Fundamentals of Environmental Biology: Exam 2
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
Ecological Succession
The process of vegetation changing over time until it meets that area
Primary Succession
We start with bare rock, then to soil as it takes thousands of years
Secondary Succession
Already soil there so things will grow more quickly (cornfields, yard)
Climax Vegetation
The final stable community in an ecological succession; where it will end up and stay in equilibrium (varies in different types of ecosystems)
What determines the extent of Vegetation?
Temperature and Precipitation
Biome
A large naturally occurring community that is home to similar plants and animals, defined by its climate and dominant vegetation
Desert
Major features: cool to mild winters, warm summers, dry all year round
Human Impacts: off-road vehicles, desertification
Plants: cactus, tumbleweed
Animals: reptiles, armadillo
Grassland
Major Features: warm summers, warm or cool winters, dry winters, moist summers
Human Impacts: overgrazing, poaching
Plants: grass, crops, trees, flowers
Animals: grazing animals, insects, rodents
Taiga
Major Features: cold, wet summers, cold, wet winters, short growing season
Human Impacts: logging
Plants: pine trees, shrubs, deciduous trees, wildflowers
Animals: Elk, moose, deer
Temperature Decidious Forest
Major Features: cool winters, warm summers, moist all year round
Human Impacts: urbanization, logging, habitat destruction
Plants: oak trees, pine trees, mushrooms, grass, flowers
Animals: skunks, deer, coyotes, rabbits, raccoons, fox
Tropical Rain Forest
Major Features: warm all year, wet all year, low soil fertility
Human Impacts: logging/habitat destruction, loss of biodiversity
Plants: palm trees, citrus fruits, flowers, vines
Animals: snakes, sloths, monkey, frogs
Tundra
Major Features: cold all year, wet summers, dry winters
Human Impacts: localized habitat destruction around mines, drilling sites,
pipelines and military bases
Plants: small trees, shrubs, moss, lycans, wildflowers
Animals: moose, cariboo, penguins, orcas, walrus, seals, polar bears
Which terrestrial ecosystem is closer to the equator?
Desert
Which terrestrial ecosystem is known as a huge migration area?
Grasslands
What kind of soil do tropical rainforests have?
Non-fertile soil
Permafrost
Even when the top surface thaws, the inner layers of the soil are frozen all year
Ecosystem
Biotic and abiotic factors in a particular area that creates a community and climate
Where does the mass of a tree come from?
Photosynthesis (water vapor + carbon dioxide)
Freshwater Ecosystems
Major Features: Divided into zones
Littoral- edge of a pond
Lymnetic- as far down as light penetrates; plants reside/produce photosynthesis
Profundal- where light stops
Benthic- bottom; contains decomposers
Human Impacts: eutrophication, acid rain
Eutrophication
Ties to the nutrient cycles (Nitrogen + Phosphorus), leeching of fertilizers and nutrients into bodies of fresh water (fish die more)
Acid Rain
Continuing issue: when we burn fossil fuels or coal, sulfur is produced and mixes with moisture, causing sulfuric acid. This falls on living things, killing ecosystems, and more.
Marine Ecosystems
Major Features:
Light Zones:
Photic- how deep the sunlight goes
Aphotic- where there is no light
Life Zones:
Intertidal- land between high tide and low tide
Nertic- always underwater, but shallow
Oceanic- open ocean/ deep water
Human Impact: pollution (oil spills), global warming
Similarities between Freshwater and Marine Ecosystems
Fish, plants growth, shellfish, pollution, recreation
Differences between Freshwater and Marine Ecosystems
Size of water, coral reefs in marine ecosystems, bigger animals, complex food webs
Hydrothermal Vent Communities
One of the only places where photosynthesis is not the main source of energy (found on the crusts of the earth)
Chemosynthesis
Breaks down sulfar compounds
Niche
All the things that make an organism fit into specific ecosystem categories; where they fit in the food chain, climate, and where they live
How do organisms of the same species interact with each other?
Reproduction and Hierarchy
How do organisms of different species interact with each other?
