Topic 1- Sex differences
1/77
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
78 Terms
sex determination in mamles
Gamites are the reproduction cromesones
Female XX
Male XY
Gamets are haploid
what is the gean that is responsable for turning the fetal gonad into teasteas
SRY
how dose the sex determin in humans
the SRY geane witch is located on the Y chromesones. Which turns the featal gonad ( witch cant telle if testes or oviries at the begging) into testesas
- In its absence, the gonad becomes an ovary
- Males are males because of the Y chromosome
What hormones are produced by early testes during male sex determination?
Early testes produce two types of hormones: Anti-Mullerian Hormone (AMH), which is defeminizing, and androgens, which are masculinizing.
the two types of hormones that the early testes make
Anti-Mullerian Hormone (defeminising)
Androgens (masculinising)
What is the female precursor system called?
The female precursor system in mammals is called the Müllerian system.
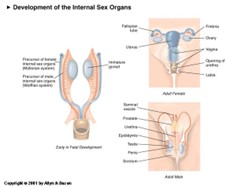
if internal system turns male what will happen?
anti maliaran - binad to recepters in maliran system then disintegrates (removes malria system)
andregion- for the wolffian system to be kkep and tp keep developing
Sex Determination in Mammals: External Sex Organs
Starts completely undifferntated
7-8 week after the gonad ahs turned intpo a teste or overir they are sensitive to androgens dht
Dht made by the testes required for external male apendiges
No recepters or no dht develops as a female externally
Gonad cascades to everything els
organizational hormones
effect remains after the hormone has been removed. Often occurs during a sensitive period.
activatinal hormones
effect is reversible, depending on presence or absence of hormone
Orginasuianal vs activation
- Increased facial hair- A
- Increased muscle mass- A
- Brest development- A
- Wider pelvis in woman- O
- Wider sholdes in men – O
- Lower voice in men- O
Puberty
- Organizational and activational role of sex hormones
- Don’t make hormeos until puberties- gonads
- Development of Secondary Sexual Characters- develop at puberty
- Pubic and axillary hair are androgen (androstenedione) sensitive in both males and females
onset of hormones
- During childhood, sex hormone levels are almost undetectably low
- Developmental timing mechanism starts puberty
- Sex differences in mechanisms and timing
studies suggets that pubity around 47kg
evlolutinal funactions
What is the role of the hypothalamus in initiating puberty?
The hypothalamus is responsible for kickstarting puberty by releasing hormones that signal the pituitary gland to stimulate the gonads.
in hypothalumas has collection of nerons
GABA/NPY witch inhibit KnDy nerons (kisspeptin) wich then woudl activate the GnRH nurons witch then would signal to the pituitrygland to create sex hormones
with
GnRH – realed in puses every 2 hours
We don’t know what that swich happen
witch then goes to the pituartary gland signalig to relice sex hormones
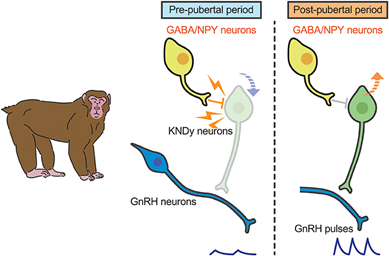
hypothalums and pituatry gland and pubity
Midline of human brain the hypothamus sits at the bottom at the brain at the bottom the grnh reasing when stimulated by the kisspeptin nerons
When ditect the gnrh ganodatroping hormin is reliced witch gose to gondaope
Hypothalumas- GnRH
Pituatry gland – gonadotropins (FSH,LH)
(GnRH)goes into the antria pituatry glands
Gonads:
- Testes: testostirosne
- Oviries: oestradiol, pojestirone
Gonadotropins- amid or goes at the gonads
folicula stimulating hormone-
female- causes foliculm to ripen
male sperm production
lutening hormone
female - inducing ovulation and formation of curpos lutum
male testostrone production
The Hypothalamus-Pituitary-Gonadal Axis: a Feedback System
-negative feedback system
keeps teasttrone around aste point
if it is below a set point the hypothalumas will relice GnRH witch will triggar the relice of
ganadtropins form the anteria pituatry
witch will go toi the gonads
whre fhs stimulate sperm production and lh produce testostrone
witch will go to the body tissue
witch will also go to the hypothalumas and indicate there is to much T in the blood stream withch will the tell it to stip relicing GnRH
so drop of t
