COMP GOPO Unit 2B: Iran Diagram | Quizlet
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
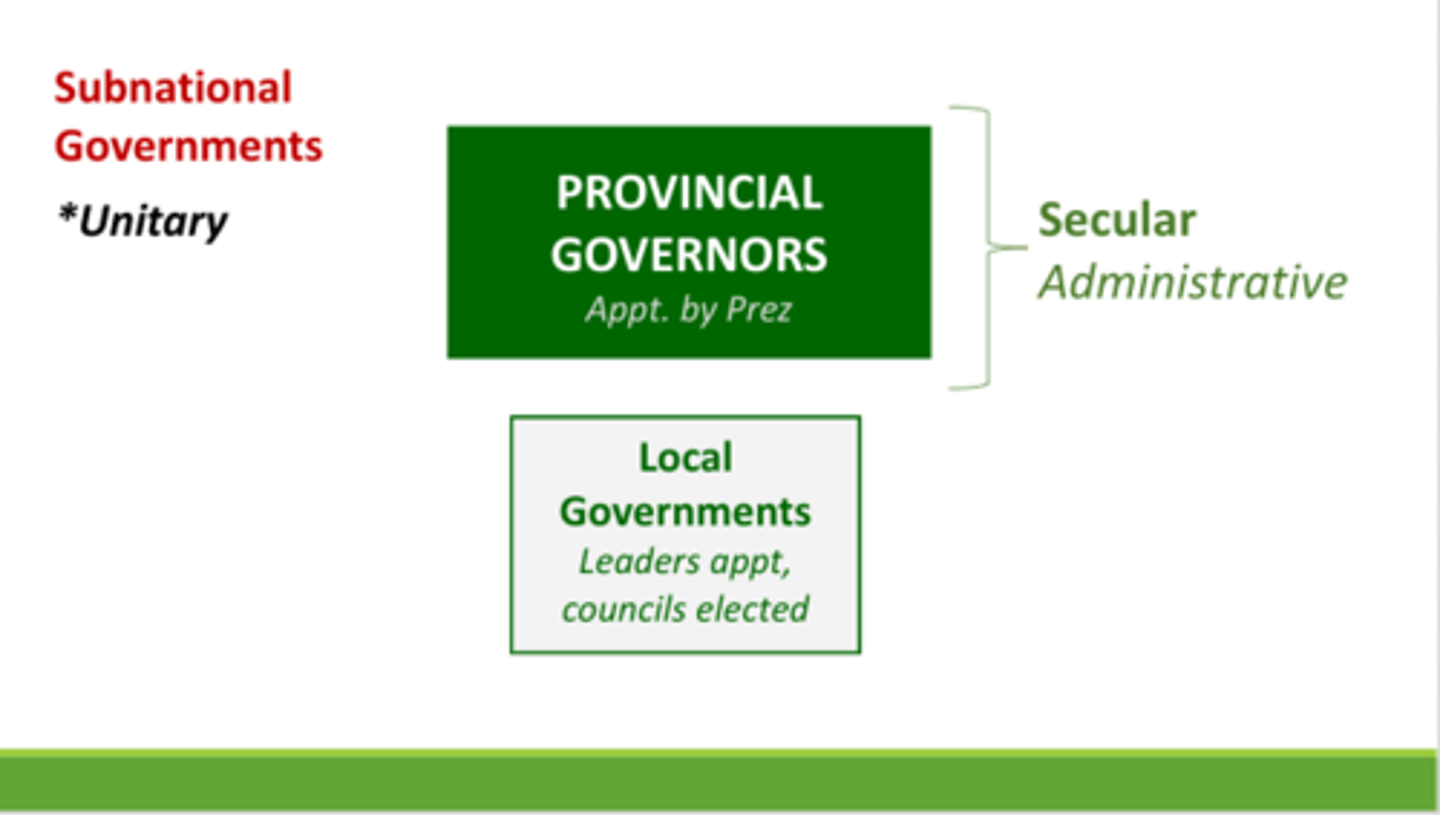
Unitary
Provincial governments are largely administrative, theocratic republic
Provincial governments are largely administrative
Provincial governments have practically no power; they just decide how laws are implemented
Theocratic Republic
Governed by religious law; Example: Iran, where Islamic clerical leaders exercise supreme power.
