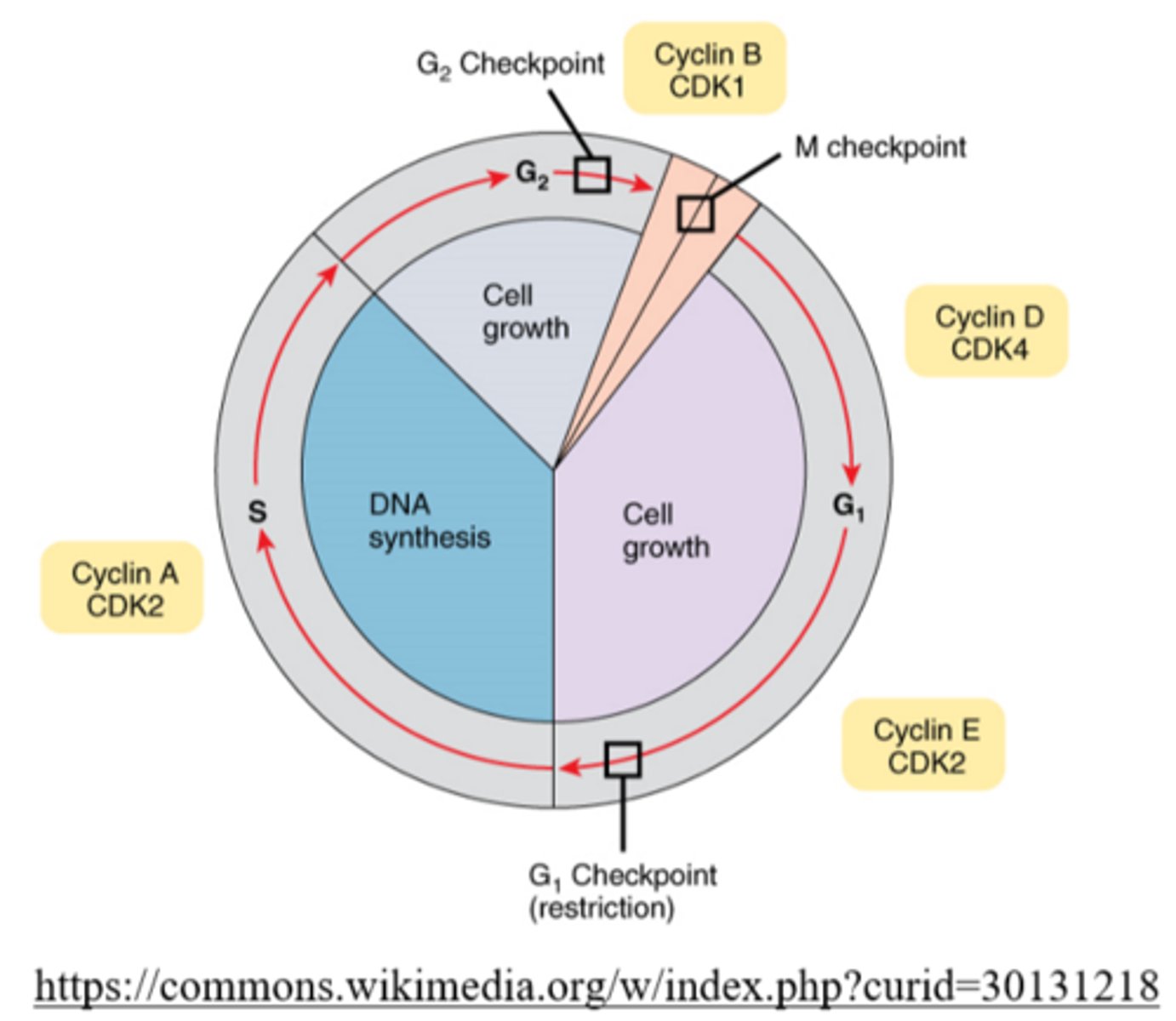
a second molecule of DNA is replicated from the first to provide sister chromatids in the _____ of interphase
S phase
the phase of interphase in which rapid cell growth occurs
G2
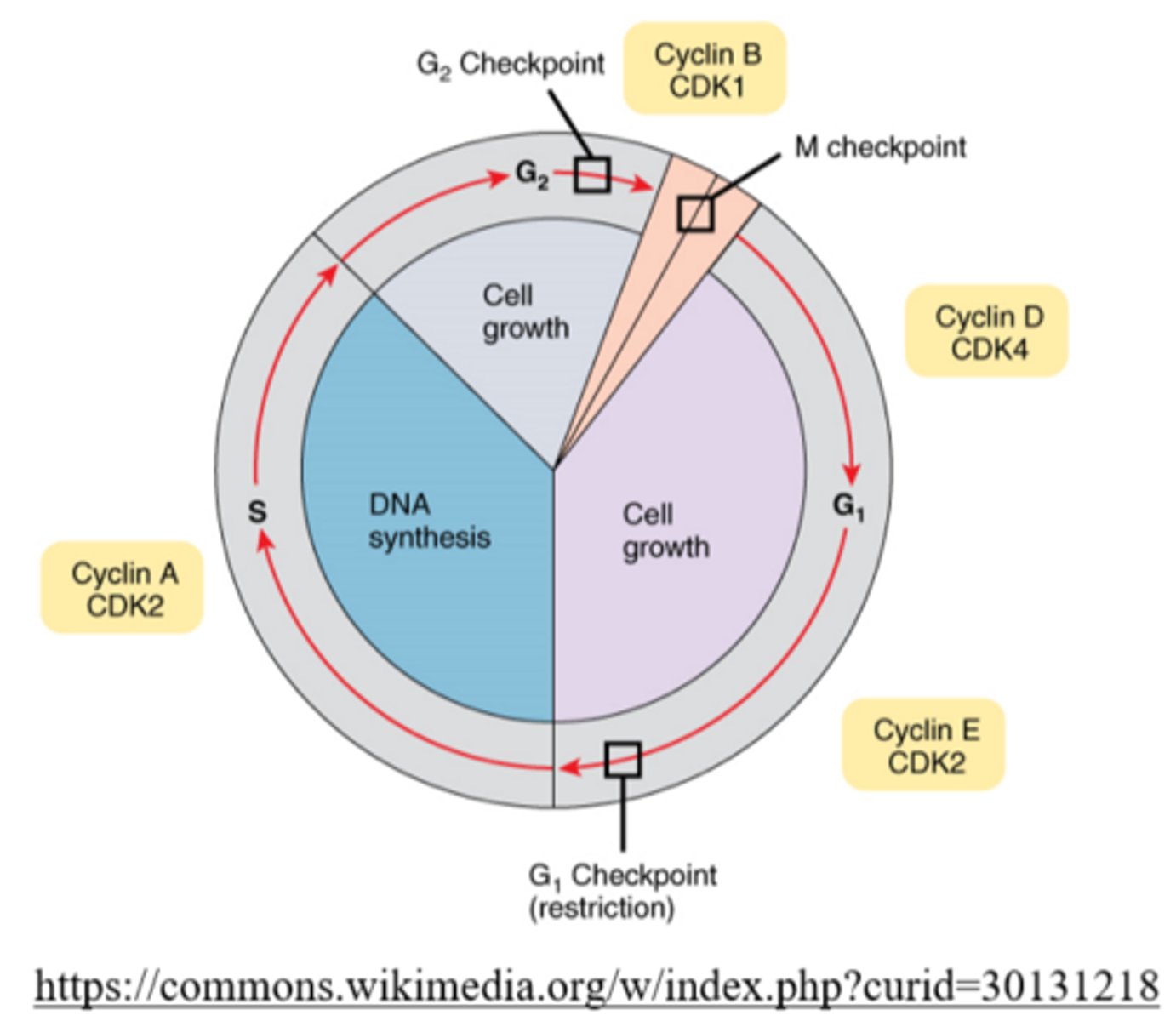
the cell prepares its genetic material for cellular division during the _____ of interphase
S phase
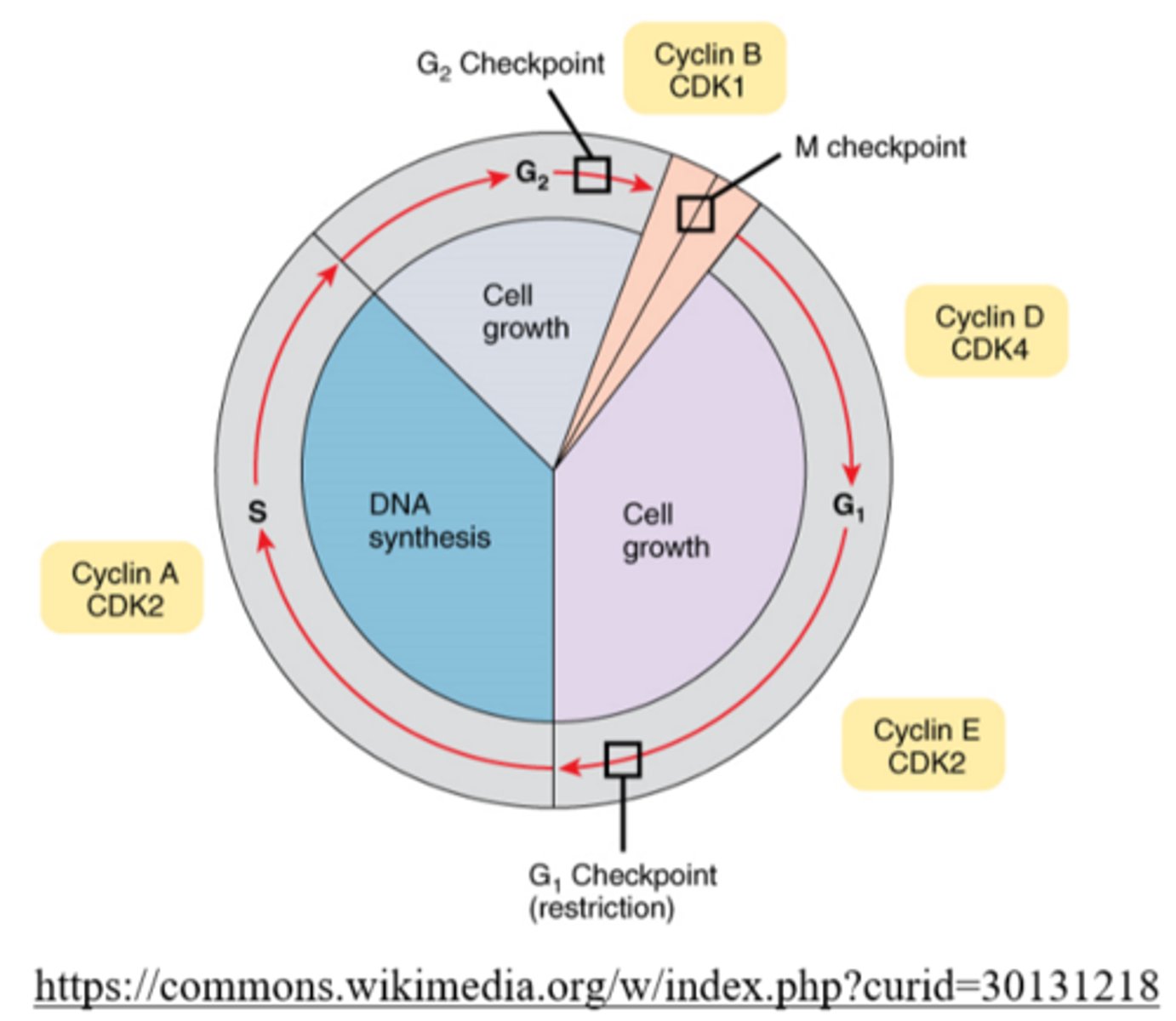
cells replicate their organelles during the _____ phase
gap 2 (G2)
when surface/volume ratio is _____, cellular exchange becomes easier
large
what happens when the surface/volume ratio is small?
the cell is unsustainably large and is pressured to divide
what happens as the genome/volume ratio decreases (volume gets bigger)?
the cell exceeds the ability of its genome to produce sufficient amounts of regulation for cellular activities
some large cells (paramecium, human skeletal muscle) are _____ to deal with problems associated with ever decreasing genome/volume ratios
multinucleated
what is the most important checkpoint of the cell cycle?
