Unit 3, AOS 2 - Ecologically Sustainable Development
1/24
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Economic models, reource extraction, principles of ESD, risk management
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
What are the 2 driving factors behind unprecedented and unsustainable increases in natural resources exploitation?
Population growth + rising per-capita consumption = increasing resource demand
Define Ecological Balance
A state of dynamic equilibrium within a community of organisms in which genetic, species and ecosystem diversity remain relatively stable, subject to gradual changes through natural succession.
Identify 3 ways human activities cause ecological imbalance
deforestation
waste production/discharge
urban expansion
intensive agricultural land use
mining
exhaustive fossil fuel extraction etc.
Outline the Linear Economy Model
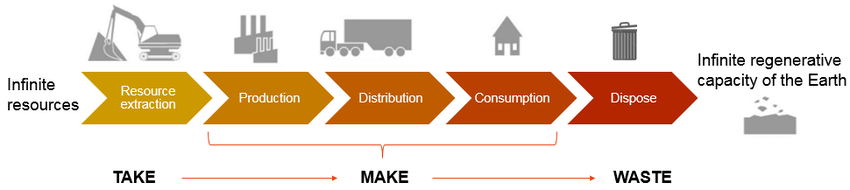
The linear economy model (take, make and waste) begins with resource extraction and ends with waste, with the desired outcome of a growing economy (more products desposed of, more products purchased).
Identify why the Linear Economy Model is unsustainable
This model relies on infinite resources, an infinite capacity of the Earth to renew these resources, and the ability of the natural environment to absorb ever-increasing amounts of waste.
Define Planned Obsolecence
When a product is planned to break down or become unusable within a planned time frame. This ensures a constant demand from consumers as they purchase replacement products.
Define Perceived Obsolecence
When something may still be functioning but is made to appear in need of replacing or inadequate compared to newer models, by the consumer.
Outline what GDP measures
GDP (Gross Domestic Product) measures the monetary value of final goods and services (those bought by a final user) produced in a country, given a period of time.
List 3-5 apsects of national progress and growth that GDP does NOT consider
Sustainability
Equality/equity
Education and career opportunites
Health and wellness
Individual rights
Healthcare access
Housing
Access to basic utilites
Personal safety
Outline the Circular Economy model
A economic system that centres around the reuse and regeneration of materials or products, and the extension of product life cycles to minimise waste output and prevent unsustainable levels of resource extraction.
Define Finite Resources
A resource is finite if it is replenished at a rate that is considerably slower than the rate of consumption, making it non-renewable and its use unsustainable.
Define Renewable Resources
Renewable resources are those that are replenished at a fast enough rate and in sufficient abundance to meet rates of consumption, making them renewable and sustainable for continued use.
Define Replacement Rate (of resources)
The replacement rate is the rate at which natural resources can be replenished by natural environmental processes, following extraction.
Define Ecologically Sustainable Development (ESD)
Development that successfully integrates economic, environmental, social and equitable considerations to meet the needs of present generations without compromising the needs of future generations.
List the 7 Principles of Environmentally Sustainable Development
Conservation of Biodiversity and Ecological Integrity
Efficient Resource Use
Cleaner Production and Waste Minimisation
Intragenerational Equity
Intergenerational Equity
Precautionary Principles
User Pays Principle
Define the principle of Conservation of Biodiversity and Ecological Integrity
Protecting the diversity of life and maintaining the quality and resilience of ecosystems should be a fundamental consideration in decision-making, to determine and minimise potential of ecological degredation.
Define the principle of Efficient Resource Use
Consumption of material and energy resources of development should be minimised through more efficient planning and design.
Define the principle of Cleaner Production and Waste Minimisation
Waste generation and discharge into the environment should be minimised. Unavoidable waste should be treated if possible and responsibly stored or disposed.
Define the principle of Intragenerational Equity
Everyone within the present generation should have equal rights to benefit from the use of natural resources and a healthy, clean environment.
Define the principle of Intergenerational Equity
The present generation should ensure that the integrity, biodiversity and productivity of the natural environment is maintained or enhanced for future generations.
Define the Precautionary Principle
If there are threats of serious or irreversible environmental damage, lack of full scientific certainty does not excuse postponing preventative measures.
Define the User Pays Principle
The users of goods and services should pay for the full life cycle costs of providing the goods/services.
Define a Life Cycle Analysis/Assessment
A quantification of the environmental impacts of a product from raw material extraction to manufacturing and end of life disposal.
Define a Risk Assessment
An evaluation of potential adverse effects of activities or substances on humans and the environment, considerating severity of hazards and the likelihood of their causing harm.
Define Risk Management
Development of strategies to minimise/mitigate risk, based on risk assessments and what the leading decision makers deem acceptable risk.