OpenStax Psychology 2e - Full
1/808
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
809 Terms
American Psychological Association
professional organization representing psychologists in the United States
behaviorism
focus on observing and controlling behavior
biopsychology
study of how biology influences behavior
biopsychosocial model
perspective that asserts that biology, psychology, and social factors interact to determine an individual's health
clinical psychology
area of psychology that focuses on the diagnosis and treatment of psychological disorders and other problematic patterns of behavior
cognitive psychology
study of cognitions, or thoughts, and their relationship to experiences and actions
counseling psychology
area of psychology that focuses on improving emotional, social, vocational, and other aspects of the lives of psychologically healthy individuals
developmental psychology
scientific study of development across a lifespan
dissertation
long research paper about research that was conducted as a part of the candidate's doctoral training
empirical method
method for acquiring knowledge based on observation, including experimentation, rather than a method based only on forms of logical argument or previous authorities
forensic psychology
area of psychology that applies the science and practice of psychology to issues within and related to the justice system
functionalism
focused on how mental activities helped an organism adapt to its environment
humanism
perspective within psychology that emphasizes the potential for good that is innate to all humans
introspection
process by which someone examines their own conscious experience in an attempt to break it into its component parts
ology
suffix that denotes "scientific study of"
PhD
(doctor of philosophy) doctoral degree conferred in many disciplinary perspectives housed in a traditional college of liberal arts and sciences
PsyD
(doctor of psychology) doctoral degree that places less emphasis on research-oriented skills and focuses more on application of psychological principles in the clinical context
personality psychology
study of patterns of thoughts and behaviors that make each individual unique
personality trait
consistent pattern of thought and behavior
postdoctoral training program
allows young scientists to further develop their research programs and broaden their research skills under the supervision of other professionals in the field
psyche
Greek word for soul
