Chapter 7: Introduction to Skeletal System; Gross Anatomy of Long Bones; Coverings and Linings of Bone
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
What are the components of the skeletal system and the main three?
bones of skeleton, cartilage, ligaments, other CT
bones, cartilage, dense regular CT
What are bones?
primary organ
2 types of bone:
Compact bone (dense or cortical) is 80% of bone mass
Spongy bone (Cancellous or trabecular bone) is located internal to compact bone, appears porous, and is 20% of bone mass
highly vascularized
What is cartilage?
semirigid CT, more flexible than bone
2 types of cartilage:
Hyaline cartilage: Attaches ribs to sternum, covers ends of some bones, within growth plates, model for bone formation
Fibrocartilage: Weight-bearing cartilage that withstands compression. Intervertebral discs, pubic symphysis, menisci of knee
What is dense regular CT (DRCT)?
Ligaments connect bone to bone
tendons connect muscle to bone
What are the classifications of bone?
long, short, flat and irregular

What are long bones?
Greater in length than width;
for example femur, humerus
What are short bones?
Length nearly equal to width
for example carpals and tarsals
What are flat bones?
Flat, thin surfaces, may be slightly curved
for example cranial bones
What are irregular bones?
Elaborate, sometimes complex shapes;
for example vertebrae
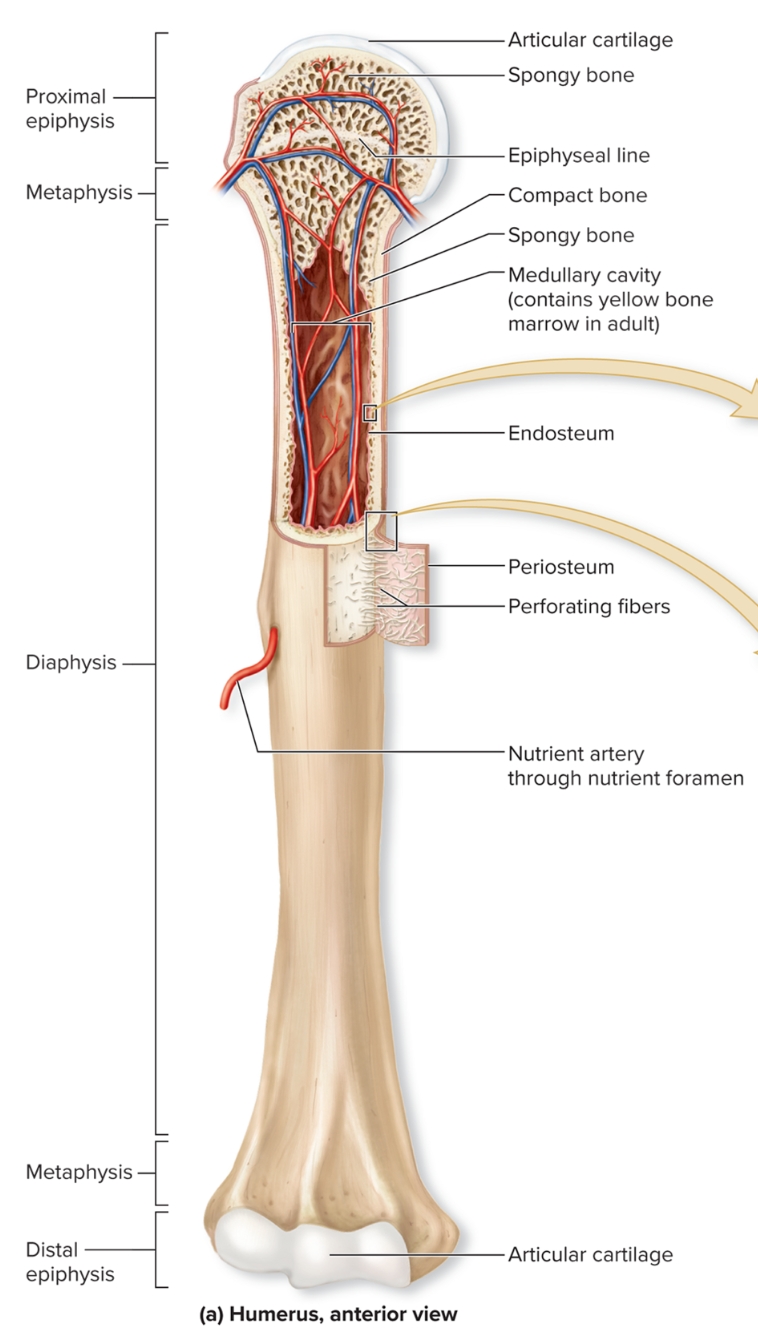
What are the regions of long bone?