Islam and its impact on power, authority, and legitimacy
Monarchy to Islamic Revolution to a theocratic democracy, national elections, election rigging, de facto state control of media
Monarchy
-Shah: title of the rulers of Iran before the 1979 Islamic Revolution
-Shahs prevented colonization
-Next 400 years (under Safavid and Qajar dynasties)=combined Persian tradition of strong kingship with Shiite beliefs in faith and obedience to rule the county (this produced stagnation though; earlier Persian history=strong kingship led to growth and domination)
-Inability of shahs to rule strongly due to just religious rule guidelines caused the collapse of the dynasties
-Military and economic power of the west showed how weak the Qajar dynasty had become; opposition to the regime increased
-Orthodox Shiites opposed to secularization
-Growing secular middle class wanted political reforms that would lead to rule of law and possibly even democracy
-King dismissed his PM, created the Majlis (the Iranian Parliament), and accepted the Constitution of 1906 (secular people=pleased with reform; clerics=angry with reform)
-Britain and Russia divided Iran into 2 zones of influence
-2nd to last shah=Pahlavi
-Pahlavi initially took power in the name of nationalism and Shiism but later turned his back on Islam and focused on modernizing Iran; Majlis were a rubber stamp; later turned his back on Clerics
-WW2=Britain and Russia occupied Iran and made Pahlavi abdicate and go into exile; was replaced by his son Mohammed Reza
-Reza's PM worsened situation (e.g. nationalized oil company but ended in chaos due to worker shortage; sdissolved upper house of parliament, confiscated royal property, suspended Supreme Court, expanded martial law
-King tried getting rid of PM but PM refused; led to US intervention/coup
-Shah alienated clerics and introduced White Revolution (the term used by the Shah to describe reforms in Iran between the end of WW2 and the downfall of his regime in 1979 [period where Shah tried to modernize Iran and increase h
Islamic Revolution
-Ayatollah Ruhollah Khoimeini: Muslim cleric who led the 1979 Revolution in Iran and was leader of the country until his death in 1989
-Shah started repressing (e.g. killing students, stopping Khoimeini's speeches, arresting him, imposing martial law)
-Khoimeini exiled to Paris for 15 years (in 1964); audiotapes of his teachings were smuggled into Iran though
-Other reasons (besides religion) that led to shah's downfall:
-Land reform=illiterate and ill-prepared peasants couldn't run farms, had to take loans they couldn't pay, then moved to the slums of cities
-Shah kept making reforms and more distant from population; Savak continued silencing dissidents
-Shah got in trouble due to relation with US (used oil to buy weapons)
-Americans made it look like they ruled Iran and Iranians disliked US' drinking and sexual openness
Theocratic Democracy
-4 periods/republics that coincide with the influence of 4 men in post-revolutionary Iran
-First period=decade where Khomeini was supreme leader
-Early 1980s=Khomeini created the Islamic Republic
-Khomeini's power reinforced by 3 important events: 444-day occupation of US embassy, Iraq=Iran War, and dangers of war made Khomeini increase level of repression against foreign and real opponents (created the Iranian Revolutionary Guard Cops--Elite military unite set up after the 1979 revolution; some claim it runs the country)
-2nd period=coincides with death of Khomeini and election of Ayatollah Hashemi Rafsanjani and President (Ayatollah Ali Khameini=replaced Khomeini as supreme leader but Rafsanjani had more power since he was more moderate and was a cleric)
-Rafsanjani=pragmatist and focused on domestic policy concerns (also became very wealthy due to getting former property and assets from the Shah; led to claims of corruption and drop in support) (but got widespread support due to major backing of the majority of conservative clerics
-Khameini=far more conservative and tried to keep the spirit of theocracy and revolution alive
-Rafsanjani made little political reform
-Khatami (next president)=made major political reform
-Khatami=more moderate and fought censorship
-Khatami's first 6 years=brought major reform (easier to form political groups, less press censorship, some open protests permitted; tried improving relations with the West and allowed the International Atomic Energy Agency to inspect nuclear facilities)
-4th period: Khameini and his conservative colleagues began reasserting the influence of those who favored retaining the goals and values of the first years of the Islamic Republic
-Forces loyal to clerics struck back at the limited political reforms of the first Khatami years
-Conservative ascended when Ahm
National Elections
Iran elects on national level a head of state and the head of government (the president), a legislature (the Majlis), and an "Assembly of Experts" (which elects the Supreme Leader). City and Village Council elections are also held every four years throughout the entire country
Election Rigging
The act of dishonestly organizing an election to get a particular result. It is an electoral fraud and an interference with the election process.
