Escherichia coli
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
family
Enterobacteriaceae family, which includes coliforms. |
gram + or -
gram negative
shape
rod
growth temp
8-45 degrees
type of organism
Mesophile
facultative anaerobe- does not require 02 but grows better with it.
Vegetative Cell (Non-Spore-Former)
Indicator-organism:
Indicator-organism:
● hygienic production
● faecal contamination
survival
Survival in beef:
▪ Chilled ‘Filet americain’: > 7 days
▪ Fermented sausages: several weeks
▪ Frozen minced beef: several months
disease
While usually a harmless inhabitant of intestines, some types can cause disease, notably E. coli O157:H7-----> Possesses an O-antigen (lipopolysaccharide) and an H-antigen (flagellar proteins): hamburger disease
EHEC: The illness is caused by a shigatoxin produced in the gut
Escherichia coli O157:H7 :HUS (Haemolytic Uremic Syndrome) in children with a fatal end. infections mostly occur in less developed countries with insufficient hygiene. Or also countries consuming raw beef
symptons
Primarily bloody diarrhoea
Complication: A severe complication, particularly in children and the elderly, is haemolytic uremic syndrome (HUS), which is a leading cause of acute renal failure
incubation time
2-3 days (but can extend up to 21 days)
d/R
Pathogenic strains are characterized by a low dose response (D/R)
Dose: As few as 10-100 cells can cause illness due to its low D/R
is there a seasonal trend
In summer more infections, more grinded beef is eaten and it is more difficult to keep the temperature below 7°C
transmision and sources
◦ Can survive for over 7 days in chilled 'Filet americain', several weeks in fermented sausages, and several months in frozen minced beef.
◦ Found in products such as hamburgers (hamburger disease), as well as vegetables like fenugreek sprouts and watercress
Most likely to find in
Most likely to find in:
Soil
Faeces
Surface water
Raw vegetables
Raw fish
prevention and control
◦ For producers: It is essential to protect foods from contact with faeces (e.g., through manure management), manage risks associated with irrigation water, and maintain good general hygiene (cleaning, storage).
◦ For industry: Good slaughtering practices are needed to reduce carcass contamination, personnel require training, and food treatments such as cooking, pasteurization, and rapid fermentation should be applied.
◦ For consumers: Education on proper heating (e.g., of hamburgers and vegetables), preventing cross-contamination, maintaining the cold chain, and using safe water is crucial.
◦ Heat treatment is a primary prevention method
z value
- 1 log decrease in D with a 5°C increase in temperature)
During practical when pouring medium VRBG, medium cannot be too hot , why?
During practical when pouring medium VRBG, medium cannot be too hot or no Enterobacteriaceae will not be detected. Enterobacteriaceae are heat sensitive. When the medium is too hot while pouring, the bacteria will be killed. The ideal temperature for pouring is hand warm (±45°C).

explain this
Different sizes and shapes can be caused by different species of Enterobacteriaceae
As this is a pour plate, the bacteria grow in different directions in the agar resulting in different shapes. Colonies in the bottom are usually larger since they are less hindered by the gelling agent
what are the 2 confirmation tests
Oxidase test
oxidative-fermentative test
oxidase test
Oxidase test
Oxidase negative but Pseudomonas spp. might grow on VRBG medium and are also a relevant spoiler for vegetables.
oxidative-fermentative test
oxidative-fermentative
Determines if bacteria can metabolise glucose by fermentation or only oxidative respiration.
Fermentative metabolism is expected for Enterobacteriaceae
Enterobacteriaceae can ferment glucose and therefore produce acid (visible as yellow colour) in the whole tube.
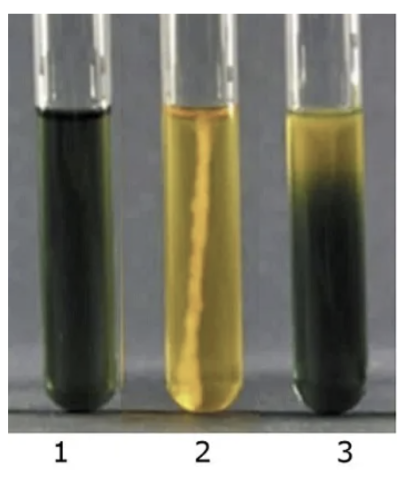
which tube is positive for Enterobacteriaceae
only 2 tube is positive