diaphysis, medullary (marrow) cavity, epiphysis, metaphysis, epiphyseal plate
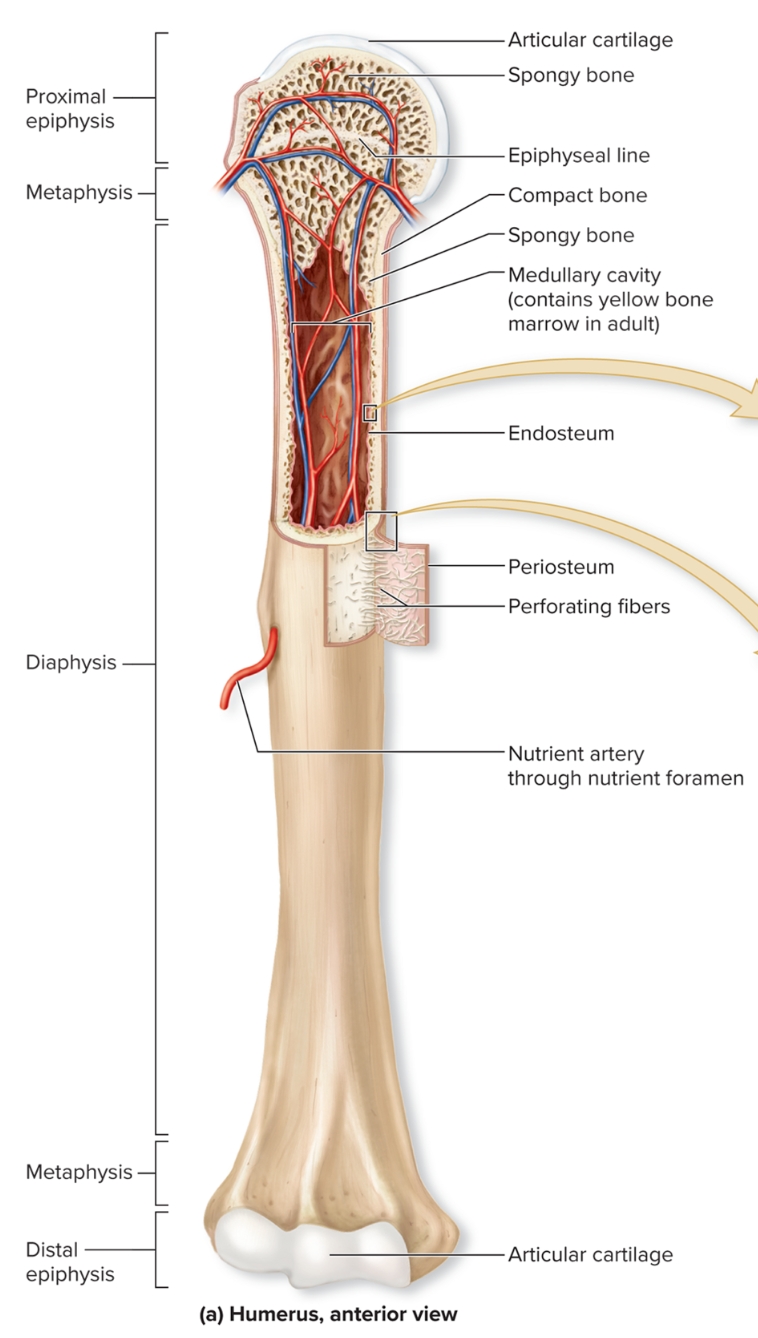
What is the diaphysis of long bones?
