CFF: Alignment and Occlusion of Dentition
1/97
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
98 Terms
___________ and ___________ include the static and dynamic relationships of the maxillary and mandibular teeth against one another
Occlusion, function
Define the following:
•Static relationship
•Between the incising or masticating surfaces of the maxillary or mandibular teeth or tooth analogues.
occlusion
Define the following:
•Dynamic relationship
•The contacts of the maxillary and mandibular teeth during mastication and deglutition
functional occlusion
4 factors that determine tooth position
Tooth, Arch, Function, Anatomy
After tooth eruption, teeth are...
Directed into certain position
the tongue pushes the teeth in a ______ direction
buccal
the lips and cheeks push the teeth in a ______ direction
lingual
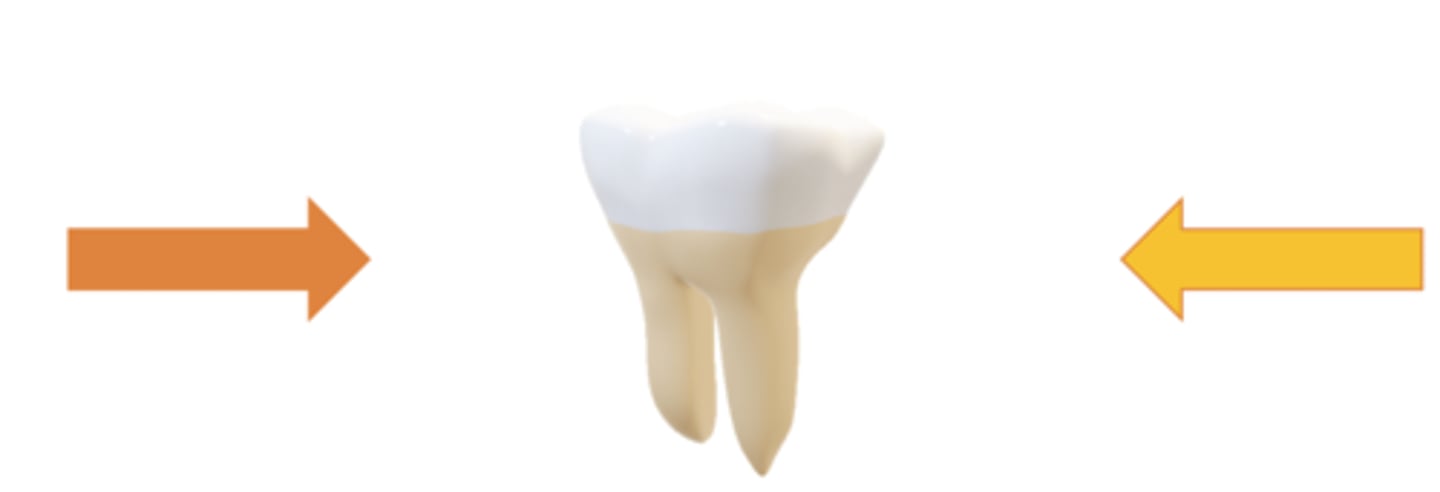
Where the labiolingual and buccolingual forces are equal, tooth stability is achieved
neutral position
Define the following:
Distal surface of most posterior tooth to distal surface of most posterior tooth opposite side through all the proximal contacts
arch length
which dental arch is 2mm longer than the other?
maxillary
What is the average length of the maxillary arch?
128mm
What is the average length of the mandibular arch?
126mm
the occlusal plane is a line drawn through all the _______ cusp tips and incisal edges of the mandibular teeth
buccal
Define the following:
Inter canine or Intermolar distance
arch width
which dental arch width is 1-2mm wider than the other?
maxillary
list the 3 types of arch forms:
U-shaped, V-shaped, Tapered
discrepancies in arch length and tooth size can lead to...
crowding
What can cause labial flaring?
Muscal instruments (clarinet, etc.) or biting on a pipe
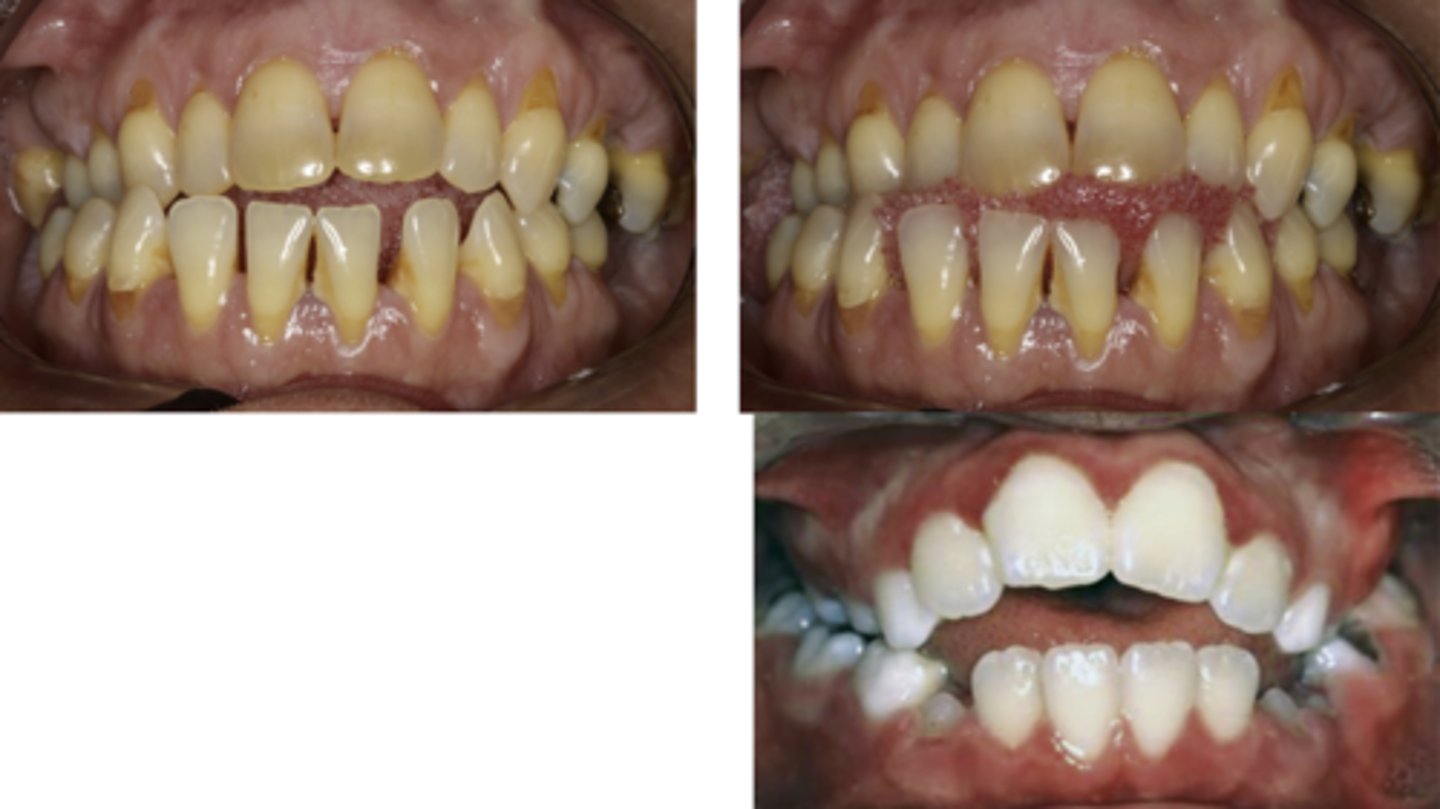
identify the type of bite:
anterior open bite
•Related to unusual tongue size or activity
•Caused by constant resting or posturing position of the tongue
•May require orthodontic correction
anterior open bite
what two things affect arch stabilization?
proximal space
occlusal contact
•Maintain the teeth in normal alignment
•Functional response of the the alveolar bone and the gingival fibers surrounding the teeth
proximal space
when a tooth is loss, what direction do the adjacent teeth move to close the space?