Competition and Predation
Competition
No two species occupy exactly the same niche at the same time (they can overlap, but can’t be the same
Interspecific- members of different species
Intraspecific- members of the same species
Predation
Factor in coevolution; develop defenses by prey; overcoming defenses by predators
Predator
These acquire energy by taking energy from other organisms, but one predator eats multiple prey during the predator’s lifetime, predators tend to be bigger than their prey, and predators typically kill their prey
Key factor in coevolution
Development of defenses by prey
Overcoming the defenses of predators
Camouflage
EX) Camelion (prey/predator), Stinkbug (prey), Deer (prey)
Warning Coloration
Warning color to predators not to hunt them again
EX) Poisonous dart frog (prey)
Mimicry
Non-toxic animals/bugs copy something else in order not to be eaten. Looks like something the predator remembers to avoid
EX) Viceray butterfly, King snake/Coral snake
Chemical Warfare
Helps protect the prey from predators
EX) Skunk (prey), Octopus (prey), Beetles, Toads, Stinkbugs
Parasitism
One benefits, one is harmed (+ -)
EX) Tick
Commensalism
One benefits, one is not affected (+ 0)
EX) Barnacles
Mutualism
Both benefit (+ +)
EX) Pollenators
Parasitism (Definition)
A parasite is usually much smaller than its host, lives a shorter period of time, often reproduces within (or on) its host, and may or may not kill its host
Factualtive Mutualism
With or without partner species
EX) Large fish and cleaner fish
Obligate Mutualism
Requires partner species
EX) Lichen= fungus + algae
Plant Mutualism
Trees are able to communicate and share nutrients (Pollination and Mycorrhizae)
Animal Mutualism
Grazing animals, sea annemomea protects crab, cleaner birds
What is determined when ecosystems live together?
Impacts how they interact with eachother; they require different resources, so more diveristy = successful ecosystem
How does predation help both prey and predators?
Prey: Natural selection, makes them stronger, controls groups
Predator: Gets nutrients
Biodiversity
Variety of living things in an ecosystem; the more diversity, the healthier the ecosystem will be
Importance: For resources, creates a sense of balance
Direct Values
Nutrients (taking something)
Agriculture- GMO crops, genetic diversity, biological pest controls, pollination
Medicine- new drugs, new hosts for beneficial or harmful organisms
Consumptive Uses- wild fruits and vegetables, fibers, beeswax, seaweed, skins, cultivated crops, domesticated animals, lumber
Indirect Values
Observing something’s beauty
Nutrient Cycles- gives options and provides nutrients (Contains everything)
Waste Disposal- decomposition, sewage treatment, breakdown of toxic chemicals
Fresh Water- wetlands, swamps, marshes, forests (can help filter water)
Soil Erosion- forests, grasslands, stream banks (by having forests and plants, we’re able to prevent this)
Climate Regulation- shade, CO2 absorption (helps moderate heat)
Ecotourism- sport fishing, hiking, birdwatching, boating (traveling to be in different ecosystems, going to protect it, helping to support programs that keep it healthy)
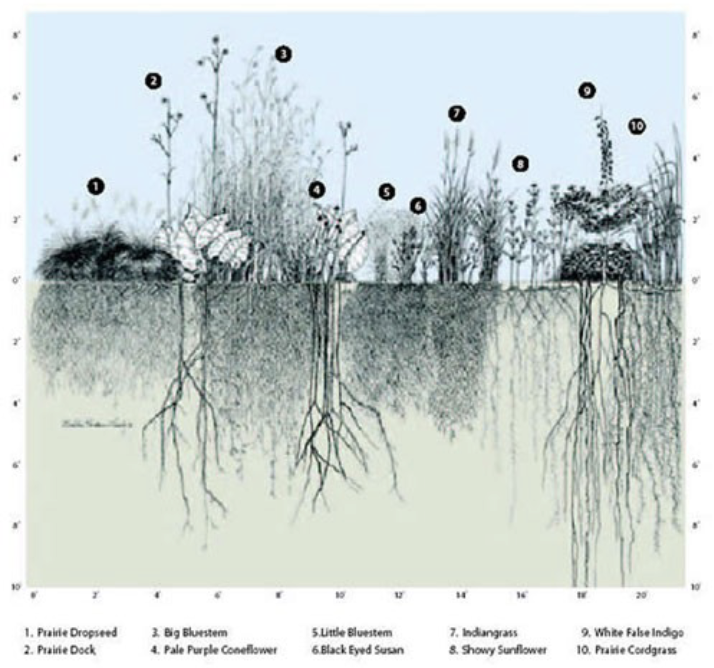
How does this diagram show competition and adaptation between these plant species?
Really long roots in order to reach the nutrients and moisture at the bottom
Really bushy fibrous roots
Some grow in order to get sunlight before the other ones
What factors affect population growth?
Birthrate, death rate, migration (immigration and emigration)
Immigration- organisms come in
Emigration- organisms leave
Exponential Growth (J-curve)
Unrestricted growth of a population; nothing limiting the rate of reproduction
Logistic Growth (S-curve)
Population reaches equilibrium
Most natural populations demonstrate logistic growth
Equilibrium
The state of balance
When a population reaches equilibrium, it doesn’t exactly stay at 100. It stays around the carrying capacity.