psychoanalytic theory
focus on the role of the unconscious in affecting conscious behavior
psychology
scientific study of the mind and behavior
sport and exercise psychology
area of psychology that focuses on the interactions between mental and emotional factors and physical performance in sports, exercise, and other activities
structuralism
understanding the conscious experience through introspection
Wilhelm Wundt
established the first psychology laboratory at the University of Leipzig, Germany
Plato
Socrates' most well known pupil. Founded an academy in Athens.
Descartes
French philosopher, nativist, and dualist
Dualism
the presumption that mind and body are two distinct entities that interact
William James
founder of functionalism; studied how humans use perception to function in our environment
Erik Erikson
famous for his 8-stage model of psychosocial development; neo-Freudian
John B. Watson
developed behaviorism ( the study of observable behavior)
Ivan Pavlov
discovered classical conditioning; trained dogs to salivate at the ringing of a bell
Albert Bandura
Social learning theory; Bobo doll experiment
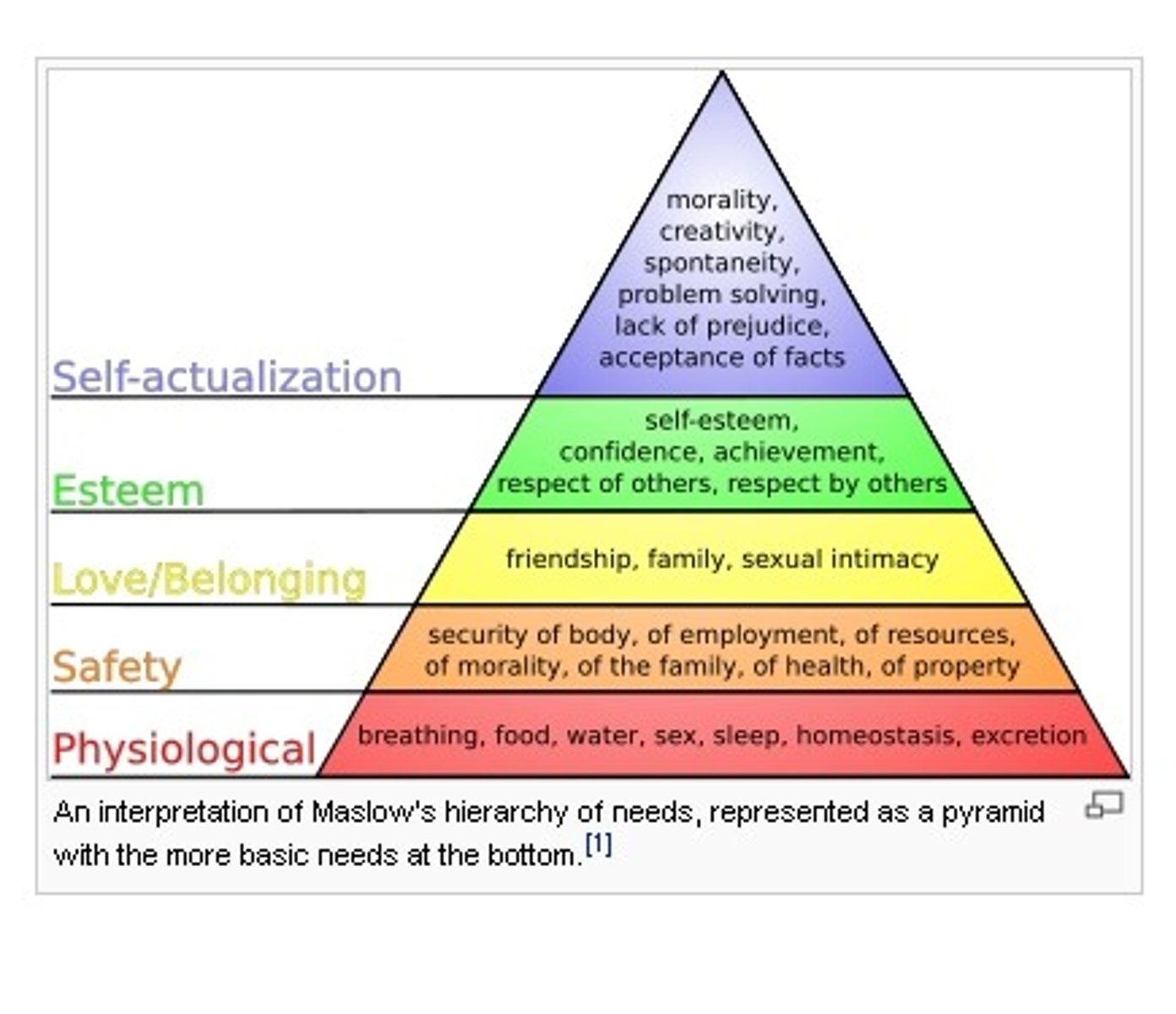
Abraham Maslow
created hierarchy of needs
Lawrence Kohlberg
Theory of Moral Development
Naomi Weisstein
Credited with starting the feminist revolution in psychology
Anna Freud
Continued her father's work in psychoanalysis with an emphasis on children.
Charles Darwin
English natural scientist who formulated a theory of evolution by natural selection (1809-1882)
Democritus
Greek philosopher that said all matter is made of tiny particles called "atomos" or atoms
behaviorist perspective
the psychological perspective primarily concerned with observable behavior that can be objectively recorded and with the relationships of observable behavior to environmental stimuli
psychoanalytic perspective
the perspective that stresses the influences of unconscious forces on human behavior
evolutionary psychology
the study of the evolution of behavior and the mind, using principles of natural selection
cognitive perspective
how we encode, process, store, and retrieve information
The Interpretation of Dreams
the Bible of Psychoanalysis by Freud
sociocultural perspective
perspective that focuses on the relationship between social behavior and culture
critical thinking
thinking that does not blindly accept arguments and conclusions. Rather, it examines assumptions, discerns hidden values, evaluates evidence, and assesses conclusions.