De facto state control of the media
The mass media in Iran is both privately and publicly owned but all channels are subject to censorship
A special court has authority to monitor the print media and may suspend publication, or revoke the licenses, of papers or journals that a jury finds guilty of publishing anti-religious or slanderous material or information detrimental to the national interest. The Iranian media is prohibited from criticizing Islamic doctrine (as interpreted by the Iranian government)
The majority of Iranians - upwards of 80 percent - get their news from government-owned media. Attempts to establish private, independent media outlets in Iran have been restricted or quashed, and Reporters Without Borders has declared Iran to have the highest number of jailed journalists in the Middle East
Executive
Dual Executive, cabinet
-Supreme Leader: appointed head of state, agenda setting, commander-in-chief, appointment/removal>Expediency Council, 1/2 Guardian Council, Chief Judge
-President: elected head of government, term limit, oversees bureaucracy/implementation of laws, foreign policy chief
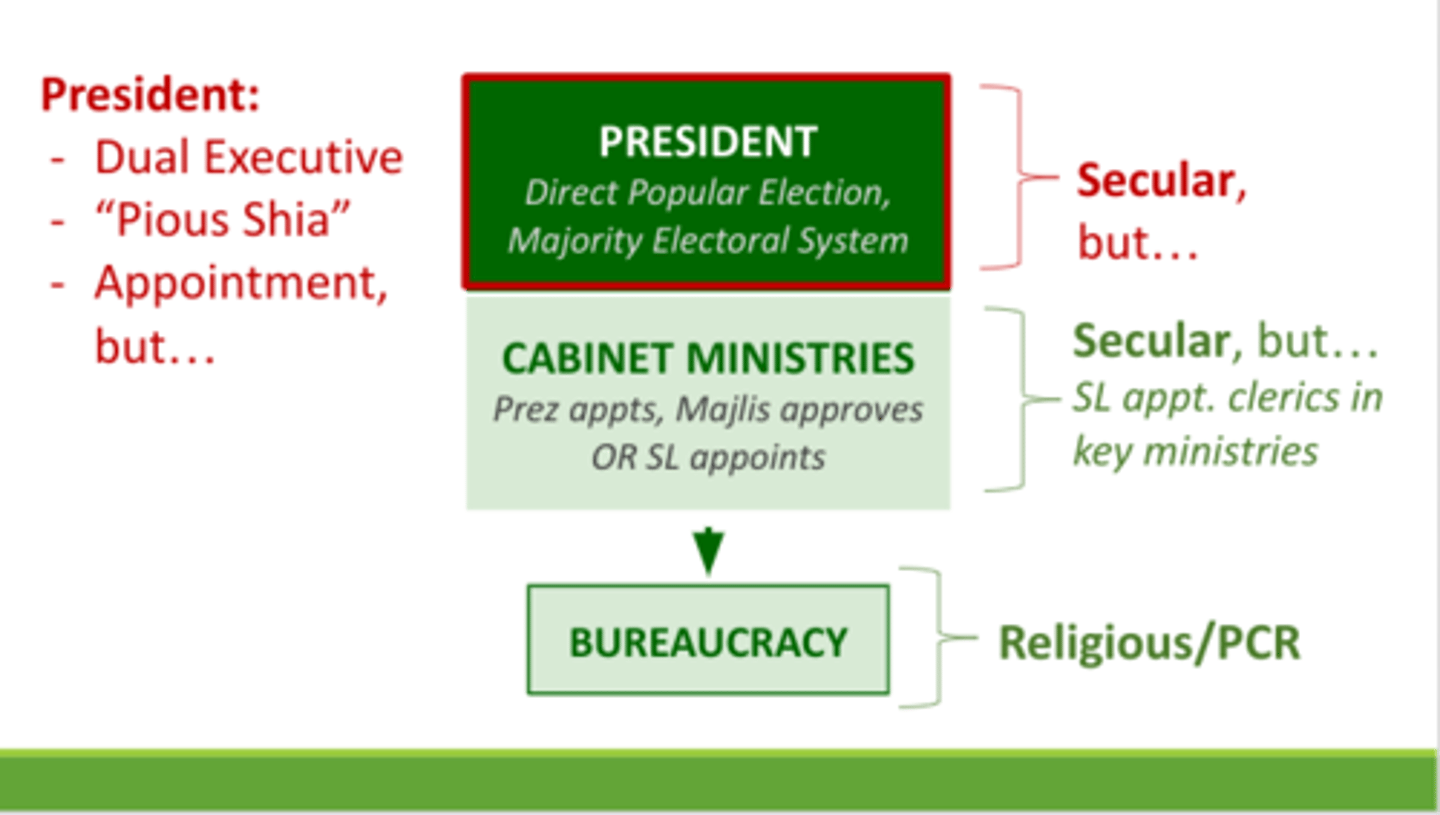
Dual Executive
two actors; head of state and head of government
-head of state=supreme leader
-head of government=president
Cabinet