the G1 checkpoint
_____ is assessed and _____ conditions are checked during the G1 checkpoint
cell growth; favorable
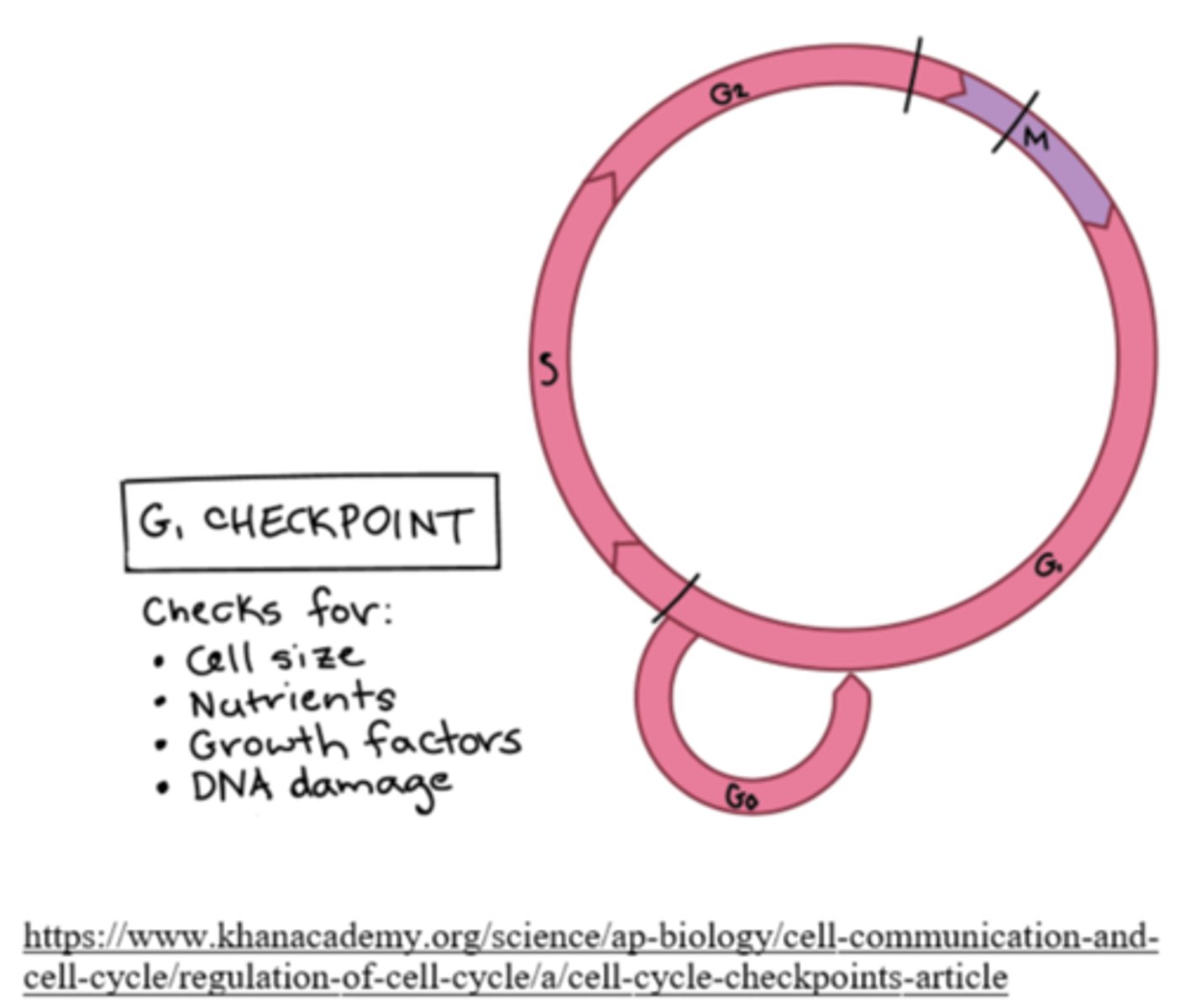
what happens if the G1 checkpoint fails?
the cell enters G0
the _____ is viewed as either an extended G1 phase, where the cell is neither dividing nor preparing to divide, or a distinct quiescent stage that occurs outside of the cell cycle
G0 phase
some cells (liver, kidney) can be _____ of G0, while some cells (nerve, muscle) _____ in G0
induced out; permanently remain
cells can either never proceed from the _____ of interphase, or they can wait until the cell is ready to divide
G0 phase
at the end of the_____, the cell evaluates the accuracy of DNA replication and signals whether to begin mitosis
G2 phase
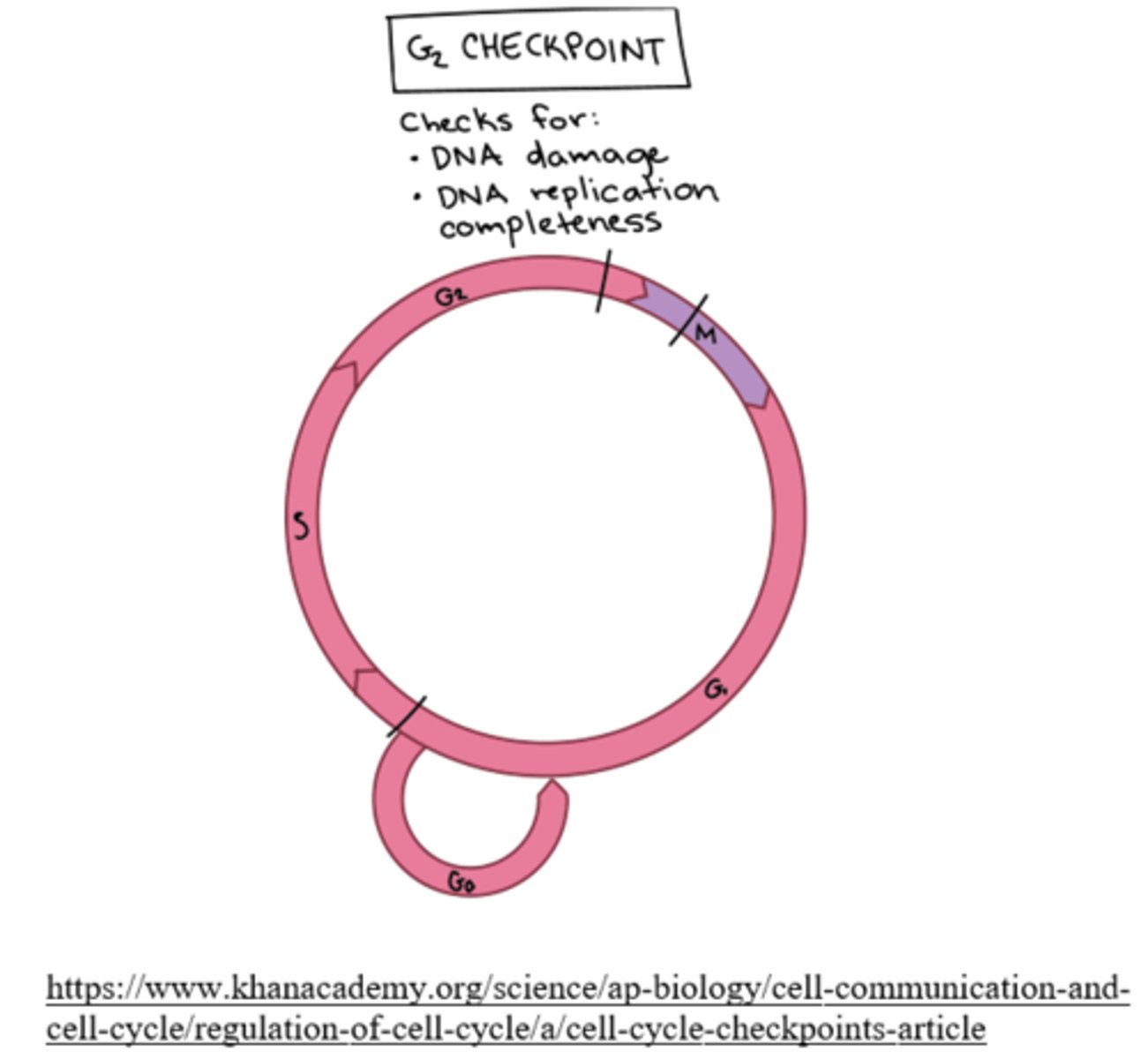
cells check for sufficient _____ levels during the G2 checkpoint and if there is a sufficient amount, the cell will proceed into the M phase
mitosis promoting factor (MPF)