Adjacent teeth tip into the space (mesial drifting toward the midline)
Define the following:
•Stabilize tooth alignment
•Prevents the extrusion or supereruption
occlusal contact
Mandible closure leads to occlusal contact, which maintains...
tooth position
If there is tooth loss, unopposed teeth will
supererupt to acheive occlusal contact
Define the following:
Tooth relationships within maxillary and mandibular arch
intra-arch alignment
In an occlusion plane, a line is drawn through all the _________ cusp tips and _________ edges of the mandibular teeth
Buccal, incisal
What permits maximal utilization of tooth contacts during function?
Curved plane
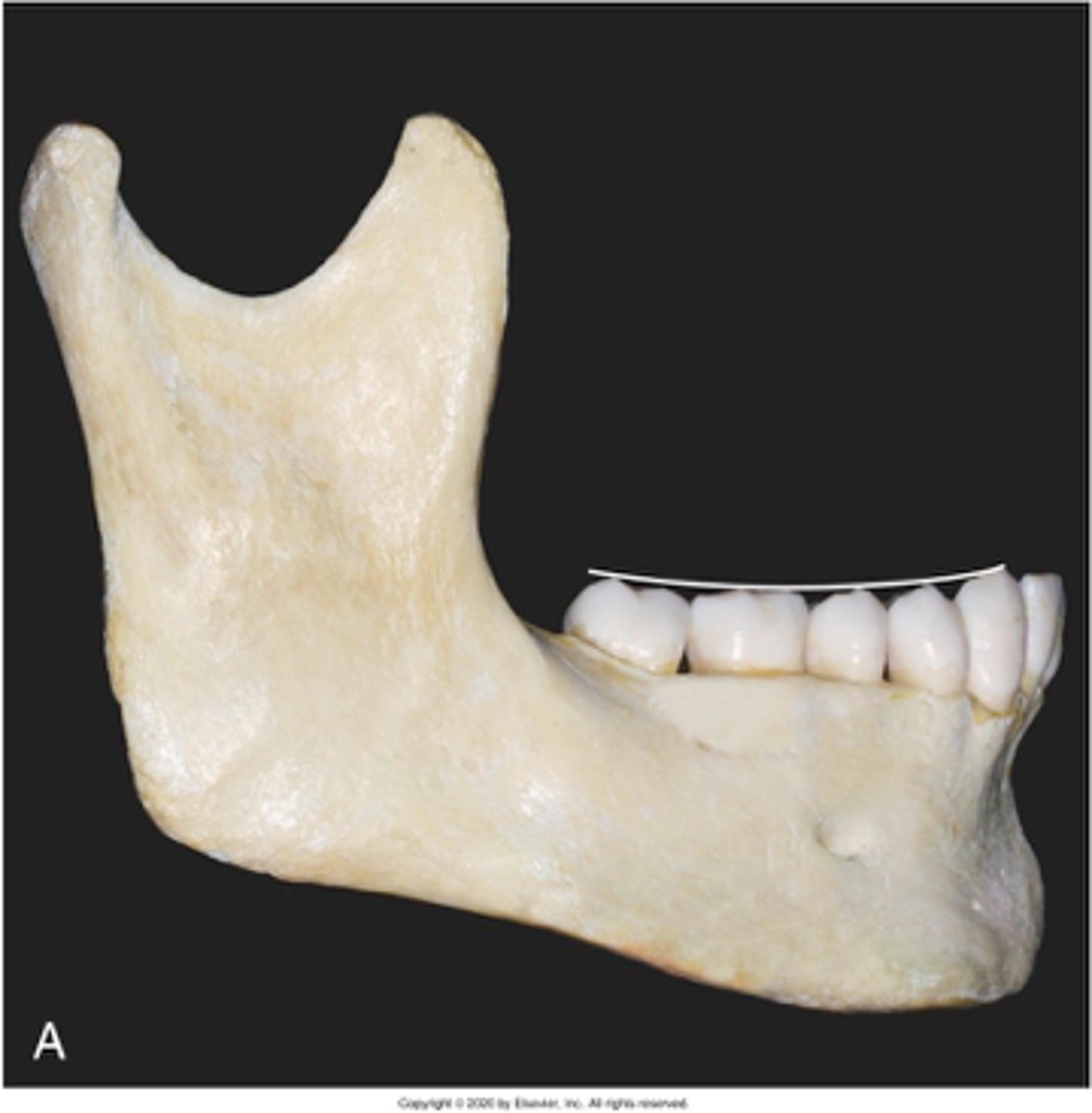
which occlusal plane is observed?
Curve of Spee
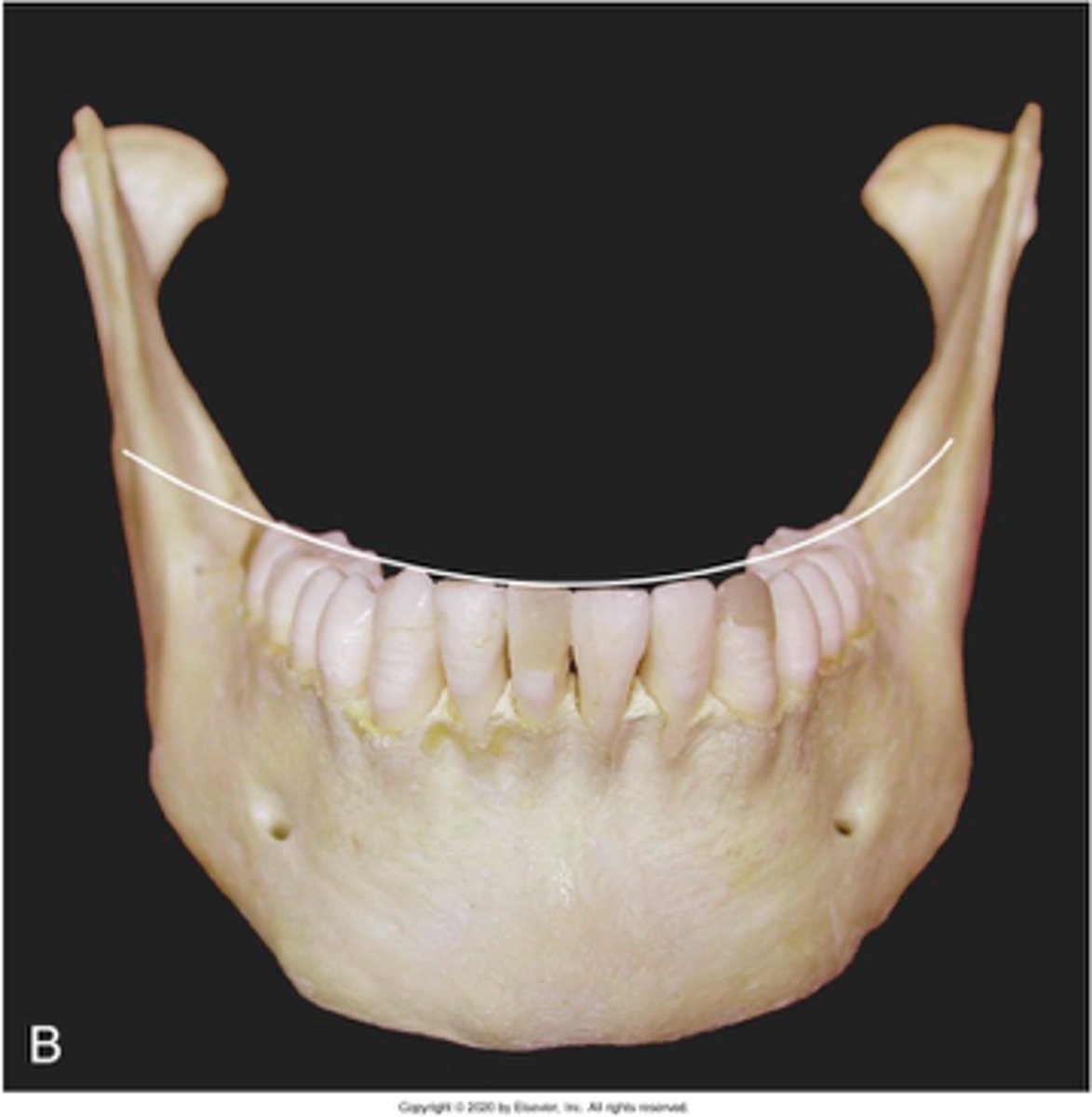
which occlusal plane is observed?