The Cabinet of Iran is a formal body composed of government officials, ministers, chosen and led by a President. Its composition must be approved by a vote in the Parliament. According to the Constitution of the Islamic Republic of Iran, the President may dismiss members of the cabinet, but must do so in writing, and new appointees must again be approved by the Parliament. The cabinet meets weekly on Saturdays in Tehran. There may be additional meetings if circumstances require it. The president chairs the meetings. The Supreme Leader (Ali Khamenei) has the power to dismiss cabinet members like ministers and vice presidents, as well as the President, at any time, regardless of the Parliament's decisions.
Supreme Leader - Appointed head of state
According to the constitution (Article 111), the Assembly of Experts is tasked with electing (following Ayatollah Khomeini), supervising, and dismissing the Supreme Leader.
-Life Tenure
Supreme Leader - Agenda Setting
Determining which public-policy questions will be debated or considered.
Supreme Leader - Commander-in-chief
The Supreme Leader is the commander-in-chief of the armed forces
Supreme Leader - Appointment/Removal (Expediency Council, 1/2 Guardian Council, Chief Judge)
Supreme leader oversees, appoints (or inaugurates) and can dismiss the following offices:
-the members of the Expediency Discernment Council for a term of 5 years.
-6 of the 12 members of the Guardian Council from among the members of the Assembly of Experts, the other 6 are chosen by the Parliament out of Islamic jurist candidates nominated by the Chief Justice of Iran who is in turn appointed by the Supreme Leader.