the M checkpoint occurs during _____
metaphase
the _____ stops division to check if the chromosomes are attached to spindle fibers
M checkpoint
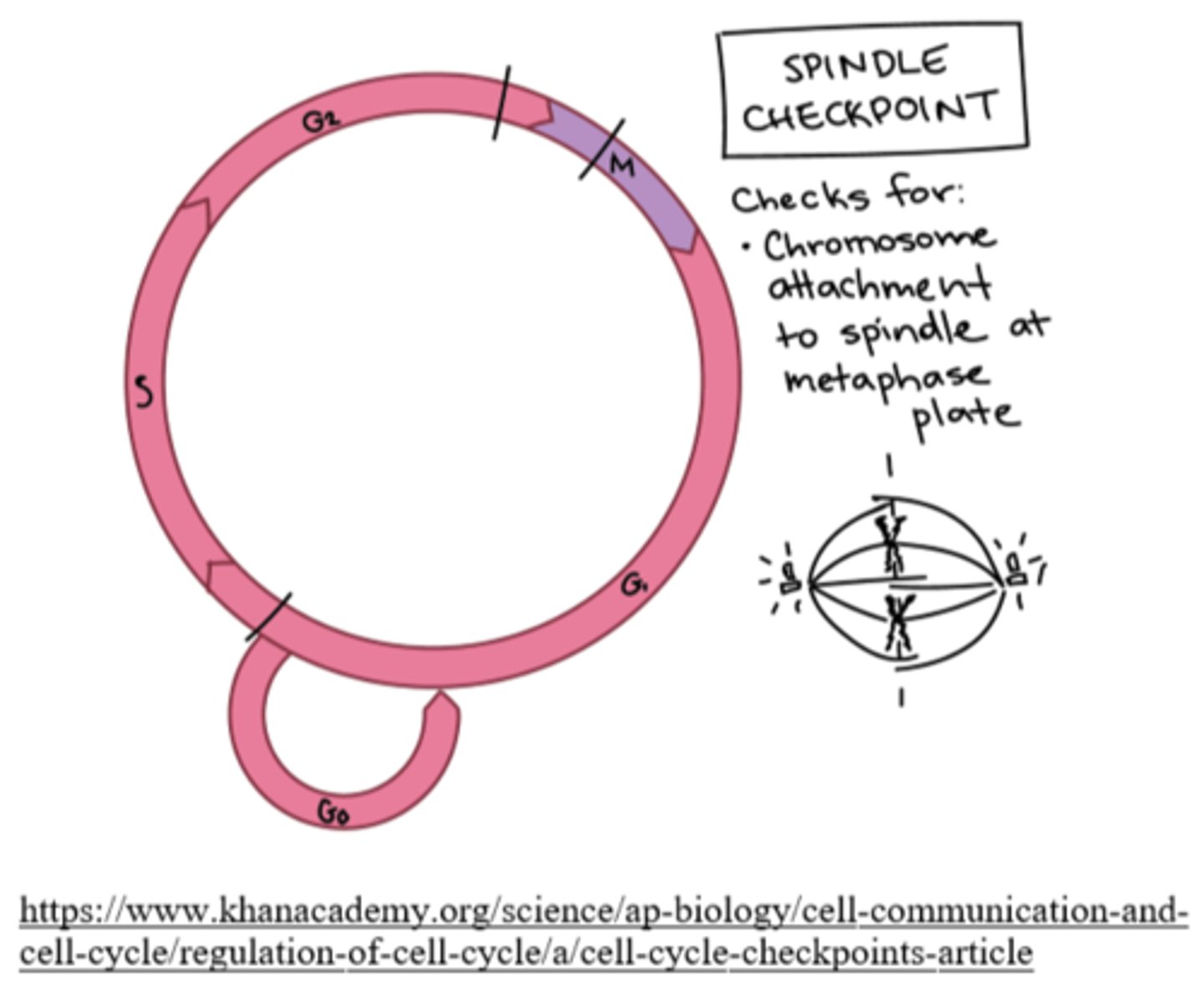
what happens if kinetochores are not attached to microtubules during the M checkpoint?
the cell will not proceed to anaphase until the appropriate connections have been made
_____ are enzymes that activate proteins, which regulate the cell cycle by phosphorylation
cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs)
_____ is a protein that activates CDKs
cyclin
how does phosphorylation impact the cell cycle?
phosphorylation of certain substances signals for progression to the next cell cycle stage, while the absence of phosphorylation signals to pause the cell cycle
the plasma membrane has receptors for _____ that stimulate cells for division (such as damaged cells)
growth factors
cells stop dividing when surrounding cell density reaches a maximum - this is called _____