Elongated, usually cylindrical shaft,
provides leverage and weight support, compact bone with thin spicules of spongy bone extending inward
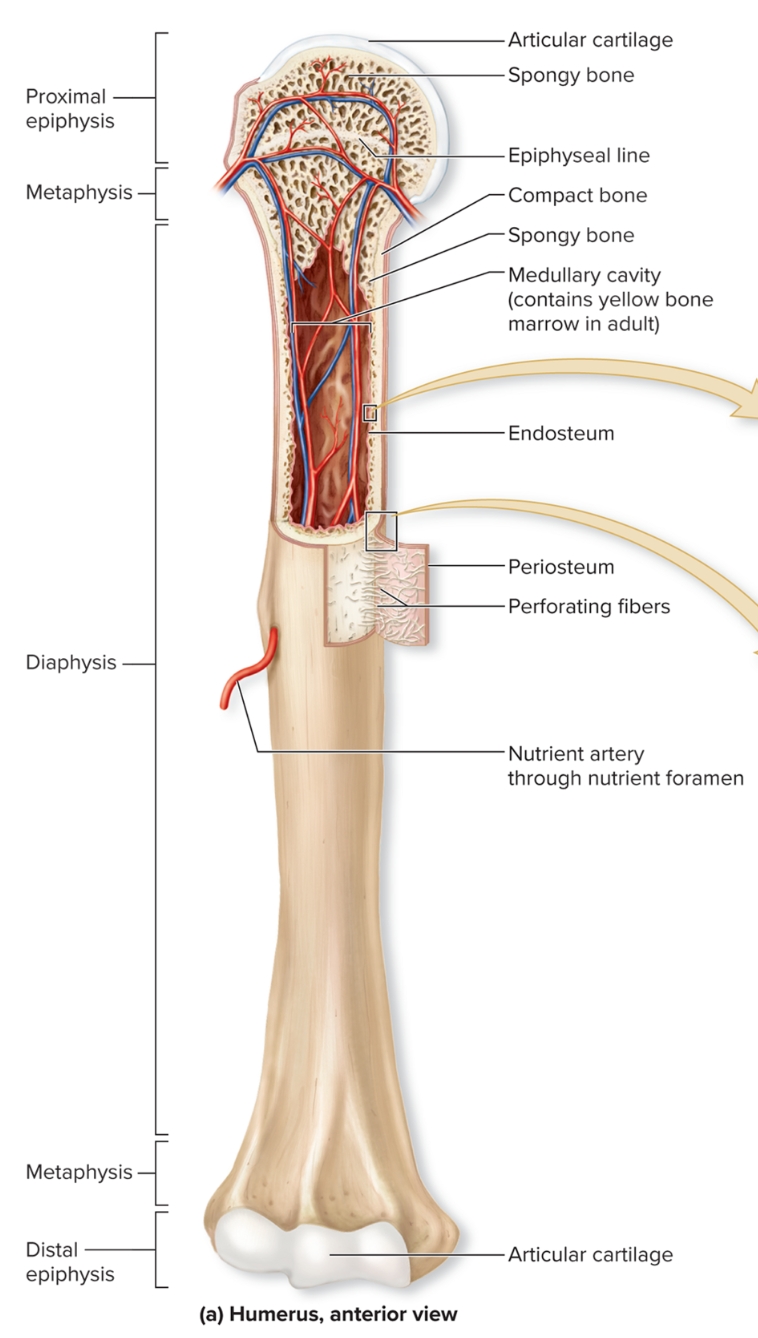
What is the medullary (marrow) cavity of long bones?
Hollow, cylindrical space within the diaphysis
contains red bone marrow in children, contains yellow bone marrow in adults
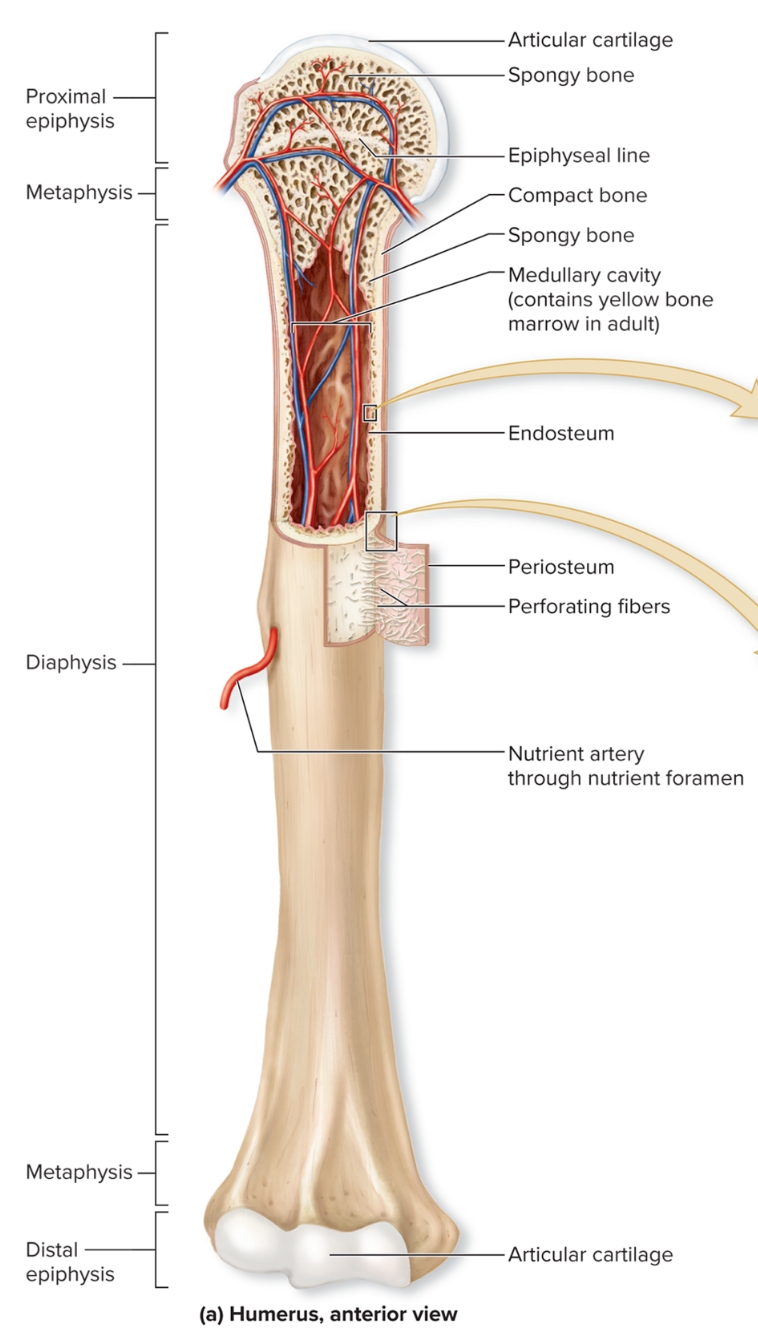
What is the epiphysis of long bones?