if low wnough it starts the loop again
the mesxnstrial cycle
Four week cycle- not sesnal breeders unlike outher animals
Intractions between hypothalumas pituatry and
Graph of four different hormones
Folcule grows with stimulation of fsh wicth produces estridile
When hits certain level witch estridile
still a feed back loop but slower (around 28 days )
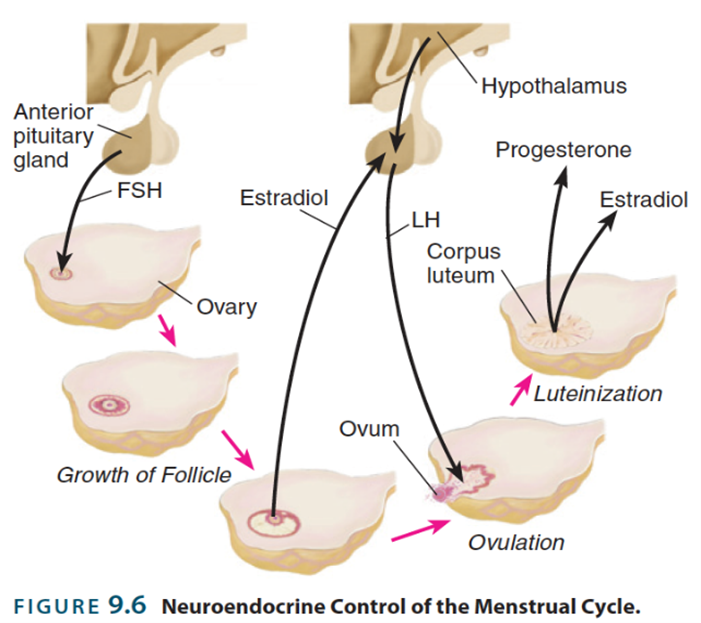
Stage one of teh menstarl cycle
in responce to an increase in FSH small spherases of cells called ovairian follciles begin to grow around individual egg cells (ova)
stage two of the mesnstratl cycles
the follicles begin to realeas estrogins such as estrodial
stage three of the menstral cycle
the estrocles stimulate the hypothalaumas to increase the realease of LH and FSH from the antirour pituartry
stage four of the menstral cycle
in responce to the LH surge, one of the follicles ruptures and realeses its ovum
stage five of the mensatral cycless
the rupptured folicle under the influnec of LH developes into a corpose lutem (yellow body) and begins to reales progetrone, which preapers the lining of the utrus for the implantation of a fertilized ovum
stage six of teh mestarl cycle
mean while the ovum is moved into the follopian tube by the rowing actio of ciliated cells if the ovum is not fertilised pogestrone and estrodol levels fall and walls of the utrus are sloughed off as meanstral flow and the cycle begins once again
Androgen insensitivity syndrome
- Gonads develop as testes
- Androgen receptors do not work
- Testosterone cannot do its normal job
- 46(total=al number of cromesons) , XY individuals develop anatomically as female, but without internal female genitalia
- Puberty is typically late, sometimes helped with hormone supplements
- They typically identify as women
teastes produce enough oestragen to go thriugh female punity without peirod
- Usaly dicribed in XY individuals
- Grow up female
- The testes make endrogiles tp go through female pubertie
- Don’t have utras or oviries
- They do produce tetstostrone but doesn’t affect the secondery male atrabutes
anti maliral is working fine - so no internal femal
external female
5α-reductase deficiency
- 5α-reductase turns testosterone into DHT
- DHT is crucial for prenatal external genital development
- 46, XY children are born with female external genitalia, but male internal genitalia
- At puberty, the high levels of testosterone can “mimic” DHT
- They develop male genitalia (“Guevedoces”)
- After puberty, they mostly identify as men
- But when hit pubity they grow a male external genitalia – genetic component
- Can be very common in small groups in like giutamala because of interbreeding
- Built into the culture
woman with 46 XX with androgen senstivity syndrome
just lack pubity hair because testorstrone is reponsable to that but are still fertial
Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia
21-hydroxylase deficiency
Hypothalamo-pituatary adrenal (HPA) Axis
Adrenal cortex makes cortisol
Ther is a ensymes 21 hydroxal is need ed to make the final step of cortisol
So they don’t make cortisol so they have symptoms of low cortisols
the precersers to curtisosl turn into testostrone
so you get some more male secondary cartoristics
so by giving external cortisol it will stop this loop because it is a negative feedbackloop - stops low cortasal and extra t
easy to spot in girls not in boys
teh extreanl will masculinise- have a partoial penius when born, some have such a devloped pienous thay are brought up as a boy
In the womb – anything before birth- high
When treaing CAH they gove externl cortical witch suproses the HAP loop wich stops the low cortisol and the increased testosterone
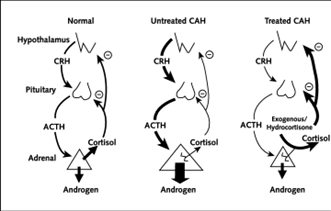
Dots get picked up everu easaly in males but in felamles dose sterigth after birth
- High levels of prenatal testosterone in girls
- Ambiguous external genitalia in girls
- Often treated once diagnosed
- Some 46,XX children assigned male at birth
- 5% of CAH girls assigned female at birth have gender dysphoria
- 12% of CA bH “girls” assigned male at birth have gender dysphoria
Shows how complex gender identity is
There are structural and functional sex differences in the brain- this can be due to the