density-dependent inhibition
most cells only divide when attached to an external surface, such as neighboring cells or the side of a culture dish - this is called _____
anchorage dependence
cancer cells defy the five cell-specific regulations in place - such cells are called _____ cells
transformed
cancer drugs that inhibit mitosis do so by disrupting the ability of _____ to separate chromosomes during anaphase, thus stopping replication
microtubules
cancerous cells are a manifestation of defective cell _____ & cell cycle _____
differentiation; regulation
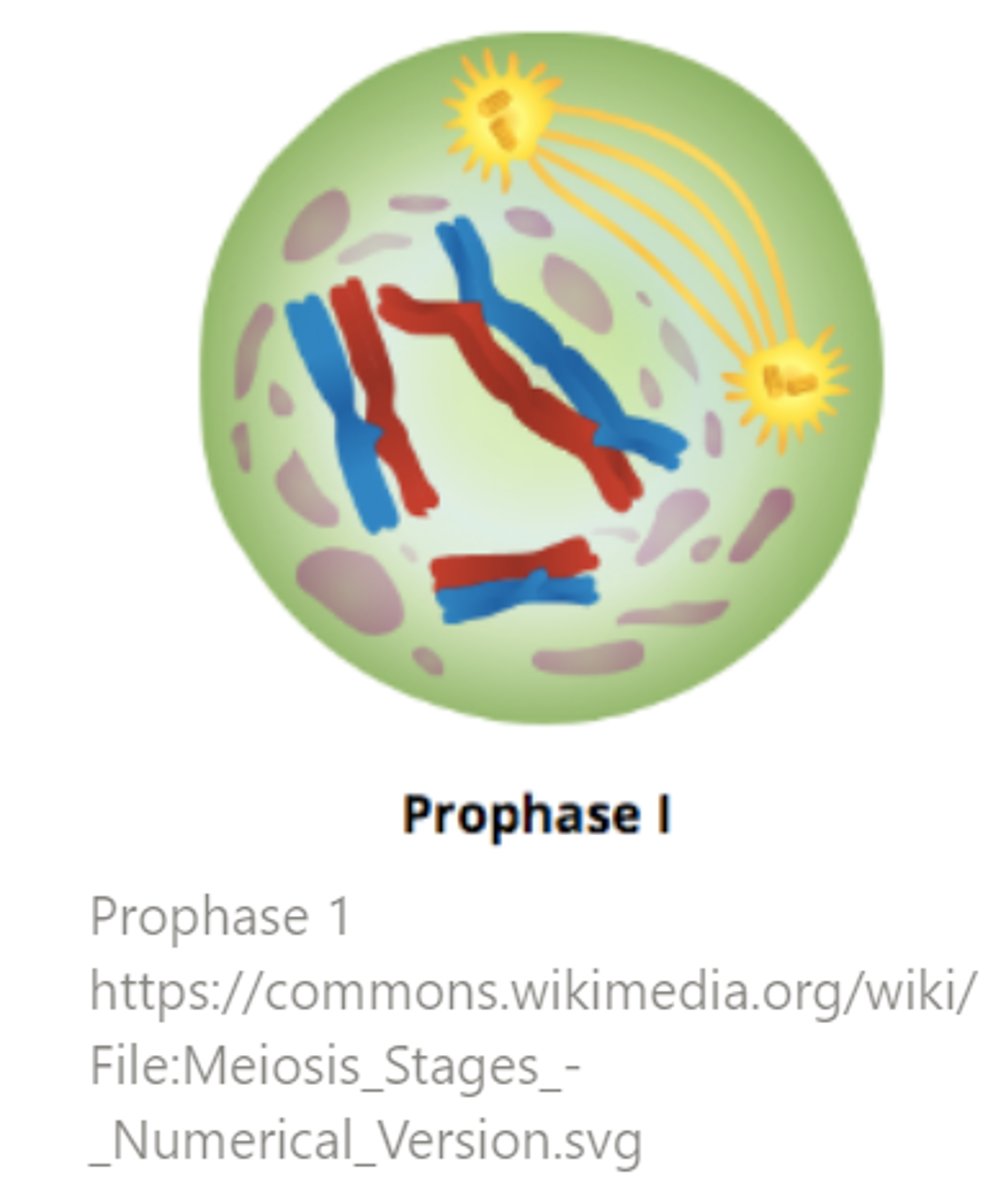
in meiosis I, crossing over occurs during _____, which introduces genetic variation to gametes
prophase I
_____ is how archaea, bacteria, and certain organelles (mitochondria and chloroplasts) reproduce
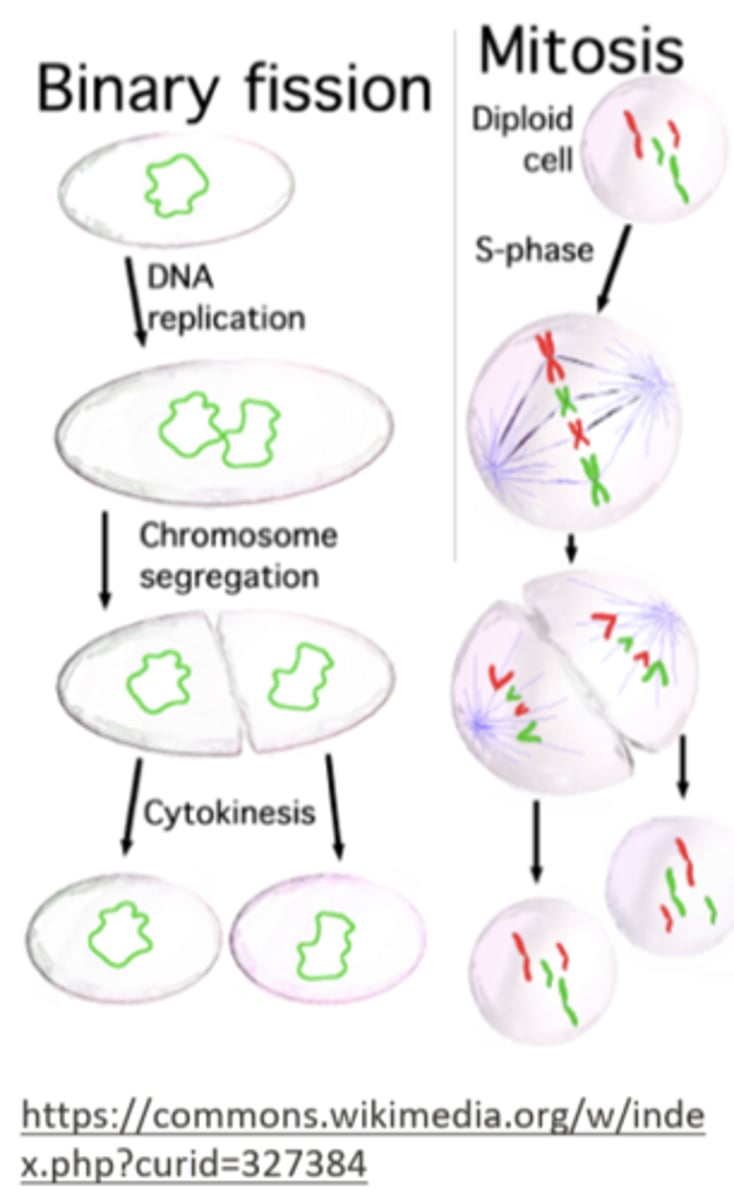
binary fission
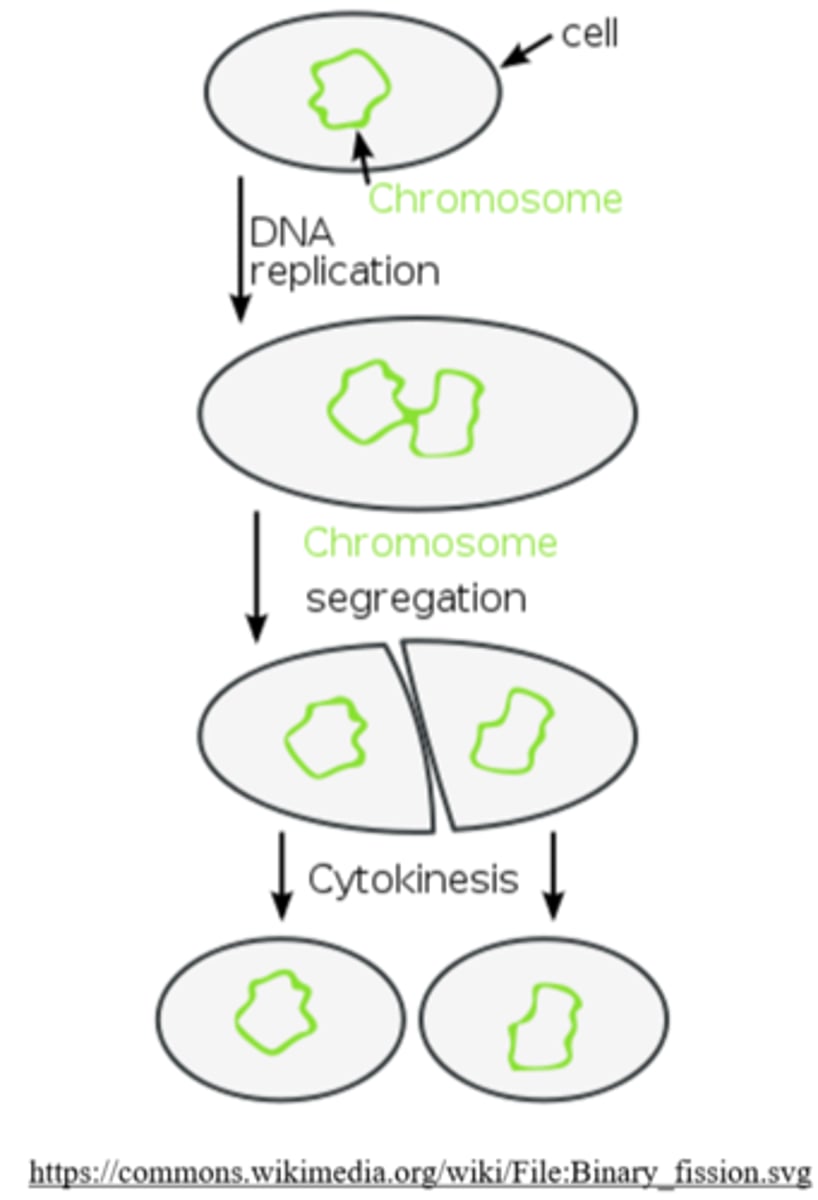
when do organisms/organelles that undergo binary fission replicate their genomes?