Hypothesis
A testable prediction, often implied by a theory
Stanley Milgram
obedience to authority; had participants administer what they believed were dangerous electrical shocks to other participants; wanted to see if Germans were an aberration or if all people were capable of committing evil actions
Albert Ellis
rational emotive behavior therapy
Critical Thinking
the objective analysis and evaluation of an issue in order to form a judgment.
Introspection
examination of one's own thoughts and feelings
Dissertation
a formal and long paper, written for a degree at a university or college
Herman Ebbinghaus (1850-1909)
created the forgetting curve and serial position effect in memory
Solomon Asch
Conducted famous conformity experiment that required subjects to match lines.
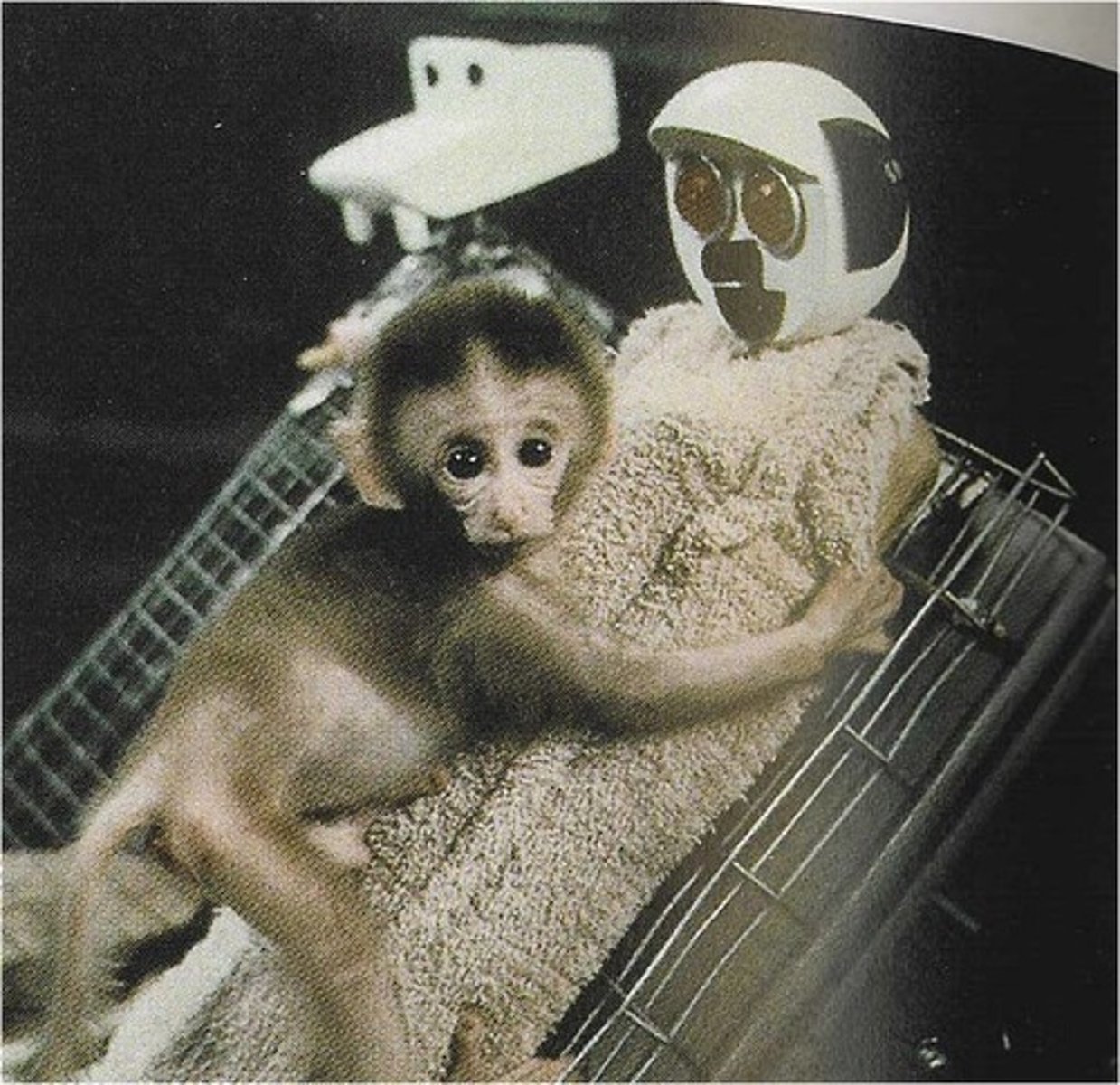
Harry Harlow
Studied attachment in monkeys with artificial mothers

Prefrontal Lobotomy
example of what happens when we rely on our subjective impressions; brain damage before and after the surgery remained the same
Heuristics
mental shortcuts or rules of thumb
Healthy Skpeticism
strive to think critically about information we encounter (regardless of the source)
Facts
observable realities
Opinions
personal judgements, conclusions, or attitudes
Theory
a well-developed set of ideas that propose an explanation of observed phenomena
Hypothesis
a testable prediction about how the world will behave if our idea is correct
Falsifiable
capable of being false
Case Study
in depth study of rare cases (does not tell cause and effect); ex: Phineas Gage, H.M., Little Albert
Anecdote
a study of one person
Naturalistic Observation
watching behavior in real-world settings
High Degree of External Validity
extent to which we can generalize our findings to the real world
Low Degree of Internal Validity
extent to which we can draw cause-and-effect inferences
Observer Bias
the tendency of the observer to unconsciously skew observations to fit the research goal/expectations
Operational Definition
being specific about what is being observed; important to specify how we're measuring our variables ahead of time
Self-Report Measures and Surveys
surveys and questionnaires;
advantages:
-easy to administer
-subtle information
disadvantages:
-may not have insight
-may not be honest
Population
everyone in a particular group
Sample