-The Chief Justice of Iran (Head of the Judiciary Branch; usually a member of the Assembly of Experts) for a term of 8 years,
President - Elected Head of government
-The procedures for presidential election and all other elections in Iran are outlined by the Supreme Leader. The President of Iran is elected for a four-year term in a national election by universal adult suffrage by everyone of at least 18 years of age. Presidents can only be reelected once if in a consecutive manner. Candidates for the presidency must be approved by the Council of Guardians, a twelve-member body consisting of six clerics (selected by Iran's Supreme Leader) and six lawyers (proposed by the Supreme Leader-appointed head of Iran's judicial system, and voted in by the Parliament)
-Within these guidelines the Council vetoes candidates who are deemed unacceptable. The approval process is considered to be a check on the president's power, and usually amounts to a small number of candidates being approved
-The council rejects most of the candidates stating that they are not "a well-known political figure", a requirement by the current law.
-The president is required to gain the Supreme Leader's official approval before being sworn in by the Parliament and the Supreme Leader has the power to dismiss the elected president if he has either been impeached by Parliament or found guilty of a constitutional violation by the Supreme Court
President - Term Limit
Four years, renewable once
President - Oversees bureaucracy/implementation of laws
-chairperson of the cabinet
-Head (Presided) of the Supreme National Security Council
-Head (Presided) of the Supreme Council of the Cultural Revolution
-Nomination of Cabinet members to the Parliament
-Issue executive orders
-Signature of treaties, protocols, contracts, after the approval of the Islamic Parliament of Iran
-The President is obliged to sign the legislation approved by the Parliament, or the result of a referendum, after it is forwarded to them and the legal stages are covered, and to forward to the relevant authorities for implementation. (He has no right to veto).
President - Foreign Policy Chief
-The deputy commander-in-chief of the Islamic Republic of Iran Army
-Sends and receives all foreign ambassadors
-Signature of treaties, protocols, contracts, after the approval of the Islamic Parliament of Iran
Legislature