as cell division is taking place
(replication of DNA + division occur simultaneously)
unlike mitosis, binary fission lacks _____ to guide chromosomes through karyokinesis
spindle apparatuses
the _____ is the region where crossing over occurs between non-sister chromatids during prophase I of meiosis I
chiasmata
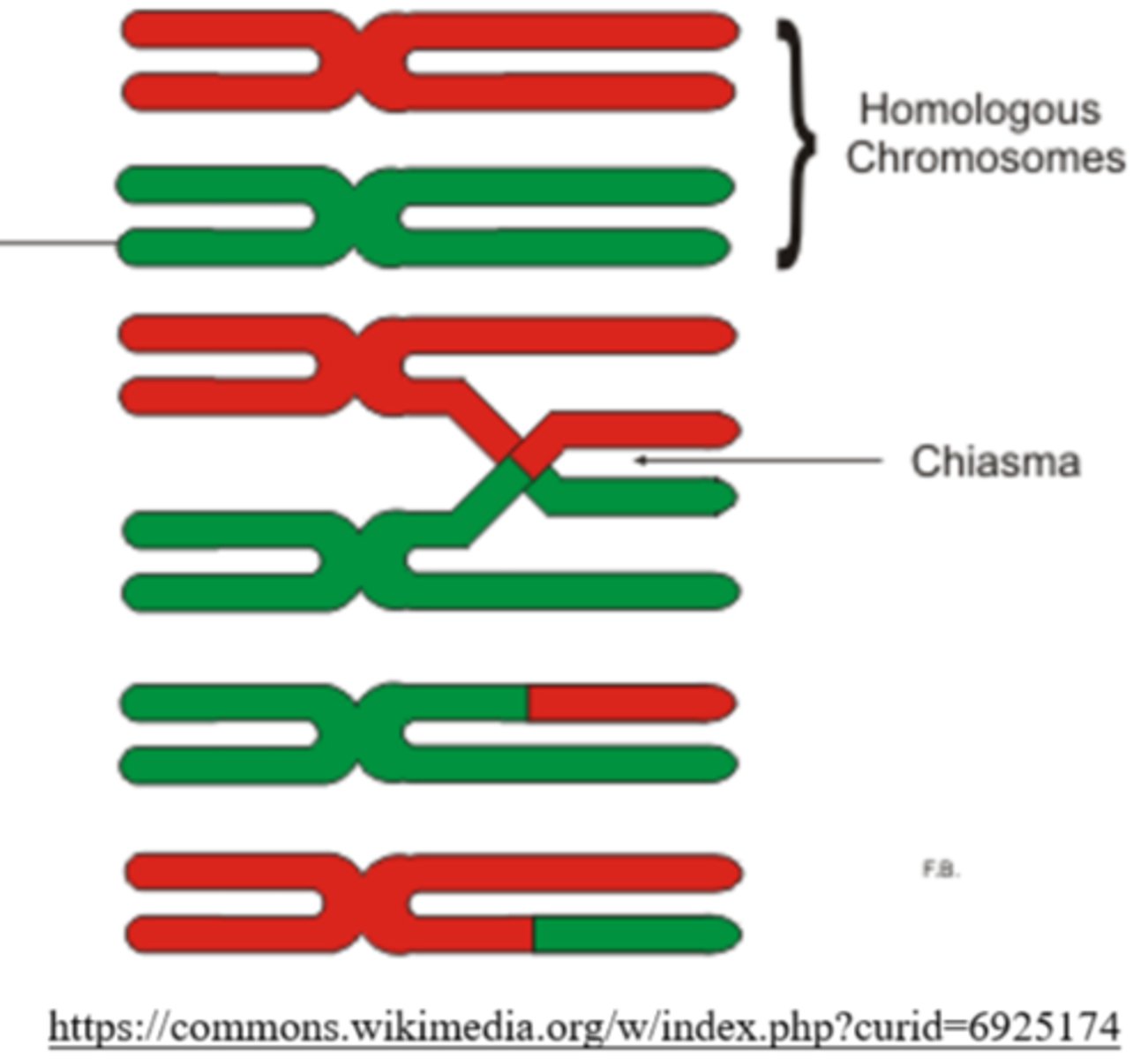
_____ describes the process when homologous chromosomes pair up during prophase I of meiosis I
synapsis

the _____ is a protein structure that temporarily forms between homologous chromosomes during prophase I of meiosis I