a portion of a population to be studied
Random Selection
procedure that ensures every person in a population has an equal chance of being chosen to participate
Reliability
repeatable/consistency in the data or results
Validity
measure of something being measured (if valid, also reliable)
Positive Impression Management
faking good (better than reality)
Malingering
faking bad (worse than reality)
Ratings Data
rating the behavior of others
Halo Effect
tendency of ratings of one positive characteristics to spill over to influence the ratings of other positive characteristics
Leniency Effect
tendency of raters to provide ratings that are overly generous (opposite of Halo Effect)
Archival Research
looking back at old records to obtain data, hard copy or electronically
Longitudinal Research
a research that tests the same group of individuals over an extended period of time
Attrition Rates
dropouts/people lost over the course of the study
Cross-sectional Research
a "snapshot;" a researcher compares multiple segments of the population at a given time
Cohort Effect
an effect that different age groups give different reaction results not necessarily due to their age
Correlational Design
research design that examines the extent to which two variables are associated; depicted in a scatter plot; correlations have predictive value; CORRELATION DOES NOT MEAN CAUSATION
Negative Correlation
as the value of one variable changes, the other goes in the opposite direction (one goes up, other goes down)
Positive Correlation
as the value of one variable changes, the other goes in the same direction (both goes up)
Confounding Variable
third-variable problem
Illusory Correlation
when people believe that relationships exist between two things when no such relationship exists
Confirmation Bias
looking for evidence to support a preexisting belief and ignoring evidence that contradicts it
Experimental Group
receives the manipulation
Control Group
does not receive the manipulation
Independent Variable
experimenter manipulates
Dependent Variable
experimenter measures to see whether manipulation had an effect
Confounds
any difference between the experimental and control groups, other than the independent variable; makes it impossible to interpret any findings
Cause and Effect
possible to infer, w/ random assignment and manipulation of independent variable
Placebo Effect
blind