Unicameral, Majles, directly elected, approves legislation, oversees the budget, confirms president's cabinet appointments
-Guardian Council: supervises the Majlies decisions, vets candidates for office
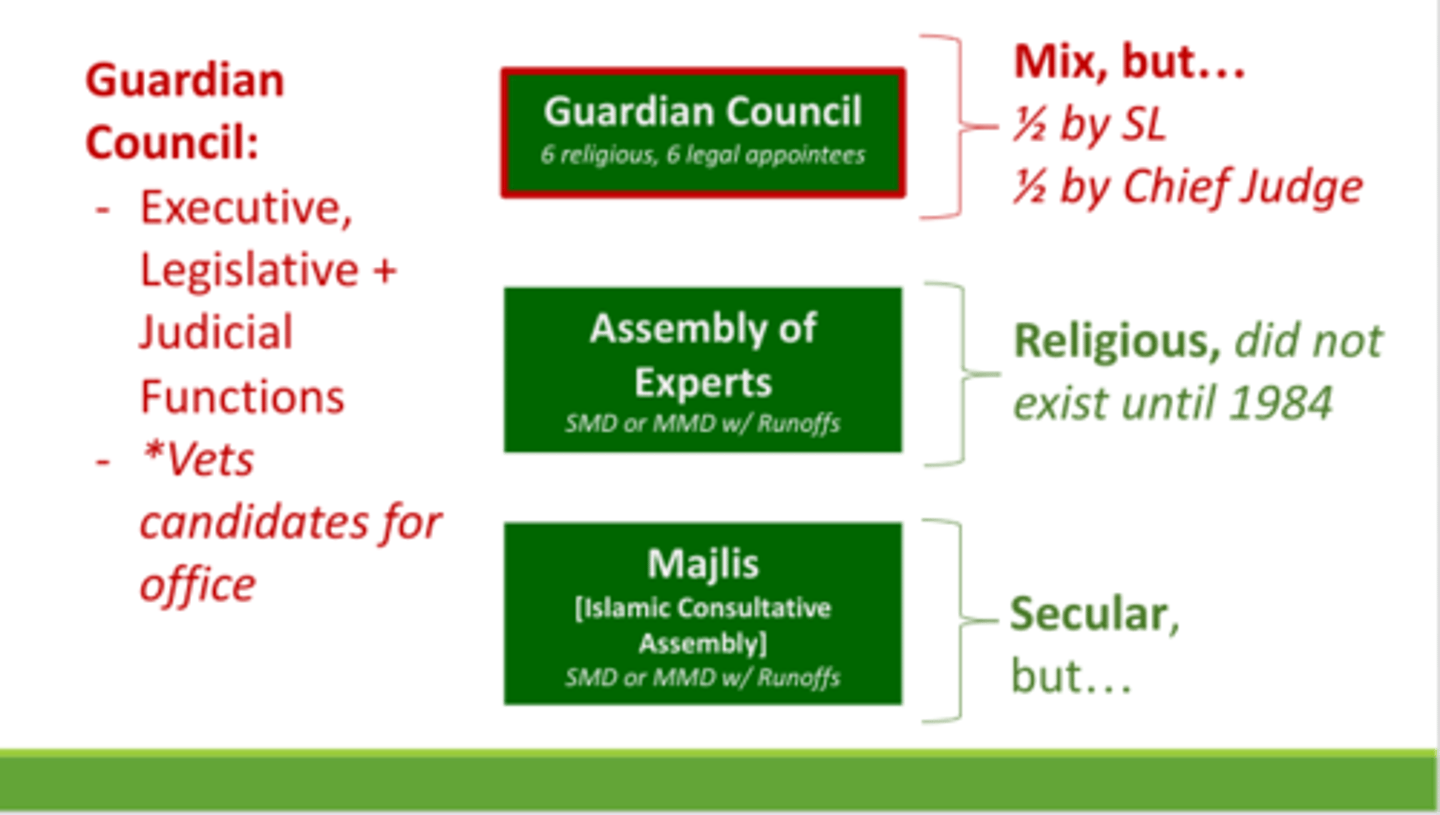
Unicameral
One-house legislature
-unicameral parliamentary chamber called Islamic Consultative Assembly
Majles
The Iranian parliament, from the Arabic term for "assembly."
Directly Elected
Members of the legislature are popularly elected for four-year terms
Approves Legislation
All legislation passed by the Islamic Consultative Assembly must be sent to the Guardian Council. The Guardian Council must review it within a maximum of ten days from its receipt with a view to ensuring its compatibility with the criteria of Islam and the Constitution. If it finds the legislation incompatible, it will return it to the Assembly for review. Otherwise the legislation will be deemed enforceable.
-All People's House of Iran candidates and all legislation from the assembly must be approved by the Guardian Council. Candidates must pledge in writing that they are committed, in theory and in practice, to the Iranian constitution
-Although the executive proposes most new laws, individual deputies of the Parliament also may introduce legislation. Deputies also may propose amendments to bills being debated. The Parliament also drafts legislation, ratifies international treaties, and approves the national budget
Oversees the budget
Parliament approves the national budget
Confirms president's cabinet appointments
The president also appoints the ministers, subject to the approval of Parliament, as well as to that of the Supreme Leader, who can dismiss or reinstate any of the ministers and vice presidents at any time, regardless of the president or parliament's decision
Guardian Council - supervises the Majiles Decisions and vets candidates for office
-All legislation passed by the Islamic Consultative Assembly must be sent to the Guardian Council. The Guardian Council must review it within a maximum of ten days from its receipt with a view to ensuring its compatibility with the criteria of Islam and the Constitution. If it finds the legislation incompatible, it will return it to the Assembly for review. Otherwise the legislation will be deemed enforceable.
-All People's House of Iran candidates and all legislation from the assembly must be approved by the Guardian Council.