- Hormones (activational and organizational)
- Genetics (genes on sex chromosomes)
- Environment (e.g. peers, culture,…)- shouldn’t rule out the enviremntal effects, structal bhevior may shap brain structure- prcatice of behvior- London taxi drivers
Sex Differentiation in the Brain: Mice
Mice- exsclude cultural influence
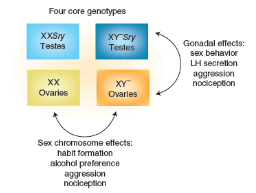
Four core genotypes and sperated them
Xy removed the sry geam meint that they have overies but have the rest of the Y geans- male geneans
XX sry- add an sry gean to make teastes but with the female geans
Are pleant of sex differences in mice
Separate the egntivcc effects and the hormone effects
Dubble sissosiation effect
Sex Differentiation in the Brain: Humans
No experimental manipulations possible
Information can be gathered from:
- Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia in 46,XX- high testosterone donst
- Complete Androgen Insensitivity in 46,XY
- Hormone treatment in transgender individuals
we can use the intesex peopole who have diifrent hormones compared to genes
dubble dissocated
can also look at transgender poeple and look at the diffrentt ages that they
Sex Differentiation in the Brain: Behavioural Differences
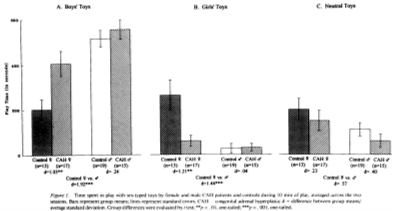
boys and girls have diffrent toy prefrences
boys and girls have different toy preferences- bab girl still goes for the dolls not always but on avarhge
gender specif toy prtrefrance not just a houman thing- highly controversial
looka t the paper
no different is absolutrte
sex diffrence- cah, cais and testostroene
- CAH 46,XX individuals have more masculine toy preferences- studied a lot in this context have hoig levels of testosterone mening thay have a more
CAH(exsperenecsed t in utro) - higher boy typical
Highly replicable
- CAIS 46,XY individuals typically have feminine toy preferences- play with girl toys -not purely cultural- cnat evan move yet but hard to pull apat- suggest that there is something hormonal to it
- Correlation between play style and prenatal testosterone- rare and hard to measure because mneed to mesure amniotic fulid
spcail and mental rotationn
- Men tend to be faster in spatial mental rotation tasks-
- CAH 46,XX individuals perform better than non-CAH 46,XX individuals
- CAH 46,XX individuals are more masculine in some measures than other 46,XX individual
- CAIS 46,XY individuals are indistinguishable from non-CAIS 46,XX individuals
- Suggests a role of testosterone in spatial mental rotation
- Exists in childhood and increases after pubity but not cativatinal- not corrlated with testosterone
- Some evidence that testortrone plays a part
Sex Differentiation in the Brain: Structural Differences
- Male brains are ~ 10% larger
- Female cortex is thicker (more grey matter)- same number of nerons overall
- No implication of them functing very differently- just structed slightly different
- Males have larger white matter volume & subcortical structures
- Female larger corsum collsums
- Some are done in the embvroyo
- CAIS 46,XY individuals have some features that are masculine (genetics), and some that are feminine (hormones or environment)
- Sex differences in the brain are complex and specific, and due to many different causes
- Both erly hormones but also the enviremntal factors
Sex Differences: Sexual orientation
- One of the most extreme sex differences
- 90-95% of human males are attracted to human females exclusively (“gynophile”)
- 85-90% of human females are attracted to human males exclusively (“androphile”)
- Old stats
Sex differences in the brain that co-vary with sexual orientation in humans
- SCN larger in androphile(attracted to dick exclusively) individuals (Swaab & Hofman 1988)
- INAH-3 smaller in androphile individuals (Levay 1991)
- Anterior commissure larger in androphile(attracted to dick exclusively) individuals (Allen & Gorski 1992)
- Sex differences in the brian are accutly the androfial and gynofile in the brain
Brain differences in sexul oprientation
- Could be causal to sexual orientation- farely unlicaly due to the scn could be corllialtion impatected by the sem hormopnal
- Could also be purely correlation, as indicators of other mechanisms (hormonal, genetic)
- Could be consequence of sexual orientation!