Curve of Wilson
the Curve of Spee is observed from what view?
sagittal
the Curve of Wilson is observed from what view?
frontal
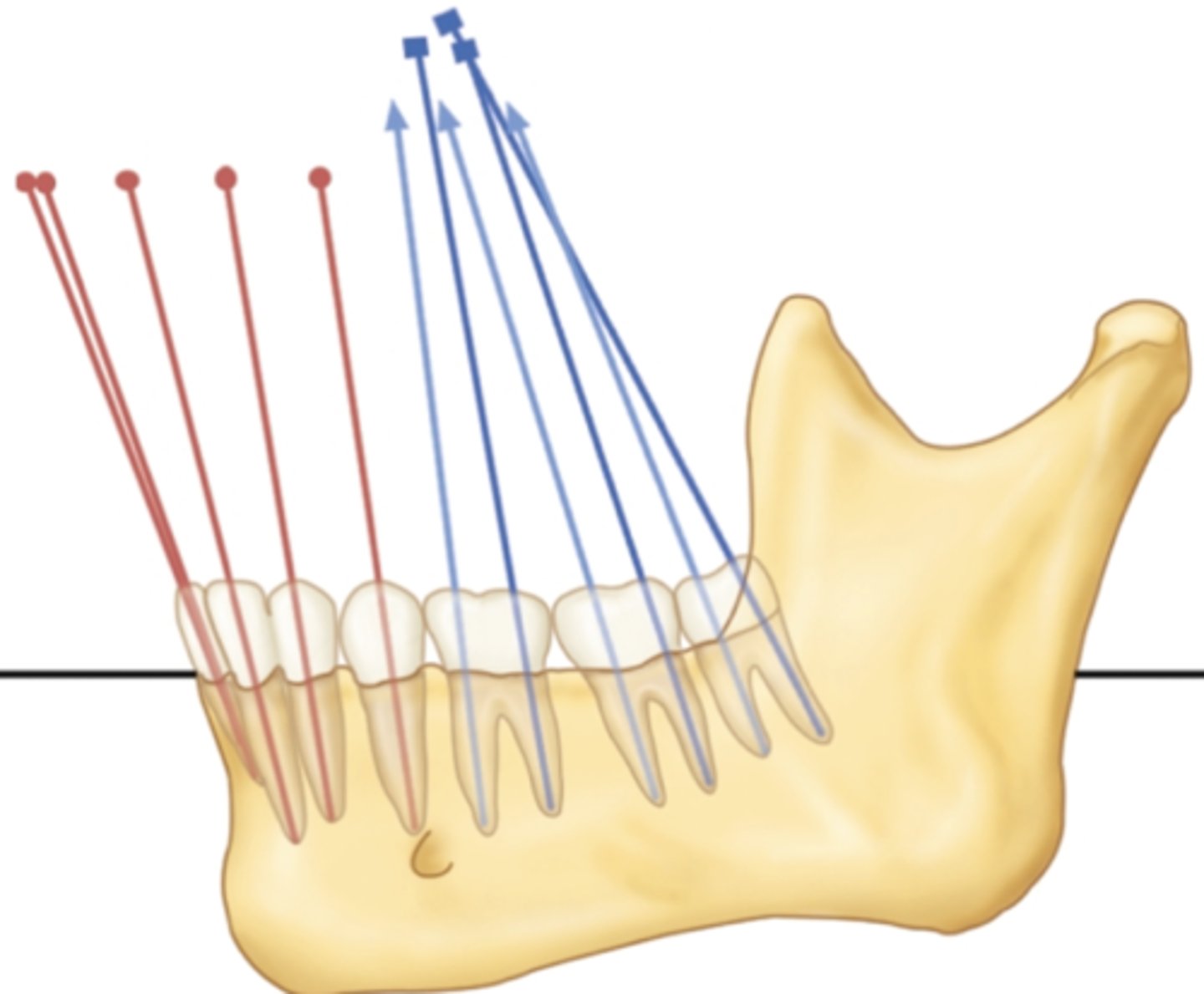
In the mandibular sagittal view, there is slight ___________ inclination of both the anterior and posterior teeth.
Mesial
which mandibular teeth have the greatest mesial inclination?
molars
which mandibular teeth have the 2nd greatest mesial inclination?
incisors
which mandibular teeth have the smallest mesial inclination?
premolars
in the mandible, which teeth have a mesial inclination?
anterior and posterior
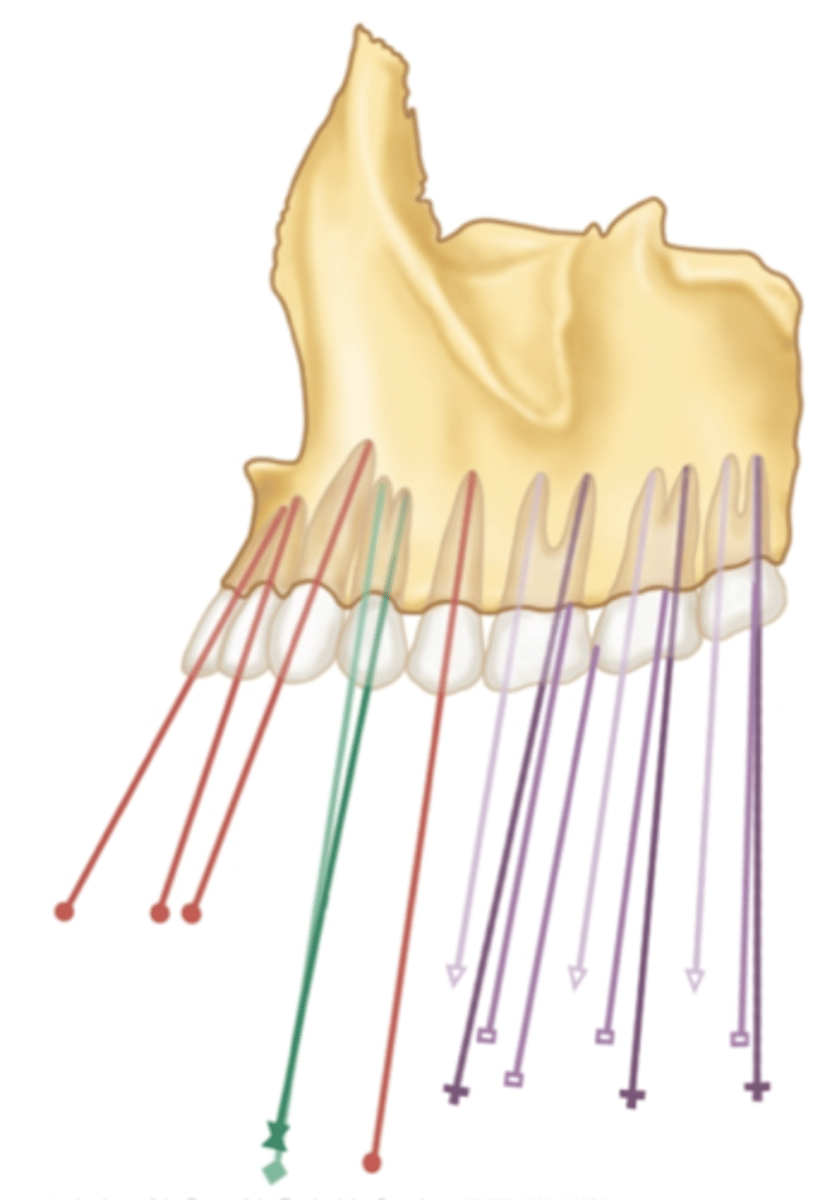
which maxillary teeth have the greatest mesial inclination?