Knobby region at each end
Proximal epiphysis: End of the bone closest to body trunk
Distal epiphysis: End farthest from trunk
Composed of outer thin layer of compact bone , Inner region of spongy bone
Articular cartilage: Covers the joint surface with a thin layer of hyaline cartilage that reduces friction and absorbs shock in moveable joints
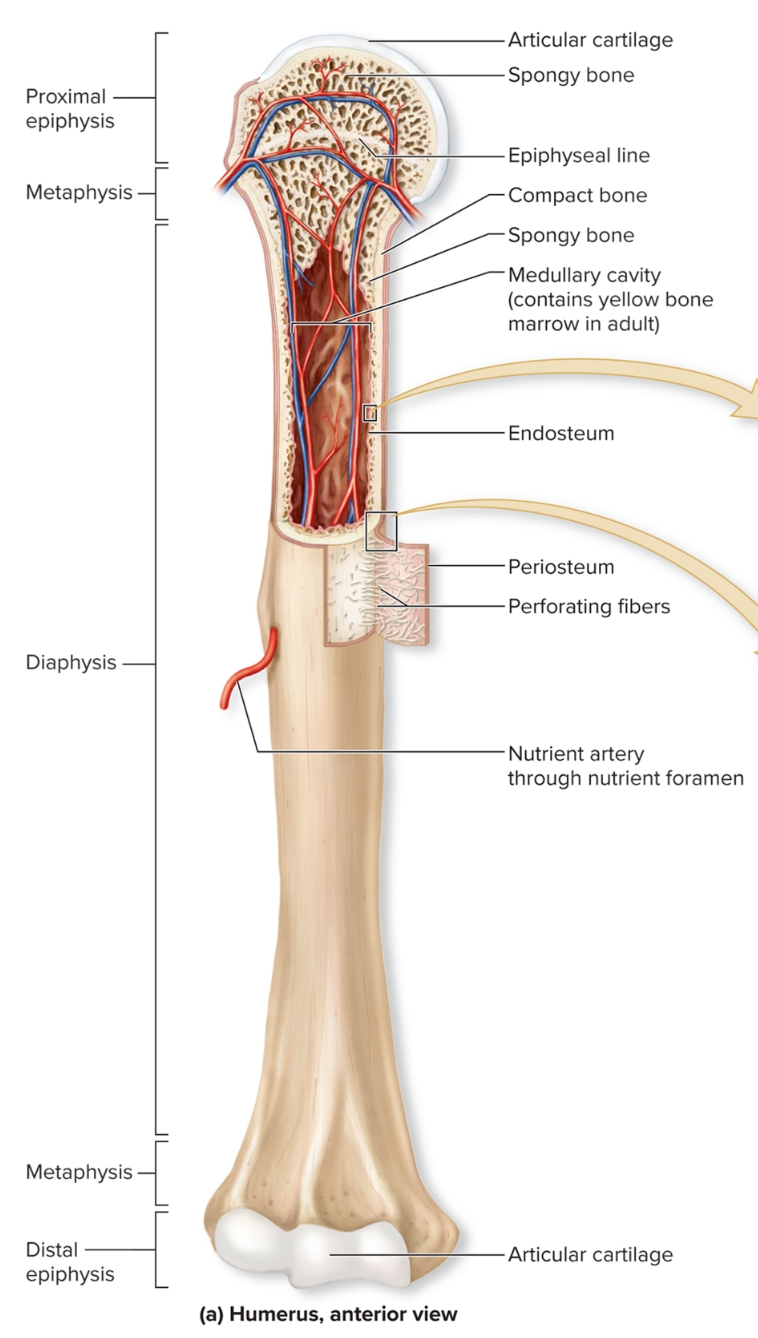
What is the metaphysis?
