3) Physical characteristics of aquatic systems
1/28
Earn XP
Description and Tags
properties of water and how they interact with ecosystems
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
what are chemical and physical properties of water
density, surface tension, viscosity, absorption of radiation
what temperature does the max density of water occur at?
4°C,
at <0°C, ice is less dense than liquid water
what does the density of water impact?
stratification/mixing in lakes
nutrients/orgs distbtn: some orgs may be stuck in one layer because they cannot tolerate another layer
what does surface tension impact?
Some insects can float on top of water due to water’s high surface tension, others can stay underwater but stick to the top
Surface has advantages and food sources
what does viscosity impact?
movement of orgs: shape of fish (elongated/smooth to not waste energy)
reduction of supporting tissues: orgs don’t have to put as much energy into supportive structures (like tree trunks/thick bones)
sedimentation rates: higher viscosity causes decreased speed
viscosity ___ as temp rises
decreases
what does absorption of light impact?
phosynth and primary production
heat and colour
where there is light there will be increased productivity
explain photosynthetically active radiation
clarity of water will impact which wavelengths and what conc of wavelengths will reach at a certain depth
light intensity ___ with depth (specific)
decreases logarithmically
in more productive water, light attenuation is ___, why?
faster, more particles
Explain the 3 types of lakes in terms of productivity
eutrophic: highly productive
mesotrophic: moderately productive
oligotrophic: low productivity
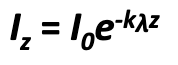
explain this formula
Lz is the quantity of light at depth Z
L0 is the quantity of light at the surface
Klambda is attenuation coeff (changes with each lake)
Z is depth
Ex: what is the depth where you have 10% of light with this klambda
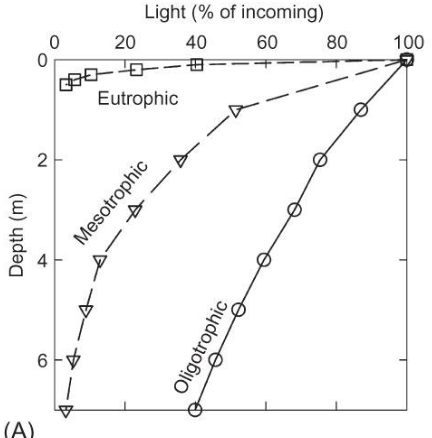
explain this graph
starting at 100% of light, by 0.25m down, eutrophic is already at 40% of light because it’s being used up, very productive ecosystem
in mesotrophic, by 1m down, 50% of light is remaining
in oligotrophic, by 1m down, 90% of light is remaining
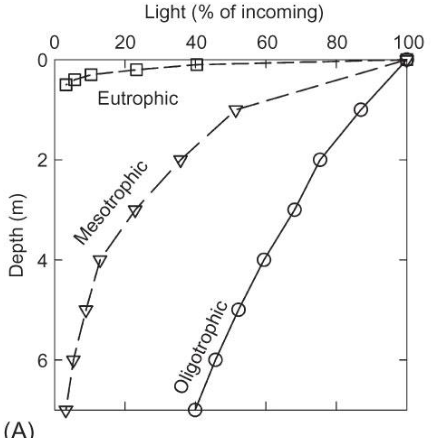
What is the compensation point? on this graphs?
Depth at which 1% of light is available, phosyn = resp at this point
eutrophic: 0.5m
mesotrophic: 7m
oligotrophic: not on graph, the whole things is photic zone
what is colour impacted by?
humic/fluvic compounds
sediment load
what is secchi depth?
where 10% of light is remaining, or where you can just no longer see the secchi disk
midway between lowered can’t see and raised can’t see
difference between apparent colour and real colour? example?
apparent colour: wavelengths absorbed and scattered back towards the eye
real colour: colour of particles, substances, substrate in the water
Peyto lake LOOKS blue because of sediments and particles in it
Pink lake IS pink, from pink bacteria in the lake
transmittance vs absorbance?
opposites
pure water will absorb much more red and transmit blue
what is stratification?
separation of discrete layers of water of different temperature in lakes resulting in change of water temp at different depths
explain different levels of stratification
epilimnion: near surface, warmer
metalimnion: thermocline, highest rate of change in water temp
hypolimnion: near bottom, cooler
what is thermal stratification the result of? explain?
heat absorption from light: surface will warm more
water density: warmer water is less dense, will float, and water cooler than 4°C
wind: mixes up the water and disrupts stratification a little bit
stratification has a large impact on ___?
which orgs with find in a lake and at what depth
Explain spring mixing
Water is isothermal (same temp at all depths), this can be mixed by wind
Surface waters are heated by solar radiation
Continues to mix, and layers start to form
Explain summer stratification?
After many calm, warm days, lake will stratify
Surface waters are heated and wind cannot mix warm surface water with dense cool water below
Mixing occurs within the epilimnion, but not between epilimnion and hypolimnion
Stratification is stable even with strong winds
Explain fall mixing
Stratification will break down when epilimnion cools to same temp as hypolimnion
If cooled water at surface decreases below temp of hypolimnion, then it wil sink to bottom
Wind can mix the entire lake
Explain winter stratification
Surface of water can freeze if temp of lake falls below 3.9C
If water temp is below 3.9, cool water at surface will remain at top where it freezes
If water temp is above 3.9, cool water from surface will sink and mix with less dense water below
Once ice covered, no mixing occurs (sealed from atmos, but light can transmit through clear ice)
Summary: stratification is 0C water near surface, and 4C water below that.
What are the lake types, explain
amictic: never circulate
meromictic: incomplete circulation, stay stratified for many year
holomictic: circulates fully at least once a year
explain types of holomictic lakes
dimictic: circulates twice per year
monomictic: ciruclates once per year
polymictic: circulates frequently
explain cold vs warm monomictic
cold monomictic: stratified in winter (most of year), warms enough in summer to mix
warm monomictic: stratified in summer, cools enough in winter to mix