anterior
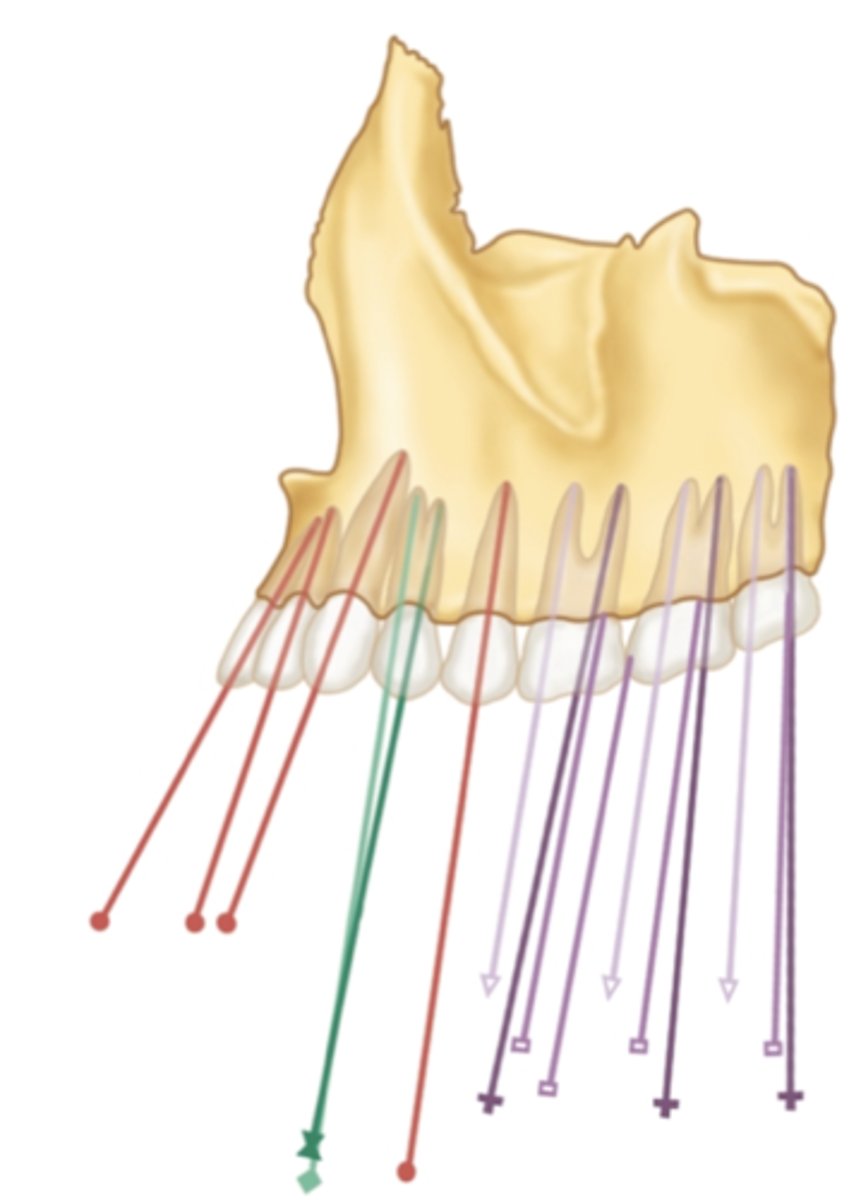
in the maxilla, which teeth have a mesial inclination?
anterior
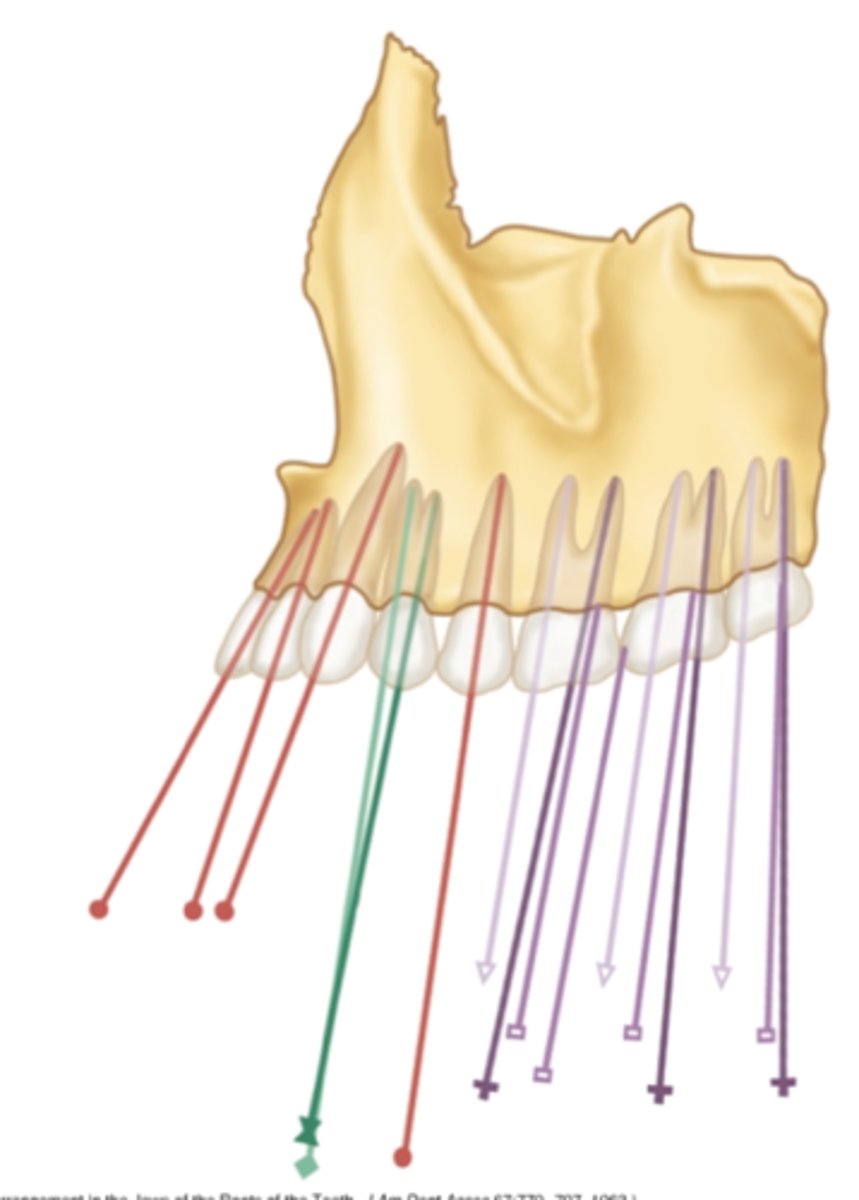
in the maxilla, which teeth have a more straight and then turns distally inclination?