synaptonemal complex
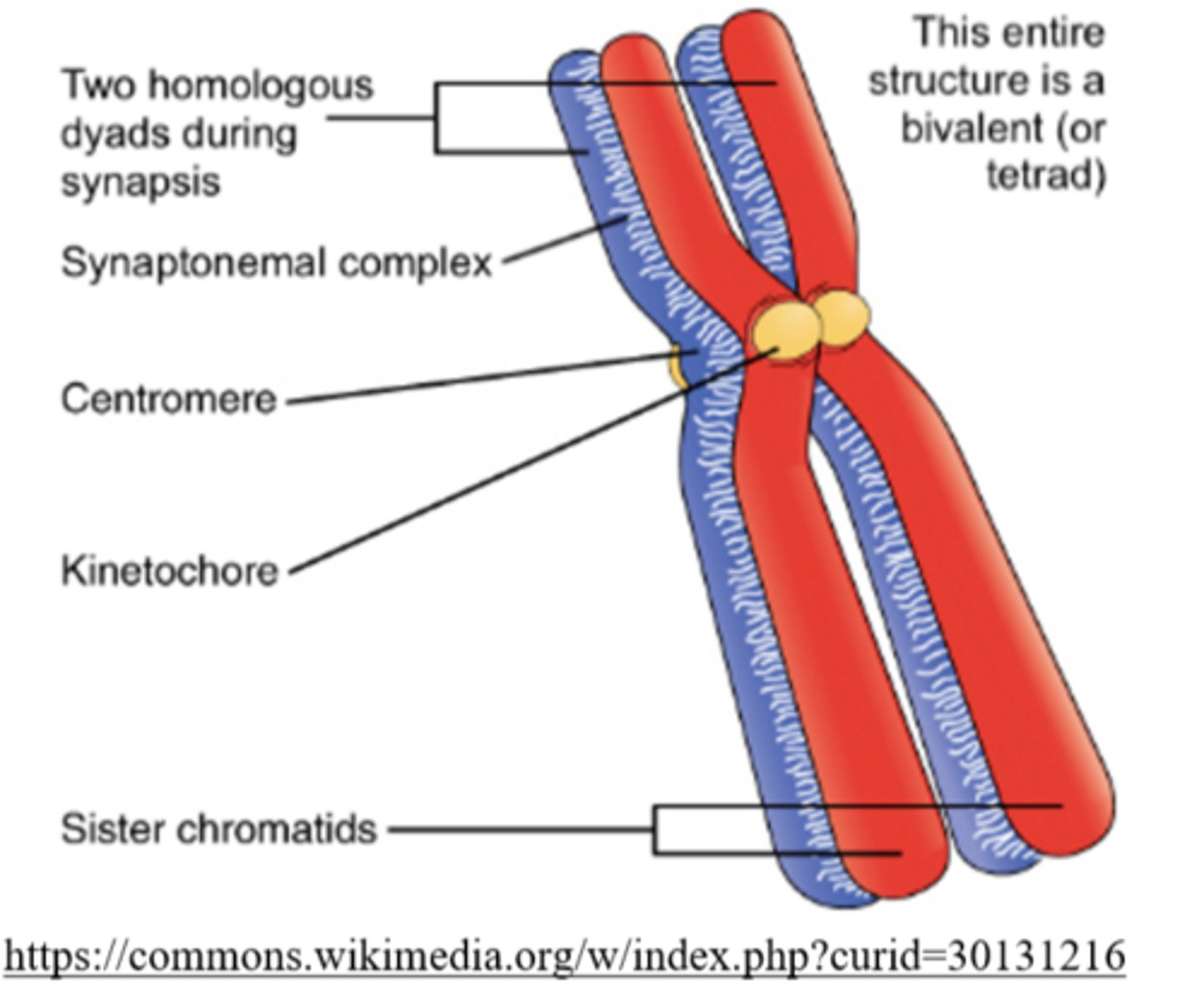
paired homologous chromosomes are referred to as _____ or _____ during early meiosis I
tetrads; bivalents
_____ are groups of 4 chromatids (due to the pairing of 2 homologous chromosomes) seen early in meiosis I
tetrads
(analogous to a bivalent)
_____ are pairs of homologous chromosomes
bivalents
what happens during the diakinesis sub-step of prophase I?
chromosomes complete condensing, the nuclear envelope begins to fragment, and tetrads/bivalents are ready for metaphase
(diakinesis is the final sub-step of prophase I)