What would cause Exponential Growth?
Resources, not a lot of predators, things aren’t reproducing faster than they can grow, physical space
Regulation of Population Growth on a S-curve Graph
Biotic Potential- max. growth rate under ideal conditions
Carrying Capacity- the maximum number that can be maintained over time
Environmental Resistance- limiting factors for the growth of a population (predation, weather, food availability, diseases, competition)
Equilibrium- population is stable
Exponential Growth- population is increasing
Density-dependent Factors
Disease, food and other resource shortages, production of toxic waste
products, predation, stress, emigration
Density-independent Factors
Natural disasters (drought, wildfires, flooding, blizzards,(drought, wildfires, flooding, blizzards, earthquakes, volcanic eruptions), human impacts, climate change
Boom and Bust Cycles (Predator + Prey Interaction)
Who is driving the ups and downs?
They both drive it. While they go up and down together, it just may be that one is dying off or moving away from the other. There are too many factors involved to determine which goes up and which goes down.
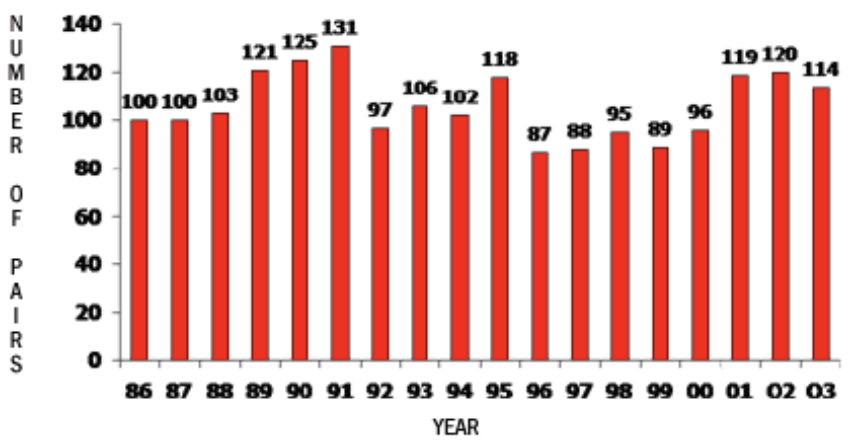
(Similar Test Question) What does the graph tell you about this population?
They are at equilibrium. There is a natural fluctuation in their population.
R Selection (strategy)
When a species has many offspring, but little parental involvement
EX) fish, turtles, frogs, insects
Benefits: safety in numbers, natural selection, does not require parental energy, and can reproduce quickly
Disadvantages: risk of laying eggs that none may survive
K Selection (strategy)
When a species does not have a lot of offspring, the parents stay to make sure they survive
EX) humans, deer, geese, kangaroos (mainly ALL mammals)
Benefits: most survive till adulthood, pass strategies for survival
Disadvantages: something big could wipe out the population easily (natural disasters), parental care energy is intensive
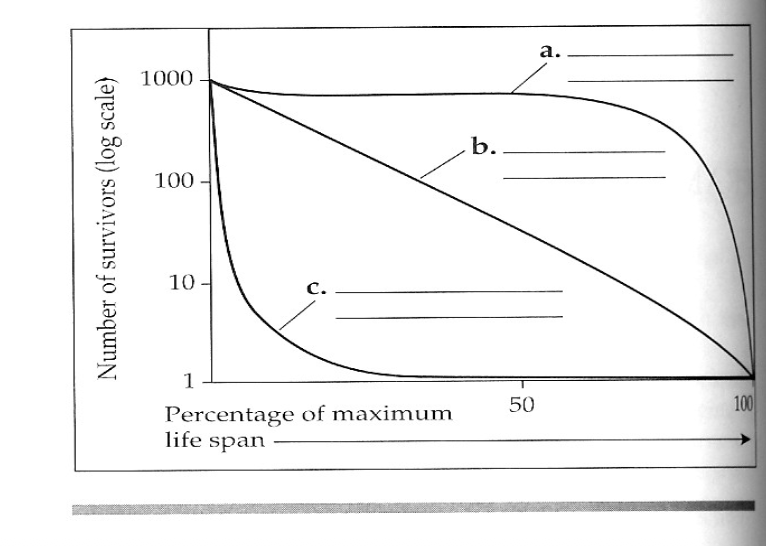
Which curve would represent r-selected species? K-selected species?
Line C represents r-selected species. Line A represents K-selected species.