posterior
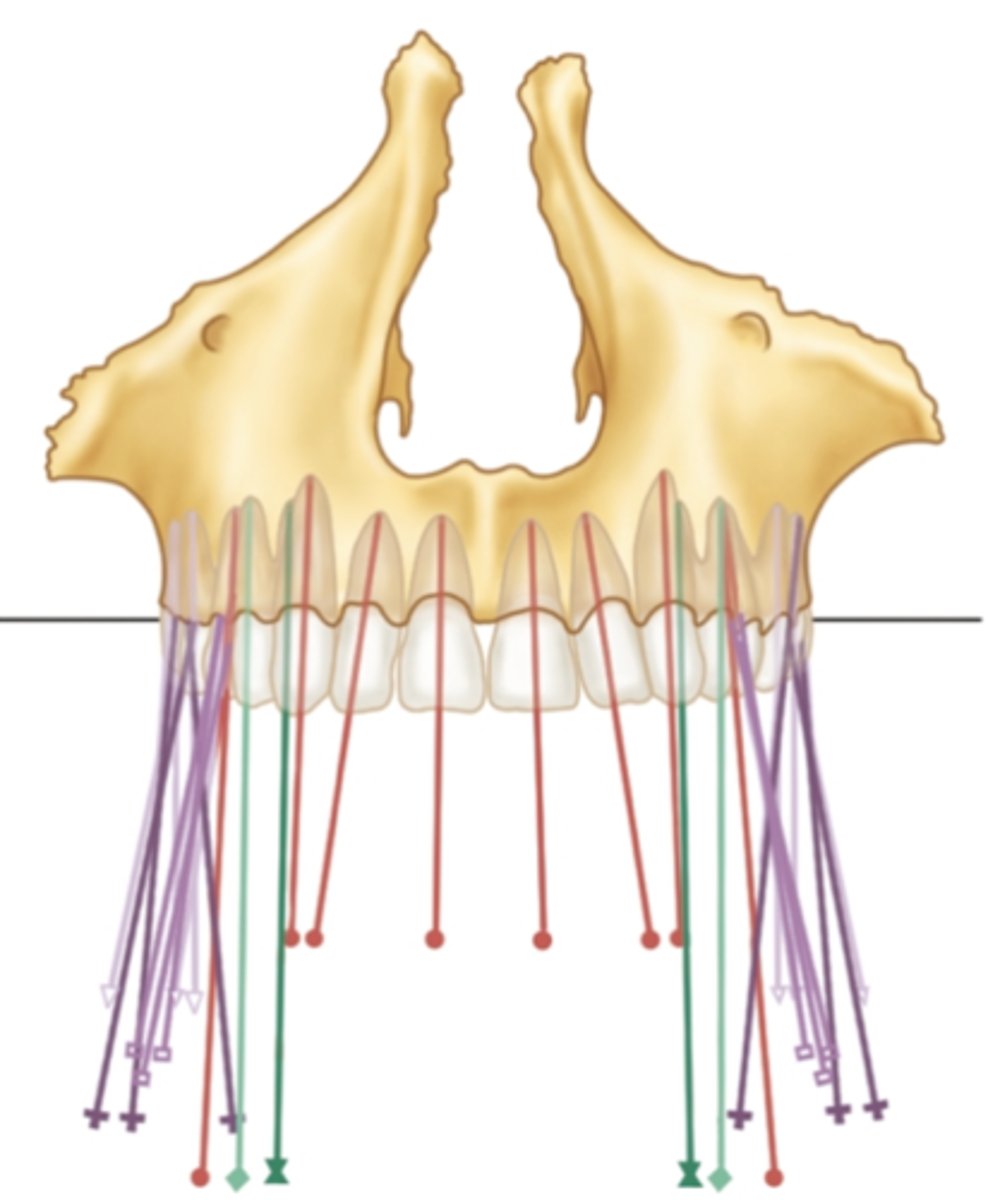
from a frontal view, the maxilla's posterior teeth have a _____ inclination
buccal
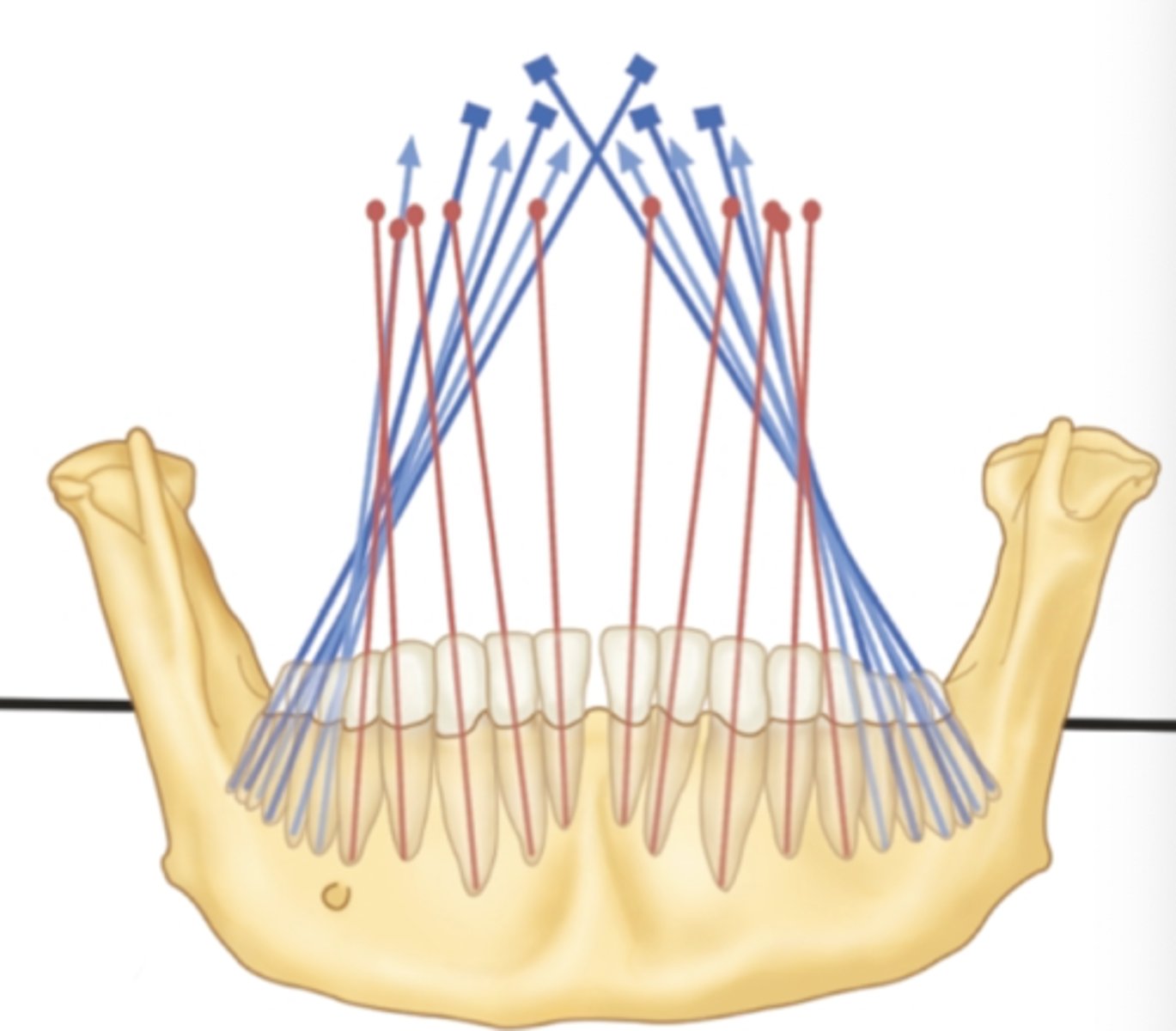
from a frontal view, the mandible's posterior teeth have a _____ inclination
lingual
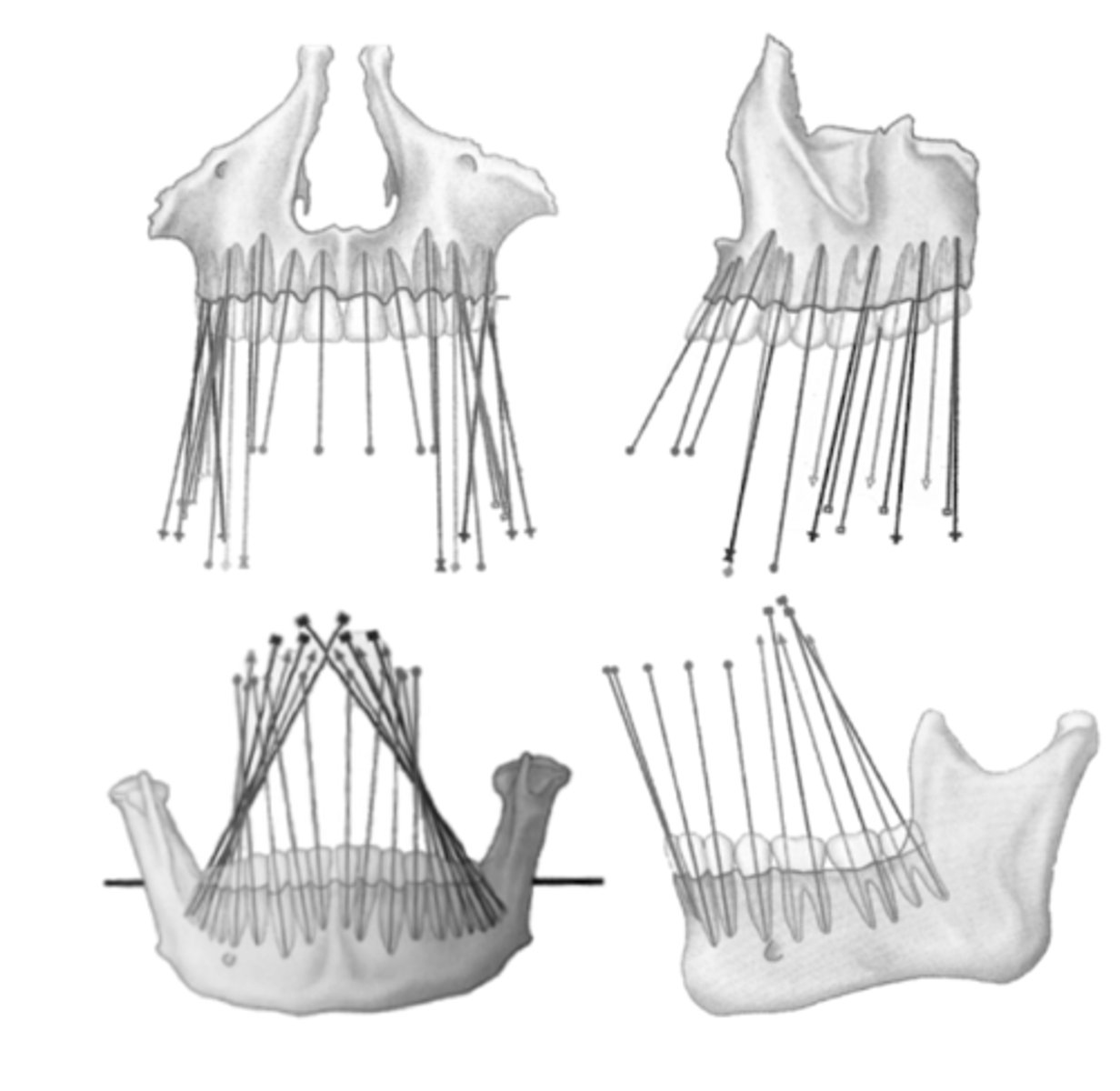
Why is it important to know tooth angulation and inclination?