chromosomes line up in _____ during metaphase I
double file
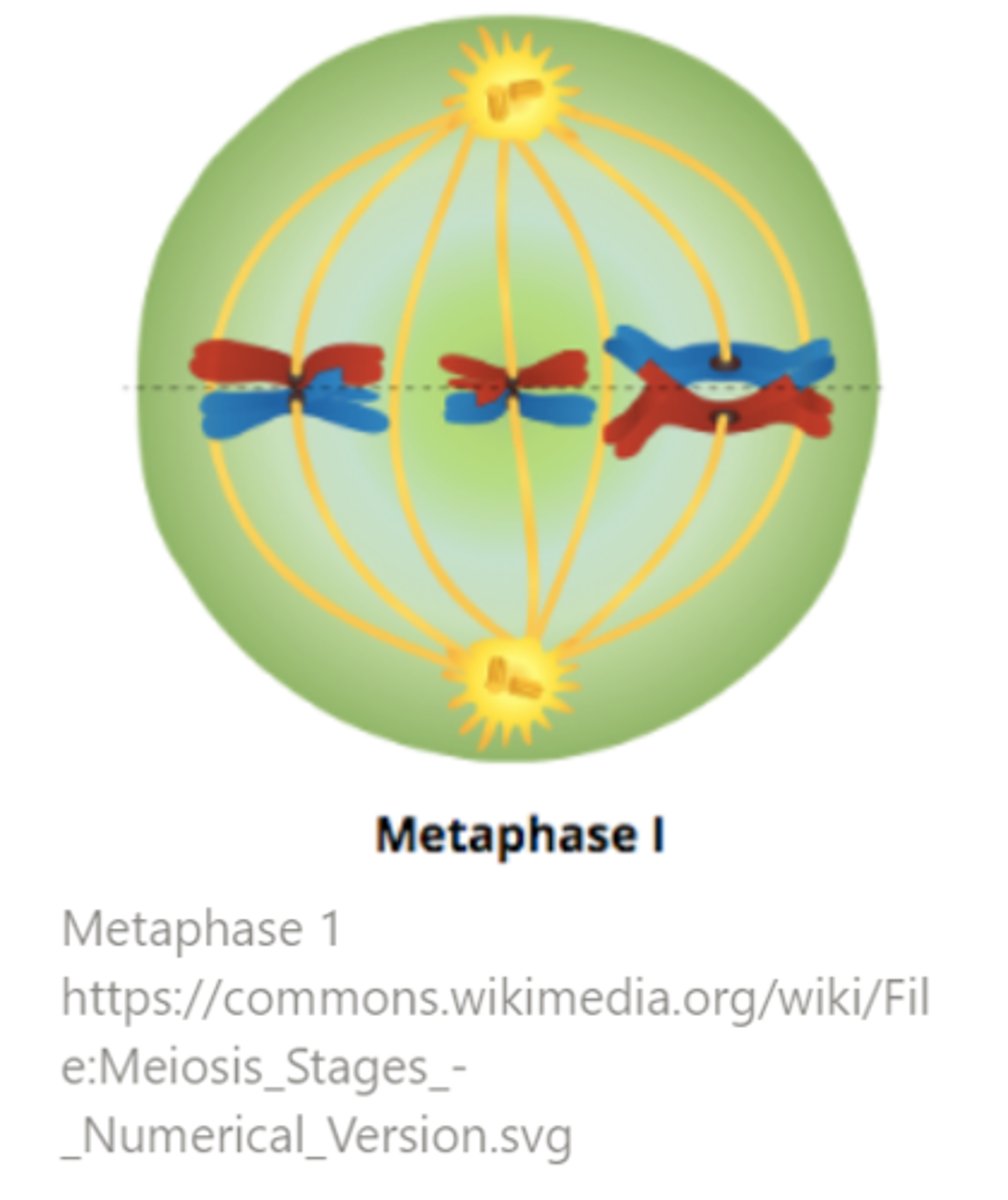
in meiosis, disjunction of homologs occurs during _____
anaphase I
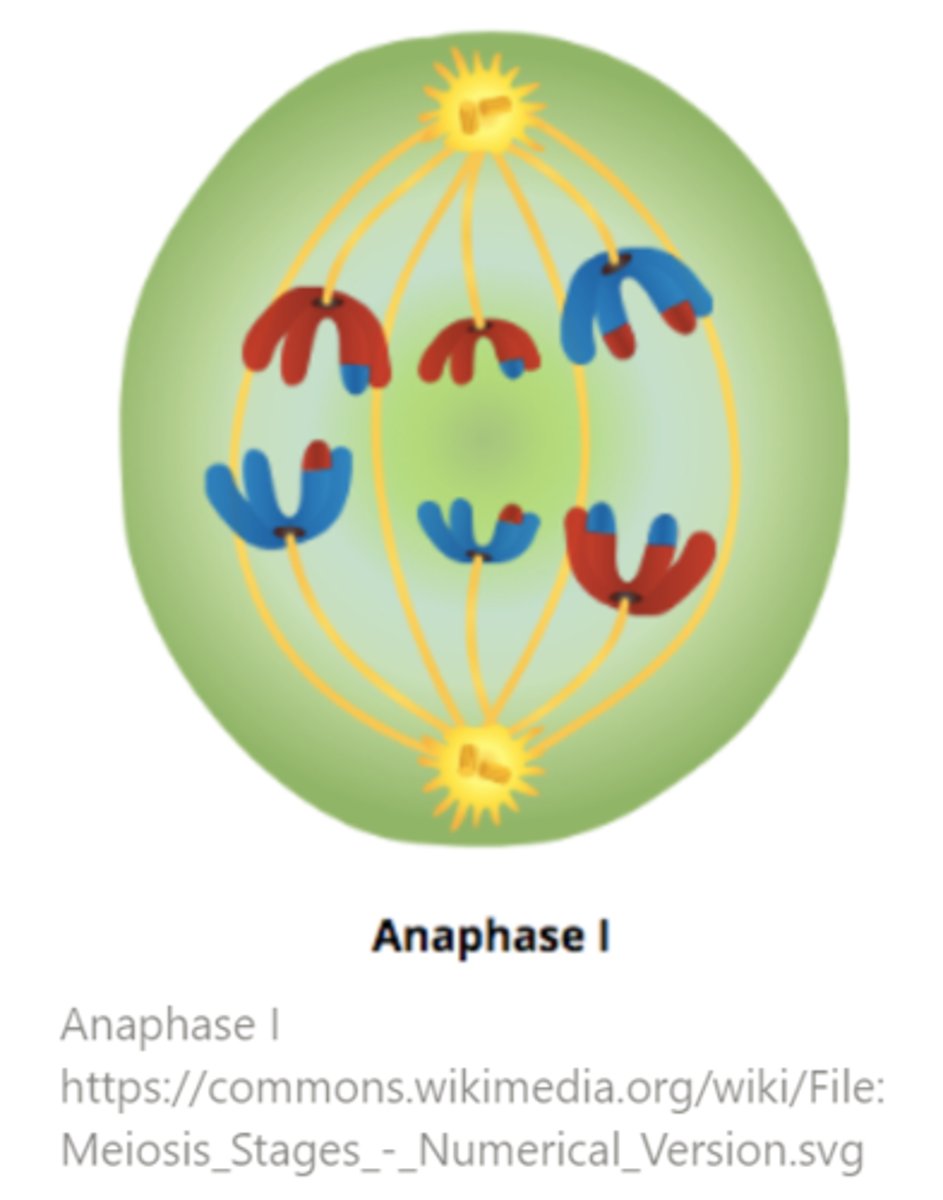
what are the conditions for anaphase I to commence?
the cell must determine that each bivalent has at least one chiasmata and each homolog in a bivalent needs to be attached to a kinetochore microtubule
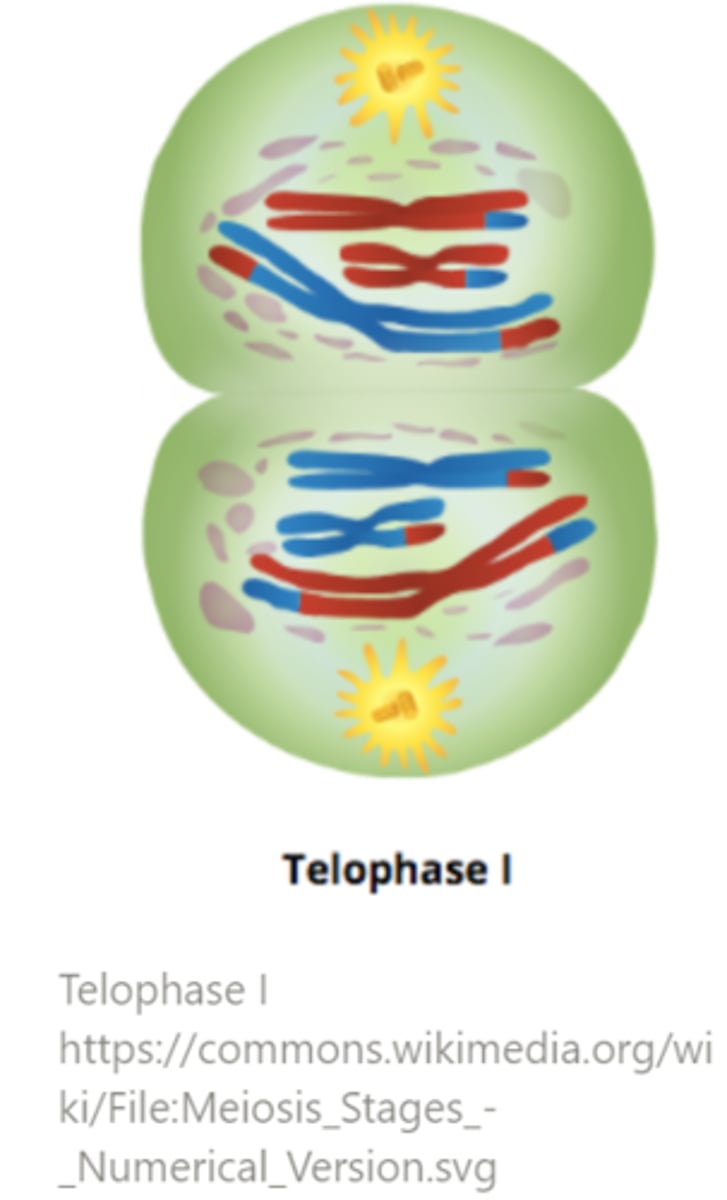
_____ is the phase of meiosis I in which each pole forms a new nucleus that now has half the number of chromosomes
telophase I