Judiciary
Appointed by the Chief Judge, Shari'a Law training is required of all judges, rule by law
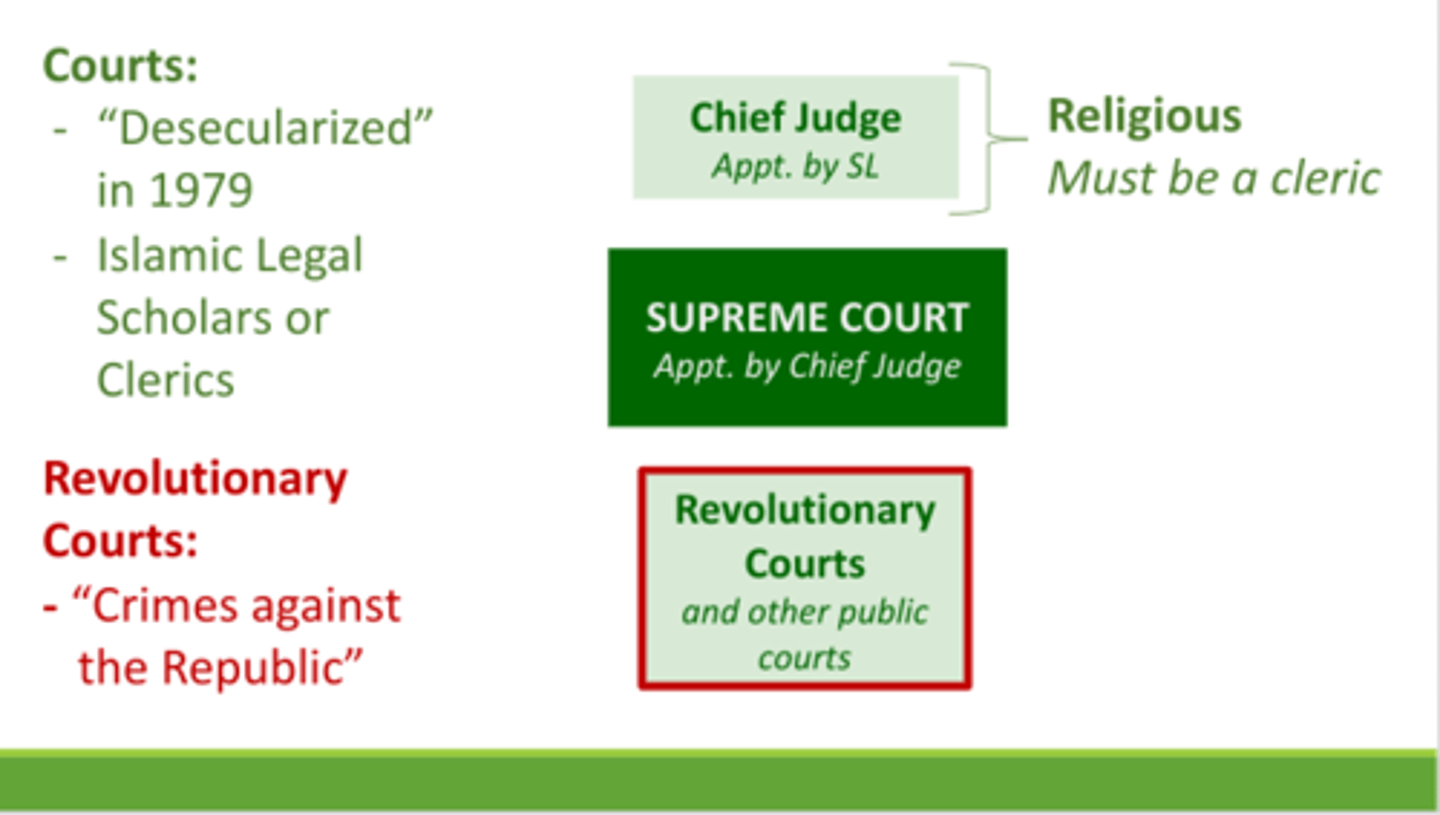
Appointed by Chief Judge
Chief Judge can appoint, dismiss, or accept resignation of members of the judiciary
Shari'a Law Training is required of all judges
The judiciary in Iran follows Islamic Law (Shari'a)
Rule by Law
Government uses the law to enforce/control its citizens

TERM
ignore this
DEFINITION
ignore this
TERM
ignore this 2
DEFINITION
ignore this 2