- It helps visualize how the X-ray bean must be directed to obtain a more accurate image
- It helps relate the direction of the occlusal forces in restoration along the long axis of the teeth
- It guides control of the orthodontics forces for proper angulation of the teeth
- It aids in using templates to place dental implants with the right angulation
Define the following:
•Area in between the buccal and palatal cusp tips
•Inner aspect of the tooth
occlusal table
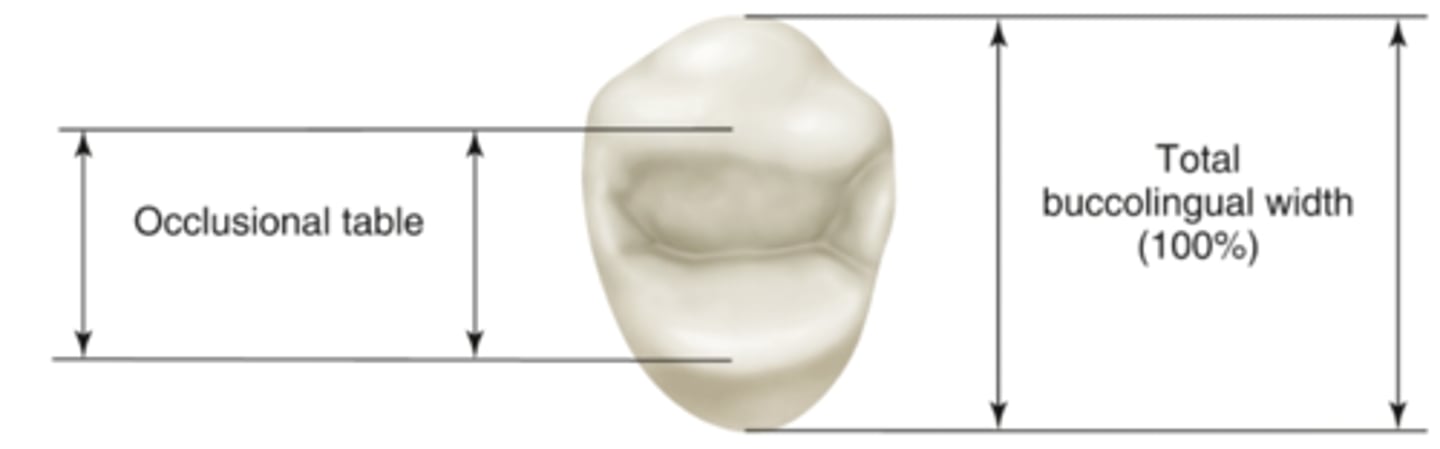
the occlusal table is about _____% of the total occlusal surface area
50-60
Occlusal table receives major masticatory force over the...
long axis of the root
The outer buccal incline represents ~_____ of the total occlusal surface area
1/3
The outer lingual/palatal incline represents ~____ of the total area
1/6
Inter-arch alignment is also known as...
Articulation
Define the following:
The relationship between maxillary and mandibular teeth as they approach or contact each other in function (speech/chewing/swallowing)
articulation (aka inter-arch alignment)
Define the following:
The static and dynamic contact relationship between the occlusal surfaces of the teeth during function
Articulation
The mandibular ________ cusps occlude along the central fossa areas of the maxillary teeth
buccal
The maxillary ______ cusps occlude along the central fossa areas of the mandibular teeth
lingual
What are the three tooth-dependent relationships?
- Centric occlusion
- Maximal intercuspal position (MIP)
- Maximal intercuspation
What are the two tooth-independent relationships?
- Centric relation (CR)
- Muscular/skeletal relationship
Maximal intercuspal position (MIP) is a tooth ________ relationship
dependent
Centric relation (CR) is a tooth _________ relationship
independent
Define the following:
•The complete intercuspation of the opposing teeth independent of condylar position
•Best fit of the teeth regardless of the condylar position
maximal intercuspal position
t/f: maximal intercuspal position is dependent on the condylar position
false
t/f: maximal intercuspal position is dependent on tooth contact
true
t/f: centric relation is dependent upon condylar position
true
What type of relationship is the centric relation?
Maxillomandibular
In centric relation, the condyle articulate in the _________-_________ position against the posterior slopes of the articular eminences; independent of tooth contact
anterior-superior
•The mandibular buccal cusps occlude along the central fossa areas of the maxillary teeth.
•The maxillary lingual cusps occlude along the central fossa areas of the mandibular teeth
INDICATES A...
normal occlusal relationship
What is a clinically useful and repeatable reference position?
Centric relation
Identify the relationship:
Normal occlusal relationship
Maxillary buccal cusps contact in the central fossa area of the mandibular teeth. (Discrepancies in skeletal arch size and may happen due to eruption patterns)
AND Mandibular lingual cusps contact in the central fossa of max teeth
INDICATES A..
cross bite

Identify the relationship:
Cross bite
if the maxillary ______ cusps are in the central fossa are of the mandibular teeth, you are at risk of biting the cheek
buccal
Identify the occlusal relationship:
centric cusps/ supporting cusps
What is a characteristic of centric cusps (supporting cusps)?
A) Broad and round
B) Sharp
C) Large contact area
D) Cusp-to-fossa relationship
A) Broad and round
Which function is associated with centric cusps?
Maintaining the vertical dimension of occlusion
T/F: Centric cusps play a major role in mastication
True
What is the relationship between centric cusps and opposing teeth?
Cusp-to-fossa
Identify the occlusal relationship:
noncentric cusps/ guiding cusps
Which of the following is a characteristic of guiding cusps?