region where bone widens and transfers weight between the diaphysis and epiphysis
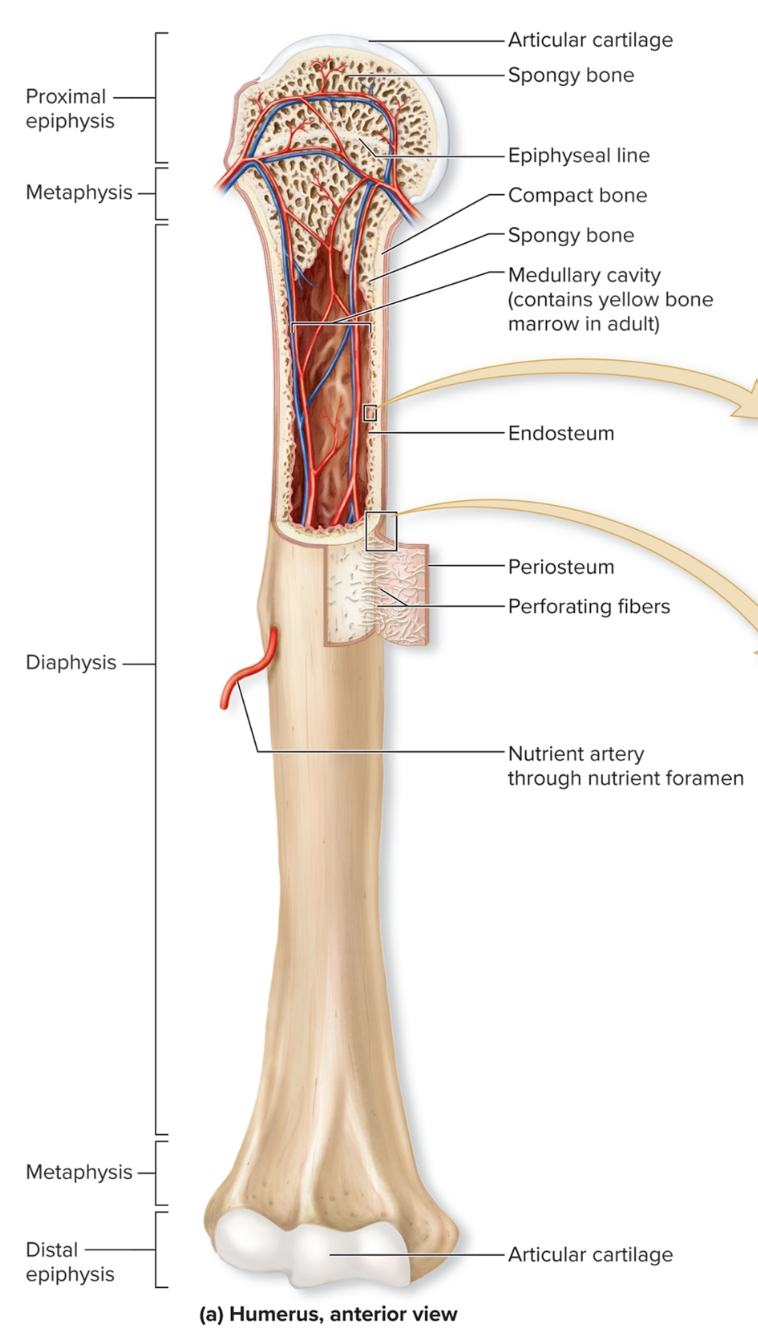
What is the epiphyseal plate?
within metaphysis
growth plate
made of a thin layer of hyaline cartilage that provides for lengthwise bone growth.
