Population: Factors
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
1
New cards
Birth Rate
Birth rate is the number of people born per 1000 people per year.
2
New cards
Death Rate
Death rate is the number of people dying per 1000 per year
3
New cards
Factors that influence population
* Food Supply
* War
* Development
* Health
* Education
* Women
* War
* Development
* Health
* Education
* Women
4
New cards
Food Supply
* Improved farming practices, including the use of pesticides and fertilizers, lead to increased production of high-quality food.
* Higher food production can help reduce the death rate and support population growth.
* Famine events, such as the potato blight, can cause a sharp decline in population over time.
* Countries affected by famines often experience long-lasting effects and struggle to recover.
* In countries like Sierra Leone, approximately 50% of the population lacks access to sufficient food.
* Higher food production can help reduce the death rate and support population growth.
* Famine events, such as the potato blight, can cause a sharp decline in population over time.
* Countries affected by famines often experience long-lasting effects and struggle to recover.
* In countries like Sierra Leone, approximately 50% of the population lacks access to sufficient food.
5
New cards
War
* War leads to population decline through various factors: casualties, migration, and reduced fertility rates.
* Healthcare and food services can be strained during wartime.
* After a war, there is often a baby boom, which helps in recovering the population.
* The baby boom can contribute to rebuilding the population that was damaged during the conflict.
* Healthcare and food services can be strained during wartime.
* After a war, there is often a baby boom, which helps in recovering the population.
* The baby boom can contribute to rebuilding the population that was damaged during the conflict.
6
New cards
Technology
* Technological advancements have the potential to improve people's lives and health in various ways.
* Developments in farming will enhance the food supply, ensuring better nutrition for the population.
* Vaccines and cures for deadly diseases will significantly improve overall health and well-being.
* Economic development and business advancements in prosperous countries will create more job opportunities and attract migrants.
* These factors collectively contribute to population growth across different region
* Developments in farming will enhance the food supply, ensuring better nutrition for the population.
* Vaccines and cures for deadly diseases will significantly improve overall health and well-being.
* Economic development and business advancements in prosperous countries will create more job opportunities and attract migrants.
* These factors collectively contribute to population growth across different region
7
New cards
Health
* Improvements in healthcare lead to increased life expectancy and lower death rates.
* Higher life expectancy contributes to population growth.
* Disparities in life expectancy exist between countries, such as Sierra Leone (average 51 years) and Ireland (average 82 years).
* Access to quality healthcare plays a crucial role in determining life expectancy and population outcomes.
* Higher life expectancy contributes to population growth.
* Disparities in life expectancy exist between countries, such as Sierra Leone (average 51 years) and Ireland (average 82 years).
* Access to quality healthcare plays a crucial role in determining life expectancy and population outcomes.
8
New cards
Education
* Well educated people will learn about family planning and will have smaller families.
* They also will have a better chance of getting a good job.
* They also will have a better chance of getting a good job.
9
New cards
Women
As women become more educated, the birth rate will fall, families will be smaller and infant mortality rates may fall.
10
New cards
Demographer
People who study population
11
New cards
Natural Increase/Decrease
When the birth/death rate exceed the other and the population increases/decreases
12
New cards
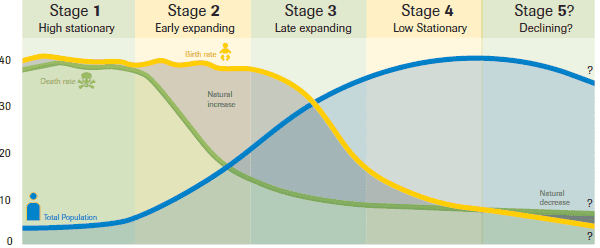
Demographic Transition Model
1. High Fluctuating (Stationary) Stage 1:
* Low total population with balanced birth and death rates.
* High birth rates due to limited education and women starting families at a young age.
* Children are used as economic assets and help support the elderly.
* High death rates due to poor medical care and lack of vaccinations.
2. Early Expanding Stage:
* Country begins to develop, leading to a rise in the total population.
* Death rates decrease due to improvements in food supply, healthcare, and sanitation.
* Aid programs contribute to better medical care, vaccinations, food, and clean water.
* Mali is an example of a country in this stage.
3. Late Expanding Stage:
* Countries like Brazil, India, Russia, and China are in this stage.
* Total population grows rapidly but at a slower pace than in stage 2.
* Birth rates decline due to family planning and fewer children needed for work.
* Government investments in medical care, vaccinations, and food/water supplies lower death rates.
* Women's role changes, with fewer children viewed as an economic asset.
* China has implemented a one-child policy, and India encourages fewer children.
4. Low Fluctuating Stage:
* Developed countries like Ireland, England, Sweden, and Poland are in this stage.
* Total population is high but balanced by low birth and death rates.
* Parents plan smaller families due to the high cost of raising children.
* Education costs and the desire for a better quality of life contribute to low birth rates.
5. Senile Stage:
* Germany is an example of a country in this stage.
* Population is high but declining due to an aging population.
* Birth rates remain low, with a continued desire for smaller families.
* Death rates surpass birth rates.
* Dependency ratio is high, with a greater number of economically inactive individuals.
* Policy measures such as extended maternity leave and increased children's allowance may be implemented.