A) Broad and rounded
B) Sharp
C) Large contact area
D) Cusp-to-fossa relationship
B) Sharp
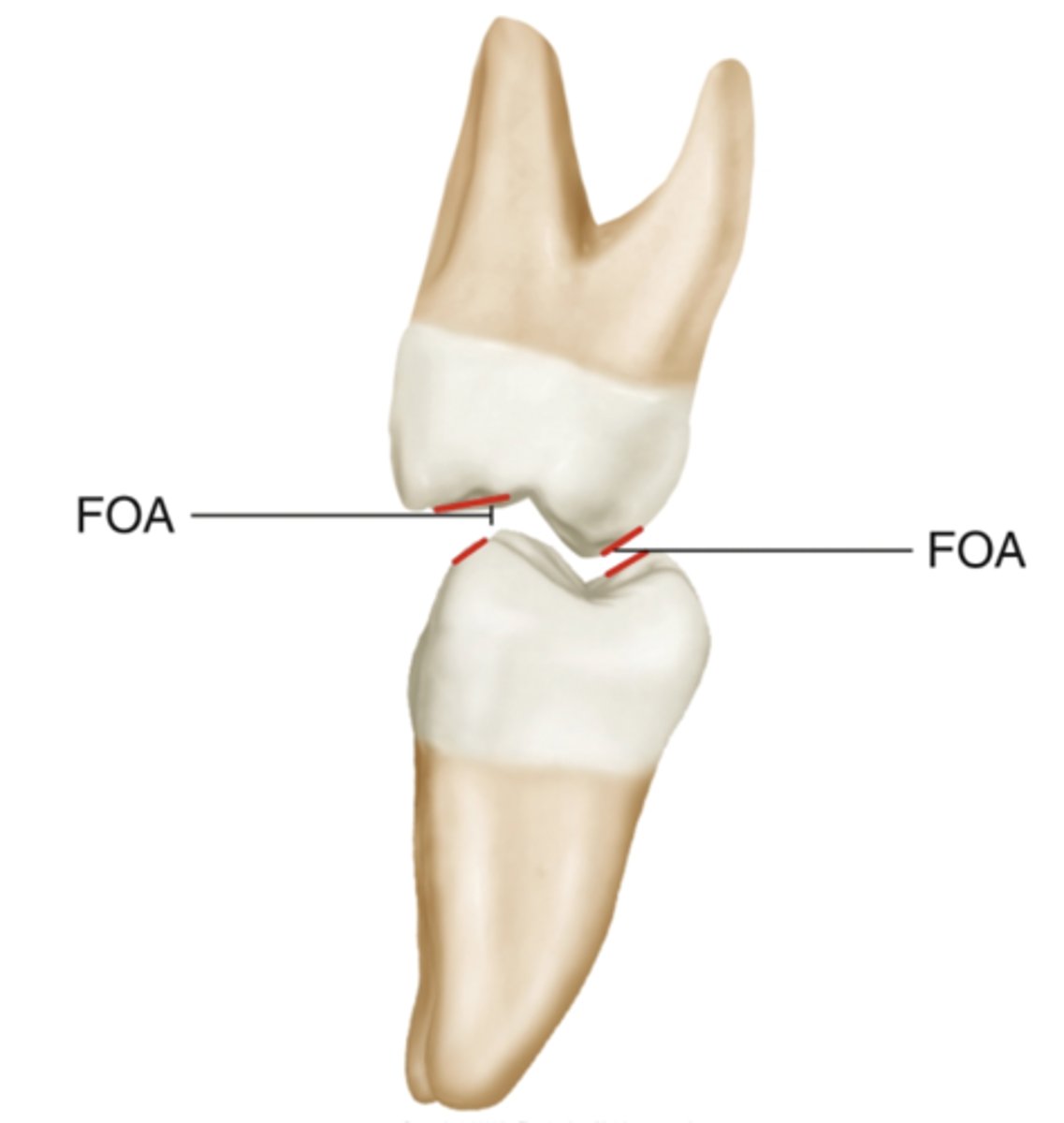
What does FOA stand for in relation to noncentric cusps?
Functional Outer Aspect
What is the Functional Outer Aspect (FOA) of noncentric cusps?
The inner incline of the noncentric cusp near the central fossa
Where does the FOA of a noncentric cusp interact?
Outer aspect of the opposing centric cusp
What part of the opposing tooth does the FOA of the centric cusp contact?
FOA of the noncentric cusp
What is a functional role of the FOA in occlusion?
Shearing food
which two cusps are the centric/supporting cusps?
maxillary lingual cusp
mandibular buccal cusp
which two cusps are the non-centric/gliding cusps
maxillary buccal cusp
mandibular lingual cusp
Identify which cusps in the occlusal relationship:
•Minimize tissue impingement
•Maintain the bolus of food on the occlusal table for mastication
•Provide mandible stability in maximum intercuspal position
noncentric cusps/ guiding cusps
Noncentric cusps are also referred to as guiding cusp because...
-if mandible moves laterally, noncentric cusps will contact and guide it
-guides mandible back to the intercuspal position during mouth closing
-provides feedback to neuromuscular system and controls chewing stroke during mastication
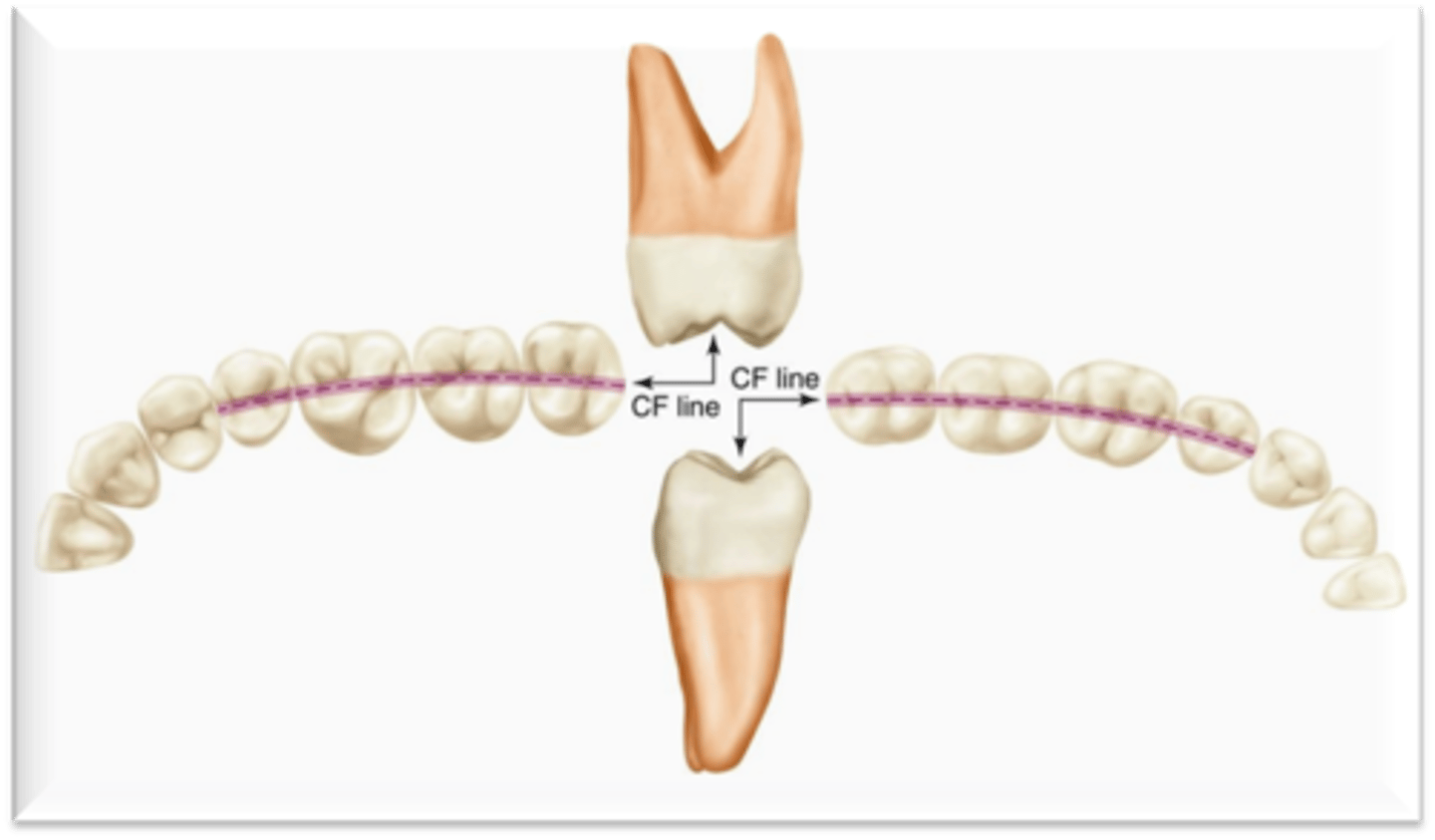
What connects the central grooves of the posterior teeth?