In adults, the epiphyseal line, is the remnant of the epiphyseal plate
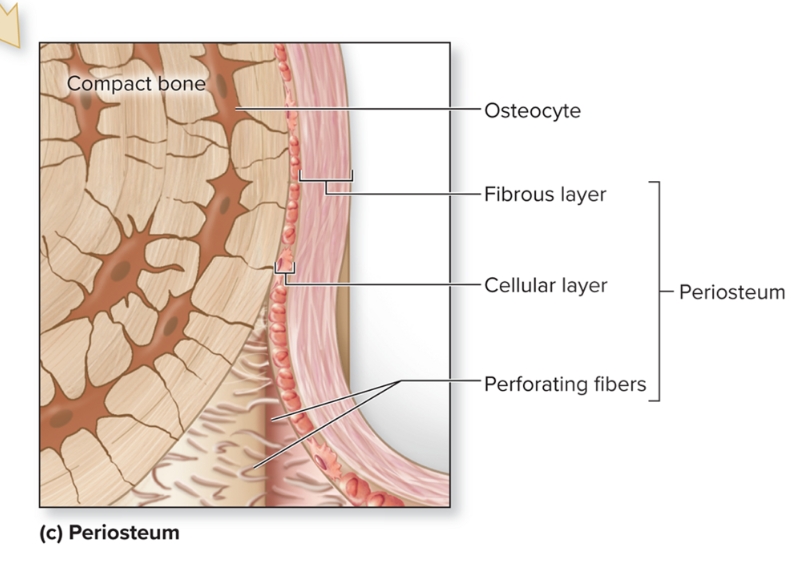
What is the periosteum?
S: outer fibrous layer of dense irregular CT, inner cellular layer includes osteoprogenitor cells, osteoblasts, osteoclasts attached to bone by numerous collagen fibers called perforating fibers
F: protects bone from surrounding structures, anchors blood vessels and nerves to bone surface, attachment site for ligaments and tendons
L: Tough sheath covering outer surface of bone
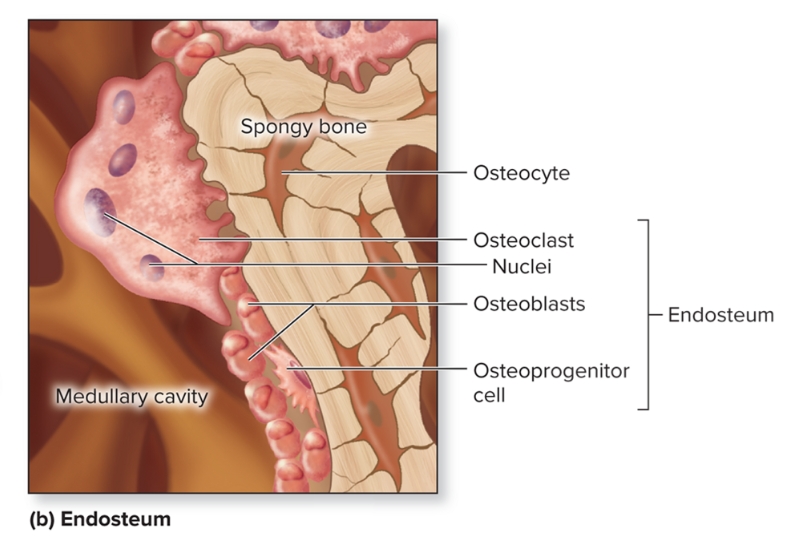
What is the endosteum?
Covers all internal surfaces of bone within medullary cavity, thin layer of CT containing osteoprogenitor cells, osteoblasts, and osteoclasts
What is the nutrient foramen?
Small opening or hole in bone
Artery entrance and vein exit here
Nerves that supply bone accompany blood vessels through foramen
Innervate bone, periosteum, endosteum, and marrow cavity
Mainly sensory nerves
What are the two types of bone marrow?
red and yellow
What is red bone marrow?
Hematopoietic (blood cell forming)
Reticular CT, developing blood cells, and adipocytes
What is yellow bone marrow?
Product of red bone marrow degeneration as children mature
fatty substance that may convert back to red bone marrow during severe anemia