- Behvior impacts brain structure
Environmental Effects on Sex Differences- sexual orientation
- Influences on brain development (e.g. what you’re exposed to in childhood)
- Effects of practice (e.g. you are better at what you spend more time doing)
- Social effects (expectations, stereotypes,…)
- HOWEVER – little to NO evidence that this affects sexual orientation
Experience and Sexual Orientation
- Most people feel their sexual orientation has always been this way
- No good evidence to support effects of parenting, learning, etc.
- Evidence from other species
sexual orientation in sheep
- 8% of male sheep are exclusively interested in other males
- Sexually Dimorphic Nucleus (SDN) of preoptic area is smaller in these males
- Size of SDN is influenced by developmental T levels in enbrotic development
- Sexually Dimorphic Nucleus (SDN) bigger in male animals
Sex Differences in Behaviour: Activational Hormonal Effects?
- Variations with varying testosterone levels
- Variations with varying estradiol levels
- Variations with the menstrual cycle
- No evidnace to show it changes who they are interested in- just the instesity of sexual feeling
Activational role of hormones?
- No differences detected in adulthood between different sexual orientations
- Hormone fluctuations, manipulations, or treatments affect sexual motivation, but not orientation
- Gay and straight men dot have diffrnec in t
Organizational Hormonal Effects
There are two periods during development during which T is high in boys:
1.Weeks 8-24 of pregnancy
- Early: external genitalia
- Late: brain differentiation
First 3 months after birth
- potential further brain differentiation
Evidence for organizational role of hormones
• Correlations with measured prenatal hormones
• Have no direct corrlation between t and sexual orientation later
• Correlations with adult correlates of prenatal hormones
• Conditions with varying prenatal hormone levels
Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia (CAH)
Androgen Insensitivity Syndrom
Correlates of embryonic T
cognative proformance
sex diffrence in 2d/4d rations - fingers
Oto-acoustic emissions
Cognitive performance
Verbal abilities are better in androphile (dick) men than gynophile men
Visuo-spatial performance is worse in androphile(dick) men than gynophile men
Mental rotation is faster in gynophile women than in androphile(dick) women
Ratio of 2nd and 4th finger lengths (2D/4D)- length of the secod diget to the fourth diget
Sex differences in 2D/4D ratios (male: 0.95, female 0.97)
Early testosterone dependent
Butch lesbians have more masculine 2D/4D
No consistent finding in androphile men, but may differ between sub-groups – 2D/4D correlates with gender non-conformity (Swift-Gallant et al., Sci Rep 2021)
Doesn’t just apply to humans applies to other spices as well
Oto-acoustic emissions
When stimulated with a click, ears make a sound back
This is louder and more frequent in women (and females of other species)
Early T- dependent in other species
Gynophile women’s OAEs closer to gynophile men’s than androphile women’s
Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia- sexual preffrance
- CAH females are also more likely to identify as gynophile
- High
- Suggesting that erly t can indicate gynophile
getic effect- twin studies
- Higher concordance in monozygotic than dizygotic twins
- Estimates from 30-100%- lost of bias so looking at neaerer 30%
- Possibly higher concordance for women than men
- Looked at minority sexual preference
gentic effect- gentic mapping
- Androphilic men often have androphilic maternal uncles
- Suggests an X-chromosome inheritance pattern
- A region of the X-chromosome has been identified as related to sexual orientation
- Regions on other chromosomes have also been identified
evolutinary concern
- Should homosexuals not have fewer offspring?- leads to lower odds of having affspring
- How does a putative genetic basis not get selected out of the population then?