Central fossa (C-F) line
Proximal contact areas are generally located slightly _______ to the C-F line
buccal
when viewing the central fossa line, which embrasure is larger, buccal or lingual?
lingual
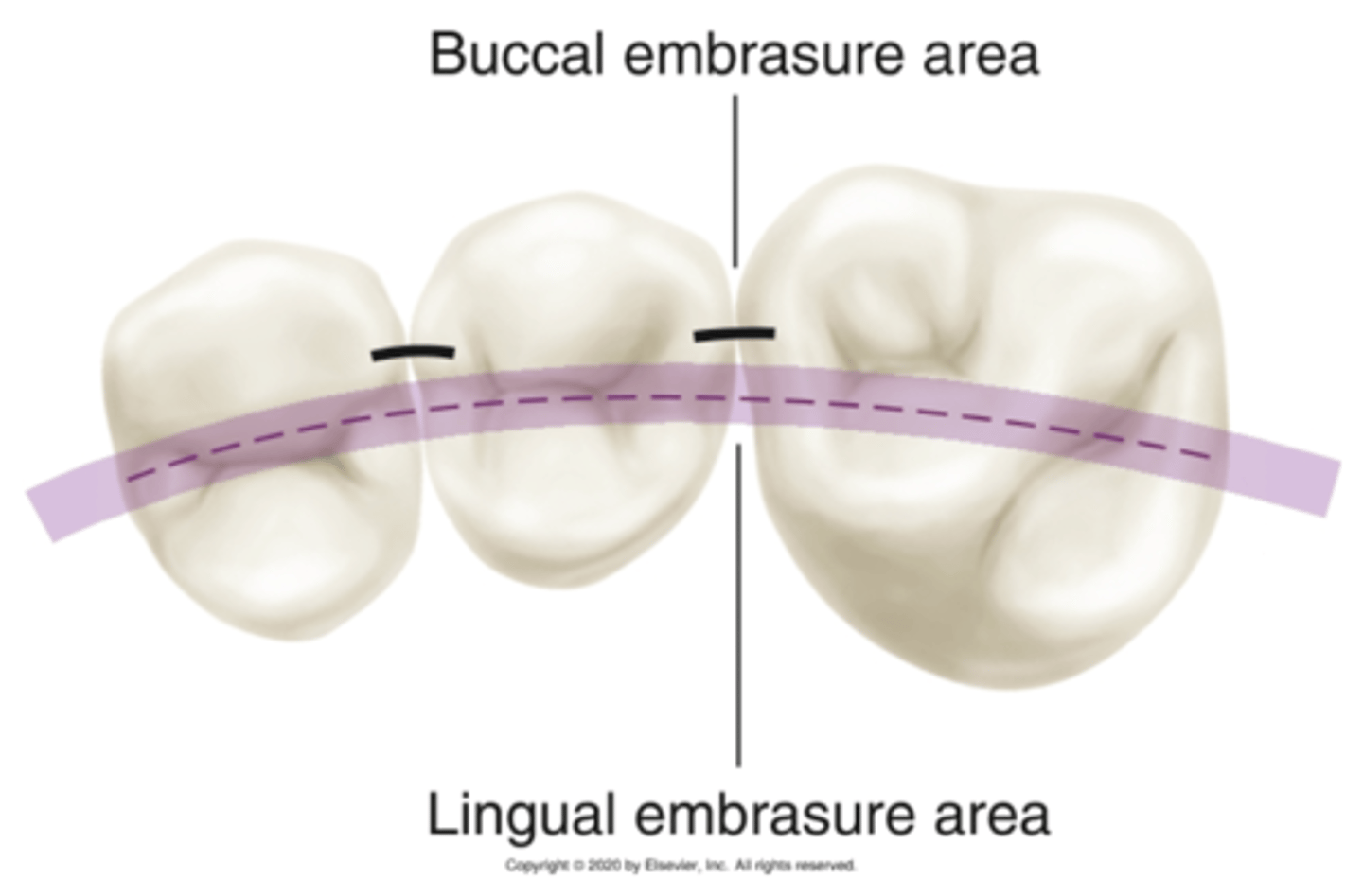
Lingual embrasure area is a
major spillway for food
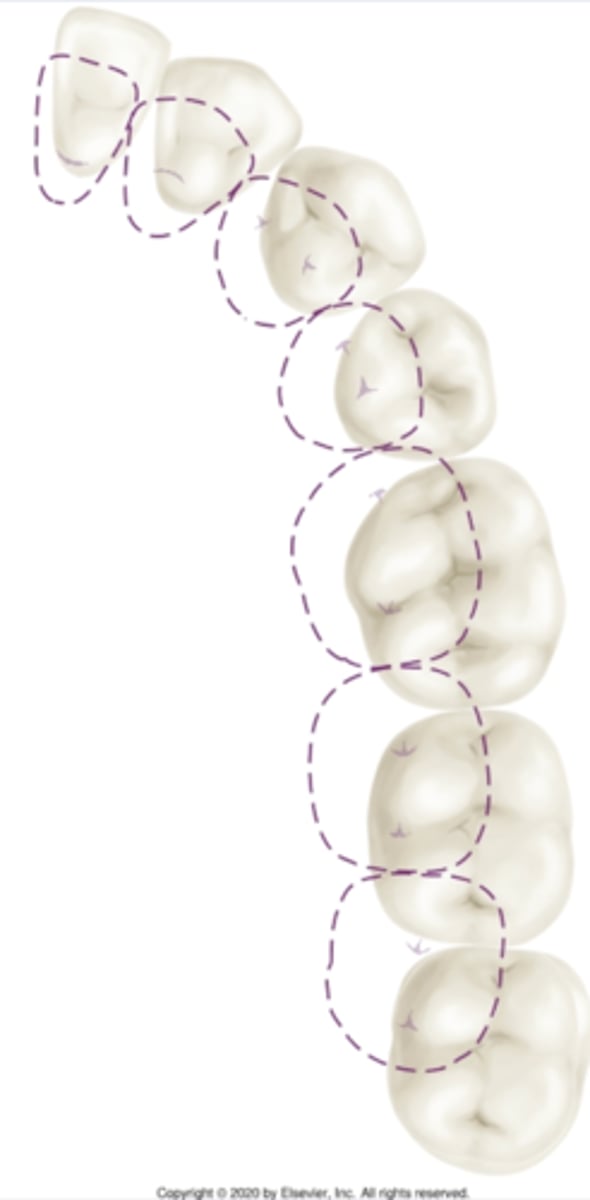
Centric cusps contact in
1. Central fossa areas
2. Marginal ridges & embrasure areas
which articulation of cusp tips compares to a pestle → mortar function?
cusp to central fossa areas (two curved surfaces)
In articulation of centric cusps, the cusp tips contact which area?
Central fossa
What is the purpose of spillways in the articulation of centric cusps?
To allow food to be crushed
How does mandibular shifting during mastication affect efficiency?
Increases efficiency
which articulation of cusp tips allows the cusp tip to penetrate through food easily and spillways are provided in all directions?
cusp to marginal ridges (contacting a flat/convex surface)
Define the following relationship:
-distributes occlusal force
-maintains arch integrity
-exceptions are mandibular central incisor and maxillary 3rd molars
One tooth to two teeth relationship
which teeth in the mouth do not have a 1-to-2 teeth contact?
mandibular central incisors
maxillary 3rd molars