Limbic System
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
What are the 4 primary functions of the limbic system?
Homeostasis
Olfaction
Memory
Emotion
What structures in the brain are for memory and learning, and are attached to an event?
The emotional response which causes attachment is mediated by what?
Hippocampus & amygdala
Hypothalamus
Where is the amygdala located?
Deep in the temporal lobe.
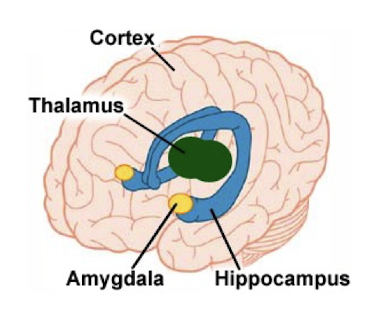
What is the function of the amygdala?
Involved in emotions and motivations. Allows us to associate an action with a consequence.
Involved in processing fear, anger, pleasure, and determining what memories are stored and where those memories are stored.
Constantly evaluates and integrates a variety of sensory information from surroundings.
Assigns this information the appropriate values of emotional dimensions.
Has connections with the medial dorsal thalamic nucleus: smell
Connections with the frontal cortex and develops as we do; shapes judgement.
What are 2 general things that happen when the amygdala is injured?
Mood disorder
No fear when lesioned bilaterally
What is valence in terms of the amygdala?
Amygdala determines how much someone likes, fears, and love/hates something.
What can happen when someone has an overactive amygdala?
Trembling
What is the Papez circuit?
Circuit of communication from hippocampus to the cingulate gyrus and back.
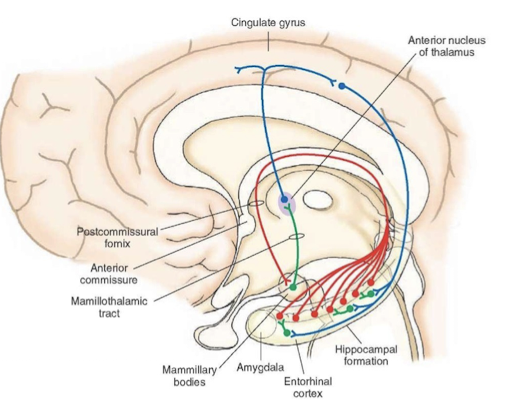
What is the function of the Papez Circuit?
Allows memory recall. You can access memories because of this circuit.
What effect does the pre-frontal cortex have on the amygdala?
Emotional evaluation
Decision making
Behavior
What affect does the amygdala have on the striatum (basal ganglia)
Motor responses
Reward or repulsion processing
What affect does the amygdala have on the basal nucleus of Meynert?
Learning
What affect does the thalamus have on the amygdala?
Exteroception (sight, sound, tactile stimuli)
Interception (heart beat, BP)
What affect does the amygdala have on the hypothalamus?
Hypothalamus affects the:
Periaqueductal gray (PAG): modulation of pain
Anterior pituitary: hormone (cortisol)
What affect does the amygdala have on the hippocampus?
Emotion modulation
Change to memory
What structure of the brain is involved with working memory*?
*Ability to hold a limited amount of information that is immediately available for a variety of cognitive functions.
Prefrontal cortex
What is another function of the prefrontal cortex that is discussed this lecture?
Self-awareness and self-recognition
Cognitive ability to differentiate between self and environmental cues; understand behaviors or emotion of others; insight.
Preferentially involves right prefrontal cortex
Perceptual deficits (run into things and wonder why their arm hurts)
What are possible symptoms of a prefrontal injury/disorder depending where the lesion is?
Apathetic, lifeless, abulic (unable to make decisions) state.
Dorsolateral lesion
Impulsive, disinhibition, poor judgement, emotional lability (constantly changing).
Orbitofrontal lesion
Depression
Left prefrontal lesion
Behavioral disturbances resembling mania, indifference, or euphoria (bipolar)
Right prefrontal lesion
AN overactive amygdala likely needs more what?
Needs more pre-frontal cortex activation.
This is why therapy works.
What is an example of a reduction in pre-frontal modulation of the amygdala?
ETOH intake.
ETOH disrupts the connections between pre-frontal cortex and amygdala.
This impairs the processing of emotions (why a drunk person may want to fight someone)
What happens when there is an abnormal increase in amygdala activity?
Anxiety; activates the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis
What hormones are increased as a result to increased amygdala activity (HPA axis activation)?
ACTH
Adrenaline
Cortisol
What brain structure is perhaps the most strongly implicated in the pathophysiology of PTSD? Why does this cause PTSD?
Amygdala; it is so active that the prefrontal cortex is under active.
The prefrontal cortex allows us to dampen anxiety and anger.
What is the relationship between the amygdala size and PTSD?
Association with smaller amygdala volumes with increased levels of fear conditioning.
What is emotion’s link with the immune system?
It treats the immune system as optional when stressed. This is okay in the short term, but if the stress response does not go down and the cortisol does not go down, bad things occur. This can cause:
Colitis (inflamed colon)
CV disorders
Adult-onset diabetes
What is the link between stress and neuronal growth rate?
increased stress = increased cortisol = decreased neuronal growth rate = may lead to decreased cognitive ability.
What is the Engram theory?
Theory of learning: a group of neurons that were active under specific circumstances and that group’s information was retained.
What are the 4 steps to making a memory?
Encoding: a perception is gained by the brain (info about the body or world)
Consolidation: information is made stable
Storage: permanent changes made to retain the information
Recall: reactivation of the information in storage under precise cues
What is the hippocampal formation? (Hippocampus as a whole)
A group of structures involved in declarative memory formation. Performs the chemical activity needed to convert short term memory to long term memory (hippocampus)
What does the hippocampal formation include?
Dentate gyrus (injured in Alzheimers dementia)
Entorhinal cortex
Relay center between cingulate gyrus and hippocampus
Participates in memory consolidation
Parahippocampus
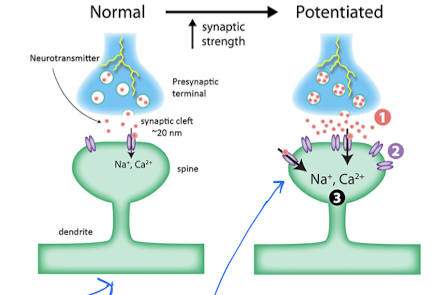
What is long-term potentiation (LTP)?
Chemical process that forms memories. It permits implicit and explicit (facts) learning.
What are the 3 stages for LTP?
Immediate (1-2 secs)
Short-term
For recognizable stimuli
Loss within 1 min unless info is rehearsed
Long-term
Relatively permanent storage (can lose it)
Consolidation
What is ultimately the biggest part of successful LTP?
Synapse strength
What happens if there is unilateral damage to the hippocampus?
cannot form new long-term memories, lose much of the short-term memory
What does the Alzheimer’s disease have to do with the hippocampus?
It is associated with loss of neurons and synapses in the hippocampus.
What is Korsakoff Syndrome?
Characterized by loss of recent memory and tendency to fabricate accounts of recent events.
Changes to hippocampus, mammillary bodies, and thalamic nuclei.