Possible mechanisms for maintaining such genes:- sexuality
- Heterozygote advantage- have both copies of a gene but having one copie of the gean means you have an advantage eg sicle cell, one coppie has protection for malaria but both cause sickle cell
- Different effects in males vs females- geanes may not have the eefcts in the male compared tpo the females the andropohilic grnas in men may cause the females to have more kids
- Kin selection- if there where a geen that inflineces a gean in men the relitives carry the geane the geans will be passed on through the realitives
faternal birth order effect
The odds of havinga androfil boy the more boys that you have had as a mother
if they have older brothers by the same mouther it increases the likelihood of being gay – male older siblings
something to dowith tehe mothers response to carrying the male babbies
Fraternal Birth Order Effect:Maternal immune hypothesis
Mother’s immune response to protein neuroligin 4 Y-linked predicts probability of having male-oriented son (Bogaert et al. PNAS 2017)
There is an immune response that is built up a responec to a single proteas
influnec om gemder idntity
- Not a single phenotype
- Genetic predispositions
- Pre-transition brain differences
gneder identity
- Gender identity evan larger than sex diffrneces than sex orientation
- Dose not seem binary
- Childhood dysphoria soe not always continue after pubity (dose for ~40%)
influences on gender identity
- Not a single phenotype
- Genetic predispositions
Pre-transition brain differences
Genetic predisposition to gender dysphoria
Stodie did on spain that looked at trans and cis people and looked at the genetic mapping off theatse people- looked like thare are specific genans with athere assosiacted with gender disforia
large sample size
gentic mapping excerisize specfic allies that are collrated with gender dysfiria
trans males having an long version of estrogen recepterbata (ERb) and the ERa corrlated with rans
trans woman corrlated with long AR short ERa and ERb
Pre-transition brain differences
• Brain volumes are in line with natal sex
• MtF individuals show more feminine cortical thickness and white matter in some brain areas
• FtM individuals show more masculine basal ganglia and some white matter tracts
• Some aspects of brain anatomy are different from both cis males and cis females
• Behvior can shape brain
What is the male precursor system called?
The male precursor system is called the Wolffian system
What is the initial state of sex organs in mammals?
Sex organs in mammals start completely undifferentiated.
What happens 7-8 weeks after the gonad has turned into a testis or ovary?
7-8 weeks after the gonad has turned into a testis or ovary, they become sensitive to androgens, particularly dihydrotestosterone (DHT).
What is required for the development of external male appendages?
DHT, which is made by the testes, is required for the development of external male appendages. Without receptors for DHT or if DHT is absent, the external organs develop as female.
what happerns if a male has no DHT receptors or DHT
they will not develop male external genatailia but have internal male oragns
if a male dosnt produce the anti mallirain hormone but created the androgin system
internal male and female structure
what dose a person with persistant mullerian uduct syndrom have
male exterbal genilaia with teasteas and female internal internal genitaila
XY, has internal female and internal and male externial
androgen insesntivity syndrone
A condition where a person with XY chromosomes is resistant to androgens, causing them to develop female external genitalia despite having male internal structures.
Term: What role do GABA and NPY play in puberty?
Definition: GABA and NPY inhibit the activation of KNDy neurons (kisspeptin), which are involved in activating GnRH neurons. witch realeaces GNRH into the blood streame
How frequently is GnRH released during puberty?
GnRH is released in pulses every 2 hours during puberty.
What does GnRH signal to the pituitary gland?
GnRH signals the anteria pituatary gland to release gonadtropins witch goe to the gonas FSH and LGH
what does FSH and LH do to males
FSH- sperm production
LH- testostrone production
what dose fsh and LH do to th efemale
fsh- folcule to ripen
lh- ovulationand formation of corpus luteum
a person with persistanat malirian duct syndrome has
male external with testes, male female internal gentailia
what is the exsternal genitalia of a person with androgen insensitivity syndrome are
female
androgen insesntive syndorme of XX, 46 leads to
lack of pubic hair